SARS-CoV-2 VOC type and biological sex affect molnupiravir efficacy in severe COVID-19 dwarf hamster model
et al., Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-022-32045-1, Jul 2022
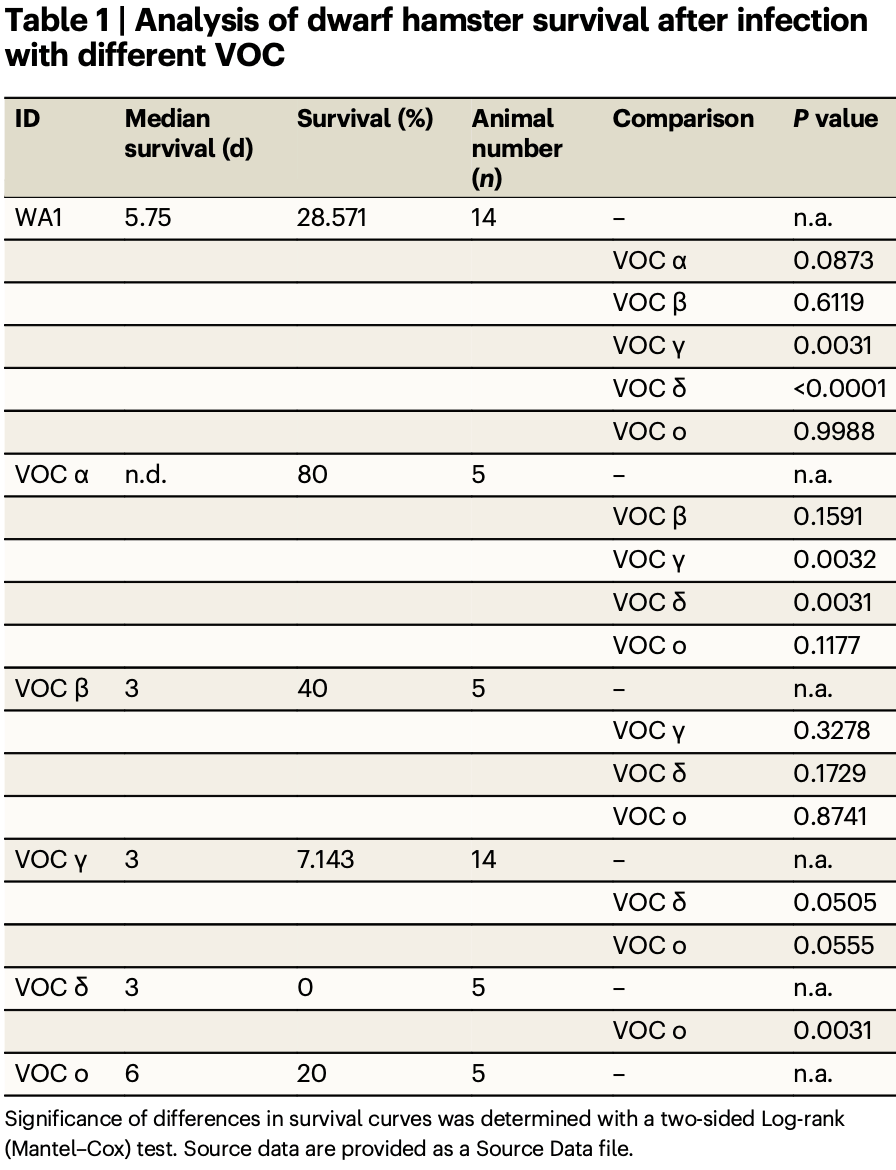
Roborovski dwarf hamster and in vitro study finding molnupiravir efficacy varied significantly by SARS-CoV-2 variant in the hamster model, in contrast to no significant difference seen in cultured cells and human organoids. Efficacy for omicron in the hamster model varied significantly based on biological sex.
Potential risks of molnupiravir include the creation of dangerous variants, and mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, and embryotoxicity1-15. Multiple analyses have identified variants potentially created by molnupiravir16-20. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury21, cardiovascular toxocity22, and neurological symptoms21. Treatment may increase viral rebound23,24.
1.
Swanstrom et al., Lethal mutagenesis as an antiviral strategy, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abn0048.
2.
Hadj Hassine et al., Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040841.
3.
Shum, C., An investigational study into the drug-associated mutational signature in SARS-CoV-2 viruses, The University of Hong Kong, PhD Thesis, hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/344396.
4.
Waters et al., Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22471.
5.
Huntsman, M., An assessment of the reproductive toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using stem cell-based embryo models, Master's Thesis, scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/items/cd11342c-b4dc-44c0-8b44-ce6e3369c40b.
6.
Huntsman (B) et al., Detection of developmental toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using gastruloid-based in vitro assays, Toxicological Sciences, doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfaf093.
7.
Zibat et al., N4-hydroxycytidine, the active compound of Molnupiravir, promotes SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis and escape from a neutralizing nanobody, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.107786.
8.
Shiraki et al., Convenient screening of the reproductive toxicity of favipiravir and antiviral drugs in Caenorhabditis elegans, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35331.
9.
Gruber et al., Molnupiravir increases SARS‐CoV‐2 genome diversity and complexity: A case‐control cohort study, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29642.
10.
Marikawa et al., An active metabolite of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir impairs mouse preimplantation embryos at clinically relevant concentrations, Reproductive Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2023.108475.
11.
Rahman, M., Elucidation of the DNA repair mechanisms involved in the repair of DNA damage caused by the Arabinosides and Anti-COVID-19 drugs, tokyo-metro-u.repo.nii.ac.jp/records/2000972.
12.
Zhou et al., β-D-N4-hydroxycytidine Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Through Lethal Mutagenesis But Is Also Mutagenic To Mammalian Cells, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab247.
13.
Chamod et al., Molnupiravir Metabolite--N4-hydroxycytidine Causes Cytotoxicity and DNA Damage in Mammalian Cells in vitro: N4-hydroxycytidine Induced Cytotoxicity DNA Damage, Asian Medical Journal and Alternative Medicine, 23:3, asianmedjam.com/index.php/amjam/article/view/1448.
14.
Standing et al., Randomized controlled trial of molnupiravir SARS-CoV-2 viral and antibody response in at-risk adult outpatients, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-45641-0.
15.
Mori et al., Reactive oxygen species-mediated cytotoxic and DNA-damaging mechanism of N4-hydroxycytidine, a metabolite of the COVID-19 therapeutic drug molnupiravir, Free Radical Research, doi:10.1080/10715762.2025.2469738.
16.
Focosi et al., The fitness of molnupiravir-signed SARS-CoV-2 variants: imputation analysis based on prescription counts and GISAID analyses by country, Intervirology, doi:10.1159/000540282.
17.
Sanderson et al., A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6.
18.
Fountain-Jones et al., Effect of molnupiravir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients: a retrospective observational study, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2.
19.
Kosakovsky Pond et al., Anti-COVID drug accelerates viral evolution, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-023-03248-3.
21.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
22.
Ozhan et al., Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary effects of repurposed COVID-19 therapeutics in healthy rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31048-4.
Lieber et al., 29 Jul 2022, USA, peer-reviewed, 15 authors.
Contact: rplemper@gsu.edu.
Abstract: nature communications
Article
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-32045-1
SARS-CoV-2 VOC type and biological sex
affect molnupiravir efficacy in severe
COVID-19 dwarf hamster model
Received: 1 March 2022
Check for updates
1234567890():,;
1234567890():,;
Accepted: 14 July 2022
Carolin M. Lieber1,5, Robert M. Cox 1,5, Julien Sourimant 1, Josef D. Wolf 1,
Kate Juergens2, Quynh Phung2, Manohar T. Saindane3, Meghan K. Smith 3,
Zachary M. Sticher 3, Alexander A. Kalykhalov3, Michael G. Natchus3,
George R. Painter3, Kaori Sakamoto4, Alexander L. Greninger2 &
Richard K. Plemper 1
SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOC) have triggered infection waves. Oral
antivirals such as molnupiravir promise to improve disease management, but
efficacy against VOC delta was questioned and potency against omicron is
unknown. This study evaluates molnupiravir against VOC in human airway
epithelium organoids, ferrets, and a lethal Roborovski dwarf hamster model of
severe COVID-19-like lung injury. VOC were equally inhibited by molnupiravir
in cells and organoids. Treatment reduced shedding in ferrets and prevented
transmission. Pathogenicity in dwarf hamsters was VOC-dependent and
highest for delta, gamma, and omicron. All molnupiravir-treated dwarf hamsters survived, showing reduction in lung virus load from one (delta) to four
(gamma) orders of magnitude. Treatment effect size varied in individual dwarf
hamsters infected with omicron and was significant in males, but not females.
The dwarf hamster model recapitulates mixed efficacy of molnupiravir in
human trials and alerts that benefit must be reassessed in vivo as VOC evolve.
By May 2022, SARS-CoV-2 has resulted in over 522 million cases and
>6.2 million deaths worldwide1. Vaccines are widely available2,3, but
recuring global infection waves have been fueled by limited longevity
of vaccine-induced immunity, the hesitancy of population subgroups
to vaccinate4,5, and increasingly contagious and/or vaccine-insensitive
variants of concern (VOC) alpha (B.1.1.7 lineage), beta (B.1.351 lineage),
gamma (P.1 lineage), delta (B.1.617.2 lineage), and omicron (B1.1.529
lineage)6,7. VOC delta was the prevalent circulating variant during
Summer and Fall 2021 due to replication to high titers, prolonged
shedding from infected individuals, and propensity to induce breakthrough infections in vaccinees8–10. Since its first appearance in
November 2021, VOC omicron has rapidly replaced delta as the
dominant circulating strain in most geographical regions11, propelled
by sharply reduced sensitivity to neutralizing antibodies directed
against earlier lineages and greatly increased infectivity12. Although
clinical signs associated with VOC omicron are typically milder than
those of its predecessors, record-high daily infection rates have driven
high absolute hospitalization numbers, creating an urgent need for
therapeutics to improve disease management.
Molnupiravir was the first orally available SARS-CoV-2 inhibitor
approved for outpatient use against COVID-1913. Intermediate results
of the early months of a large efficacy trial revealed an encouraging
50% reduction in hospitalizations in the treatment group, but later
analysis of the full dataset showed only a 30% lower hospitalization
rate overall14. Based on the geographical location of trial participants
and VOC prevalence in the earlier versus later phase of the trial, an
1
Center for Translational Antiviral Research, Institute for Biomedical Sciences, Georgia State..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-32045-1",
"ISSN": [
"2041-1723"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-32045-1",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOC) have triggered infection waves. Oral antivirals such as molnupiravir promise to improve disease management, but efficacy against VOC delta was questioned and potency against omicron is unknown. This study evaluates molnupiravir against VOC in human airway epithelium organoids, ferrets, and a lethal Roborovski dwarf hamster model of severe COVID-19-like lung injury. VOC were equally inhibited by molnupiravir in cells and organoids. Treatment reduced shedding in ferrets and prevented transmission. Pathogenicity in dwarf hamsters was VOC-dependent and highest for delta, gamma, and omicron. All molnupiravir-treated dwarf hamsters survived, showing reduction in lung virus load from one (delta) to four (gamma) orders of magnitude. Treatment effect size varied in individual dwarf hamsters infected with omicron and was significant in males, but not females. The dwarf hamster model recapitulates mixed efficacy of molnupiravir in human trials and alerts that benefit must be reassessed in vivo as VOC evolve.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"32045"
],
"article-number": "4416",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "1 March 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "14 July 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "29 July 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1,
"value": "M.G.N. and G.R.P. are coinventors on patent 20190022116, N<sup>4</sup>-Hydroxycytidine and derivatives and anti-viral uses related thereto, covering composition of matter and method of use of EIDD-2801 for antiviral therapy. This study could affect their personal financial status. All other authors declare no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lieber",
"given": "Carolin M.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0620-1674",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Cox",
"given": "Robert M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1660-1666",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sourimant",
"given": "Julien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2507-6944",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Wolf",
"given": "Josef D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Juergens",
"given": "Kate",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phung",
"given": "Quynh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saindane",
"given": "Manohar T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8491-3824",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Meghan K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7022-1410",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sticher",
"given": "Zachary M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kalykhalov",
"given": "Alexander A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Natchus",
"given": "Michael G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Painter",
"given": "George R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sakamoto",
"given": "Kaori",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Greninger",
"given": "Alexander L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2034-2107",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Plemper",
"given": "Richard K.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nature Communications",
"container-title-short": "Nat Commun",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-29T19:04:06Z",
"timestamp": 1659121446000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-29T19:07:19Z",
"timestamp": 1659121639000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000060",
"award": [
"AI071002",
"AI141222"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases"
},
{
"name": "U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-29T19:41:53Z",
"timestamp": 1659123713634
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
29
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1659052800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1659052800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-32045-1.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-32045-1",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-32045-1.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
29
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
29
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"key": "32045_CR1",
"unstructured": "WHO. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard, <https://covid19.who.int> (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2034577",
"author": "FP Polack",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2603",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "32045_CR2",
"unstructured": "Polack, F. P. et al. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 383, 2603–2615 (2020).",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2022483",
"author": "LA Jackson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1920",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "32045_CR3",
"unstructured": "Jackson, L. A. et al. An mRNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 - preliminary report. N. Engl. J. Med. 383, 1920–1931 (2020).",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10654-020-00671-y",
"author": "AA Dror",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "775",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Epidemiol.",
"key": "32045_CR4",
"unstructured": "Dror, A. A. et al. Vaccine hesitancy: the next challenge in the fight against COVID-19. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 35, 775–779 (2020).",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M20-3569",
"author": "KA Fisher",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "964",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intern. Med.",
"key": "32045_CR5",
"unstructured": "Fisher, K. A. et al. Attitudes toward a potential SARS-CoV-2 vaccine: a survey of U.S. adults. Ann. Intern. Med. 173, 964–973 (2020).",
"volume": "173",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.013",
"author": "WF Garcia-Beltran",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2372",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "32045_CR6",
"unstructured": "Garcia-Beltran, W. F. et al. Multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants escape neutralization by vaccine-induced humoral immunity. Cell 184, 2372–2383.e2379 (2021).",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.037",
"author": "D Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2348",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "32045_CR7",
"unstructured": "Zhou, D. et al. Evidence of escape of SARS-CoV-2 variant B.1.351 from natural and vaccine-induced sera. Cell 184, 2348–2361 e2346 (2021).",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03944-y",
"author": "P Mlcochova",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "114",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "32045_CR8",
"unstructured": "Mlcochova, P. et al. SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 Delta variant replication and immune evasion. Nature 599, 114–119 (2021).",
"volume": "599",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-021-01986-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "32045_CR9",
"unstructured": "Reardon, S. How the Delta variant achieves its ultrafast spread. Nature, https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-021-01986-w (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03777-9",
"author": "D Planas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "276",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "32045_CR10",
"unstructured": "Planas, D. et al. Reduced sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 variant Delta to antibody neutralization. Nature 596, 276–280 (2021).",
"volume": "596",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.acz9928",
"author": "K Kupferschmidt",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "32045_CR11",
"unstructured": "Kupferschmidt, K. & Vogel, G. Omicron threat remains fuzzy as cases explode. Science 375, 9–10 (2022).",
"volume": "375",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-022-01705-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "32045_CR12",
"unstructured": "Perez-Then, E. et al. Neutralizing antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron variants following heterologous CoronaVac plus BNT162b2 booster vaccination. Nat. Med., https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-022-01705-6 (2022)."
},
{
"key": "32045_CR13",
"unstructured": "GOV.UK First oral antiviral for COVID-19, Lagevrio (molnupiravir), approved by MHRA https://www.gov.uk/government/news/first-oral-antiviral-for-covid-19-lagevrio-molnupiravir-approved-by-mhra. (2021)."
},
{
"key": "32045_CR14",
"unstructured": "Molnupiravir - US Food and Drug Administration (https://www.fda.gov/media/154472/download). (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-021-03667-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "32045_CR15",
"unstructured": "Kozlov, M. Merck’s COVID pill loses its lustre: what that means for the pandemic. Nature (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.11.23.469695",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "32045_CR16",
"unstructured": "Prince, T. et al. Antiviral activity of molnupiravir precursor NHC against SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern (VOCs) and its therapeutic window in a human lung cell model. bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.11.23.469695 (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.05.19.444875",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "32045_CR17",
"unstructured": "Sourimant, J. et al. 4’-Fluorouridine is an oral antiviral that blocks respiratory syncytial virus and SARS-CoV-2 replication. Science, eabj5508 (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-020-00835-2",
"author": "RM Cox",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "Nat. Microbiol.",
"key": "32045_CR18",
"unstructured": "Cox, R. M., Wolf, J. D. & Plemper, R. K. Therapeutically administered ribonucleoside analogue MK-4482/EIDD-2801 blocks SARS-CoV-2 transmission in ferrets. Nat. Microbiol. 6, 11–18 (2021).",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-26760-4",
"author": "RM Cox",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "32045_CR19",
"unstructured": "Cox, R. M. et al. Oral prodrug of remdesivir parent GS-441524 is efficacious against SARS-CoV-2 in ferrets. Nat. Commun. 12, 6415 (2021).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/03009858211057197",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "32045_CR20",
"unstructured": "Gruber, A. D., Firsching, T. C., Trimpert, J. & Dietert, K. Hamster models of COVID-19 pneumonia reviewed: how human can they be? Vet. Pathol., 3009858211057197, https://doi.org/10.1177/03009858211057197 (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.coviro.2021.03.009",
"author": "CY Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "73",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Virol.",
"key": "32045_CR21",
"unstructured": "Lee, C. Y. & Lowen, A. C. Animal models for SARS-CoV-2. Curr. Opin. Virol. 48, 73–81 (2021).",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108488",
"author": "J Trimpert",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "108488",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep.",
"key": "32045_CR22",
"unstructured": "Trimpert, J. et al. The Roborovski Dwarf hamster is a highly susceptible model for a rapid and fatal course of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Cell Rep. 33, 108488 (2020).",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/21505594.2021.1972201",
"author": "C Zhai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2430",
"journal-title": "Virulence",
"key": "32045_CR23",
"unstructured": "Zhai, C. et al. Roborovski hamster (Phodopus roborovskii) strain SH101 as a systemic infection model of SARS-CoV-2. Virulence 12, 2430–2442 (2021).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.02428-20",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "32045_CR24",
"unstructured": "Painter, W. P. et al. Human safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of molnupiravir, a novel broad-spectrum oral antiviral agent with activity against SARS-CoV-2. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.02428-20 (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/B978-0-12-380920-9.00037-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "32045_CR25",
"unstructured": "Bauer, B. A. & Besch-Williford, C. in The Laboratory Rabbit, Guinea Pig, Hamster, and Other Rodents (eds. M. A. Suckow, K. A. Stevens, & R. P. Wilson) Ch. 37, 935–946 (Academic Press, 2012)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-22580-8",
"author": "K Rosenke",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "32045_CR26",
"unstructured": "Rosenke, K. et al. Orally delivered MK-4482 inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication in the Syrian hamster model. Nat. Commun. 12, 2295 (2021).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03312-w",
"author": "A Wahl",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "451",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "32045_CR27",
"unstructured": "Wahl, A. et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection is effectively treated and prevented by EIDD-2801. Nature 591, 451–457 (2021).",
"volume": "591",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.aax5866",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "32045_CR28",
"unstructured": "Toots, M. et al. Characterization of orally efficacious influenza drug with high resistance barrier in ferrets and human airway epithelia. Sci. Transl. Med. 11, https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aax5866 (2019)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abe5901",
"author": "BB Oude Munnink",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "172",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "32045_CR29",
"unstructured": "Oude Munnink, B. B. et al. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 on mink farms between humans and mink and back to humans. Science 371, 172–177 (2021).",
"volume": "371",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1503/cmaj.211248",
"author": "DN Fisman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "E1619",
"journal-title": "CMAJ",
"key": "32045_CR30",
"unstructured": "Fisman, D. N. & Tuite, A. R. Evaluation of the relative virulence of novel SARS-CoV-2 variants: a retrospective cohort study in Ontario, Canada. CMAJ 193, E1619–E1625 (2021).",
"volume": "193",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab721",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "32045_CR31",
"unstructured": "Ong, S. W. X. et al. Clinical and virological features of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern: a retrospective cohort study comparing B.1.1.7 (Alpha), B.1.315 (Beta), and B.1.617.2 (Delta). Clin. Infect. Dis., https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab721 (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01358-1",
"author": "A Sheikh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2461",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "32045_CR32",
"unstructured": "Sheikh, A. et al. SARS-CoV-2 Delta VOC in Scotland: demographics, risk of hospital admission, and vaccine effectiveness. Lancet 397, 2461–2462 (2021).",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00056-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "32045_CR33",
"unstructured": "Nealon, J. & Cowling, B. J. Omicron severity: milder but not mild. Lancet, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00056-3 (2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01965-17",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "32045_CR34",
"unstructured": "Urakova, N. et al. beta-d-N (4)-hydroxycytidine is a potent anti-alphavirus compound that induces a high level of mutations in the viral genome. J. Virol. 92, https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01965-17 (2018)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01348-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "32045_CR35",
"unstructured": "Agostini, M. L. et al. Small-molecule antiviral beta-d-N (4)-hydroxycytidine inhibits a proofreading-intact coronavirus with a high genetic barrier to resistance. J. Virol. 93, https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01348-19 (2019)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.00766-18",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "32045_CR36",
"unstructured": "Yoon, J. J. et al. Orally efficacious broad-spectrum ribonucleoside analog inhibitor of influenza and respiratory syncytial viruses. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 62, https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00766-18 (2018)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-17367-2",
"author": "M Richard",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "32045_CR37",
"unstructured": "Richard, M. et al. SARS-CoV-2 is transmitted via contact and via the air between ferrets. Nat. Commun. 11, 3496 (2020).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.368.6496.1169",
"author": "M Enserink",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1169",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "32045_CR38",
"unstructured": "Enserink, M. Coronavirus rips through Dutch mink farms, triggering culls. Science 368, 1169 (2020).",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0002-9343(70)80129-2",
"author": "H Remmer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "617",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Med.",
"key": "32045_CR39",
"unstructured": "Remmer, H. The role of the liver in drug metabolism. Am. J. Med. 49, 617–629 (1970).",
"volume": "49",
"year": "1970"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JCM.01881-16",
"author": "AL Greninger",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "177",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Microbiol.",
"key": "32045_CR40",
"unstructured": "Greninger, A. L. et al. Rapid metagenomic next-generation sequencing during an investigation of hospital-acquired human parainfluenza virus 3 infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 55, 177–182 (2017).",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JCM.02226-20",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "32045_CR41",
"unstructured": "Addetia, A. et al. Sensitive recovery of complete SARS-CoV-2 genomes from clinical samples by use of swift biosciences’ SARS-CoV-2 multiplex amplicon sequencing panel. J. Clin. Microbiol. 59, https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.02226-20 (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2019.12.17.879320",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "32045_CR42",
"unstructured": "Lin, M. J., Shean, R. C., Makhsous, N. & Greninger, A. L. LAVA: a streamlined visualization tool for longitudinal analysis of viral alleles. bioRxiv, https://doi.org/10.1101/2019.12.17.879320 (2019)."
}
],
"reference-count": 42,
"references-count": 42,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-32045-1"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Physics and Astronomy",
"General Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology",
"General Chemistry",
"Multidisciplinary"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "SARS-CoV-2 VOC type and biological sex affect molnupiravir efficacy in severe COVID-19 dwarf hamster model",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "13"
}