Anti-COVID drug accelerates viral evolution
et al., Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-023-03248-3, Oct 2023
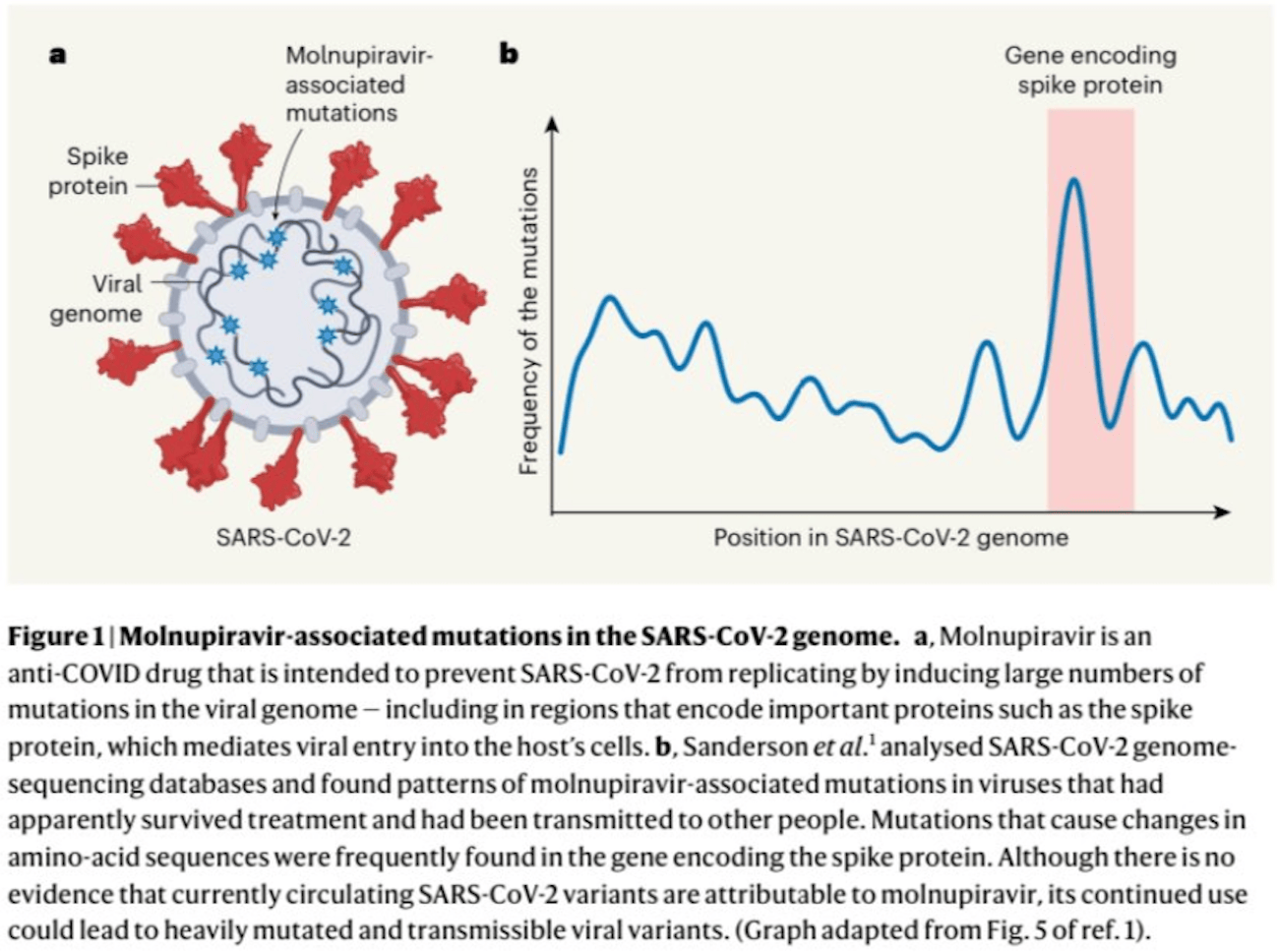
Discussion of the creation of new COVID-19 variants via treatment with molnupiravir. Sanderson et al.1 showed that thousands of viruses with many mutations - sometimes more than 100 - survived molnupiravir treatment, and that mutated viruses were transmitted between individuals and continued to accumulate mutations.
The prevalence of viral genomes with signatures of molnupiravir-induced mutations was strongly correlated with when, where, and how often molnipiravir was used. The mutational signatures were also more common in viruses from older individuals, who tended to be treated with molnupiravir more often.
Authors note that in addition to the evidence of new variants being created, molnupiravir has shown low efficacy2, and data indicates interaction with, and therefore potentially mutatation of, host DNA3,4.
Potential risks of molnupiravir include the creation of dangerous variants, and mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, and embryotoxicity3-17. Multiple analyses have identified variants potentially created by molnupiravir1,18-21 . Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury22, cardiovascular toxocity23, and neurological symptoms22. Treatment may increase viral rebound24,25.
1.
Sanderson et al., A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6.
2.
Butler et al., Molnupiravir plus usual care versus usual care alone as early treatment for adults with COVID-19 at increased risk of adverse outcomes (PANORAMIC): an open-label, platform-adaptive randomised controlled trial, The Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1.
3.
Swanstrom et al., Lethal mutagenesis as an antiviral strategy, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abn0048.
4.
Zhou et al., β-D-N4-hydroxycytidine Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Through Lethal Mutagenesis But Is Also Mutagenic To Mammalian Cells, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab247.
5.
Hadj Hassine et al., Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040841.
6.
Shum, C., An investigational study into the drug-associated mutational signature in SARS-CoV-2 viruses, The University of Hong Kong, PhD Thesis, hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/344396.
7.
Waters et al., Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22471.
8.
Huntsman, M., An assessment of the reproductive toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using stem cell-based embryo models, Master's Thesis, scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/items/cd11342c-b4dc-44c0-8b44-ce6e3369c40b.
9.
Huntsman (B) et al., Detection of developmental toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using gastruloid-based in vitro assays, Toxicological Sciences, doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfaf093.
10.
Zibat et al., N4-hydroxycytidine, the active compound of Molnupiravir, promotes SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis and escape from a neutralizing nanobody, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.107786.
11.
Shiraki et al., Convenient screening of the reproductive toxicity of favipiravir and antiviral drugs in Caenorhabditis elegans, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35331.
12.
Gruber et al., Molnupiravir increases SARS‐CoV‐2 genome diversity and complexity: A case‐control cohort study, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29642.
13.
Marikawa et al., An active metabolite of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir impairs mouse preimplantation embryos at clinically relevant concentrations, Reproductive Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2023.108475.
14.
Rahman, M., Elucidation of the DNA repair mechanisms involved in the repair of DNA damage caused by the Arabinosides and Anti-COVID-19 drugs, tokyo-metro-u.repo.nii.ac.jp/records/2000972.
15.
Chamod et al., Molnupiravir Metabolite--N4-hydroxycytidine Causes Cytotoxicity and DNA Damage in Mammalian Cells in vitro: N4-hydroxycytidine Induced Cytotoxicity DNA Damage, Asian Medical Journal and Alternative Medicine, 23:3, asianmedjam.com/index.php/amjam/article/view/1448.
16.
Standing et al., Randomized controlled trial of molnupiravir SARS-CoV-2 viral and antibody response in at-risk adult outpatients, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-45641-0.
17.
Mori et al., Reactive oxygen species-mediated cytotoxic and DNA-damaging mechanism of N4-hydroxycytidine, a metabolite of the COVID-19 therapeutic drug molnupiravir, Free Radical Research, doi:10.1080/10715762.2025.2469738.
18.
Focosi et al., The fitness of molnupiravir-signed SARS-CoV-2 variants: imputation analysis based on prescription counts and GISAID analyses by country, Intervirology, doi:10.1159/000540282.
19.
Fountain-Jones et al., Effect of molnupiravir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients: a retrospective observational study, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2.
20.
Kosakovsky Pond et al., Anti-COVID drug accelerates viral evolution, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-023-03248-3.
22.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
23.
Ozhan et al., Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary effects of repurposed COVID-19 therapeutics in healthy rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31048-4.
24.
Shah et al., SARS-CoV-2 infectious shedding and rebound among adults with and without oral antiviral use: two case-ascertained prospective household studies, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101227.
25.
Prager et al., Viral kinetics in adults with Covid-19 treated with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir or molnupiravir: a population-based, observational cohort study, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-025-03057-2.
26.
Shen et al., Carboxylesterase Factors Influencing the Therapeutic Activity of Common Antiviral Medications Used for SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics17070832.
27.
Bacigalupo et al., Unveiling patenting strategies of therapeutics and vaccines: evergreening in the context of COVID-19 pandemic, Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1287542.
28.
Boretti, A., On the choice of Molnupiravir and Paxlovid as the only antivirals permitted for COVID-19 infection in Australia, Clinical and Experimental Medicine, doi:10.1007/s10238-023-01010-7.
29.
Anonymous, Treating a Pandemic Respiratory Disease with a Mutagen is a Doomsday Scenario, Authorea, doi:10.22541/au.163854323.34557301/v1.
Kosakovsky Pond et al., 24 Oct 2023, peer-reviewed, 2 authors.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-023-03248-3",
"ISSN": [
"0028-0836",
"1476-4687"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/d41586-023-03248-3",
"alternative-id": [
"CM26185304"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kosakovsky Pond",
"given": "Sergei L.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "Darren",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nature",
"container-title-short": "Nature",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-24T10:05:40Z",
"timestamp": 1698141940000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-24T10:17:07Z",
"timestamp": 1698142627000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-25T05:37:45Z",
"timestamp": 1698212265311
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
24
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springernature.com/gp/researchers/text-and-data-mining",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-24T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1698105600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springernature.com/gp/researchers/text-and-data-mining",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-24T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1698105600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-023-03248-3.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-023-03248-3",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-023-03248-3.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
24
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
24
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"author": "T. Sanderson",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "CM26185304_CR1",
"unstructured": "Sanderson, T. et al. Nature https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6 (2023).",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01348-19",
"author": "M. L. Agostini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e01348",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "CM26185304_CR2",
"unstructured": "Agostini, M. L. et al. J. Virol. 93, e01348-19 (2019).",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pbio.3002214",
"author": "G. Lobinska",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e3002214",
"journal-title": "PLoS Biol.",
"key": "CM26185304_CR3",
"unstructured": "Lobinska, G., Pilpel, Y. & Nowak, M. A. PLoS Biol. 21, e3002214 (2023).",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.100943",
"author": "C. Chaguza",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100943",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep. Med.",
"key": "CM26185304_CR4",
"unstructured": "Chaguza, C. et al. Cell Rep. Med. 4, 100943 (2023).",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1",
"author": "C. C. Butler",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "281",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "CM26185304_CR5",
"unstructured": "Butler, C. C. et al. Lancet 401, 281–293 (2023).",
"volume": "401",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abn0048",
"author": "R. Swanstrom",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "CM26185304_CR6",
"unstructured": "Swanstrom, R. & Schinazi, R. F. Science 375, 497–498 (2022).",
"volume": "375",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiab247",
"author": "S. Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "415",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "CM26185304_CR7",
"unstructured": "Zhou, S. et al. J. Infect. Dis. 224, 415–419 (2021).",
"volume": "224",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 7,
"references-count": 7,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-023-03248-3"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Multidisciplinary"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Anti-COVID drug accelerates viral evolution",
"type": "journal-article"
}