Molnupiravir increases SARS‐CoV‐2 genome diversity and complexity: A case‐control cohort study
et al., Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29642, May 2024
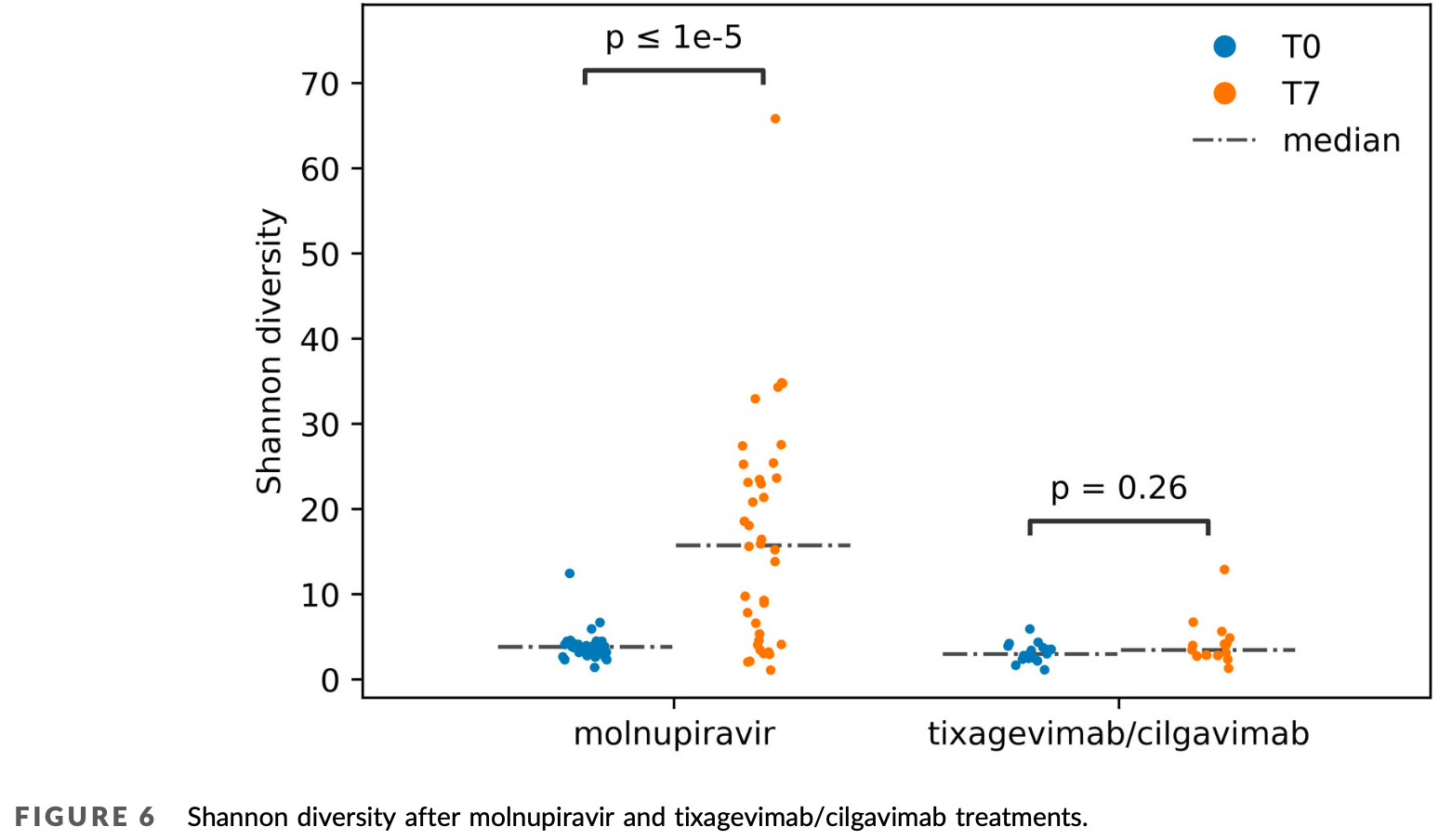
Analysis of 38 COVID-19 outpatients treated with molnupiravir showing significantly increased SARS-CoV-2 genetic diversity and complexity compared to 17 patients treated with tixagevimab/cilgavimab. Molnupiravir increased the mutation rate, specifically the G to A and C to T transitions. Additionally, an increase in the diversity and complexity of viral quasispecies was observed, suggesting that molnupiravir-induced variants can lead to significant genetic changes in SARS-CoV-2. The findings confirm that molnupiravir can induce the generation of new SARS-CoV-2 variants in both immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients.
Potential risks of molnupiravir include the creation of dangerous variants, and mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, and embryotoxicity1-15. Multiple analyses have identified variants potentially created by molnupiravir16-20. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury21, cardiovascular toxocity22, and neurological symptoms21. Treatment may increase viral rebound23,24.
1.
Swanstrom et al., Lethal mutagenesis as an antiviral strategy, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abn0048.
2.
Hadj Hassine et al., Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040841.
3.
Shum, C., An investigational study into the drug-associated mutational signature in SARS-CoV-2 viruses, The University of Hong Kong, PhD Thesis, hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/344396.
4.
Waters et al., Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22471.
5.
Huntsman, M., An assessment of the reproductive toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using stem cell-based embryo models, Master's Thesis, scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/items/cd11342c-b4dc-44c0-8b44-ce6e3369c40b.
6.
Huntsman (B) et al., Detection of developmental toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using gastruloid-based in vitro assays, Toxicological Sciences, doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfaf093.
7.
Zibat et al., N4-hydroxycytidine, the active compound of Molnupiravir, promotes SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis and escape from a neutralizing nanobody, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.107786.
8.
Shiraki et al., Convenient screening of the reproductive toxicity of favipiravir and antiviral drugs in Caenorhabditis elegans, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35331.
9.
Gruber et al., Molnupiravir increases SARS‐CoV‐2 genome diversity and complexity: A case‐control cohort study, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29642.
10.
Marikawa et al., An active metabolite of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir impairs mouse preimplantation embryos at clinically relevant concentrations, Reproductive Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2023.108475.
11.
Rahman, M., Elucidation of the DNA repair mechanisms involved in the repair of DNA damage caused by the Arabinosides and Anti-COVID-19 drugs, tokyo-metro-u.repo.nii.ac.jp/records/2000972.
12.
Zhou et al., β-D-N4-hydroxycytidine Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Through Lethal Mutagenesis But Is Also Mutagenic To Mammalian Cells, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab247.
13.
Chamod et al., Molnupiravir Metabolite--N4-hydroxycytidine Causes Cytotoxicity and DNA Damage in Mammalian Cells in vitro: N4-hydroxycytidine Induced Cytotoxicity DNA Damage, Asian Medical Journal and Alternative Medicine, 23:3, asianmedjam.com/index.php/amjam/article/view/1448.
14.
Standing et al., Randomized controlled trial of molnupiravir SARS-CoV-2 viral and antibody response in at-risk adult outpatients, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-45641-0.
15.
Mori et al., Reactive oxygen species-mediated cytotoxic and DNA-damaging mechanism of N4-hydroxycytidine, a metabolite of the COVID-19 therapeutic drug molnupiravir, Free Radical Research, doi:10.1080/10715762.2025.2469738.
16.
Focosi et al., The fitness of molnupiravir-signed SARS-CoV-2 variants: imputation analysis based on prescription counts and GISAID analyses by country, Intervirology, doi:10.1159/000540282.
17.
Sanderson et al., A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6.
18.
Fountain-Jones et al., Effect of molnupiravir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients: a retrospective observational study, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2.
19.
Kosakovsky Pond et al., Anti-COVID drug accelerates viral evolution, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-023-03248-3.
21.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
22.
Ozhan et al., Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary effects of repurposed COVID-19 therapeutics in healthy rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31048-4.
Gruber et al., 6 May 2024, retrospective, Italy, peer-reviewed, median age 76.0, 18 authors, study period July 2022 - September 2022.
Contact: martina.rueca@inmi.it.
Molnupiravir increases SARS‐CoV‐2 genome diversity and complexity: A case‐control cohort study
Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29642
Molnupiravir, an oral direct-acting antiviral effective in vitro against SARS-CoV-2, has been largely employed
effective transmission of newly drug-induced possibly emerging variants. In conclusions, our data confirm the suspect that molnupiravir-generated variants can be generated also in immunocompetent outpatients 33 and highlight the importance of genomic surveillance in the characterization of new, potentially transmissible drug-derived variants.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS Cesare Ernesto Maria Gruber, Emanuela Giombini, Martina Rueca, and Daniele Focosi conceived the study and developed the study protocol. Enrico Girardi and Fabrizio Maggi provided oversight and supervision. Martina Rueca, Lavinia Fabeni, Giulia Berno, Ornella Butera, Eliana Specchiarello, and Fabrizio Carletti did the molecular assays and sequencing. Valentina Mazzotta, Ilaria Mastrorosa, Silvia Rosati, Emanuele Nicastri, and Andrea Antinori collected the clinical data. Fabio Giovanni Tucci, Emanuela Giombini, and Cesare Ernesto Maria Gruber did the bioinformatic analyses of the data. Cesare Ernesto Maria Gruber, Emanuela Giombini, and Fabio Giovanni Tucci wrote the original draft of the manuscript. Fabrizio Maggi, Andrea Antinori, and Daniele Focosi critically reviewed the manuscript. All authors had access to the data in the study and were ultimately responsible for deciding to submit it for publication.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT The authors declare no conflict of interest.
ETHICS STATEMENT The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of
References
Abbate, Vlassi, Rozera, Detection of quasispecies variants predicted to use CXCR4 by ultra-deep pyrosequencing during early HIV infection, AIDS, doi:10.1097/QAD.0b013e328343489e
Alteri, Fox, Scutari, A proof-of-concept study on the genomic evolution of Sars-Cov-2 in molnupiravir-treated, paxlovid-treated and drug-naïve patients, Commun Biol
Bernal, Da Silva, Musungaie, Molnupiravir for oral treatment of Covid-19 in nonhospitalized patients, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2116044
Bloom, Beichman, Neher, Harris, Evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 Mutational Spectrum, Mol Biol Evol, doi:10.1093/molbev/msad085
Bloom, Beichman, Neher, Harris, Evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 mutational spectrum, Mol Biol Evol, doi:10.1093/molbev/msad085
Bolger, Lohse, Usadel, Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data, Bioinformatics, doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
Caraco, Crofoot, Moncada, Phase 2/3 trial of molnupiravir for treatment of Covid-19 in nonhospitalized adults, NEJM Evid, doi:10.1056/EVIDoa2100043
Curtis, Merck presentation about molnupiravir for the U.S. Food & Drug Administration Antimicrobial Drugs Advisory Committee
Donovan-Banfield, Penrice-Randal, Goldswain, Characterisation of SARS-CoV-2 genomic variation in response to molnupiravir treatment in the AGILE phase IIa clinical trial, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-022-34839-9
Focosi, Casadevall, A critical analysis of the use of cilgavimab plus tixagevimab monoclonal antibody cocktail (Evusheld™) for COVID-19 prophylaxis and treatment, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14091999
Fountain-Jones, Vanhaeften, Williamson, Effect of molnupiravir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients: a retrospective observational study, Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2
Giorgio, Martignano, Torcia, Mattiuz, Conticello, Evidence for host-dependent RNA editing in the transcriptome of SARS-CoV-2, Sci Adv, doi:10.1126/sciadv.abb5813
Gregori, Perales, Rodriguez-Frias, Esteban, Quer et al., Viral quasispecies complexity measures, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2016.03.017
Hakmaoui, Khan, Liacini, Relevant SARS-CoV-2 genome variation through six months of worldwide monitoring, BioMed Res Int, doi:10.1155/2021/5553173
Kabinger, Stiller, Schmitzová, Mechanism of molnupiravirinduced SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis, Nat Struct Mol Biol, doi:10.1038/s41594-021-00651-0
Koboldt, Chen, Wylie, VarScan: variant detection in massively parallel sequencing of individual and pooled samples, Bioinformatics, doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp373
Nakamura, Fujimoto, Hasegawa, A phase I, randomized, placebo-controlled study of molnupiravir in healthy Japanese to support special approval in Japan to treat COVID-19, Clin Transl Sci, doi:10.1111/cts.13395
Penrice-Randal, Bentley, Sharma, The effect of molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir on SARS-CoV-2 genome diversity in infected and immune suppressed mice. bioRxiv, J Med Virol
Roy, Mandal, Mondal, Trends of mutation accumulation across global SARS-CoV-2 genomes: implications for the evolution of the novel coronavirus, Genomics, doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.11.003
Rueca, Bartolini, Gruber, Compartmentalized replication of SARS-Cov-2 in upper vs. lower respiratory tract assessed by whole genome quasispecies analysis, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms8091302
Rueca, Giombini, Messina, The easy-to-use SARS-CoV-2 assembler for genome sequencing: development study, JMIR Bioinform Biotech
Sanderson, Hisner, Donovan-Banfield, A molnupiravirassociated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6
Sanderson, Hisner, Donovan-Banfield, A molnupiravirassociated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6
Sheahan, Stevens, Narowski, The antiviral mechanism of action of molnupiravir in humans with COVID-19, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.11.21.23298766
Stavrou, Ross, APOBEC3 proteins in viral immunity, J Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1501504
Swanstrom, Schinazi, Lethal mutagenesis as an antiviral strategy, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abn0048
Syed, Molnupiravir: first approval, Drugs, doi:10.1007/s40265-022-01684-5
Tian, Tong, Sun, Mutation N501Y in RBD of spike protein strengthens the interaction between COVID-19 and its receptor ACE2. bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.02.14.431117
Wang, Wang, Zhang, Intra-host variation and evolutionary dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 populations in COVID-19 patients, Genome Med, doi:10.1186/s13073-021-00847-5
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.29642",
"ISSN": [
"0146-6615",
"1096-9071"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jmv.29642",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>Molnupiravir, an oral direct‐acting antiviral effective in vitro against SARS‐CoV‐2, has been largely employed during the COVID‐19 pandemic, since December 2021. After marketing and widespread usage, a progressive increase in SARS‐CoV‐2 lineages characterized by a higher transition/transversion ratio, a characteristic signature of molnupiravir action, appeared in the Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data (GISAID) and International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration (INSDC) databases. Here, we assessed the drug effects by SARS‐CoV‐2 whole‐genome sequencing on 38 molnupiravir‐treated persistently positive COVID‐19 outpatients tested before and after treatment. Seventeen tixagevimab/cilgavimab‐treated outpatients served as controls. Mutational analyses confirmed that SARS‐CoV‐2 exhibits an increased transition/transversion ratio seven days after initiation of molnupiravir. Moreover we observed an increased G‐>A ratio compared to controls, which was not related to apolipoprotein B mRNAediting enzyme, catalytic polypeptide‐like (APOBEC) activity. In addition, we demonstrated for the first time an increased diversity and complexity of the viral quasispecies.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/jmv.29642"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2024-03-05"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2024-04-22"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2024-05-06"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8831-3380",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Virology National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Gruber",
"given": "Cesare Ernesto Maria",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biology University of Rome Tor Vergata Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Tucci",
"given": "Fabio Giovanni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Virology National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Giombini",
"given": "Emanuela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0240-7504",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical and Research Infectious Diseases Department National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mazzotta",
"given": "Valentina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Virology National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Spezia",
"given": "Pietro Giorgio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5162-046X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Virology National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Rueca",
"given": "Martina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical and Research Infectious Diseases Department National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Mastrorosa",
"given": "Ilaria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Virology National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Fabeni",
"given": "Lavinia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Virology National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Berno",
"given": "Giulia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Microbiology National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Butera",
"given": "Ornella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical and Research Infectious Diseases Department National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Rosati",
"given": "Silvia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Virology National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Specchiarello",
"given": "Eliana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Virology National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Carletti",
"given": "Fabrizio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8811-195X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "North‐Western Tuscany Blood Bank Pisa University Hospital Pisa Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Focosi",
"given": "Daniele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical and Research Infectious Diseases Department National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Nicastri",
"given": "Emanuele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Scientific Direction National Institute for Infectious Diseases “L. Spallanzani”—IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Girardi",
"given": "Enrico",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical and Research Infectious Diseases Department National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Antinori",
"given": "Andrea",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Virology National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Maggi",
"given": "Fabrizio",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Medical Virology",
"container-title-short": "Journal of Medical Virology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-06T10:40:21Z",
"timestamp": 1714992021000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-06T10:40:30Z",
"timestamp": 1714992030000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100000780",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "European Commission"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100003196",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Ministero della Salute"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-07T00:31:43Z",
"timestamp": 1715041903785
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 5,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1714953600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/jmv.29642",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
6
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_2_1",
"unstructured": "Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for Lagevrio™ (molnupiravir) capsules. Accessed January 12 2024.https://www.fda.gov/media/155054/download"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40265-022-01684-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_3_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_4_1",
"unstructured": "EMA Assessment Report. Use of molnupiravir for the treatment of COVID‐19. Accessed January 12 2024.https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/referral/lagevrio-also-known-molnupiravir-or-mk-4482-covid-19-article-53-procedure-assessment-report_en.pdf"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41594-021-00651-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.02.14.431117",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_10_6_1",
"unstructured": "TianF TongB SunL et al. Mutation N501Y in RBD of spike protein strengthens the interaction between COVID‐19 and its receptor ACE2.bioRxiv. Preprint posted online February 18 2021.doi:10.1101/2021.02.14.431117"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cts.13395",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/EVIDoa2100043",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116044",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_9_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_10_1",
"unstructured": "European Medicine Agency. Lagevrio.2023. Accessed May 26 2023.https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/summaries-opinion/lagevrio"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abn0048",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/molbev/msad085",
"article-title": "Evolution of the SARS‐CoV‐2 Mutational Spectrum",
"author": "Bloom JD",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Mol Biol Evol",
"key": "e_1_2_10_13_1",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/molbev/msad085",
"article-title": "Evolution of the SARS‐CoV‐2 mutational spectrum",
"author": "Bloom JD",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Mol Biol Evol",
"key": "e_1_2_10_14_1",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_15_1",
"unstructured": "Sean Curtis. Merck presentation about molnupiravir for the U.S. Food & Drug Administration Antimicrobial Drugs Advisory Committee. November 30 2021. Accessed October 6 2022. https://www.fda.gov/media/154472/download"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.abb5813",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1501504",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/QAD.0b013e328343489e",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms8091302",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_19_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13073-021-00847-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_20_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42003-022-04322-8",
"article-title": "A proof‐of‐concept study on the genomic evolution of Sars‐Cov‐2 in molnupiravir‐treated, paxlovid‐treated and drug‐naïve patients",
"author": "Alteri C",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Commun Biol",
"key": "e_1_2_10_21_1",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-34839-9",
"article-title": "Characterisation of SARS‐CoV‐2 genomic variation in response to molnupiravir treatment in the AGILE phase IIa clinical trial",
"author": "Donovan‐Banfield I",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7284",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "e_1_2_10_22_1",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_10_23_1",
"unstructured": "Fountain‐Jones NM Vanhaeften R Williamson J et al. Effect of molnupiravir on SARS‐CoV‐2 evolution in immunocompromised patients: a retrospective observational study. Lancet Microbe. Published online March 22 2024. doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2016.03.017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_24_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v14091999",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2196/31536",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bioinformatics/btp373",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_28_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_29_1",
"unstructured": "UK Health Security Agency. England COVID19 (Coronavirus) Dashboard-Potential MOV sequences. Accessed January 12 2024.https://ukcovid.xyz/molnupiravir/"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_30_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2023.11.21.23298766",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_10_31_1",
"unstructured": "SheahanTP StevensLJ NarowskiTM et al. The antiviral mechanism of action of molnupiravir in humans with COVID‐19.medRxiv. Preprint posted online November 27 2023.doi:10.1101/2023.11.21.23298766"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.11.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_32_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2021/5553173",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_33_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2024.02.27.582110",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_10_34_1",
"unstructured": "Penrice‐RandalR BentleyEG SharmaP et al. The effect of molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir on SARS‐CoV‐2 genome diversity in infected and immune suppressed mice. bioRxiv. Preprint posted online February 28 2024.doi:10.1101/2024.02.27.582110"
}
],
"reference-count": 33,
"references-count": 33,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jmv.29642"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Molnupiravir increases SARS‐CoV‐2 genome diversity and complexity: A case‐control cohort study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "96"
}