Effect of molnupiravir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients: a retrospective observational study
et al., The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2, Mar 2024
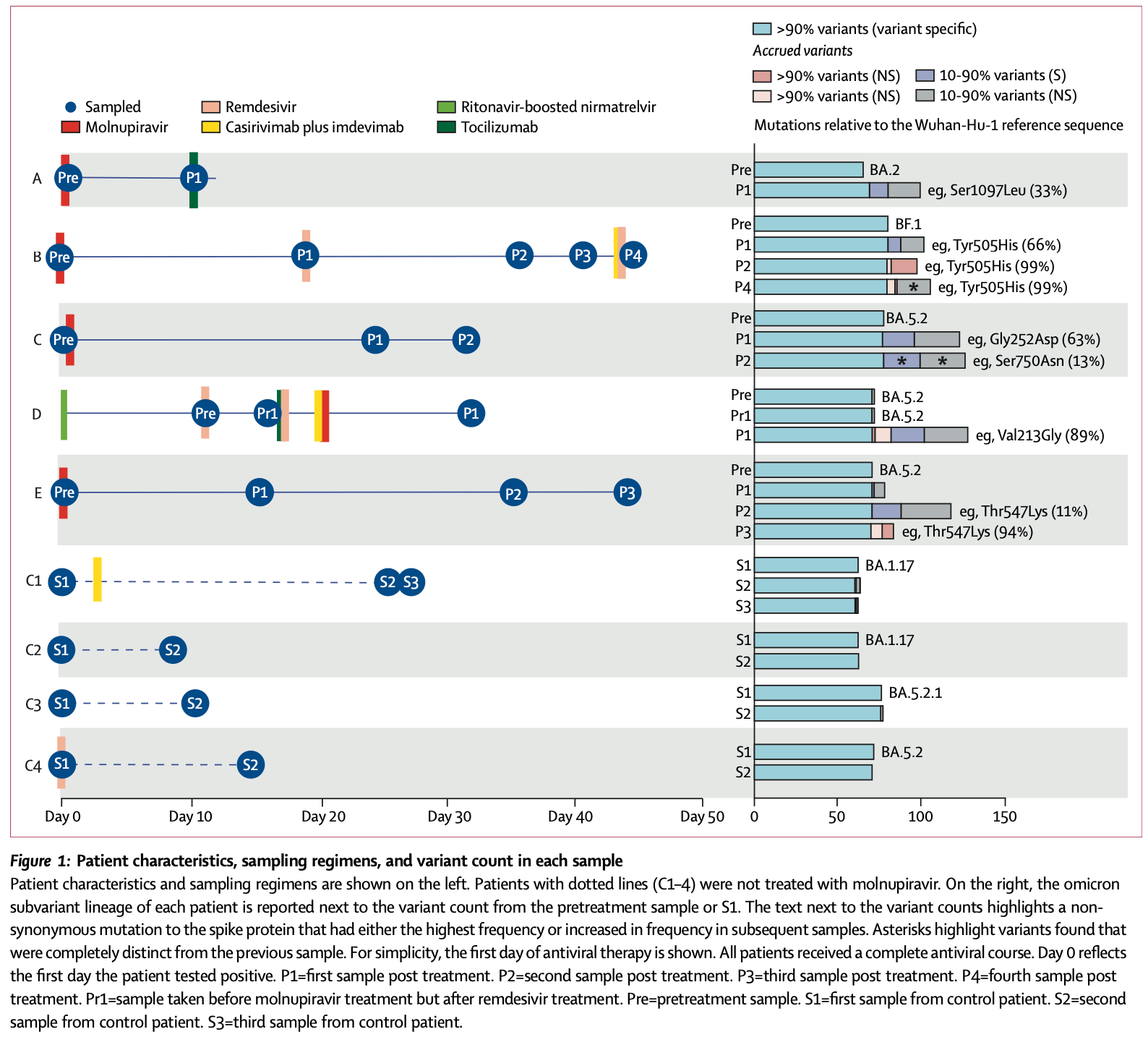
Analysis of immunocompromised COVID-19 showing rapid creation of new variants with molnupiravir. Some mutations became fixed in the viral population and the distinctive mutational pattern, dominated by G-to-A and C-to-T transitions, persisted up to 44 days post-treatment. Treated patients maintained PCR positivity for the duration of monitoring, indicating potential for transmission of mutated virus and subsequent emergence of novel variants. Authors note that uncontrolled use may generate new variants with a transmission advantage that prolongs the pandemic and makes other therapeutics less effective.
Potential risks of molnupiravir include the creation of dangerous variants, and mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, and embryotoxicity1-15. Multiple analyses have identified variants potentially created by molnupiravir16-20. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury21, cardiovascular toxocity22, and neurological symptoms21. Treatment may increase viral rebound23,24.
1.
Swanstrom et al., Lethal mutagenesis as an antiviral strategy, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abn0048.
2.
Hadj Hassine et al., Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040841.
3.
Shum, C., An investigational study into the drug-associated mutational signature in SARS-CoV-2 viruses, The University of Hong Kong, PhD Thesis, hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/344396.
4.
Waters et al., Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22471.
5.
Huntsman, M., An assessment of the reproductive toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using stem cell-based embryo models, Master's Thesis, scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/items/cd11342c-b4dc-44c0-8b44-ce6e3369c40b.
6.
Huntsman (B) et al., Detection of developmental toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using gastruloid-based in vitro assays, Toxicological Sciences, doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfaf093.
7.
Zibat et al., N4-hydroxycytidine, the active compound of Molnupiravir, promotes SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis and escape from a neutralizing nanobody, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.107786.
8.
Shiraki et al., Convenient screening of the reproductive toxicity of favipiravir and antiviral drugs in Caenorhabditis elegans, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35331.
9.
Gruber et al., Molnupiravir increases SARS‐CoV‐2 genome diversity and complexity: A case‐control cohort study, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29642.
10.
Marikawa et al., An active metabolite of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir impairs mouse preimplantation embryos at clinically relevant concentrations, Reproductive Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2023.108475.
11.
Rahman, M., Elucidation of the DNA repair mechanisms involved in the repair of DNA damage caused by the Arabinosides and Anti-COVID-19 drugs, tokyo-metro-u.repo.nii.ac.jp/records/2000972.
12.
Zhou et al., β-D-N4-hydroxycytidine Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Through Lethal Mutagenesis But Is Also Mutagenic To Mammalian Cells, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab247.
13.
Chamod et al., Molnupiravir Metabolite--N4-hydroxycytidine Causes Cytotoxicity and DNA Damage in Mammalian Cells in vitro: N4-hydroxycytidine Induced Cytotoxicity DNA Damage, Asian Medical Journal and Alternative Medicine, 23:3, asianmedjam.com/index.php/amjam/article/view/1448.
14.
Standing et al., Randomized controlled trial of molnupiravir SARS-CoV-2 viral and antibody response in at-risk adult outpatients, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-45641-0.
15.
Mori et al., Reactive oxygen species-mediated cytotoxic and DNA-damaging mechanism of N4-hydroxycytidine, a metabolite of the COVID-19 therapeutic drug molnupiravir, Free Radical Research, doi:10.1080/10715762.2025.2469738.
16.
Focosi et al., The fitness of molnupiravir-signed SARS-CoV-2 variants: imputation analysis based on prescription counts and GISAID analyses by country, Intervirology, doi:10.1159/000540282.
17.
Sanderson et al., A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6.
18.
Fountain-Jones et al., Effect of molnupiravir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients: a retrospective observational study, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2.
19.
Kosakovsky Pond et al., Anti-COVID drug accelerates viral evolution, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-023-03248-3.
21.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
22.
Ozhan et al., Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary effects of repurposed COVID-19 therapeutics in healthy rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31048-4.
Fountain-Jones et al., 22 Mar 2024, Australia, peer-reviewed, 7 authors.
Contact: nick.fountainjones@utas.edu.au.
Effect of molnupiravir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients: a retrospective observational study
doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-
Introduction Continued SARS-CoV-2 infection among immunocompromised individuals is likely to play a role in generating genomic diversity and the emergence of novel variants. Antiviral treatments such as molnupiravir are used to mitigate severe COVID-19 outcomes, but the extended effects of these drugs on viral evolution in patients with chronic infections remain uncertain. This study investigates how molnupiravir affects SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients with prolonged infections.
Methods The study included five immunocompromised patients treated with molnupiravir and four patients not treated with molnupiravir (two immunocompromised and two non-immunocompromised). We selected patients who had been infected by similar SARS-CoV-2 variants and with high-quality genomes across timepoints to allow comparison between groups. Throat and nasopharyngeal samples were collected in patients up to 44 days post treatment and were sequenced using tiled amplicon sequencing followed by variant calling. The UShER pipeline and University of California Santa Cruz genome viewer provided insights into the global context of variants. Treated and untreated patients were compared, and mutation profiles were visualised to understand the impact of molnupiravir on viral evolution. Findings Patients treated with molnupiravir showed a large increase in low-to-mid-frequency variants in as little as 10 days after treatment, whereas no such change was observed in untreated patients. Some of these variants became fixed in the viral population, including non-synonymous mutations in the spike protein. The variants were distributed across the genome and included unique mutations not commonly found in global omicron genomes. Notably, G-to-A and C-to-T mutations dominated the mutational profile of treated patients, persisting up to 44 days post treatment. Interpretation Molnupiravir treatment in immunocompromised patients led to the accumulation of a distinctive pattern of mutations beyond the recommended 5 days of treatment. Treated patients maintained persistent PCR positivity for the duration of monitoring, indicating clear potential for transmission and subsequent emergence of novel variants.
References
Bloom, Beichman, Neher, Harris, Evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 mutational spectrum, Mol Biol Evol
Donovan-Banfield, Penrice-Randal, Goldswain, Characterisation of SARS-CoV-2 genomic variation in response to molnupiravir treatment in the AGILE phase IIa clinical trial, Nat Commun
Fantini, Yahi, Colson, Chahinian, Scola et al., The puzzling mutational landscape of the SARS-2-variant omicron, J Med Virol
Gold, Kelleher, Magid, Dispensing of oral antiviral drugs for treatment of COVID-19 by zip code-level social vulnerability-United States, December 23, 2021, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Gupta, Konnova, Smet, Host immunological responses facilitate development of SARS-CoV-2 mutations in patients receiving monoclonal antibody treatments, J Clin Invest
Kabinger, Stiller, Schmitzová, Mechanism of molnupiravir-induced SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis, Nat Struct Mol Biol
Karim, Moosa, Gosnell, Persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection and intra-host evolution in association with advanced HIV infection, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.06.03.21258228
Lynch, Macori, Fanning, Genomic evolution of SARS-CoV-2 virus in immunocompromised patient, Ireland, Emerg Infect Dis
Ragonnet-Cronin, Nutalai, Huo, Generation of SARS-CoV-2 escape mutations by monoclonal antibody therapy, Nat Commun
Rambaut, Loman, Pybus, Preliminary genomic characterisation of an emergent SARS-CoV-2 lineage in the UK defined by a novel set of spike mutations
Sanderson, Hisner, Donovan-Banfield, A molnupiravirassociated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes, Nature
Singh, Singh, Singh, Misra, An updated practical guideline on use of molnupiravir and comparison with agents having emergency use authorization for treatment of COVID-19, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Tegally, Wilkinson, Giovanetti, Detection of a SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern in South Africa, Nature
Turakhia, Thornlow, Hinrichs, Ultrafast sample placement on existing trees (UShER) enables real-time phylogenetics for the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, Nat Genet
Viana, Moyo, Amoako, Rapid epidemic expansion of the SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant in southern Africa, Nature
Wickam, ggplot2: elegant graphics for data analysis
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2666-5247(23)00393-2",
"ISSN": [
"2666-5247"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2",
"alternative-id": [
"S2666524723003932"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Effect of molnupiravir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients: a retrospective observational study"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "The Lancet Microbe"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9248-8493",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Fountain-Jones",
"given": "Nicholas M",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vanhaeften",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williamson",
"given": "Jan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maskell",
"given": "Janelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chua",
"given": "I-Ly J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Charleston",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cooley",
"given": "Louise",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Lancet Microbe",
"container-title-short": "The Lancet Microbe",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"thelancet.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-22T19:52:45Z",
"timestamp": 1711137165000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-22T20:30:02Z",
"timestamp": 1711139402000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100000923",
"award": [
"DP190102020"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Australian Research Council"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-23T01:04:40Z",
"timestamp": 1711155880396
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1709251200000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-21T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1700524800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2666524723003932?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2666524723003932?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection and intra-host evolution in association with advanced HIV infection",
"author": "Karim",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2_bib1",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03402-9",
"article-title": "Detection of a SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern in South Africa",
"author": "Tegally",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "438",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2_bib2",
"volume": "592",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "An updated practical guideline on use of molnupiravir and comparison with agents having emergency use authorization for treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Singh",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2_bib4",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41594-021-00651-0",
"article-title": "Mechanism of molnupiravir-induced SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis",
"author": "Kabinger",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "740",
"journal-title": "Nat Struct Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2_bib5",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6",
"article-title": "A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes",
"author": "Sanderson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "594",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2_bib6",
"volume": "623",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/molbev/msad085",
"article-title": "Evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 mutational spectrum",
"author": "Bloom",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Mol Biol Evol",
"key": "10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2_bib7",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7125e1",
"article-title": "Dispensing of oral antiviral drugs for treatment of COVID-19 by zip code-level social vulnerability—United States, December 23, 2021–May 21, 2022",
"author": "Gold",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "825",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2_bib8",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Characterisation of SARS-CoV-2 genomic variation in response to molnupiravir treatment in the AGILE phase IIa clinical trial",
"author": "Donovan-Banfield",
"first-page": "7284",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2_bib10",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41588-021-00862-7",
"article-title": "Ultrafast sample placement on existing trees (UShER) enables real-time phylogenetics for the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic",
"author": "Turakhia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "809",
"journal-title": "Nat Genet",
"key": "10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2_bib11",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "Wickam",
"key": "10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2_bib12",
"series-title": "ggplot2: elegant graphics for data analysis",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27577",
"article-title": "The puzzling mutational landscape of the SARS-2-variant omicron",
"author": "Fantini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2019",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2_bib13",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Genomic evolution of SARS-CoV-2 virus in immunocompromised patient, Ireland",
"author": "Lynch",
"first-page": "2499",
"journal-title": "Emerg Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2_bib14",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "Rambaut",
"key": "10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2_bib15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04411-y",
"article-title": "Rapid epidemic expansion of the SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant in southern Africa",
"author": "Viana",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "679",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2_bib16",
"volume": "603",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Generation of SARS-CoV-2 escape mutations by monoclonal antibody therapy",
"author": "Ragonnet-Cronin",
"first-page": "3334",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2_bib17",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI166032",
"article-title": "Host immunological responses facilitate development of SARS-CoV-2 mutations in patients receiving monoclonal antibody treatments",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2_bib18",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 16,
"references-count": 16,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2666524723003932"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Virology",
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)",
"Microbiology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effect of molnupiravir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients: a retrospective observational study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}