Real-world data of Azvudine-induced hepatotoxicity among hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China: a retrospective case-control study
et al., Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1558054, Jun 2025
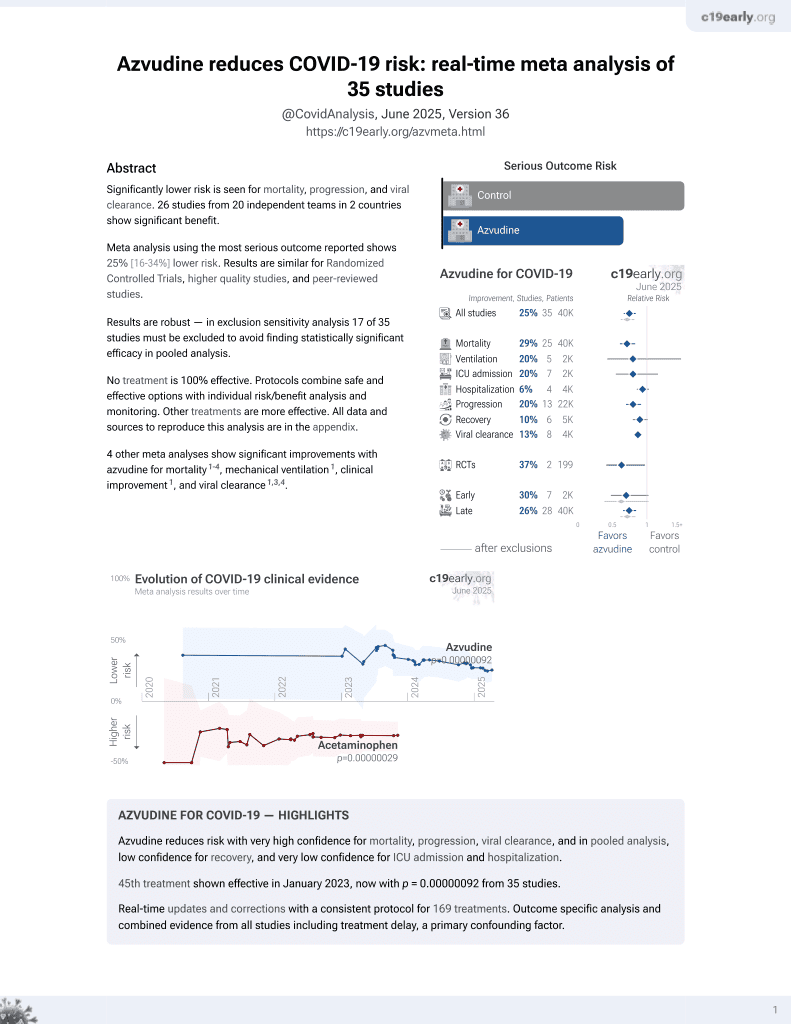
Azvudine for COVID-19
48th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2023, now with p = 0.0000000041 from 40 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective case-control study of 669 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China showing significant hepatotoxicity associated with azvudine treatment.
Xiong et al., 4 Jun 2025, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, median age 70.0, 9 authors, study period December 2022 - May 2023.
Contact: 13469996809@qq.com, yangge@tmmu.edu.cn, rm002397@outlook.com.
Real-world data of Azvudine-induced hepatotoxicity among hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China: a retrospective case-control study
Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1558054
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, has led to global health crisis. Although several antiviral drugs have been used to mitigate the severity and mortality of COVID-19, the safety profile remained a critical concern. Azvudine, a new nucleoside analog, has been approved for emergency use in China for COVID-19. However, the incidence and risk factors associated with Azvudine-induced hepatotoxicity in hospitalized patients remained unclear. Objects: To assess the prevalence, risk factors, clinical patterns, and outcomes of Azvudine-induced hepatotoxicity by real-world data.
Methods: We conducted a single-center retrospective case-control study at Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, including patients administered Azvudine for COVID-19 treatment between December 2022 and May 2023. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were preformed to assess risk factors for Azvudine-associated or -induced hepatotoxicity. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was performed to calculate the area under the ROC curve (AUC). Results: In total, 669 patients were included in the Azvudine-associated hepatotoxicity research. 47.1% patients exhibited hepatotoxicity, abnormal liver function on admission [OR: 5.55 (3.94-7.90), P < 0.001] and antithrombotic drugs [OR: 1.79 (1.27-2.54), P = 0.001] were independent predictors of Azvudineassociated hepatotoxicity, with the area under the ROC curve (AUC) was 0.756 [95% CI: 0.719-0.792, P < 0.001]. Further studies of Azvudine-induced hepatotoxicity revealed 294 cases, of which 27.2% showed hepatotoxicity. The concomitant use of antivirals [OR: 3.80 (1.47-10.1), P = 0.006] and anticoagulant drugs [OR: 3.12 (1.77-5.61), P < 0.001], particularly 2), P = 0.008], Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin Calcium [OR: 3.00 (1.69-5.33), P < 0.001], and Enoxaparin [OR: 2.68 (0.99-7.10), P = 0.047], were significantly associated with an increased risk of hepatotoxicity. Most hepatotoxicity cases were mild, and recovered or improved after drug withdrawal and treatment, whereas severe cases contributed to the progression of the primary disease and increased mortality risk.
Conclusion: Our study provided evidence of the significant association between Azvudine and hepatotoxicity in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. These findings
Ethics statement The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants' legal guardians/next of kin because This study is a single-center retrospective cohort study.
Author contributions
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1558054/ full#supplementary-material
References
Abdallah, Al-Helal, Asad, Ganciclovir-induced acute liver injury in a patient with lupus nephritis, Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl, doi:10.4103/1319-2442.139947
Allison, Guraka, Shawa, Tripathi, Moritz et al., Drug induced liver injury -a 2023 update, J. Toxicol. Environ. Health, Part B, doi:10.1080/10937404.2023.2261848
Alqahtani, Schattenberg, Liver injury in COVID-19: the current evidence, United Eur. Gastroenterol. J, doi:10.1177/2050640620924157
Andrade, Aithal, Björnsson, Kaplowitz, Kullak-Ublick et al., EASL clinical practice guidelines: drug-induced liver injury, J. Hepatol, doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2019.02.014
Andrade, Chalasani, Björnsson, Suzuki, Kullak-Ublick et al., Drug-induced liver injury, Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim, doi:10.1038/s41572-019-0105-0
Baden, El Sahly, Essink, Kotloff, Frey et al., Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2035389
Caines, Moonka, Drug hepatotoxicity: causality assessment, Clin. Liver Dis, doi:10.1016/j.cld.2019.09.001
Chen, Lin, Lu, Wu, Pan et al., Real-world effectiveness of molnupiravir, azvudine and paxlovid against mortality and viral clearance among hospitalized patients with COVID-19 infection during the omicron wave in China: a retrospective cohort study, Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2024.116353
Chen, Shi, Zhan, Yang, Liu et al., Drug-induced liver injury in COVID-19 patients during hospitalization, Med. Baltim, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000033294
Chow, Uyeki, Chu, The effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on community respiratory virus activity, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-022-00807-9
Danan, Teschke, Drug-induced liver injury: why is the Roussel Uclaf causality assessment method (RUCAM) still used 25 Years after its launch?, Drug Saf, doi:10.1007/s40264-018-0654-2
Danan, Teschke, RUCAM in drug and herb induced liver injury: the update, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms17010014
Deng, Li, Sun, Jin, Zhou et al., Real-world effectiveness of azvudine versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.28756
Grein, Ohmagari, Shin, Diaz, Asperges et al., Compassionate use of Remdesivir for patients with severe Covid-19, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007016
Gupta, Madhavan, Sehgal, Nair, Mahajan et al., Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0968-3
Han, Gao, Li, Yuan, Cui et al., Real-world effectiveness of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir versus azvudine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 during the omicron wave in Beijing: a multicenter retrospective cohort study, BMC Infect. Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-023-08965-8
Han, Li, Yuan, Cui, Han et al., Associations of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir treatment with death and clinical improvement in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 during the Omicron wave in Beijing, China: a multicentre, retrospective cohort study, Ann. Med. (Helsinki), doi:10.1080/07853890.2024.2313062
He, Li, Mu, Yang, Effect of azovudine on hepatic and renal function in patients with COVID-19:a case series study, Chin. General Pract, doi:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0117
Hu, Jiang, Shu, Zhao, Cao et al., Liver injury in COVID-19: a minireview, World J. Gastroenterol, doi:10.3748/wjg.v28.i47.6716
Hykin, Prevost, Vasconcelos, Murphy, Kelly et al., Clinical effectiveness of intravitreal therapy with ranibizumab vs aflibercept vs bevacizumab for macular edema secondary to central retinal vein occlusion: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA Ophthalmol, doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2019.3305
Kevadiya, Machhi, Herskovitz, Oleynikov, Blomberg et al., Diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2 infections, Nat. Mater, doi:10.1038/s41563-020-00906-z
Kumar, Delu, Ulasov, Kumar, Singh et al., Pharmacological insights: mitochondrial ROS generation by FNC (azvudine) in dalton's lymphoma cells revealed by super resolution imaging, Cell biochem. Biophys, doi:10.1007/s12013-024-01238-4
Kumar, Kumar, Shukla, Mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis as a therapeutic target for FNC(2′-deoxy-2′-b-fuoro-4′-azidocytidine)-induced inhibition of Dalton′s lymphoma growth and proliferation, Discov. Oncol, doi:10.1007/s12672-023-00829-6
Kwok, The significance of advanced COVID-19 diagnostic testing in pandemic control measures, Int. J. Biol. Sci, doi:10.7150/ijbs.72837
Lan, Li, Li, Zhou, Lin, 112 cases of adverse drug reactions induced by azvudine tablets in patients with COVID-19, Cent. South Pharm, doi:10.7539/j.issn.1672-2981.2024.06.040
Liu, Lin, Liao, Gao, Chen et al., Efficacy and safety of azvudine in the treatment of COVID-19, Pract. Pharm. And Clin. Remedies, doi:10.14053/j.cnki.ppcr.202310007
Liu, Liu, Fang, Li, Zhao et al., A real-world study of azivudine tablets for drug-induced liver injury caused by novel coronavirus pneumonia, Chin. J. Hosp. Pharm, doi:10.13286/j.1001-5213.2024.09.12
Liu, Yang, Zhang, Liu, Sensitivity analyses in longitudinal clinical trials via distributional imputation, Stat. Methods Med. Res, doi:10.1177/09622802221135251
Lu, Zeng, Shi, Liu, Gong et al., Low albumin combined with low-molecular-weight heparin as risk factors for liver injury using azvudine: evidence from an analysis of COVID-19 patients in a national prospective pharmacovigilance database, Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther, doi:10.5414/CP204544
Nanaw, Sherchan, Fernandez, Strassle, Powell et al., Racial/ethnic differences in the associations between trust in the U.S. healthcare system and willingness to test for and vaccinate against COVID-19, BMC Public Health, doi:10.1186/s12889-024-18526-6
Naseralallah, Aboujabal, Geryo, Al Boinin, Al Hattab et al., The determination of causality of drug induced liver injury in patients with COVID-19 clinical syndrome, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0268705
Rajaram, Jayaraman, Khoo, Saravanaa, Kukreja et al., Liver dysfunction in adults with COVID -19 infection: a longitudinal study with transient elastography evaluation, JGH Open, doi:10.1002/jgh3.13118
Ren, Luo, Yu, Song, Liang et al., A randomized, open-label, controlled clinical trial of azvudine tablets in the treatment of mild and Common COVID-19, a pilot study, Adv. Sci, doi:10.1002/advs.202001435
Rodriguez-Espada, Salgado-De La Mora, Rodriguez-Paniagua, Limon-De La Rosa, Martinez-Gutierrez et al., Histopathological impact of SARS-CoV-2 on the liver: cellular damage and long-term complications, World J. gastroenterology WJG, doi:10.3748/wjg.v30.i22.2866
Rubin, COVID-19 testing moves out of the clinic and into the home, JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc, doi:10.1001/jama.2021.15679
Russo, Hoofnagle, Gu, Fontana, Barnhart et al., Spectrum of statin hepatotoxicity: experience of the drug-induced liver injury network, Hepatology, doi:10.1002/hep.27157
Shang, Li, Guo, Zhang, Wang, Comparative analysis of the safety and effectiveness of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir and azvudine in older patients with COVID-19: a retrospective study from a tertiary hospital in China, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1362345
Sheng, Li, Li, Wang, Wang et al., Selectively T cell phosphorylation activation of azvudine in the thymus tissue with immune protection effect, Acta Pharm. Sin. B, doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2024.03.032
Shi, Zuo, Yu, Lao, Li et al., Real-world data of tigecycline-associated drug-induced liver injury among patients in China: a 3-year retrospective study as assessed by the updated RUCAM, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.761167
Su, Yang, Wang, Azvudine versus paxlovid for oral treatment of COVID-19 in Chinese patients, BMC Infect. Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-023-08828-2
Teschke, Méndez-Sánchez, Eickhoff, Liver injury in COVID-19 patients with drugs as causatives: a systematic review of 996 DILI cases published 2020/ 2021 based on RUCAM as causality assessment method, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms23094828
Wang, Sun, Zhang, Li, Qin et al., Antiviral effectiveness and survival correlation of azvudine and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in elderly severe patients with COVID-19: a retrospective real-world study, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468
Wang, Xie, Wang, Fan, Zhang et al., Effectiveness of azvudine in reducing mortality of COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and metaanalysis, Virol. J, doi:10.1186/s12985-024-02316-y
Xie, Zhao, Lian, Lin, Xie et al., Clinical characteristics of non-ICU hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 and liver injury: a retrospective study, Liver Int, doi:10.1111/liv.14449
Yang, Li, Guo, Guan, Tan et al., Comparison of the effects of low-molecular-weight heparin and Fondaparinux on liver function in patients with pulmonary embolism, J. Clin. Pharmacol, doi:10.1002/jcph.1686
Yang, Wang, Wang, Zhang, Han, Costeffectiveness of azvudine for high-risk outpatients with mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease 2019 in China, Clin. Ther, doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2024.07.009
Yang, Zhang, Wang, Xu, Wang et al., Adherence and recommended optimal treatment to azvudine application for the treatment of outpatient COVID-19 patients: a real-world retrospective study, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30619
Yang, Zhao, Xu, Luo, Yang et al., Analysis of the efficacy and safety of azvudine in treating moderate COVID-19 in kidney transplant recipients, Chin. J. New Clin. Med, doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-3806.2023.10.06
Yu, Chang, Azvudine (FNC): a promising clinical candidate for COVID-19 treatment, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00351-z
Yu, Chang, The first Chinese oral anti-COVID-19 drug azvudine launched, Innov, doi:10.1016/j.xinn.2022.100321
Yu, Mao, Chen, Chen, Chen et al., CSH guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of drug-induced liver injury, Hepatol. Int, doi:10.1007/s12072-017-9793-2
Zhang, Li, Wang, Liu, Lu et al., Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6
Zhao, Wang, Lai, Wang, Yu et al., Validation of the revised electronic version of RUCAM for diagnosis of DILI in Chinese patients, Hepatol. Commun, doi:10.1097/HC9.0000000000000235
Zhao, Wang, Zhang, Wang, Xie, Drug-induced liver injury from anti-tuberculosis treatment: a retrospective cohort study, Med. Sci. Monit, doi:10.12659/MSM.920350
Zhi, Wu, Tan, Dou, Qu, Adverse reaction of azvudine in elderly patients with COVID-19 over 75 years old, Drug Eval. Res, doi:10.7501/j.issn.1674-6376.2023.10.019
Zhong, Xu, Yang, Shen, Wang et al., COVID-19associated gastrointestinal and liver injury: clinical features and potential mechanisms, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00373-7
Zhou, Liu, Jiang, Zhang, Zhang et al., Azvudine and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with moderate-to-severe COVID-19: emulation of a randomized target trial, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.29318
Zoubek, Lucena, Andrade, Stephens, Systematic review: ibuprofen-induced liver injury, Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther, doi:10.1111/apt.15645
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2025.1558054",
"ISSN": [
"1663-9812"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2025.1558054",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, has led to global health crisis. Although several antiviral drugs have been used to mitigate the severity and mortality of COVID-19, the safety profile remained a critical concern. Azvudine, a new nucleoside analog, has been approved for emergency use in China for COVID-19. However, the incidence and risk factors associated with Azvudine-induced hepatotoxicity in hospitalized patients remained unclear.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Objects</jats:title><jats:p>To assess the prevalence, risk factors, clinical patterns, and outcomes of Azvudine-induced hepatotoxicity by real-world data.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>We conducted a single-center retrospective case-control study at Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, including patients administered Azvudine for COVID-19 treatment between December 2022 and May 2023. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were preformed to assess risk factors for Azvudine-associated or -induced hepatotoxicity. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was performed to calculate the area under the ROC curve (AUC).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>In total, 669 patients were included in the Azvudine-associated hepatotoxicity research. 47.1% patients exhibited hepatotoxicity, abnormal liver function on admission [OR: 5.55 (3.94–7.90), <jats:italic>P &lt;</jats:italic> 0.001] and antithrombotic drugs [OR: 1.79 (1.27–2.54), <jats:italic>P =</jats:italic> 0.001] were independent predictors of Azvudine-associated hepatotoxicity, with the area under the ROC curve (AUC) was 0.756 [95% CI: 0.719–0.792, <jats:italic>P &lt;</jats:italic> 0.001]. Further studies of Azvudine-induced hepatotoxicity revealed 294 cases, of which 27.2% showed hepatotoxicity. The concomitant use of antivirals [OR: 3.80 (1.47–10.1), <jats:italic>P =</jats:italic> 0.006] and anticoagulant drugs [OR: 3.12 (1.77–5.61), <jats:italic>P &lt;</jats:italic> 0.001], particularly Ganciclovir [OR: 4.11 (1.45–12.2), <jats:italic>P =</jats:italic> 0.008], Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin Calcium [OR: 3.00 (1.69–5.33), <jats:italic>P &lt;</jats:italic> 0.001], and Enoxaparin [OR: 2.68 (0.99–7.10), <jats:italic>P =</jats:italic> 0.047], were significantly associated with an increased risk of hepatotoxicity. Most hepatotoxicity cases were mild, and recovered or improved after drug withdrawal and treatment, whereas severe cases contributed to the progression of the primary disease and increased mortality risk.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>Our study provided evidence of the significant association between Azvudine and hepatotoxicity in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. These findings underscored the importance of monitoring liver function during Azvudine treatment and caution against concomitant use of certain medications. Further research was warranted to elucidate the mechanisms underlying Azvudine-induced hepatotoxicity and optimize clinical management strategies.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fphar.2025.1558054"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xiong",
"given": "Yuanguo",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xin",
"given": "Hao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shi",
"given": "Cai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guo",
"given": "Xianxi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Ying",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Caifei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ma",
"given": "Fuwang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Ge",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Jian",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Pharmacology",
"container-title-short": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2025-06-04T16:54:48Z",
"timestamp": 1749056088000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2025-06-04T16:54:55Z",
"timestamp": 1749056095000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2025-06-05T04:14:47Z",
"timestamp": 1749096887588,
"version": "3.41.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
4
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2025-06-04T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1748995200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1558054/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
4
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
4
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.4103/1319-2442.139947",
"article-title": "Ganciclovir-induced acute liver injury in a patient with lupus nephritis",
"author": "Abdallah",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1084",
"journal-title": "Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl.",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10937404.2023.2261848",
"article-title": "Drug induced liver injury - a 2023 update",
"author": "Allison",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "442",
"journal-title": "J. Toxicol. Environ. Health, Part B",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/2050640620924157",
"article-title": "Liver injury in COVID-19: the current evidence",
"author": "Alqahtani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "509",
"journal-title": "United Eur. Gastroenterol. J.",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2019.02.014",
"article-title": "EASL clinical practice guidelines: drug-induced liver injury",
"author": "Andrade",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1222",
"journal-title": "J. Hepatol.",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "70",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41572-019-0105-0",
"article-title": "Drug-induced liver injury",
"author": "Andrade",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "58",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim.",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "5",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2035389",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine",
"author": "Baden",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "403",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cld.2019.09.001",
"article-title": "Drug hepatotoxicity: causality assessment",
"author": "Caines",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "25",
"journal-title": "Clin. Liver Dis.",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2024.116353",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of molnupiravir, azvudine and paxlovid against mortality and viral clearance among hospitalized patients with COVID-19 infection during the omicron wave in China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "116353",
"journal-title": "Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000033294",
"article-title": "Drug-induced liver injury in COVID-19 patients during hospitalization",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e33294",
"journal-title": "Med. Baltim.",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "102",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-022-00807-9",
"article-title": "The effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on community respiratory virus activity",
"author": "Chow",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "195",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms17010014",
"article-title": "RUCAM in drug and herb induced liver injury: the update",
"author": "Danan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "14",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40264-018-0654-2",
"article-title": "Drug-induced liver injury: why is the Roussel Uclaf causality assessment method (RUCAM) still used 25 Years after its launch?",
"author": "Danan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "735",
"journal-title": "Drug Saf.",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28756",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of azvudine versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Deng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e28756",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "B14",
"unstructured": "Notice on the issuance of diagnosis and treatment protocol for novel coronavirus infection (trial version 9)\n \n \n 2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007016",
"article-title": "Compassionate use of Remdesivir for patients with severe Covid-19",
"author": "Grein",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2327",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0968-3",
"article-title": "Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1017",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-023-08965-8",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir versus azvudine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 during the omicron wave in Beijing: a multicenter retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "57",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "24",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07853890.2024.2313062",
"article-title": "Associations of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir treatment with death and clinical improvement in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 during the Omicron wave in Beijing, China: a multicentre, retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2313062",
"journal-title": "Ann. Med. (Helsinki)",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "56",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0117",
"article-title": "Effect of azovudine on hepatic and renal function in patients with COVID-19:a case series study",
"author": "He",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2476",
"journal-title": "Chin. General Pract.",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2019.3305",
"article-title": "Clinical effectiveness of intravitreal therapy with ranibizumab vs aflibercept vs bevacizumab for macular edema secondary to central retinal vein occlusion: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Hykin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1256",
"journal-title": "JAMA Ophthalmol.",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "137",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41563-020-00906-z",
"article-title": "Diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2 infections",
"author": "Kevadiya",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "593",
"journal-title": "Nat. Mater.",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12013-024-01238-4",
"article-title": "Pharmacological insights: mitochondrial ROS generation by FNC (azvudine) in dalton’s lymphoma cells revealed by super resolution imaging",
"author": "Kumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "873",
"journal-title": "Cell biochem. Biophys.",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "82",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12672-023-00829-6",
"article-title": "Mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis as a therapeutic target for FNC(2′-deoxy-2′-b-fuoro-4′-azidocytidine)-induced inhibition of Dalton′s lymphoma growth and proliferation",
"author": "Kumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "16",
"journal-title": "Discov. Oncol.",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "1",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/ijbs.72837",
"article-title": "The significance of advanced COVID-19 diagnostic testing in pandemic control measures",
"author": "Kwok",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4610",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Biol. Sci.",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7539/j.issn.1672-2981.2024.06.040",
"article-title": "112 cases of adverse drug reactions induced by azvudine tablets in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Lan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1658",
"journal-title": "Cent. South Pharm.",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/09622802221135251",
"article-title": "Sensitivity analyses in longitudinal clinical trials via distributional imputation",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "181",
"journal-title": "Stat. Methods Med. Res.",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "32",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.13286/j.1001-5213.2024.09.12",
"article-title": "A real-world study of azivudine tablets for drug-induced liver injury caused by novel coronavirus pneumonia",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1082",
"journal-title": "Chin. J. Hosp. Pharm.",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14053/j.cnki.ppcr.202310007",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of azvudine in the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "899",
"journal-title": "Pract. Pharm. And Clin. Remedies",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "26",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.5414/CP204544",
"article-title": "Low albumin combined with low-molecular-weight heparin as risk factors for liver injury using azvudine: evidence from an analysis of COVID-19 patients in a national prospective pharmacovigilance database",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "222",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12889-024-18526-6",
"article-title": "Racial/ethnic differences in the associations between trust in the U.S. healthcare system and willingness to test for and vaccinate against COVID-19",
"author": "Nanaw",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1084",
"journal-title": "BMC Public Health",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0268705",
"article-title": "The determination of causality of drug induced liver injury in patients with COVID-19 clinical syndrome",
"author": "Naseralallah",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0268705",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jgh3.13118",
"article-title": "Liver dysfunction in adults with COVID ‐19 infection: a longitudinal study with transient elastography evaluation",
"author": "Rajaram",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e13118",
"journal-title": "JGH Open",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/advs.202001435",
"article-title": "A randomized, open-label, controlled clinical trial of azvudine tablets in the treatment of mild and Common COVID-19, a pilot study",
"author": "Ren",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2001435",
"journal-title": "Adv. Sci.",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3748/wjg.v30.i22.2866",
"article-title": "Histopathological impact of SARS-CoV-2 on the liver: cellular damage and long-term complications",
"author": "Rodriguez-Espada",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2866",
"journal-title": "World J. gastroenterology WJG",
"key": "B34",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.15679",
"article-title": "COVID-19 testing moves out of the clinic and into the home",
"author": "Rubin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1362",
"journal-title": "JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc.",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "326",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.27157",
"article-title": "Spectrum of statin hepatotoxicity: experience of the drug-induced liver injury network",
"author": "Russo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "679",
"journal-title": "Hepatology",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2024.1362345",
"article-title": "Comparative analysis of the safety and effectiveness of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir and azvudine in older patients with COVID-19: a retrospective study from a tertiary hospital in China",
"author": "Shang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1362345",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.03.032",
"article-title": "Selectively T cell phosphorylation activation of azvudine in the thymus tissue with immune protection effect",
"author": "Sheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3140",
"journal-title": "Acta Pharm. Sin. B",
"key": "B38",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.761167",
"article-title": "Real-world data of tigecycline-associated drug-induced liver injury among patients in China: a 3-year retrospective study as assessed by the updated RUCAM",
"author": "Shi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "761167",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "B39",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-023-08828-2",
"article-title": "Azvudine versus paxlovid for oral treatment of COVID-19 in Chinese patients",
"author": "Su",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "44",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B40",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23094828",
"article-title": "Liver injury in COVID-19 patients with drugs as causatives: a systematic review of 996 DILI cases published 2020/2021 based on RUCAM as causality assessment method",
"author": "Teschke",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4828",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "B41",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468",
"article-title": "Antiviral effectiveness and survival correlation of azvudine and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in elderly severe patients with COVID-19: a retrospective real-world study",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102468",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "B42",
"volume": "69",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-024-02316-y",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of azvudine in reducing mortality of COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "46",
"journal-title": "Virol. J.",
"key": "B43",
"volume": "21",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.3748/wjg.v28.i47.6716",
"article-title": "Liver injury in COVID-19: a minireview",
"author": "Wen-Shu Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6716",
"journal-title": "World J. Gastroenterol.",
"key": "B44",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/liv.14449",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of non‐ICU hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 and liver injury: a retrospective study",
"author": "Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1321",
"journal-title": "Liver Int.",
"key": "B45",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clinthera.2024.07.009",
"article-title": "Cost-effectiveness of azvudine for high-risk outpatients with mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease 2019 in China",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1",
"journal-title": "Clin. Ther.",
"key": "B46",
"volume": "46",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30619",
"article-title": "Adherence and recommended optimal treatment to azvudine application for the treatment of outpatient COVID-19 patients: a real-world retrospective study",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e30619",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "B47",
"volume": "10",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.3969/j.issn.1674-3806.2023.10.06",
"article-title": "Analysis of the efficacy and safety of azvudine in treating moderate COVID-19 in kidney transplant recipients",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1011",
"journal-title": "Chin. J. New Clin. Med.",
"key": "B48",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcph.1686",
"article-title": "Comparison of the effects of low-molecular-weight heparin and Fondaparinux on liver function in patients with pulmonary embolism",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1671",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Pharmacol.",
"key": "B49",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-00351-z",
"article-title": "Azvudine (FNC): a promising clinical candidate for COVID-19 treatment",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "236",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "B50",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xinn.2022.100321",
"article-title": "The first Chinese oral anti-COVID-19 drug azvudine launched",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100321",
"journal-title": "Innov. (New York, NY)",
"key": "B51",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12072-017-9793-2",
"article-title": "CSH guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of drug-induced liver injury",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "221",
"journal-title": "Hepatol. Int.",
"key": "B52",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6",
"article-title": "Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "414",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "B53",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12659/MSM.920350",
"article-title": "Drug-induced liver injury from anti-tuberculosis treatment: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e920350",
"journal-title": "Med. Sci. Monit.",
"key": "B54",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/HC9.0000000000000235",
"article-title": "Validation of the revised electronic version of RUCAM for diagnosis of DILI in Chinese patients",
"author": "Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0235",
"journal-title": "Hepatol. Commun.",
"key": "B55",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7501/j.issn.1674-6376.2023.10.019",
"article-title": "Adverse reaction of azvudine in elderly patients with COVID-19 over 75 years old",
"author": "Zhi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2208",
"journal-title": "Drug Eval. Res.",
"key": "B56",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-00373-7",
"article-title": "COVID-19-associated gastrointestinal and liver injury: clinical features and potential mechanisms",
"author": "Zhong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "256",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "B57",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.29318",
"article-title": "Azvudine and nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in hospitalized patients with moderate‐to‐severe COVID‐19: emulation of a randomized target trial",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e29318",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "B58",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apt.15645",
"article-title": "Systematic review: ibuprofen-induced liver injury",
"author": "Zoubek",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "603",
"journal-title": "Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther.",
"key": "B59",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 59,
"references-count": 59,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1558054/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Real-world data of Azvudine-induced hepatotoxicity among hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China: a retrospective case-control study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "16"
}