Real-world effectiveness and safety of Azvudine in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a multicenter, retrospective cohort study
et al., Journal of Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355, NCT06349655, Nov 2024
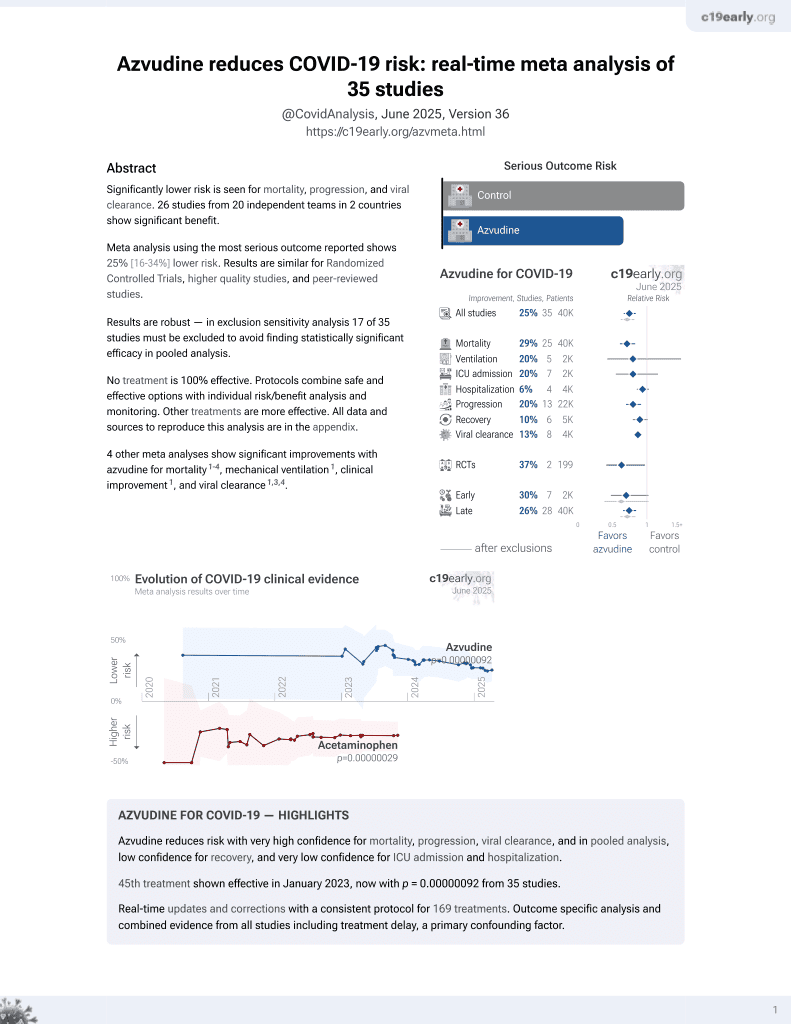
Azvudine for COVID-19
48th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2023, now with p = 0.0000000041 from 40 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
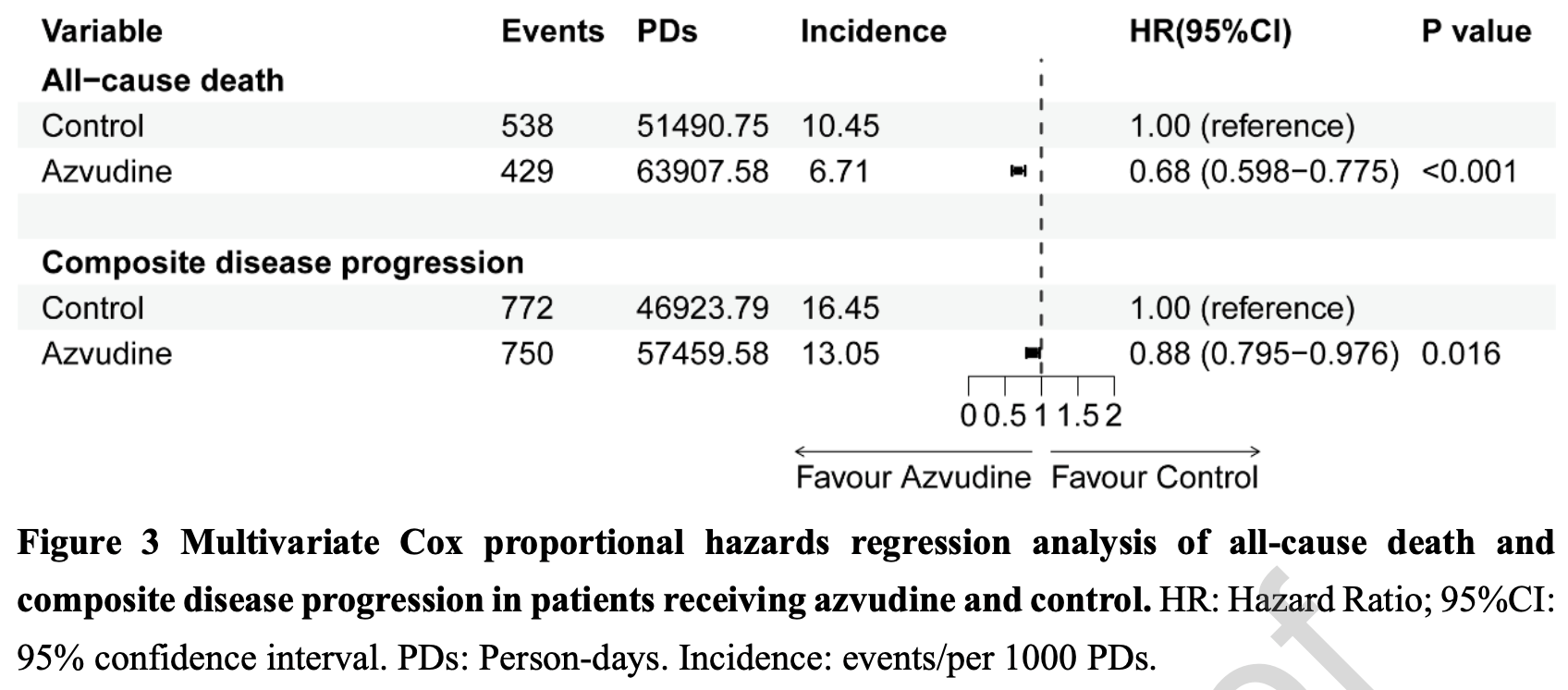
PSM retrospective 32,864 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China showing lower all-cause mortality and disease progression with azvudine treatment.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments3.
|
risk of death, 32.0% lower, HR 0.68, p < 0.001, treatment 5,735, control 5,735, adjusted per study, propensity score matching, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of progression, 12.0% lower, HR 0.88, p = 0.01, treatment 5,735, control 5,735, adjusted per study, progression to severe disease or death, propensity score matching, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Xiong et al., Real-world data of Azvudine-induced hepatotoxicity among hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China: a retrospective case-control study, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1558054.
Ren et al., 17 Nov 2024, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 22 authors, study period 5 December, 2022 - 31 January, 2023, trial NCT06349655 (history).
Contact: fccrenzg@zzu.edu.cn, changjunbiao@zzu.edu.cn, johnyuem@zzu.edu.cn.
Real-world effectiveness and safety of Azvudine in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a multicenter, retrospective cohort study
Journal of Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355
Objectives Azvudine has been designated as a priority treatment for patients infected with SARS-CoV-2, however, clinical evidence in hospitalized cases remains insufficient.
Methods We performed a multi-center, retrospective cohort study to evaluate effectiveness and safety of azvudine in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 in China (NCT06349655). Kaplan-Meier method, Cox regression model, subgroup analysis and seven sensitive analyses were employed. Results A total of 32864 hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 were enrolled, in which 5735 azvudine recipients and 5735 controls were selected using 1:1 propensity score matching. Based on Kaplan-Meier analysis, azvudine significantly reduced rates of all-cause death (P < 0.0001) and composite disease progression (P = 0.00019). Cox regression analysis demonstrated that hazard ratios of all-cause death and composite disease progression were 0.68 (95%CI: 0.598-0.775, P < 0.001) and 0.88 (95% CI: 0.795-0.976, P = 0.016), respectively. Subgroup analysis showed preference of azvudine for patients receiving antibiotics in reducing all-cause death and composite disease progression. Seven sensitivity analyses verified the robustness of our results. Safety analysis on adverse events showed no significant difference between both groups.
Conclusions This study suggested that azvudine may reduce all-cause death and composite disease progression in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection without serious adverse events. However, the findings are susceptible to some potential biases, and further studies still need to identify the efficacy of azvudine.
Contributors Zhigang Ren, Mengzhao Yang, Guanyue Su, Guowu Qian, and Yiqiang Yuan contributed equally to this work. Zhigang Ren, Junbiao Chang and Zujiang Yu conceived and designed the study; Zujiang Yu, Zhigang Ren, Guowu Qian, Yiqiang Yuan, Silin Li, Hong Luo, Shixi Zhang, Guangming Li, Donghua Zhang, and Guotao Li managed the patients; Mengzhao Yang, Guanyue Su, Jia Yu, Haiyu Wang, Ming Cheng, Ling Wang, Guowu Qian, Xiaoli Jin, Juan Wang and Mingming Wang collected and verified the underlying data; Changshuang Wang and Mingxia Lu collected the vaccination data; Mengzhao Yang, and Jia Yu analyzed the data; Guanyue Su wrote the manuscript. All authors had full access to all the data in the study and agree to submit the manuscript for publication.
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare no competing interests that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethics approval and consent to participate This study was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board from The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University (2023-KY-0865-001). The study was registered with ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT06349655). All participants in the retrospective study were anonymous and did not need individual informed consent.
Declaration of Competing Interest ☒ The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. ☐ The author is an..
References
Agarwal, Hunt, Stegemann, Rochwerg, Lamontagne et al., A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19, BMJ
Andrews, Herman, Gandhi, Treatments for COVID-19, Annu Rev Med
Arbel, Sagy, Hoshen, Battat, Lavie et al., Nirmatrelvir Use and Severe Covid-19 Outcomes during the Omicron Surge, N Engl J Med
Bernal, Da Silva, Musungaie, Kovalchuk, Gonzalez et al., Molnupiravir for Oral Treatment of Covid-19 in Nonhospitalized Patients, N Engl J Med
De Souza, Cabral, Da Silva, Arruda, Cabral et al., Phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study: a study on the safety and clinical efficacy of AZVUDINE in moderate COVID-19 patients, J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f Front Med
Guo, Cao, Hong, Tan, Chen et al., The origin, transmission and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak -an update on the status, Mil Med Res
Gupta, Gupta, Singh, Singhal, Emergence of COVID-19 Variants: An Update, Cureus
J O U R N A L P R E, None
Jin, Cai, Cheng, Cheng, Deng et al., A rapid advice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infected pneumonia (standard version), Mil Med Res
Lewnard, Mclaughlin, Malden, Hong, Puzniak et al., Effectiveness of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in preventing hospital admissions and deaths in people with COVID-19: a cohort study in a large US health-care system, Lancet Infect Dis
Looi, Covid-19: WHO adds JN.1 as new variant of interest, BMJ
Lévesque, Hanley, Kezouh, Suissa, Problem of immortal time bias in cohort studies: example using statins for preventing progression of diabetes, BMJ
Miyata, Lee, Susuki-Miyata, Wang, Xu et al., Glucocorticoids J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f 21 suppress inflammation via the upregulation of negative regulator IRAK-M, Nat Commun
Platt, Hutcheon, Suissa, Immortal Time Bias in Epidemiology, Curr Epidemiol Rep
Postmus, Demissei, Hillege, Estimating cumulative incidences in the presence of right-censoring and competing risks: an introduction with illustrations from the COACH study, EuroIntervention
Ren, Luo, Yu, Song, Liang et al., A Randomized, Open-Label, Controlled Clinical Trial of Azvudine Tablets in the Treatment of Mild and Common COVID-19, a Pilot Study, Advanced Science
Shen, Xiao, Sun, Li, Wu, Real-world effectiveness of Azvudine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.01.23.23284899
Sun, Dian, Shen, Zeng, Chen, Oral Azvudine for hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing conditions: a retrospective cohort study, eClinicalMedicine
Wong, Au, Lau, Lau, Cowling et al., Real-world effectiveness of early molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 without supplemental oxygen requirement on admission during Hong Kong's omicron BA.2 wave: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet Infect Dis
Yang, Wang, Jiang, Zhang, Zhang et al., Oral Azvudine for mildto-moderate COVID-19 in high risk, nonhospitalized adults: Results of a real-world study, J Med Virol
Yu, Chang, A Nearly 20-Year Journey to Success of Azvudine for Antiviral Therapy, Chinese J Chem
Yu, Chang, Azvudine (FNC): a promising clinical candidate for COVID-19 treatment, Signal Transduct Target Ther
Yu, Chang, The first Chinese oral anti-COVID-19 drug Azvudine launched, Innovation (Camb)
Yu, He, Wu, Xie, Liu et al., Dysregulated adaptive immune response contributes to severe COVID-19, Cell Res
Zhang, Li, Wang, Liu, Lu et al., Azvudine is a thymushoming anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients, Signal Transduct Target Ther
Zheng, Ma, Wang, Cheng, Zhou et al., Efficacy and safety of Paxlovid for COVID-19:a meta-analysis, J Infect
Zhou, Zheng, Xiao, Xie, Rang et al., Effectiveness and safety of Azvudine in older adults with mild and moderate COVID-19: a retrospective observational study, BMC. Infect Dis
Zong, Zhou, Li, Jiang, Liu et al., Azvudine reduces the in-hospital mortality of COVID-19 patients: A retrospective cohort study, Acta Pharm Sin B
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355",
"ISSN": [
"0163-4453"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355",
"alternative-id": [
"S0163445324002901"
],
"article-number": "106355",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Real-world effectiveness and safety of Azvudine in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a multicenter, retrospective cohort study"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Journal of Infection"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd on behalf of The British Infection Association."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0798-3444",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ren",
"given": "Zhigang",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Mengzhao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4067-0696",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Su",
"given": "Guanyue",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qian",
"given": "Guowu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yuan",
"given": "Yiqiang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yu",
"given": "Jia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Silin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Changshuang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lu",
"given": "Mingxia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Luo",
"given": "Hong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Shixi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Guangming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Donghua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Ling",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Guotao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jin",
"given": "Xiaoli",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Juan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Mingming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cheng",
"given": "Ming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Haiyu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chang",
"given": "Junbiao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yu",
"given": "Zujiang",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Infection",
"container-title-short": "Journal of Infection",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"journalofinfection.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-17T06:37:55Z",
"timestamp": 1731825475000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-17T08:46:21Z",
"timestamp": 1731833181000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-17T09:10:18Z",
"timestamp": 1731834618386,
"version": "3.28.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1730419200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/legal/tdmrep-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1730419200000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 12,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-13T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1731456000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0163445324002901?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0163445324002901?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "106355",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.p2975",
"article-title": "Covid-19: WHO adds JN.1 as new variant of interest",
"author": "Looi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2975",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib1",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Emergence of COVID-19 Variants: An Update",
"author": "Gupta",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib2",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib3",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-med-052422-020316",
"article-title": "Treatments for COVID-19",
"author": "Andrews",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "145",
"journal-title": "Annu Rev Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib4",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"article-title": "A rapid advice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infected pneumonia (standard version)",
"author": "Jin",
"first-page": "4",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Mil Med Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib5",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m3379",
"article-title": "A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19",
"author": "Agarwal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m3379",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib6",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib7",
"unstructured": "General Office of the National Health Commission. Diagnosis and treatment protocol for COVID-19 in China (trial version 10). 〈https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2023-01/06/content_5735343.htm〉. Accessed 31 Aug 2023."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2204919",
"article-title": "Nirmatrelvir Use and Severe Covid-19 Outcomes during the Omicron Surge",
"author": "Arbel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "790",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib8",
"volume": "387",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2022.09.027",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of Paxlovid for COVID-19:a meta-analysis",
"author": "Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "66",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib9",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116044",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir for Oral Treatment of Covid-19 in Nonhospitalized Patients",
"author": "Jayk Bernal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "509",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib10",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-00351-z",
"article-title": "Azvudine (FNC): a promising clinical candidate for COVID-19 treatment",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "236",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct Target Ther",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib11",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "The first Chinese oral anti-COVID-19 drug Azvudine launched",
"author": "Yu",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Innovation (Camb)",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib12",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6",
"article-title": "Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "414",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct Target Ther",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib13",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/advs.202001435",
"article-title": "A Randomized, Open‐Label, Controlled Clinical Trial of Azvudine Tablets in the Treatment of Mild and Common COVID‐19, a Pilot Study",
"author": "Ren",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "Advanced Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib14",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study: a study on the safety and clinical efficacy of AZVUDINE in moderate COVID-19 patients",
"author": "de Souza",
"journal-title": "Front Med (Lausanne)",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib15",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007",
"article-title": "Azvudine reduces the in-hospital mortality of COVID-19 patients: A retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Acta Pharm Sin B",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib16",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-023-08944-z",
"article-title": "Effectiveness and safety of Azvudine in older adults with mild and moderate COVID-19: a retrospective observational study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "47",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC. Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib17",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101981",
"article-title": "Oral Azvudine for hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing conditions: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "eClinicalMedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib18",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28947",
"article-title": "Oral Azvudine for mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in high risk, nonhospitalized adults: Results of a real-world study",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib19",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40471-019-0180-5",
"article-title": "Immortal Time Bias in Epidemiology",
"author": "Platt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "23",
"journal-title": "Curr Epidemiol Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib20",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.b5087",
"article-title": "Problem of immortal time bias in cohort studies: example using statins for preventing progression of diabetes",
"author": "Lévesque",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "b5087",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib21",
"volume": "340",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00118-4",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in preventing hospital admissions and deaths in people with COVID-19: a cohort study in a large US health-care system",
"author": "Lewnard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "806",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib22",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of early molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 without supplemental oxygen requirement on admission during Hong Kong's omicron BA.2 wave: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1681",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib23",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "The origin, transmission and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak - an update on the status",
"author": "Guo",
"first-page": "11",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Mil Med Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib24",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of Azvudine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Shen",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib25",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ncomms7062",
"article-title": "Glucocorticoids suppress inflammation via the upregulation of negative regulator IRAK-M",
"author": "Miyata",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6062",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib26",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-0391-9",
"article-title": "Dysregulated adaptive immune response contributes to severe COVID-19",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "814",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib27",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cjoc.202300361",
"article-title": "Nearly 20-Year Journey to Success of Azvudine for Antiviral Therapy",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3349",
"issue": "23",
"journal-title": "Chinese J Chem",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib28",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4244/EIJV11I11A256",
"article-title": "Estimating cumulative incidences in the presence of right-censoring and competing risks: an introduction with illustrations from the COACH study",
"author": "Postmus",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1322",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "EuroIntervention",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355_bib29",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2016"
}
],
"reference-count": 29,
"references-count": 29,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0163445324002901"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Real-world effectiveness and safety of Azvudine in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a multicenter, retrospective cohort study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}