Efficacy of azvudine plus dexamethasone in severe hospitalized patients with Omicron infection: a prospective multicenter study
et al., Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2024.1390098, Nov 2024
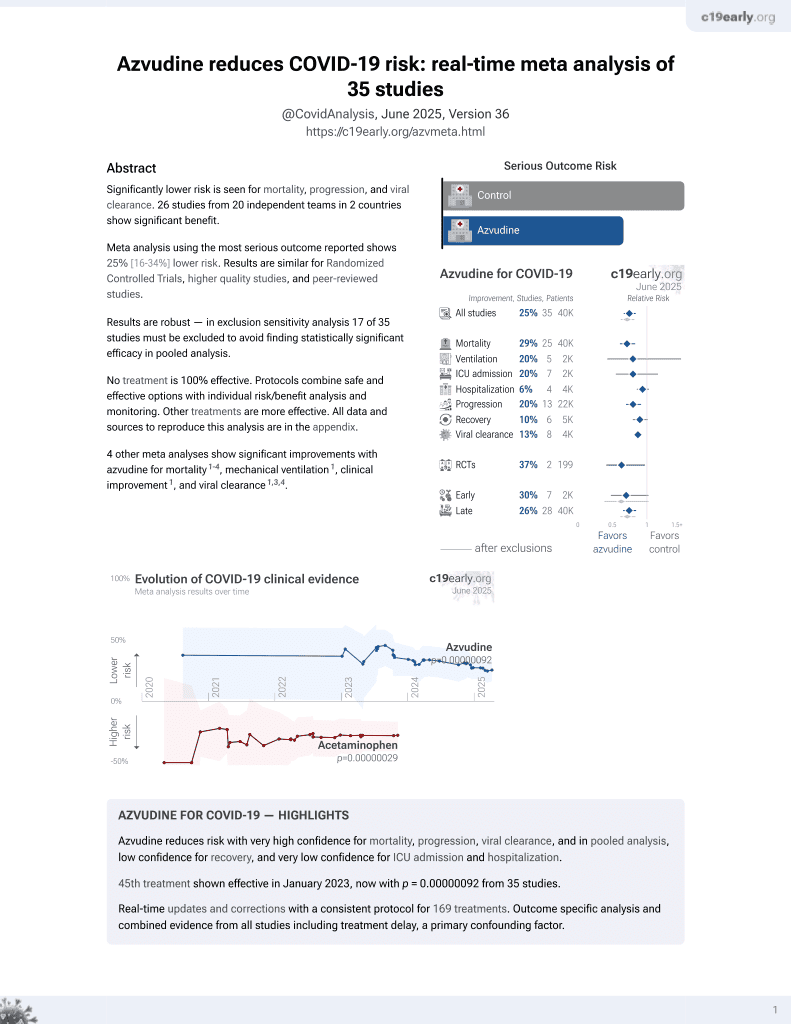
Azvudine for COVID-19
48th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2023, now with p = 0.0000000041 from 40 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
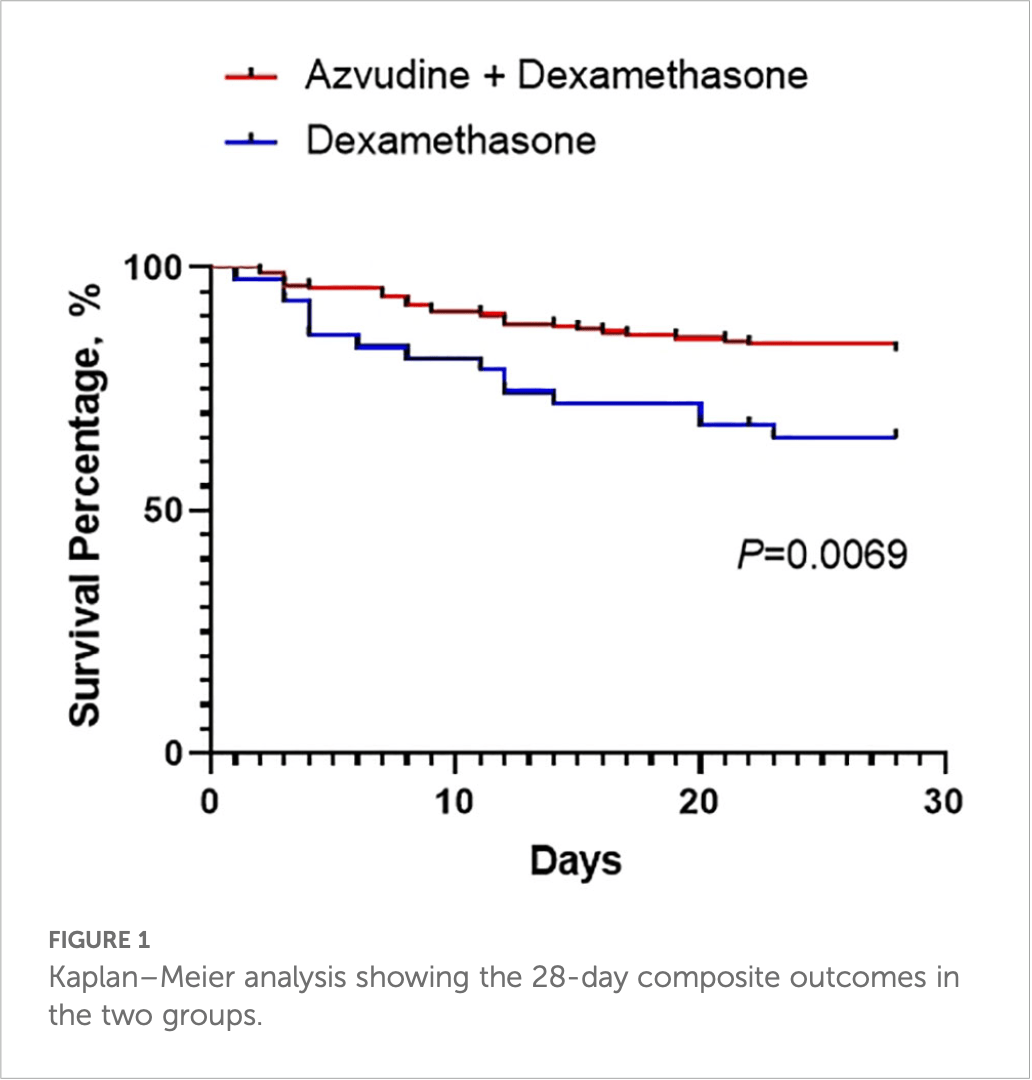
Prospective multicenter study of 209 severe hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China showing improved 28-day composite outcomes, faster viral clearance, and higher PaO2/FiO2 levels with azvudine plus dexamethasone compared to dexamethasone alone.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments3.
|
risk of progression, 42.6% lower, RR 0.57, p = 0.03, treatment 28 of 165 (17.0%), control 13 of 44 (29.5%), NNT 8.0, death, ICU, or mechanical ventilation, day 28.
|
|
time to viral-, 14.4% lower, relative time 0.86, p = 0.02, treatment 165, control 44.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Xiong et al., Real-world data of Azvudine-induced hepatotoxicity among hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China: a retrospective case-control study, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1558054.
Zhang et al., 22 Nov 2024, prospective, China, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, study period 15 December, 2022 - 30 April, 2023.
Contact: zengdaxiong@suda.edu.cn, xuguopeng2046@foxmail.com.
Efficacy of azvudine plus dexamethasone in severe hospitalized patients with Omicron infection: a prospective multicenter study
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2024.1390098
Background: Azvudine (AZV), the first Chinese oral anti-coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) drug, has shown substantial clinical benefits to viral clearance and prognosis in patients with mild and common COVID-19. However, there is no evidence in severe hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
Methods: In this multicenter study, we analyzed 209 severe hospitalized COVID-19 patients in four hospitals. All the clinical data and the 28-day composite outcomes were recorded. All of the patients were categorized into two groups according to drug: the dexamethasone (DXM) group and the azvudine plus dexamethasone (AZV+DXM) group. Results: There were no differences in sex, age, BMI, and underlying diseases between the two groups. The ratio of the 28-day composite outcome was lower for the AZV+DXM group than that for the DXM group (16.97% vs. 31.82%, p = 0.029). The viral clearance time was shorter in the AZV+DXM group than in the DXM group (7.32 ± 2.57 vs. 8.55 ± 2.34 days, p = 0.017). The PaO 2 /FiO 2 levels on day 5 (258.89 ± 55.22 vs. 233.12 ± 60.51, p = 0.026) and day 10 (289.48 ± 44.09 vs. 261.52 ± 37.34, p = 0.015) were higher in the AZV +DXM group than the DXM group. However, data on the hospitalization duration of the two groups were similar. Cox analysis showed the benefit of AZV+DXM in the subgroups of ≥65 years old, multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS), cerebrovascular disease, C-reactive protein (CRP) ≥70mg/L, and D-dimer ≥1 µg/L.
Conclusion: This study is the first to indicate that treatment with AZV+DXM might benefit severe Omicron-infected patients compared with DXM treatment alone. This finding demonstrates, at least partly, the necessity of antiviral treatment in severe patients.
Ethics statement This study was approved by the institutional review board of Dushu Lake Hospital Affiliated to Soochow University (220143) . The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The written informed consent was waived as we only collected all clinical data from anonymized data according to the policy for public health outbreak investigation of emerging infectious diseases issued by the National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China.
Author contributions
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Al Sulaiman, Aljuhani, Korayem, Altebainawi, Alharbi et al., Evaluation of the use of methylprednisolone and dexamethasone in asthma critically ill patients with COVID-19: a multicenter cohort study, BMC Pulm Med, doi:10.1186/s12890-023-02603-4
Bernal, Garcıá-Villalba, Pons, Hernańdez, Baǵuena et al., Remdesivir plus dexamethasone is associated to improvement in the clinical outcome of COVID-19 hospitalized patients regardless of their vaccination status, Med. Clin. (Barc), doi:10.1016/j.medcli.2023.03.025
Bouadma, Mekontso-Dessap, Burdet, Merdji, Poissy et al., High-dose dexamethasone and oxygen support strategies in intensive care unit patients with severe COVID-19 acute hypoxemic respiratory failure: the COVIDICUS randomized clinical trial, JAMA Intern. Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.2168
Chen, Tian, Efficacy and safety of azvudine in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20153
Chen, Zhu, Hong, Zeng, He et al., Associations of clinical characteristics and treatment regimens with the duration of viral RNA shedding in patients with COVID-19, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.06.091
Chin, None, Med. J. Pulm Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1016/j.pccm.2023.08.004
Dastenae, Bahadori, Dehghani, Asadi-Samani, Izadi et al., Comparison of the effect of intravenous dexamethasone and methylprednisolone on the treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2022.07.019
Deng, Li, Sun, Jin, Zhou et al., Real-world effectiveness of Azvudine versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.28756
Dian, Meng, Sun, Deng, Zeng, Azvudine versus Paxlovid for oral treatment of COVID-19 in Chinese patients with pre-existing comorbidities, J. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2023.05.012
Fan, Li, Zhang, Wan, Zhang et al., SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: recent progress and future perspectives, Signal Transduct Target Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-022-00997-x
Feng, Li, Yao, Yu, Zhou et al., Clinical factors associated with progression and prolonged viral shedding in COVID-19 patients: A multicenter study, Aging Dis, doi:10.14336/AD.2020.0630
Gao, Luo, Ren, Duan, Han et al., Antiviral effect of azvudine and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir among hospitalized patients with COVID-19, J. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.023
Granholm, Munch, Myatra, Vijayaraghavan, Cronhjort et al., Dexamethasone 12 mg versus 6 mg for patients with COVID-19 and severe hypoxaemia: a pre-planned, secondary Bayesian analysis of the COVID STEROID 2 trial, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-021-06573-1
Gressens, Esnault, De Castro, Sellier, Sene et al., Remdesivir in combination with dexamethasone for patients hospitalized with COVID-19: A retrospective multicenter study, PloS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0262564
Ji, Zhang, Shao, Xie, Zhong et al., Glucocorticoid therapy does not delay viral clearance in COVID-19 patients, Crit. Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03287-6
Ko, Wu, Mehta, Wald-Dickler, Yang et al., A comparison of methylprednisolone and dexamethasone in intensive care patients with COVID-19, J. Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1177/0885066621994057
Koeckerling, Barker, Accelerating the evolution of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2: A risk of combining dexamethasone and tocilizumab for severe coronavirus disease 2019, J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab328
Leding, Bodilsen, Brieghel, Harboe, Helleberg et al., Treatment effect modifiers in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 receiving remdesivir and dexamethasone, Infect. Dis. (Lond), doi:10.1080/23744235.2023.2187081
Li, Liao, Zhou, Wang, Yang et al., Association between glucocorticoids treatment and viral clearance delay in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, BMC Infect. Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06548-z
Lin, Lee, Huang, Chiu, Chang et al., Effects of dexamethasone use on viral clearance among patients with COVID-19: a multicenter cohort study, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2023.01.011
Lu, Chen, Xu, Huang, Yang et al., Liver dysfunction on admission worsens clinical manifestations and outcomes of coronavirus disease
Marrone, Nevola, Sellitto, Cozzolino, Romano et al., Remdesivir plus dexamethasone versus dexamethasone alone for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients requiring supplemental O2 therapy: A prospective controlled nonrandomized study, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac014
Pantazopoulos, Mavrovounis, Kyritsis, Perlepe, Miziou et al., Early corticosteroid initiation delays viral RNA clearance in respiratory secretions of COVID-19 patients, Adv. Respir. Med, doi:10.5603/ARM.a2021.0112
Ranjbar, Moghadami, Mirahmadizadeh, Fallahi, Khaloo et al., Methylprednisolone or dexamethasone, which one is superior corticosteroid in the treatment of hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a tripleblinded randomized controlled trial, BMC Infect. Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06045-3
Recovery Collaborative Group, Horby, Lim, Emberson, Mafham et al., Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with covid-19, N Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436
Ren, Luo, Yu, Song, Liang et al., A randomized, openlabel, controlled clinical trial of azvudine tablets in the treatment of mild and common COVID-19, a pilot study, Adv. Sci. (Weinh), doi:10.1002/advs.202001435
Sattoju, Gattu, Merugu, Anneboina, Ganapaka, Dexamethasone, dexamethasone + remdesivir in treating moderate to severe COVID-19: retrospective observational cohort study, J. Infect. Dev. Ctries, doi:10.3855/jidc.17971
Snow, Arulkumaran, Singer, Choi, Effect of dexamethasone dose on outcomes in acute COVID-19 disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis, J. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2023.09.008
Spagnuolo, Guffanti, Galli, Poli, Querini et al., Viral clearance after early corticosteroid treatment in patients with moderate or severe covid-19, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-78039-1
Sun, Jin, Dian, Shen, Zeng et al., Oral Azvudine for hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing conditions: a retrospective cohort study, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101981
Taboada, Rodrıǵuez, Varela, Rodrıǵuez, Abelleira et al., Effect of high versus low dose of dexamethasone on clinical worsening in patients hospitalised with moderate or severe COVID-19 pneumonia: an open-label, randomised clinical trial, Eur. Respir. J, doi:10.1183/13993003.02518-2021
Tang, Feng, Ni, Zhang, Liu et al., Early use of corticosteroid may prolong SARS-coV-2 shedding in non-intensive care unit patients with COVID-19 pneumonia: A multicenter, single-blind, randomized control trial, Respiration, doi:10.1159/000512063
Tomazini, Maia, Cavalcanti, Berwanger, Rosa et al., Effect of dexamethasone on days alive and ventilator-free in patients with moderate or severe acute respiratory distress syndrome and COVID-19: the coDEX randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.17021
Van Paassen, Vos, Hoekstra, Neumann, Boot et al., Corticosteroid use in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis on clinical outcomes, Crit. Care, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-52240/v2
Wei, Liu, Liu, Zhang, Su et al., Clinical characteristics and manifestations in older patients with COVID-19, BMC Geriatr, doi:10.1186/s12877-020-01811-5
Wong, Lau, Au, Xiong, Chung et al., Optimal timing of remdesivir initiation in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) administered with dexamethasone, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciab728
Yang, Wang, Jiang, Zhang, Zhang et al., Oral azvudine for mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in high risk, nonhospitalized adults: Results of a real-world study, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.28947
Yu, Chang, Azvudine (FNC): a promising clinical candidate for COVID-19 treatment, Signal Transduct Target Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00351-z
Zhang, Li, Wang, Liu, Lu et al., Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients, Signal Transduct Target Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6
Zhang, Yu, Huang, Zeng, Prolonged viral RNA shedding duration in COVID-19, Am. J. Ther, doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001200
Zhao, Cheng, Zhang, Qianda, Zhouma et al., Efficacy of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir versus azvudine for COVID-19 treatment in tibet: A retrospective study, Infect. Drug Resist, doi:10.2147/IDR.S423725
Zhao, Zheng, Han, Feng, Xia et al., Is azvudine comparable to nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in real-world efficacy and safety for hospitalized patients with COVID-19? A retrospective cohort study, Infect. Dis. Ther, doi:10.1007/s40121-023-00845-7
Zheng, Peng, Zhou, Pulmonary fibrosis: A short-or long-term sequelae of severe COVID-19? Chin, Med. J. Pulm Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1016/j.pccm.2022.12.002
Zhong, Yang, Jiang, Duan, Wang et al., Factors associated with prolonged viral shedding in older patients infected with Omicron BA.2.2, Front. Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2022.1087800
Zhu, Efficacy and safety evaluation of Azvudine in the prospective treatment of COVID-19 based on four phase III clinical trials, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1228548
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2024.1390098",
"ISSN": [
"2235-2988"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2024.1390098",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>Azvudine (AZV), the first Chinese oral anti-coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) drug, has shown substantial clinical benefits to viral clearance and prognosis in patients with mild and common COVID-19. However, there is no evidence in severe hospitalized COVID-19 patients.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>In this multicenter study, we analyzed 209 severe hospitalized COVID-19 patients in four hospitals. All the clinical data and the 28-day composite outcomes were recorded. All of the patients were categorized into two groups according to drug: the dexamethasone (DXM) group and the azvudine plus dexamethasone (AZV+DXM) group.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>There were no differences in sex, age, BMI, and underlying diseases between the two groups. The ratio of the 28-day composite outcome was lower for the AZV+DXM group than that for the DXM group (16.97% <jats:italic>vs</jats:italic>. 31.82%, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.029). The viral clearance time was shorter in the AZV+DXM group than in the DXM group (7.32 ± 2.57 <jats:italic>vs</jats:italic>. 8.55 ± 2.34 days, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.017). The PaO<jats:sub>2</jats:sub>/FiO<jats:sub>2</jats:sub> levels on day 5 (258.89 ± 55.22 <jats:italic>vs</jats:italic>. 233.12 ± 60.51, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.026) and day 10 (289.48 ± 44.09 <jats:italic>vs</jats:italic>. 261.52 ± 37.34, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.015) were higher in the AZV+DXM group than the DXM group. However, data on the hospitalization duration of the two groups were similar. Cox analysis showed the benefit of AZV+DXM in the subgroups of ≥65 years old, multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS), cerebrovascular disease, C-reactive protein (CRP) ≥70mg/L, and D-dimer ≥1 µg/L.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>This study is the first to indicate that treatment with AZV+DXM might benefit severe Omicron-infected patients compared with DXM treatment alone. This finding demonstrates, at least partly, the necessity of antiviral treatment in severe patients.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fcimb.2024.1390098"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Meng-Lan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wei",
"given": "Xiao-Ying",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Su",
"given": "Nan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jiang",
"given": "Jung-Hong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Guo-Peng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zeng",
"given": "Da-Xiong",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology",
"container-title-short": "Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-22T06:19:02Z",
"timestamp": 1732256342000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-22T06:19:05Z",
"timestamp": 1732256345000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-23T05:15:26Z",
"timestamp": 1732338926722,
"version": "3.28.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
22
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-22T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1732233600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2024.1390098/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
22
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
22
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12890-023-02603-4",
"article-title": "Evaluation of the use of methylprednisolone and dexamethasone in asthma critically ill patients with COVID-19: a multicenter cohort study",
"author": "Al Sulaiman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "315",
"journal-title": "BMC Pulm Med.",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medcli.2023.03.025",
"article-title": "Remdesivir plus dexamethasone is associated to improvement in the clinical outcome of COVID-19 hospitalized patients regardless of their vaccination status",
"author": "Bernal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "139",
"journal-title": "Med. Clin. (Barc)",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "161",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.2168",
"article-title": "High-dose dexamethasone and oxygen support strategies in intensive care unit patients with severe COVID-19 acute hypoxemic respiratory failure: the COVIDICUS randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Bouadma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "906",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern. Med.",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.06.091",
"article-title": "Associations of clinical characteristics and treatment regimens with the duration of viral RNA shedding in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "252",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20153",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of azvudine in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.07.019",
"article-title": "Comparison of the effect of intravenous dexamethasone and methylprednisolone on the treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Dastenae",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "659",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "122",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28756",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of Azvudine versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Deng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.05.012",
"article-title": "Azvudine versus Paxlovid for oral treatment of COVID-19 in Chinese patients with pre-existing comorbidities",
"author": "Dian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e24",
"journal-title": "J. Infect.",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-022-00997-x",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: recent progress and future perspectives",
"author": "Fan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "141",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct Target Ther.",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14336/AD.2020.0630",
"article-title": "Clinical factors associated with progression and prolonged viral shedding in COVID-19 patients: A multicenter study",
"author": "Feng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1069",
"journal-title": "Aging Dis.",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.023",
"article-title": "Antiviral effect of azvudine and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir among hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e158",
"journal-title": "J. Infect.",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-021-06573-1",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone 12 mg versus 6 mg for patients with COVID-19 and severe hypoxaemia: a pre-planned, secondary Bayesian analysis of the COVID STEROID 2 trial",
"author": "Granholm",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "45",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med.",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0262564",
"article-title": "Remdesivir in combination with dexamethasone for patients hospitalized with COVID-19: A retrospective multicenter study",
"author": "Gressens",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PloS One",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03287-6",
"article-title": "Glucocorticoid therapy does not delay viral clearance in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Ji",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "565",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0885066621994057",
"article-title": "A comparison of methylprednisolone and dexamethasone in intensive care patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Ko",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "673",
"journal-title": "J. Intensive Care Med.",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiab328",
"article-title": "Accelerating the evolution of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2: A risk of combining dexamethasone and tocilizumab for severe coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Koeckerling",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "934",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "224",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/23744235.2023.2187081",
"article-title": "Treatment effect modifiers in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 receiving remdesivir and dexamethasone",
"author": "Leding",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "351",
"journal-title": "Infect. Dis. (Lond)",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06548-z",
"article-title": "Association between glucocorticoids treatment and viral clearance delay in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1063",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.01.011",
"article-title": "Effects of dexamethasone use on viral clearance among patients with COVID-19: a multicenter cohort study",
"author": "Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "257",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "128",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pccm.2023.08.004",
"article-title": "Liver dysfunction on admission worsens clinical manifestations and outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "181",
"journal-title": "Chin. Med. J. Pulm Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac014",
"article-title": "Remdesivir plus dexamethasone versus dexamethasone alone for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients requiring supplemental O2 therapy: A prospective controlled nonrandomized study",
"author": "Marrone",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e403",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5603/ARM.a2021.0112",
"article-title": "Early corticosteroid initiation delays viral RNA clearance in respiratory secretions of COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Pantazopoulos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "624",
"journal-title": "Adv. Respir. Med.",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "89",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06045-3",
"article-title": "Methylprednisolone or dexamethasone, which one is superior corticosteroid in the treatment of hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a triple-blinded randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Ranjbar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "337",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00510-X",
"article-title": "Higher dose corticosteroids in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 who are hypoxic but not requiring ventilatory support (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1499",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "401",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with covid-19",
"author": "Horby",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "N Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/advs.202001435",
"article-title": "A randomized, open-label, controlled clinical trial of azvudine tablets in the treatment of mild and common COVID-19, a pilot study",
"author": "Ren",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Adv. Sci. (Weinh)",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3855/jidc.17971",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone, dexamethasone + remdesivir in treating moderate to severe COVID-19: retrospective observational cohort study",
"author": "Sattoju",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "953",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dev. Ctries",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.09.008",
"article-title": "Effect of dexamethasone dose on outcomes in acute COVID-19 disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Snow",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "490",
"journal-title": "J. Infect.",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-78039-1",
"article-title": "Viral clearance after early corticosteroid treatment in patients with moderate or severe covid-19",
"author": "Spagnuolo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "21291",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101981",
"article-title": "Oral Azvudine for hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing conditions: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "101981",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.02518-2021",
"article-title": "Effect of high versus low dose of dexamethasone on clinical worsening in patients hospitalised with moderate or severe COVID-19 pneumonia: an open-label, randomised clinical trial",
"author": "Taboada",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2102518",
"journal-title": "Eur. Respir. J.",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000512063",
"article-title": "Early use of corticosteroid may prolong SARS-coV-2 shedding in non-intensive care unit patients with COVID-19 pneumonia: A multicenter, single-blind, randomized control trial",
"author": "Tang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "116",
"journal-title": "Respiration",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.17021",
"article-title": "Effect of dexamethasone on days alive and ventilator-free in patients with moderate or severe acute respiratory distress syndrome and COVID-19: the coDEX randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Tomazini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1307",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-52240/v2",
"article-title": "Corticosteroid use in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis on clinical outcomes",
"author": "van Paassen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "696",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care",
"key": "B34",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12877-020-01811-5",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics and manifestations in older patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Wei",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "395",
"journal-title": "BMC Geriatr.",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab728",
"article-title": "Optimal timing of remdesivir initiation in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) administered with dexamethasone",
"author": "Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e499",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28947",
"article-title": "Oral azvudine for mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in high risk, nonhospitalized adults: Results of a real-world study",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-00351-z",
"article-title": "Azvudine (FNC): a promising clinical candidate for COVID-19 treatment",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "236",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct Target Ther.",
"key": "B38",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6",
"article-title": "Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "414",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct Target Ther.",
"key": "B39",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MJT.0000000000001200",
"article-title": "Prolonged viral RNA shedding duration in COVID-19",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e759",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Ther.",
"key": "B40",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IDR.S423725",
"article-title": "Efficacy of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir versus azvudine for COVID-19 treatment in tibet: A retrospective study",
"author": "Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6053",
"journal-title": "Infect. Drug Resist.",
"key": "B41",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-023-00845-7",
"article-title": "Is azvudine comparable to nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in real-world efficacy and safety for hospitalized patients with COVID-19? A retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2087",
"journal-title": "Infect. Dis. Ther.",
"key": "B42",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pccm.2022.12.002",
"article-title": "Pulmonary fibrosis: A short- or long-term sequelae of severe COVID-19",
"author": "Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "77",
"journal-title": "Chin. Med. J. Pulm Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "B43",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2022.1087800",
"article-title": "Factors associated with prolonged viral shedding in older patients infected with Omicron BA.2.2",
"author": "Zhong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front. Public Health",
"key": "B44",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2023.1228548",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety evaluation of Azvudine in the prospective treatment of COVID-19 based on four phase III clinical trials",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "B45",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 45,
"references-count": 45,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2024.1390098/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Efficacy of azvudine plus dexamethasone in severe hospitalized patients with Omicron infection: a prospective multicenter study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "14"
}