Oral azvudine for mild‐to‐moderate COVID‐19 in high risk, nonhospitalized adults: Results of a real‐world study
et al., Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.28947, Jul 2023
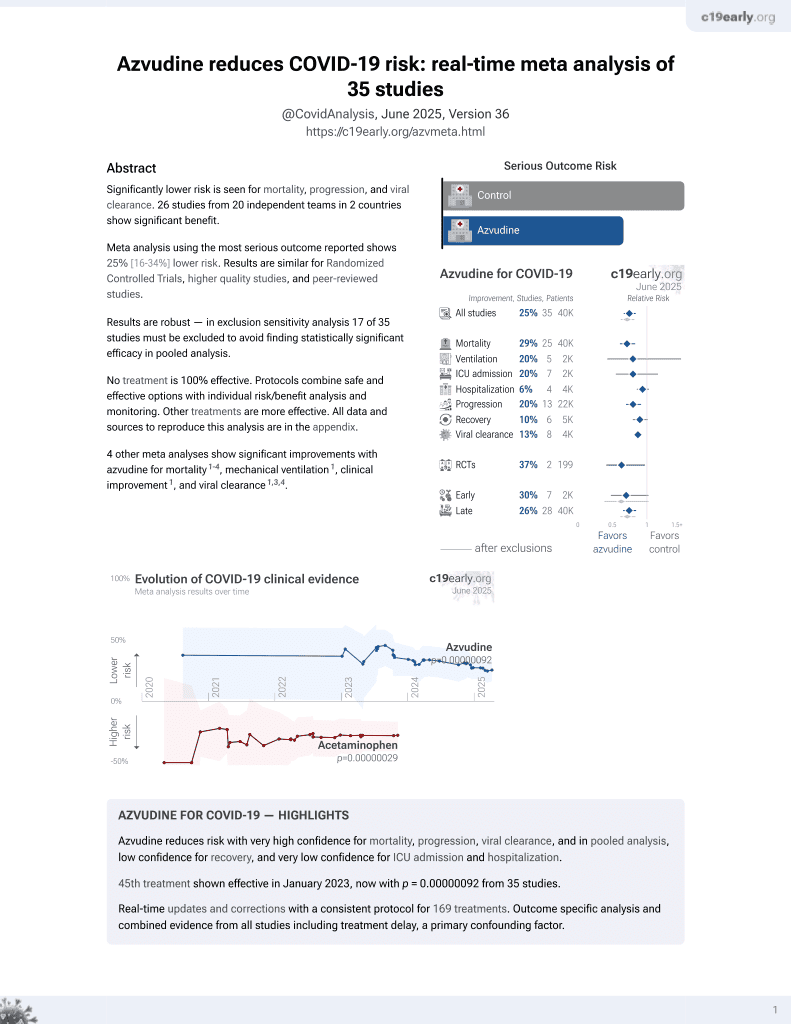
Azvudine for COVID-19
48th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2023, now with p = 0.0000000041 from 40 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
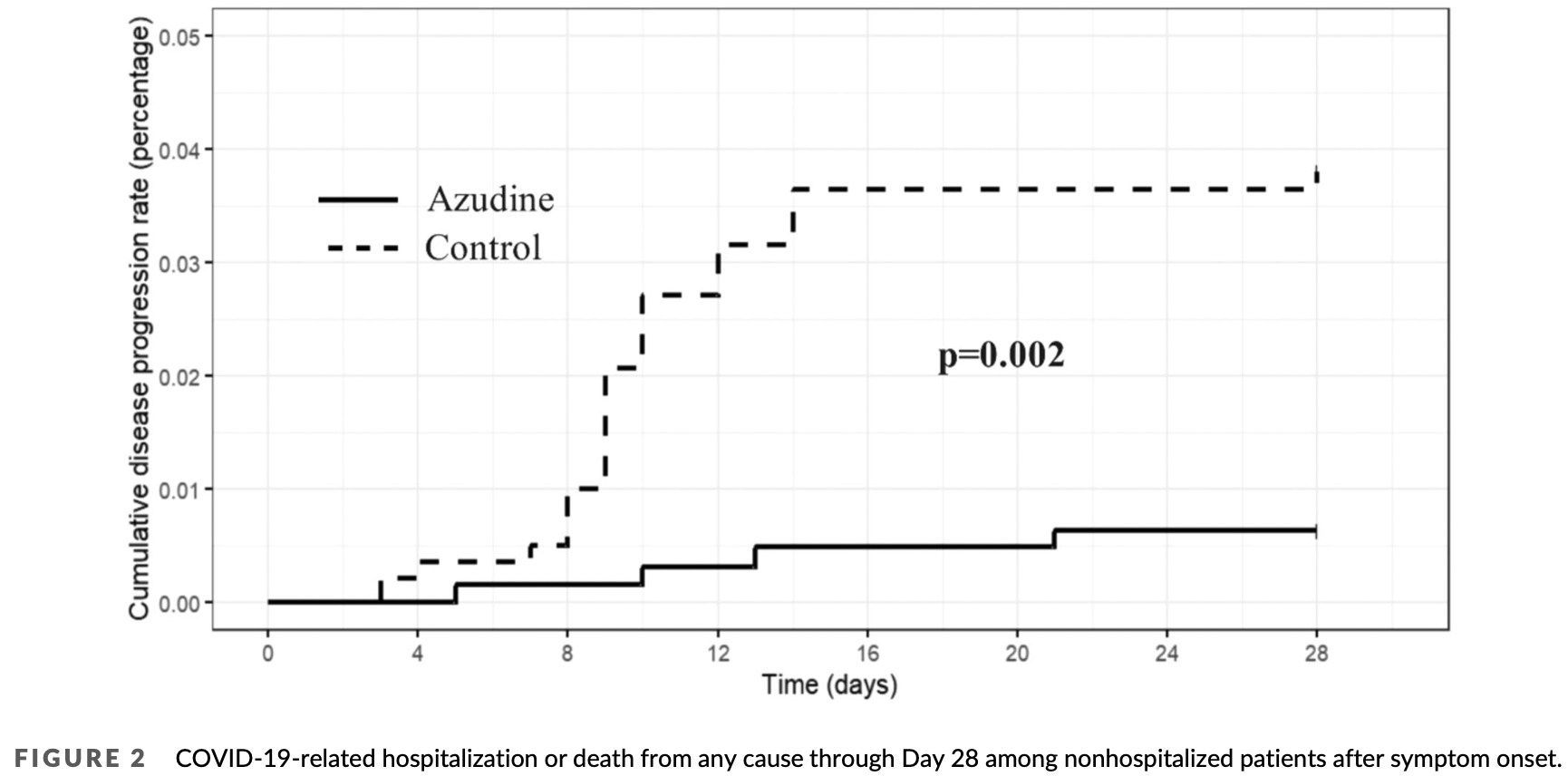
PSM retrospective 804 high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with mild to moderate COVID-19 in China. The study compared outcomes between 317 patients who received azvudine with 487 patients who received standard supportive treatment only. The azvudine group had a lower rate of disease progression (composite of death or COVID-19 hospitalization) at 28 days, as well as a lower rate of COVID-19 hospitalization specifically after adjusting for factors. In addition, azvudine shortened the duration of fever if given within 3 days of symptom onset. However, azvudine treatment was associated with a higher incidence of adverse effects, including mainly mild gastrointestinal and nervous system effects.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments3.
|
risk of death, 90.8% lower, RR 0.09, p = 0.09, treatment 0 of 317 (0.0%), control 6 of 487 (1.2%), NNT 81, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 74.8% lower, RR 0.25, p = 0.047, treatment 317, control 487, propensity score weighting.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 16.0% lower, RR 0.84, p = 0.19, treatment 317, control 487, propensity score weighting.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Xiong et al., Real-world data of Azvudine-induced hepatotoxicity among hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China: a retrospective case-control study, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1558054.
Yang et al., 20 Jul 2023, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 11 authors, study period 19 December, 2022 - 5 January, 2023.
Contact: anzhuoling@bjcyh.com, tongzhaohuicy@sina.com.
Oral azvudine for mild‐to‐moderate COVID‐19 in high risk, nonhospitalized adults: Results of a real‐world study
Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.28947
Azvudine is recommended by Chinese health authorities for COVID-19 treatment but has not been tested in real-world clinical studies. This study aimed to evaluate the realworld effectiveness of Azvudine among COVID-19 nonhospitalized patients. This was a retrospective cohort study, looking at nonhospitalized patients who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. Patients admitted between December 19, 2022 and January 5, 2023 were included. Those who received Azvudine treatment were in the Azvudine group, while those who received supportive treatment were the control group. The primary outcome was the disease progression rate by Day 28. Secondary outcomes were individual disease progression outcomes (death or COVID-19-related hospitalization) and duration of fever. The safety outcomes were assessed based on adverse events (AEs) overall, as well as AEs that were considered to be related to the drug. A total of 804 patients with high risk for progression were enrolled in our study. Among them, 317 (39.43%) received treatment with Azvudine. Our study found that Azvudine could reduce the rate of disease progression, as well as rate of COVID-19-related hospitalization in patients comparing the control group. Furthermore, if taken within 3 days of the onset of symptoms, it could also shorten the duration of fever. Despite a higher incidence of drug-related AEs compared to supportive treatment, the majority of these were mild. Azvudine has been found to be effective in reducing the rate of disease progression of COVID-19, albeit with a slight increase in AEs.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS Zhuoling An and Zhaohui Tong designed the experiments. Chunguo Jiang was responsible for clinical assessment of patients. Hui Yang, Zhaojian Wang, Yi Zhang, Man Xu, Ying Zhang, Yushu Wang, and Yi Zhang collected the data. Zhaojian Wang was responsible for data management. Hui Yang and Zhaojian Wang conducted the statistical analysis. This article was written by Hui Yang, and reviewed by Xuefeng Liu, Zhuoling An, and Zhaohui Tong. All authors reviewed the article.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT The authors declare no conflict of interest.
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Additional supporting information can be found online in the Supporting Information section at the end of this article.
References
Burki, Omicron variant and booster COVID-19 vaccines, Lancet Respir Med
Callaway, Omicron likely to weaken COVID vaccine protection, Nature
Cao, Gao, Bao, VV116 versus Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir for oral treatment of Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Collie, Champion, Moultrie, Bekker, Gray, Effectiveness of BNT162b2 vaccine against Omicron variant in South Africa, N Engl J Med
Cui, Liu, Wang, Structural and functional characterizations of infectivity and immune evasion of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron, Cell
Da Silva, Abreu Cabral, Souza, Serial viral load analysis by DDPCR to evaluate FNC efficacy and safety in the treatment of mild cases of COVID-19, Frontiers in Medicine
Desai, Franklin, Alternative approaches for confounding adjustment in observational studies using weighting based on the propensity score: a primer for practitioners, BMJ
Gentile, Scotto, Moriello, Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and molnupiravir in the treatment of mild/moderate COVID-19: results of a real-life study, Vaccines
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Kaabi, Zhang, Xia, Effect of 2 inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccines on symptomatic COVID-19 infection in adults: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Lamontagne, Agarwal, Rochwerg, A living WHO guideline on drugs for Covid-19, BMJ
Ren, Luo, Yu, A randomized, open-label, controlled clinical trial of azvudine tablets in the treatment of mild and common COVID-19, a pilot study, Adv Sci
Sun, Peng, Yu, Mechanistic insight into antiretroviral potency of 2′-deoxy-2′-β-fluoro-4′-azidocytidine (FNC) with a Long-Lasting effect on HIV-1 prevention, J Med Chem
Vitiello, Ferrara, Auti, Domenico, Boccellino, Advances in the Omicron variant development, J Intern Med
Xia, Duan, Zhang, Effect of an inactivated vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 on safety and immunogenicity outcomes: interim analysis of 2 randomized clinical trials, JAMA
Xia, Zhang, Wang, Safety and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, BBIBP-CorV: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1/2 trial, Lancet Infect Dis
Yu, Chang, Azvudine (FNC): a promising clinical candidate for COVID-19 treatment, Signal Transduct Target Ther
Yu, Chang, The first Chinese oral anti-COVID-19 drug azvudine launched, Innovation
Zhang, Li, Wang, Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients, Signal Transduct Target Ther
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28947",
"ISSN": [
"0146-6615",
"1096-9071"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jmv.28947",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>Azvudine is recommended by Chinese health authorities for COVID‐19 treatment but has not been tested in real‐world clinical studies. This study aimed to evaluate the real‐world effectiveness of Azvudine among COVID‐19 nonhospitalized patients. This was a retrospective cohort study, looking at nonhospitalized patients who tested positive for SARS‐CoV‐2. Patients admitted between December 19, 2022 and January 5, 2023 were included. Those who received Azvudine treatment were in the Azvudine group, while those who received supportive treatment were the control group. The primary outcome was the disease progression rate by Day 28. Secondary outcomes were individual disease progression outcomes (death or COVID‐19‐related hospitalization) and duration of fever. The safety outcomes were assessed based on adverse events (AEs) overall, as well as AEs that were considered to be related to the drug. A total of 804 patients with high risk for progression were enrolled in our study. Among them, 317 (39.43%) received treatment with Azvudine. Our study found that Azvudine could reduce the rate of disease progression, as well as rate of COVID‐19‐related hospitalization in patients comparing the control group. Furthermore, if taken within 3 days of the onset of symptoms, it could also shorten the duration of fever. Despite a higher incidence of drug‐related AEs compared to supportive treatment, the majority of these were mild. Azvudine has been found to be effective in reducing the rate of disease progression of COVID‐19, albeit with a slight increase in AEs.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/jmv.28947"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2023-05-06"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2023-06-27"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2023-07-20"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Beijing Chao‐Yang Hospital Capital Medical University Beijing China"
}
],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Hui",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Beijing Chao‐Yang Hospital Capital Medical University Beijing China"
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Zhaojian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Beijing Chao‐Yang Hospital, Beijing Institute of Respiratory Medicine Capital Medical University Beijing China"
}
],
"family": "Jiang",
"given": "Chunguo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Beijing Chao‐Yang Hospital Capital Medical University Beijing China"
}
],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Yi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Beijing Chao‐Yang Hospital Capital Medical University Beijing China"
}
],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Ying",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Beijing Chao‐Yang Hospital Capital Medical University Beijing China"
}
],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Man",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Beijing Chao‐Yang Hospital Capital Medical University Beijing China"
}
],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Yi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Beijing Chao‐Yang Hospital Capital Medical University Beijing China"
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Yushu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9922-9627",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Departments of Pathology, Urology, and Radiation Oncology The Ohio State University Columbus Ohio USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Xuefeng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Beijing Chao‐Yang Hospital Capital Medical University Beijing China"
}
],
"family": "An",
"given": "Zhuoling",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5341-6857",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Beijing Chao‐Yang Hospital, Beijing Institute of Respiratory Medicine Capital Medical University Beijing China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tong",
"given": "Zhaohui",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Medical Virology",
"container-title-short": "Journal of Medical Virology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-20T09:21:50Z",
"timestamp": 1689844910000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-04T09:25:50Z",
"timestamp": 1696411550000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-25T07:41:50Z",
"timestamp": 1700898110321
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 2,
"issue": "7",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "7",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 19,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1689811200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/jmv.28947",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
20
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_2_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines10101731",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_3_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-00351-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/advs.202001435",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_6_1"
},
{
"article-title": "The first Chinese oral anti‐COVID‐19 drug azvudine launched",
"author": "Yu B",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Innovation",
"key": "e_1_2_10_7_1",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2022.01.019",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_8_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_9_1",
"unstructured": "Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Epidemic Situation of Novel Coronavirus Infection in China. 2023.https://www.chinacdc.cn/jkzt/crb/zl/szkb_11803/jszl_13141/202304/t20230401_264798.html"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m3379",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2208822",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.l5657",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c00940",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2023.1143485",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_14_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.8565",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30831-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.15543",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13478",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-021-03672-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_19_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00559-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_20_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2119270",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_21_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 20,
"references-count": 20,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jmv.28947"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Virology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Oral azvudine for mild‐to‐moderate COVID‐19 in high risk, nonhospitalized adults: Results of a real‐world study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "95"
}