Systematic evaluation of therapeutic effectiveness of Azvudine in treating COVID-19 hospitalized patients: a retrospective cohort study
et al., Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2024.1453234, Nov 2024
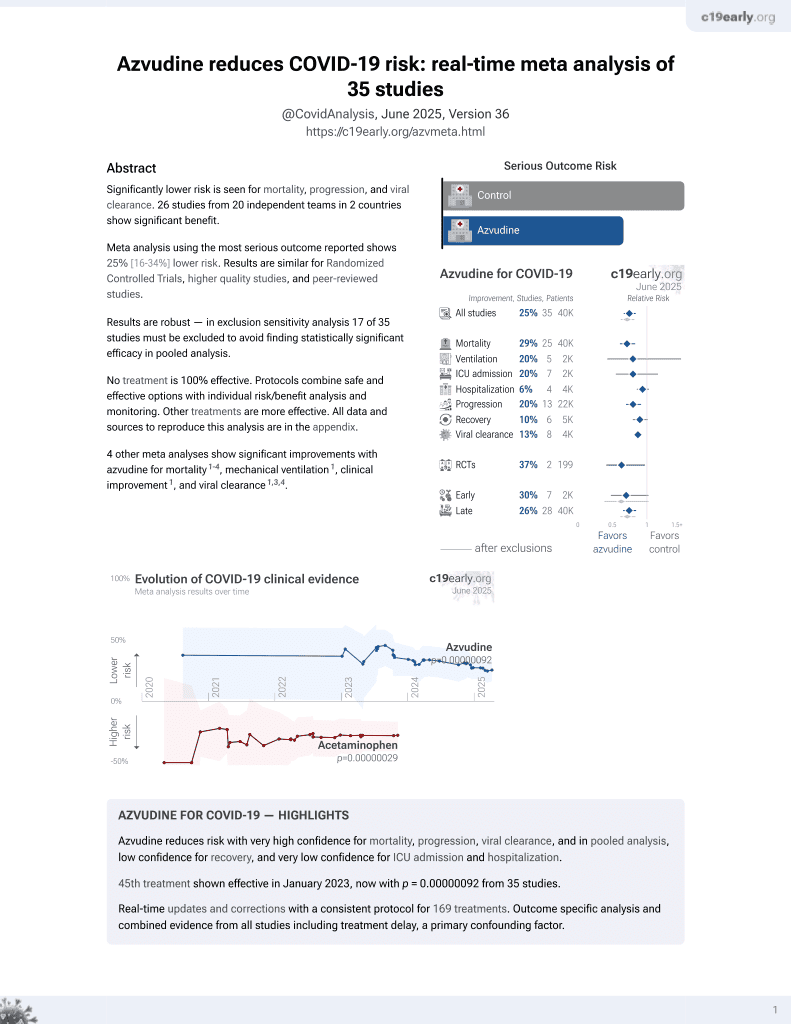
Azvudine for COVID-19
48th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2023, now with p = 0.0000000041 from 40 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 264 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China showing lower risk of composite disease progression and all-cause mortality with azvudine treatment.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments3.
|
risk of death, 75.0% lower, HR 0.25, p = 0.02, treatment 132, control 132, adjusted per study, propensity score matching, multivariable.
|
|
risk of progression, 63.0% lower, HR 0.37, p = 0.02, treatment 132, control 132, adjusted per study, respiratory support, ICU admission, or death, propensity score matching, multivariable.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Xiong et al., Real-world data of Azvudine-induced hepatotoxicity among hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China: a retrospective case-control study, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1558054.
Xu et al., 7 Nov 2024, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, study period 1 December, 2022 - 31 January, 2023.
Contact: liulei890207@163.com, wangli851217@163.com.
Systematic evaluation of therapeutic effectiveness of Azvudine in treating COVID-19 hospitalized patients: a retrospective cohort study
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2024.1453234
Background: Azvudine, a repurposed oral small molecule antiviral drug, has potential effects in combating the SARS-CoV-2 virus. However, studies on its clinical efficacy in patients with COVID-19 are still limited and controversial, and further research and validation are necessary. Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted on COVID-19 patients who were hospitalized in the General Hospital of Central Theater Command from 1 December 2022 to 31 January 2023. We included 132 patients treated with Azvudine and 132 controls after screening and propensity score matching. The primary outcomes including all-cause mortality and a composite outcome of disease progression such as non-invasive respiratory support, invasive respiratory support, admission to intensive care unit (ICU), and death were compared. Results: Azvudine recipients had a much lower incidence rate of composite disease progression outcome than controls (13.9075/1000 person-days versus 25.7731/1000 person-days, P<0.05). Azvudine recipients also possessed a lower all-cause mortality rate than controls (2.6797/1000 person-days versus 8.5910/ 1000 person-days, P<0.01). Azvudine treatment significantly reduced the risk of composite disease progression (HR: 0.37, 95% CI: 0.16-0.84, P=0.017) and allcause death (HR: 0.25, 95% CI: 0.08-0.81, P=0.021) after adjusting potential confounding factors such as age, sex, severity of COVID-19, complications, concomitant therapy, time from symptoms to treatment, and important laboratory indicators. The subgroup analyses of composite disease progression outcome and all-cause death indicated robustness of Azvudine's in treating COVID-19 patients in general.
Ethics statement The studies involving humans were approved by Research Ethics Committee of General Hospital of Central Theater Command. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants' legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Austin, Some methods of propensity-score matching had superior performance to others: Results of an empirical investigation and monte carlo simulations, Biom J, doi:10.1002/bimj.200810488
Bai, Du, Wang, Lau, Fung et al., Public health impact of paxlovid as treatment for covid-19, United States, Emerging Infect. Dis. J, doi:10.3201/eid3002.230835
Bernal, Gomes Da Silva, Musungaie, Kovalchuk, Gonzalez et al., Molnupiravir for oral treatment of covid-19 in nonhospitalized patients, N Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2116044
Chakraborty, Maity, Covid-19 outbreak: Migration, effects on society, global environment and prevention, Sci. Total Environ, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138882
Chen, Guo, Deng, Wang, Gao et al., All-cause mortality in moderate and severe covid-19 patients with myocardial injury receiving versus not receiving azvudine: A propensity score-matched analysis, Cardiol. Plus, doi:10.1097/CP9.0000000000000049
Chen, Jiang, Rang, Zhuo, Zhou, Comparison of azvudine, molnupiravir, and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in adult patients with mild-to-moderate covid-19: A retrospective cohort study, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-53862-y
Da Silva, Gebe Abreu Cabral, De Souza, Arruda, Cabral et al., Serial viral load analysis by ddpcr to evaluate fnc efficacy and safety in the treatment of mild cases of covid-19, Front. Med, doi:10.37247/PAMED5ED.5.23.7
Dresser, Spence, Bailey, Pharmacokineticpharmacodynamic consequences and clinical relevance of cytochrome p450 3a4 inhibition, Clin. Pharmacokinet, doi:10.2165/00003088-200038010-00003
Gao, Luo, Ren, Duan, Han et al., Antiviral effect of azvudine and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir among hospitalized patients with covid-19, J. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.023
Grandvuillemin, Rocher, Valnet-Rabier, Drici, Dautriche, Pharmacovigilance follow-up of patients in the context of the covid-19 pandemic, Therapie, doi:10.1016/j.therap.2023.01.004
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Abreu, Bao et al., Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with covid-19, N Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2118542
Han, Han, Wang, Wang, Cui et al., Effectiveness and Optimal timing of Azvudine in COVID-19 Patients: A Multi-center Retrospective Study in Beijing, China, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-3145554/v1
Jiang, Sun, Zhao, Zhang, Liu et al., Presence of the m184i mutation after short-term exposure to azvudine for covid-19 in people living with hiv, AIDS, doi:10.1097/QAD.0000000000003564
Kellogg, Equils, The role of the thymus in covid-19 disease severity: Implications for antibody treatment and immunization, Hum. Vaccines Immunotherapeutics, doi:10.1080/21645515.2020.1818519
Najjar-Debbiny, Gronich, Weber, Khoury, Amar et al., Effectiveness of paxlovid in reducing severe coronavirus disease 2019 and mortality in high-risk patients, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac443
Qi, Yang, Gong, Li, Liang, Real-world effectiveness of azvudine for patients infected with the sars-cov-2 omicron subvariant ba.5 in an intensive care unit, J. Thorac. Dis, doi:10.21037/jtd-23-1093
Reis, Metzendorf, Kuehn, Popp, Gagyor et al., Nirmatrelvir combined with ritonavir for preventing and treating covid-19, Cochrane Database Syst. Rev, doi:10.1097/QAD.0000000000003564
Ren, Luo, Yu, Song, Liang et al., A randomized, openlabel, controlled clinical trial of azvudine tablets in the treatment of mild and common covid-19, a pilot study, Adv. Sci. (Weinh), doi:10.1002/advs.202001435
Rizk, Kalantar-Zadeh, Mehra, Lavie, Rizk et al., Pharmaco-immunomodulatory therapy in covid-19, Drugs, doi:10.1007/s40265-020-01367-z
Sun, Jin, Dian, Shen, Zeng et al., Oral azvudine for hospitalised patients with covid-19 and pre-existing conditions: A retrospective cohort study, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101981
Vujcǐc, Outcomes of covid-19 among patients with liver disease, World J. Gastroenterol, doi:10.3748/wjg.v29.i5.815
Yan, Zhou, Zhu, Chen, Lu et al., The feasibility, safety, and efficacy of paxlovid treatment in sars-cov-2-infected children aged 6-14 years: A cohort study, Ann. Transl. Med, doi:10.21037/atm-22-2791
Yang, Liu, Liu, Zhang, Wan et al., Covid-19: immunopathogenesis and immunotherapeutics, Signal Transduction Targeted Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00243-2
Yu, Chang, Azvudine (fnc): A promising clinical candidate for covid-19 treatment, Signal Transduct Target Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00351-z
Yu, Chang, The first chinese oral anti-covid-19 drug azvudine launched, Innovation (Camb), doi:10.1016/j.xinn.2022.100321
Yu, Du, Yan, Guo, He et al., Liver injury in covid-19: Clinical features and treatment management, Virol. J, doi:10.1186/s12985-021-01593-1
Zhang, Li, Wang, Liu, Lu et al., Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-sars-cov-2 drug effective in treating covid-19 patients, Signal Transduct Target Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6
Zhu, Efficacy and safety evaluation of azvudine in the prospective treatment of covid-19 based on four phase iii clinical trials, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1228548
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2024.1453234",
"ISSN": [
"2235-2988"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2024.1453234",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>Azvudine, a repurposed oral small molecule antiviral drug, has potential effects in combating the SARS-CoV-2 virus. However, studies on its clinical efficacy in patients with COVID-19 are still limited and controversial, and further research and validation are necessary.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>A retrospective cohort study was conducted on COVID-19 patients who were hospitalized in the General Hospital of Central Theater Command from 1 December 2022 to 31 January 2023. We included 132 patients treated with Azvudine and 132 controls after screening and propensity score matching. The primary outcomes including all-cause mortality and a composite outcome of disease progression such as non-invasive respiratory support, invasive respiratory support, admission to intensive care unit (ICU), and death were compared.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>Azvudine recipients had a much lower incidence rate of composite disease progression outcome than controls (13.9075/1000 person-days versus 25.7731/1000 person-days, <jats:italic>P</jats:italic>&lt;0.05). Azvudine recipients also possessed a lower all-cause mortality rate than controls (2.6797/1000 person-days versus 8.5910/1000 person-days, <jats:italic>P</jats:italic>&lt;0.01). Azvudine treatment significantly reduced the risk of composite disease progression (HR: 0.37, 95% CI: 0.16-0.84, <jats:italic>P</jats:italic>=0.017) and all-cause death (HR: 0.25, 95% CI: 0.08-0.81, <jats:italic>P</jats:italic>=0.021) after adjusting potential confounding factors such as age, sex, severity of COVID-19, complications, concomitant therapy, time from symptoms to treatment, and important laboratory indicators. The subgroup analyses of composite disease progression outcome and all-cause death indicated robustness of Azvudine’s in treating COVID-19 patients in general.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>Our study demonstrates that Azvudine has a significant positive impact on the clinical recovery of hospitalized patients with COVID-19. These findings provide important support for the use of Azvudine as a therapeutic option for COVID-19, given the current divergent views on its therapeutic efficacy and its importance in public health and medical care.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fcimb.2024.1453234"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Yingkai",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Yuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yuan",
"given": "Zihan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Wanbing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Li",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Lei",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology",
"container-title-short": "Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-07T06:12:18Z",
"timestamp": 1730959938000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-07T06:12:20Z",
"timestamp": 1730959940000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-08T05:15:19Z",
"timestamp": 1731042919890,
"version": "3.28.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
7
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-07T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1730937600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2024.1453234/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
7
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1002/bimj.200810488",
"article-title": "Some methods of propensity-score matching had superior performance to others: Results of an empirical investigation and monte carlo simulations",
"author": "Austin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "171",
"journal-title": "Biom J.",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid3002.230835",
"article-title": "Public health impact of paxlovid as treatment for covid-19, United States",
"author": "Bai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "262",
"journal-title": "Emerging Infect. Dis. J.",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138882",
"article-title": "Covid-19 outbreak: Migration, effects on society, global environment and prevention",
"author": "Chakraborty",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "138882",
"journal-title": "Sci. Total Environ.",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "728",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CP9.0000000000000049",
"article-title": "All-cause mortality in moderate and severe covid-19 patients with myocardial injury receiving versus not receiving azvudine: A propensity score-matched analysis",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "103",
"journal-title": "Cardiol. Plus",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-024-53862-y",
"article-title": "Comparison of azvudine, molnupiravir, and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in adult patients with mild-to-moderate covid-19: A retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3318",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.37247/PAMED5ED.5.23.7",
"article-title": "Serial viral load analysis by ddpcr to evaluate fnc efficacy and safety in the treatment of mild cases of covid-19",
"author": "da Silva",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1143485",
"journal-title": "Front. Med. (Lausanne)",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2165/00003088-200038010-00003",
"article-title": "Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic consequences and clinical relevance of cytochrome p450 3a4 inhibition",
"author": "Dresser",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "41",
"journal-title": "Clin. Pharmacokinet.",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.023",
"article-title": "Antiviral effect of azvudine and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir among hospitalized patients with covid-19",
"author": "Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e158",
"journal-title": "J. Infect.",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.therap.2023.01.004",
"article-title": "Pharmacovigilance follow-up of patients in the context of the covid-19 pandemic",
"author": "Grandvuillemin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "523",
"journal-title": "Therapie",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with covid-19",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "N Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "Han",
"key": "B11",
"volume-title": "Effectiveness and Optimal timing of Azvudine in COVID-19 Patients: A Multi-center Retrospective Study in Beijing, China",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116044",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir for oral treatment of covid-19 in nonhospitalized patients",
"author": "Jayk Bernal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "509",
"journal-title": "N Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/QAD.0000000000003564",
"article-title": "Presence of the m184i mutation after short-term exposure to azvudine for covid-19 in people living with hiv",
"author": "Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1341",
"journal-title": "AIDS",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/21645515.2020.1818519",
"article-title": "The role of the thymus in covid-19 disease severity: Implications for antibody treatment and immunization",
"author": "Kellogg",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "638",
"journal-title": "Hum. Vaccines Immunotherapeutics",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac443",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of paxlovid in reducing severe coronavirus disease 2019 and mortality in high-risk patients",
"author": "Najjar-Debbiny",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e342",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21037/jtd-23-1093",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of azvudine for patients infected with the sars-cov-2 omicron subvariant ba.5 in an intensive care unit",
"author": "Qi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4925",
"journal-title": "J. Thorac. Dis.",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/QAD.0000000000003564",
"article-title": "Nirmatrelvir combined with ritonavir for preventing and treating covid-19",
"author": "Reis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "Cd015395",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst. Rev.",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/advs.202001435",
"article-title": "A randomized, open-label, controlled clinical trial of azvudine tablets in the treatment of mild and common covid-19, a pilot study",
"author": "Ren",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Adv. Sci. (Weinh)",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40265-020-01367-z",
"article-title": "Pharmaco-immunomodulatory therapy in covid-19",
"author": "Rizk",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1267",
"journal-title": "Drugs",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101981",
"article-title": "Oral azvudine for hospitalised patients with covid-19 and pre-existing conditions: A retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "101981",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3748/wjg.v29.i5.815",
"article-title": "Outcomes of covid-19 among patients with liver disease",
"author": "Vujčić",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "815",
"journal-title": "World J. Gastroenterol.",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21037/atm-22-2791",
"article-title": "The feasibility, safety, and efficacy of paxlovid treatment in sars-cov-2-infected children aged 6-14 years: A cohort study",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "619",
"journal-title": "Ann. Transl. Med.",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-00243-2",
"article-title": "Covid-19: immunopathogenesis and immunotherapeutics",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "128",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduction Targeted Ther.",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-00351-z",
"article-title": "Azvudine (fnc): A promising clinical candidate for covid-19 treatment",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "236",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct Target Ther.",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xinn.2022.100321",
"article-title": "The first chinese oral anti-covid-19 drug azvudine launched",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100321",
"journal-title": "Innovation (Camb)",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-021-01593-1",
"article-title": "Liver injury in covid-19: Clinical features and treatment management",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "121",
"journal-title": "Virol. J.",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6",
"article-title": "Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-sars-cov-2 drug effective in treating covid-19 patients",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "414",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct Target Ther.",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2023.1228548",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety evaluation of azvudine in the prospective treatment of covid-19 based on four phase iii clinical trials",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 28,
"references-count": 28,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2024.1453234/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Systematic evaluation of therapeutic effectiveness of Azvudine in treating COVID-19 hospitalized patients: a retrospective cohort study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "14"
}