Azvudine reduces the in-hospital mortality of COVID-19 patients: A retrospective cohort study
et al., Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007, Jul 2023
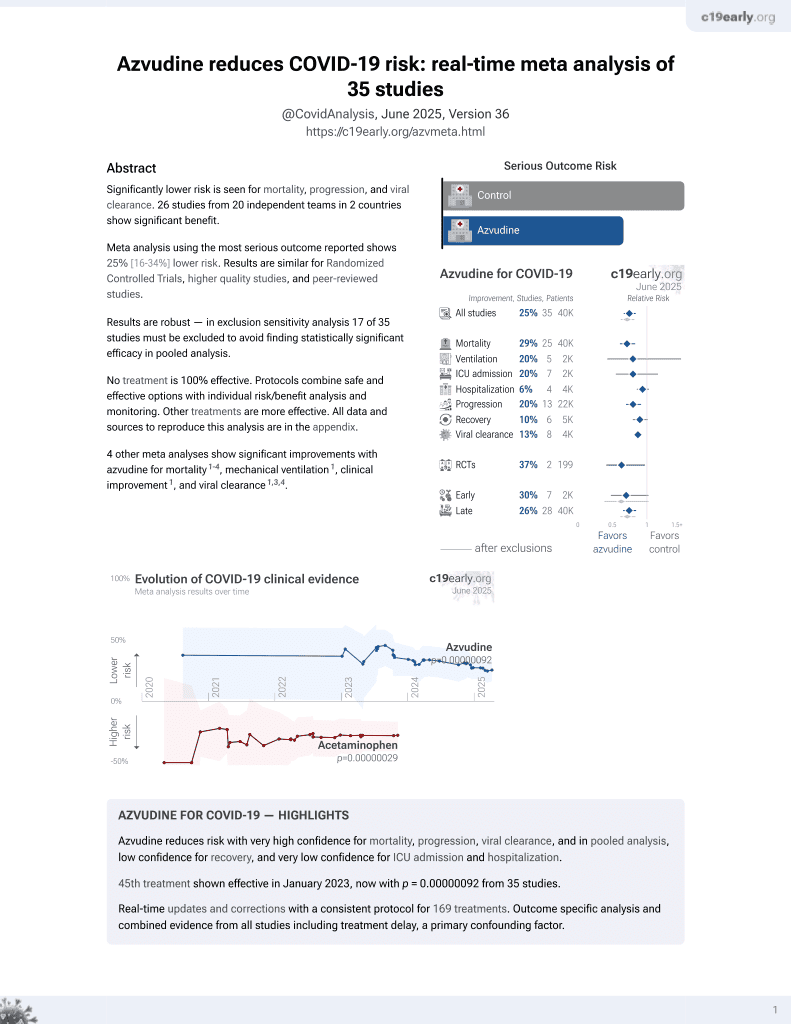
Azvudine for COVID-19
48th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2023, now with p = 0.0000000041 from 40 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
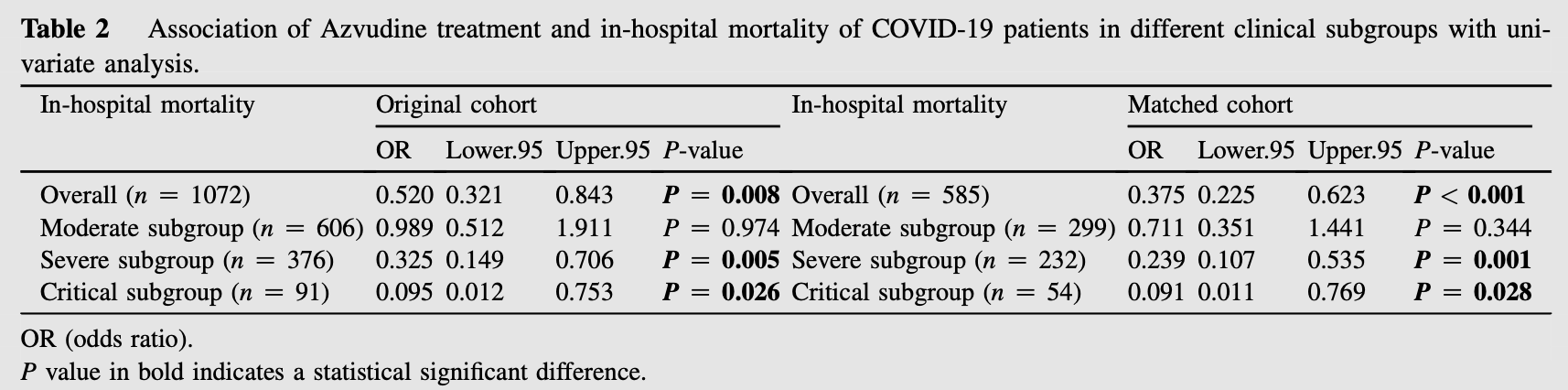
PSM retrospective 1072 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in China, showing lower mortality with azvudine treatment.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments3.
|
risk of death, 62.5% lower, OR 0.38, p < 0.001, treatment 195, control 390, propensity score matching, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Xiong et al., Real-world data of Azvudine-induced hepatotoxicity among hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China: a retrospective case-control study, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1558054.
Zong et al., 13 Jul 2023, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, study period 8 December, 2022 - 20 January, 2023.
Contact: adeleli@163.com, 302946@hospital.cqmu.edu.cn.
Azvudine reduces the in-hospital mortality of COVID-19 patients: A retrospective cohort study
Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007
In our retrospective cohort study, we aim to explore whether Azvudine modifies the risk of death in COVID-19 patients. It was conducted on the medical records of patients, consecutively admitted for COVID-19 pneumonia to two hospitals in Chongqing, China. Based on Azvudine treatment exposure, the patients were divided into Azvudine group and non-Azvudine group. We used 1:2 ratio propensity score matching (PSM) in our study to adjust for confounding factors and differences between Azvudine and non-Azvudine groups. There were 1072 patients included in our original cohort. With 1:2 ratio PSM, the Azvudine group included 195 patients and non-Azvudine group included 390 patients. The results showed that Azvudine treatment was associated with improved in-hospital mortality in overall population (OR 0.375, 95% CI 0.225e0.623, P < 0.001), severe subgroup (OR 0.239, 95% CI 0.107e0.535, P Z 0.001), critical subgroup (OR 0.091, 95% CI 0.011e0.769, P Z 0.028) in matched cohort with univariate analysis. And there was a significantly lower in-hospital mortality in overall population (11% vs. 24%, P<0.001), severe sub-group (10% vs. 32%, P < 0.001) and critical sub-group (5% vs. 34%, P Z 0.017) in matched cohort. These results suggest Azvudine can reduce in-hospital mortality in overall COVID-19 patients, severe, and critical subgroup population.
Author contributions Kaican Zong and Shiying Li conceived and designed the study and took responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. All authors collected the data and had full access to all of the data in the study. All authors critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual content and gave final approval for the version to be published.
Conflicts of interest The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
References
Bhatraju, Ghassemieh, Nichols, Kim, Jerome et al., COVID-19 in critically Ill patients in the Seattle region-case series, N Engl J Med
Chang, Elhusseiny, Yeh, Sun, COVID-19 ICU and mechanical ventilation patient characteristics and outcomesda systematic review and meta-analysis, PLoS One
Deng, Li, Sun, Zhou, Xiao, Real-world effectiveness of Azvudine versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study, J Med Virol
Dian, Meng, Sun, Deng, Zeng, Azvudine versus Paxlovid for oral treatment of COVID-19 in Chinese patients with pre-existing comorbidities, J Infect
Ehrmann, Li, Ibarra-Estrada, Perez, Pavlov et al., Awake prone positioning meta-trial group. Awake prone positioning for COVID-19 acute hypoxaemic respiratory failure: a randomised, controlled, multinational, open-label meta-trial, Lancet Respir Med
Gao, Luo, Ren, Duan, Han et al., Antiviral effect of azvudine and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir among hospitalized patients with COVID-19, J Infect
Grasselli, Greco, Zanella, Albano, Antonelli et al., COVID-19 lombardy ICU network. Risk factors associated with mortality among patients with COVID-19 in intensive care units in Lombardy, Italy, JAMA Intern Med
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Nair, Haritha, Behera, Kayina, Maitra et al., Comparison of high-flow nasal cannula and noninvasive ventilation in acute hypoxemic respiratory failure due to severe COVID-19 pneumonia, Respir Care
Phua, Weng, Ling, Egi, Lim et al., Asian Critical Care Clinical Trials Group. Intensive care management of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): challenges and recommendations, Lancet Respir Med
Popowicz, Leonard, Noninvasive ventilation and oxygenation strategies, Surg Clin
Ren, Luo, Yu, Song, Liang et al., A randomized, openlabel, controlled clinical trial of Azvudine tablets in the treatment of mild and common COVID-19, a pilot study, Adv Sci
Soin, Kumar, Choudhary, Sharma, Mehta et al., Tocilizumab plus standard care versus standard care in patients in India with moderate to severe COVID-19-associated cytokine release syndrome (COVINTOC): an open-label, multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial, Lancet Respir Med
Sun, Dian, Shen, Zeng, Chen, Oral Azvudine for hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing conditions: a retrospective cohort study, EClinicalMedicine
Who, Weekly epidemiological update on COVID-19-22 February
Winck, Ambrosino, COVID-19 pandemic and non invasive respiratory management: every Goliath needs a David. An evidence based evaluation of problems, Pulmonology
Yang, Yu, Xu, Shu, Xia et al., Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study, Lancet Respir Med
Yelin, Wirtheim, Vetter, Kalil, Bruchfeld et al., Long-term consequences of COVID-19: research needs, Lancet Infect Dis
Yu, Chang, The first Chinese oral anti-COVID-19 drug Azvudine launched, Innovation
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007",
"ISSN": [
"2211-3835"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007",
"alternative-id": [
"S2211383523002575"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Azvudine reduces the in-hospital mortality of COVID-19 patients: A retrospective cohort study"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zong",
"given": "Kaican",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Hui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Wen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jiang",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Yi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Shiying",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B",
"container-title-short": "Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-13T02:02:50Z",
"timestamp": 1689213770000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-27T06:05:56Z",
"timestamp": 1698386756000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004374",
"award": [
"kryc-yq-2204"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Chongqing Medical University"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100005230",
"award": [
"CSTB2022NSCQ-MSX0901"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-28T12:12:53Z",
"timestamp": 1698495173270
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "11",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "11",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1698796800000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-07T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1688688000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2211383523002575?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2211383523002575?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "4655-4660",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30701-5",
"article-title": "Long-term consequences of COVID-19: research needs",
"author": "Yelin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1115",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007_bib1",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00081-3",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab plus standard care versus standard care in patients in India with moderate to severe COVID-19-associated cytokine release syndrome (COVINTOC): an open-label, multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial",
"author": "Soin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "511",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007_bib3",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "The first Chinese oral anti-COVID-19 drug Azvudine launched",
"author": "Yu",
"journal-title": "Innovation",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007_bib4",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007_bib5",
"unstructured": "China National Health Commission. Chinese clinical guidance for COVID-19 pneumonia diagnosis and treatment. Available from: http://kjfy.meetingchina. org/msite/news/show/cn/3337."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007_bib6",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30161-2",
"article-title": "Asian Critical Care Clinical Trials Group. Intensive care management of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): challenges and recommendations",
"author": "Phua",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "506",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007_bib7",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101981",
"article-title": "Oral Azvudine for hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing conditions: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007_bib8",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.023",
"article-title": "Antiviral effect of azvudine and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir among hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e158",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007_bib9",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/advs.202001435",
"article-title": "A randomized, open-label, controlled clinical trial of Azvudine tablets in the treatment of mild and common COVID-19, a pilot study",
"author": "Ren",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Adv Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007_bib10",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Azvudine versus Paxlovid for oral treatment of COVID-19 in Chinese patients with pre-existing comorbidities",
"author": "Dian",
"first-page": "290",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007_bib11",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28756",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of Azvudine versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Deng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007_bib12",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3539",
"article-title": "COVID-19 lombardy ICU network. Risk factors associated with mortality among patients with COVID-19 in intensive care units in Lombardy, Italy",
"author": "Grasselli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1345",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007_bib13",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5",
"article-title": "Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "475",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007_bib14",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2004500",
"article-title": "COVID-19 in critically Ill patients in the Seattle region‒case series",
"author": "Bhatraju",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2012",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007_bib15",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007_bib16",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19 ICU and mechanical ventilation patient characteristics and outcomes—a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Chang",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007_bib17",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Noninvasive ventilation and oxygenation strategies",
"author": "Popowicz",
"first-page": "149",
"journal-title": "Surg Clin",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007_bib18",
"volume": "102",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00356-8",
"article-title": "Awake prone positioning meta-trial group. Awake prone positioning for COVID-19 acute hypoxaemic respiratory failure: a randomised, controlled, multinational, open-label meta-trial",
"author": "Ehrmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1387",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007_bib19",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pulmoe.2020.04.013",
"article-title": "COVID-19 pandemic and non invasive respiratory management: every Goliath needs a David. An evidence based evaluation of problems",
"author": "Winck",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "213",
"journal-title": "Pulmonology",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007_bib20",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4187/respcare.09130",
"article-title": "Comparison of high-flow nasal cannula and noninvasive ventilation in acute hypoxemic respiratory failure due to severe COVID-19 pneumonia",
"author": "Nair",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1824",
"journal-title": "Respir Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007_bib21",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 20,
"references-count": 20,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2211383523002575"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Pharmacology, Toxicology and Pharmaceutics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Azvudine reduces the in-hospital mortality of COVID-19 patients: A retrospective cohort study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "13"
}