Nafamostat Mesylate Monotherapy in Patients with Moderate COVID-19: a Single-Center, Retrospective Study
et al., Japanese Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.7883/yoken.JJID.2021.699, Sep 2022
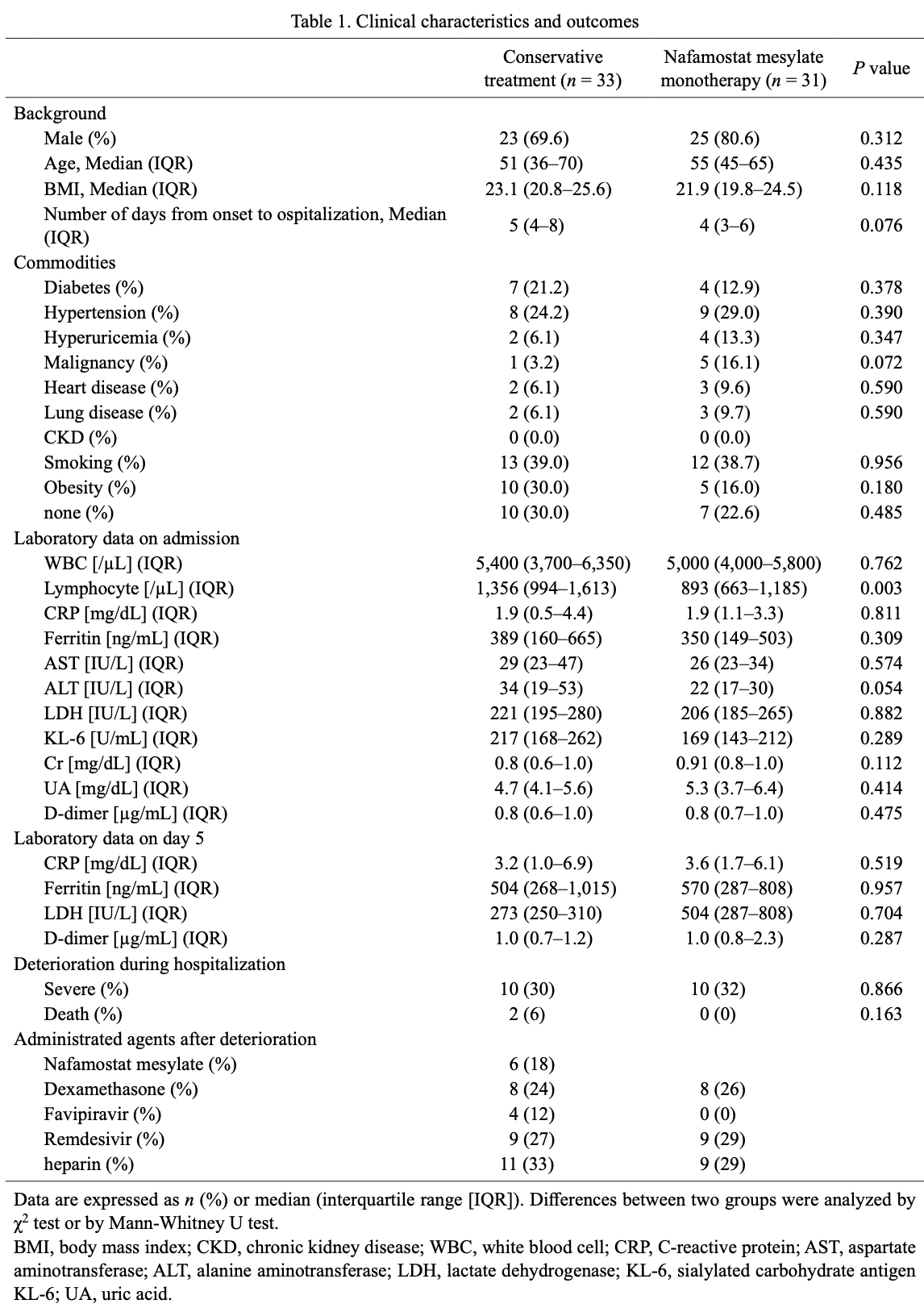
Retrospective 64 hospitalized patients with moderate COVID-19 showing no significant difference in clinical outcomes with nafamostat mesylate.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
Japan, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
Study covers TMPRSS2 inhibitors and nafamostat.
|
risk of death, 79.5% lower, RR 0.20, p = 0.49, treatment 0 of 31 (0.0%), control 2 of 33 (6.1%), NNT 16, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of severe case, 6.5% higher, RR 1.06, p = 1.00, treatment 10 of 31 (32.3%), control 10 of 33 (30.3%).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Soma et al., 30 Sep 2022, retrospective, Japan, peer-reviewed, 9 authors, study period 29 March, 2020 - 21 January, 2021.
Contact: kfujii225@gmail.com.
Nafamostat Mesylate Monotherapy in Patients with Moderate COVID-19: a Single-Center, Retrospective Study
Japanese Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.7883/yoken.jjid.2021.699
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) has spread dramatically worldwide. Nafamostat mesylate inhibits intracellular entry of the novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and is believed to have therapeutic potential for treating patients with COVID-19. In this study, patients with moderate COVID-19 who were admitted to our hospital were retrospectively analyzed. Thirty-one patients received monotherapy with nafamostat mesylate, and 33 patients were treated conservatively. Nafamostat mesylate was administered with continuous intravenous infusion for an average of 4.5 days. Compared with the conservative treatment, nafamostat mesylate did not improve outcomes or laboratory data 5 days after admission. In addition, no significant differences in laboratory data 5 days after admission and outcomes in high-risk patients were observed. The incidence of hyperkalemia was significantly higher in the nafamostat mesylate group; however, none of the patients required additional treatment. In conclusion, monotherapy with nafamostat mesylate did not improve clinical outcomes in patients with moderate COVID-19. This study did not examine the therapeutic potential of combining nafamostat mesylate with other antiviral agents, and further investigation is required. Because of the high incidence of hyperkalemia, regular laboratory monitoring is required during the use of nafamostat mesylate.
Conflict of interest None to declare.
References
Abdulgabbar, Clinical efficacy of nafamostat mesylate in combination with favipiravir for COVID-19 pneumonia treatment review article, Ann Med Surg
Asakura, Ogawa, Potential of heparin and nafamostat combination therapy for COVID-19, J Thromb Haemost
Becker, COVID-19 update: Covid-19-associated coagulopathy, J Thromb Thrombolysis
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19-final report, N Engl J Med
Doi, Ikeda, Hayase, Nafamostat mesylate treatment in combination with favipiravir for patients critically ill with Covid-19: a case series, Crit Care
Dougan, Nirula, Azizad, Bamlanivimab plus etesevimab in mild or moderate Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Gordon, Mouncey, Al-Beidh, Interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in critically ill patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell
Hoffmann, Schroeder, Kleine-Weber, Nafamostat mesylate blocks activation of SARS-CoV-2: new treatment option for COVID-19, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Hofmann-Winkler, Moerer, Alt-Epping, Camostat mesylate may reduce severity of coronavirus disease 2019 sepsis: a first observation, Crit Care Explor
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Muto, Imai, Asano, Mechanisms of hyperkalemia caused by nafamostat mesilate, Gen Pharmacol
Okajima, Takahashi, Kaji, Nafamostat mesylateinduced hyperkalemia in critically ill patients with COVID-19: four case reports, World J Clin Cases
Tang, Bai, Chen, Anticoagulant treatment is associated with decreased mortality in severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients with coagulopathy, J Thromb Haemost
Wiersinga, Rhodes, Cheng, Pathophysiology, transmission, diagnosis, and treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review, JAMA
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, JAMA
Yamamoto, Kiso, Sakai-Tagawa, The anticoagulant nafamostat potently inhibits SARS-CoV-2 S protein-mediated fusion in a cell fusion assay system and viral infection in vitro in a cell-type-dependent manner, Viruses
Yamamoto, Matsuyama, Li, Identification of nafamostat as a potent inhibitor of middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus S protein-mediated membrane fusion using the split-protein-based cell-cell fusion assay, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.7883/yoken.jjid.2021.699",
"ISSN": [
"1344-6304",
"1884-2836"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.7883/yoken.JJID.2021.699",
"article-number": "JJID.2021.699",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Nephrology, Japan Community Health care Organization Saitama Medical Center, Japan"
}
],
"family": "Soma",
"given": "Tomomi",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Nephrology, Tokyo Saiseikai Central Hospital, Japan"
}
],
"family": "Fujii",
"given": "Kentaro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Nephrology, Tokyo Saiseikai Central Hospital, Japan"
}
],
"family": "Yoshifuji",
"given": "Ayumi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Disease Control and Prevention Center, National Center for Global Health and Medicine, Japan"
}
],
"family": "Maruki",
"given": "Taketomo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of General Internal Medicine, Tokyo Saiseikai Central Hospital, Japan"
}
],
"family": "Itoh",
"given": "Kazuto",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Disease, Showa General Hospital, Japan"
}
],
"family": "Taniyama",
"given": "Daisuke",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Hematology, Tokyo Saiseikai Central Hospital, Japan"
}
],
"family": "Kikuchi",
"given": "Takahide",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Keio University School of Medicine, Japan"
}
],
"family": "Hasegawa",
"given": "Naoki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pulmonary Medicine, National Hospital Organization Kanagawa Hospital, Japan"
}
],
"family": "Nakamura",
"given": "Morio",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Japanese Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"container-title-short": "Jpn J Infect Dis",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-27T22:10:30Z",
"timestamp": 1651097430000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-24T04:52:20Z",
"timestamp": 1663995140000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-25T05:15:19Z",
"timestamp": 1716614119851
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 4,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
30
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/yoken/75/5/75_JJID.2021.699/_pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "4631",
"original-title": [],
"page": "484-489",
"prefix": "10.7883",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
30
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
30
]
]
},
"publisher": "Editorial Committee of Japanese Journal of Infectious Diseases, National Institute of Infectious Dis",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1",
"unstructured": "1. Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. 2020;323:1239-1242."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.12839",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2",
"unstructured": "2. Wiersinga WJ, Rhodes A, Cheng AC, et al. Pathophysiology, transmission, diagnosis, and treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review. JAMA. 2020;324:782-793."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "3",
"unstructured": "3. Horby P, Lim WS, Emberson JR, et al. ; RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:693-704."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2100433",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "4",
"unstructured": "4. Gordon AC, Mouncey PR, Al-Beidh F, et al. Interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in critically ill patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:1491-1502."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2022236",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "5",
"unstructured": "5. Beigel JH, Tomashek KM, Dodd LE, et al. Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19―final report. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1813-1826."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v12060629",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "6",
"unstructured": "6. Yamamoto M, Kiso M, Sakai-Tagawa Y, et al. The anticoagulant nafamostat potently inhibits SARS-CoV-2 S protein-mediated fusion in a cell fusion assay system and viral infection in vitro in a cell-type-dependent manner. Viruses. 2020;12:629."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03078-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "7",
"unstructured": "7. Doi K, Ikeda M, Hayase N, et al. ; COVID-UTH Study Group. Nafamostat mesylate treatment in combination with favipiravir for patients critically ill with Covid-19: a case series. Crit Care. 2020; 24:392."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCE.0000000000000284",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "8",
"unstructured": "8. Hofmann-Winkler H, Moerer O, Alt-Epping S, et al. Camostat mesylate may reduce severity of coronavirus disease 2019 sepsis: a first observation. Crit Care Explor. 2020;2:e0284."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2102685",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "9",
"unstructured": "9. Dougan M, Nirula A, Azizad M, et al. Bamlanivimab plus etesevimab in mild or moderate Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:1382-1392."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.14817",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10",
"unstructured": "10. Tang N, Bai H, Chen X, et al. Anticoagulant treatment is associated with decreased mortality in severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients with coagulopathy. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18:1094-1099."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.14858",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "11",
"unstructured": "11. Asakura H, Ogawa H. Potential of heparin and nafamostat combination therapy for COVID-19. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18:1521-1522."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11239-020-02134-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "12",
"unstructured": "12. Becker RC. COVID-19 update: Covid-19-associated coagulopathy. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2020;50:54-67."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.01043-16",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "13",
"unstructured": "13. Yamamoto M, Matsuyama S, Li X, et al. Identification of nafamostat as a potent inhibitor of middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus S protein-mediated membrane fusion using the split-protein-based cell-cell fusion assay. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016;60:6532-6539."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "14",
"unstructured": "14. Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S, et al. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell. 2020;181:271-280."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.00754-20",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "15",
"unstructured": "15. Hoffmann M, Schroeder S, Kleine-Weber H, et al. Nafamostat mesylate blocks activation of SARS-CoV-2: new treatment option for COVID-19. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020;64:e00754-20."
},
{
"DOI": "10.12998/wjcc.v8.i21.5320",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "16",
"unstructured": "16. Okajima M, Takahashi Y, Kaji T, et al. Nafamostat mesylate-induced hyperkalemia in critically ill patients with COVID-19: four case reports. World J Clin Cases. 2020;8:5320-5325."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0306-3623(95)00072-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "17",
"unstructured": "17. Muto S, Imai M, Asano Y. Mechanisms of hyperkalemia caused by nafamostat mesilate. Gen Pharmacol. 1995;26:1627-1632."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amsu.2021.102560",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "18",
"unstructured": "18. Abdulgabbar MH. Clinical efficacy of nafamostat mesylate in combination with favipiravir for COVID-19 pneumonia treatment review article. Ann Med Surg. 2021;68:102560."
}
],
"reference-count": 18,
"references-count": 18,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/yoken/75/5/75_JJID.2021.699/_article"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Nafamostat Mesylate Monotherapy in Patients with Moderate COVID-19: a Single-Center, Retrospective Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "75"
}
soma