Quercetin effectiveness in patients with COVID-19 associated pneumonia
et al., Zaporozhye Med. J., doi:10.14739/2310-1210.2021.5.231714, Sep 2021
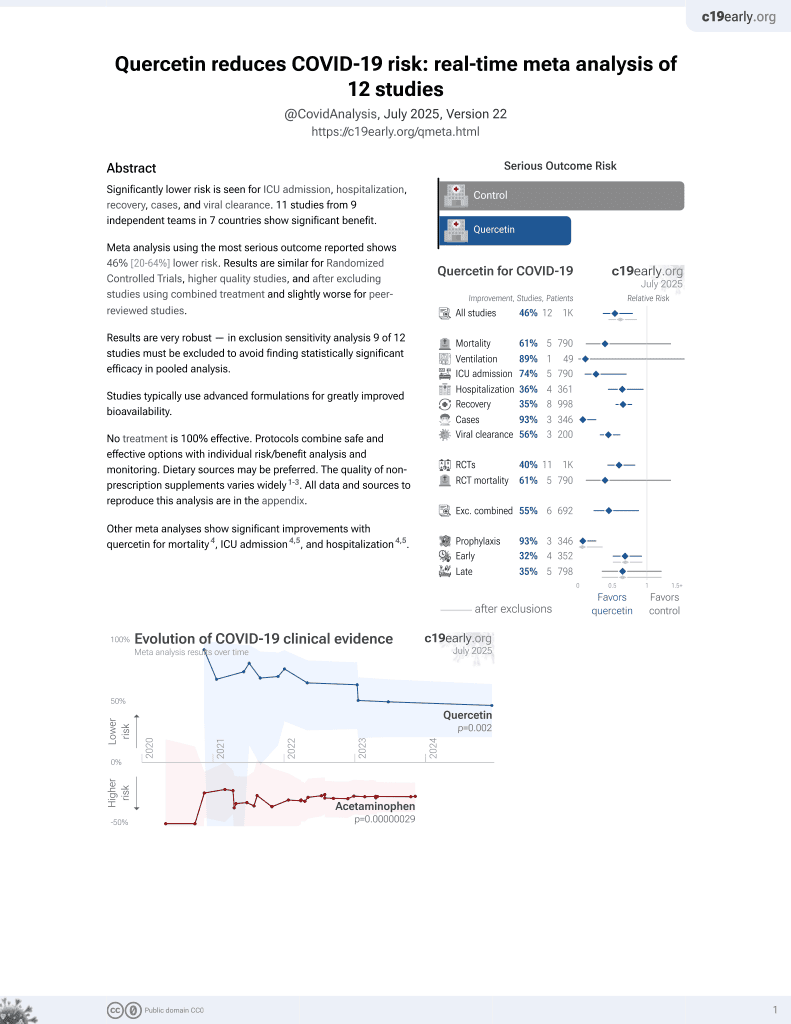
Quercetin for COVID-19
36th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2022, now with p = 0.0018 from 9 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
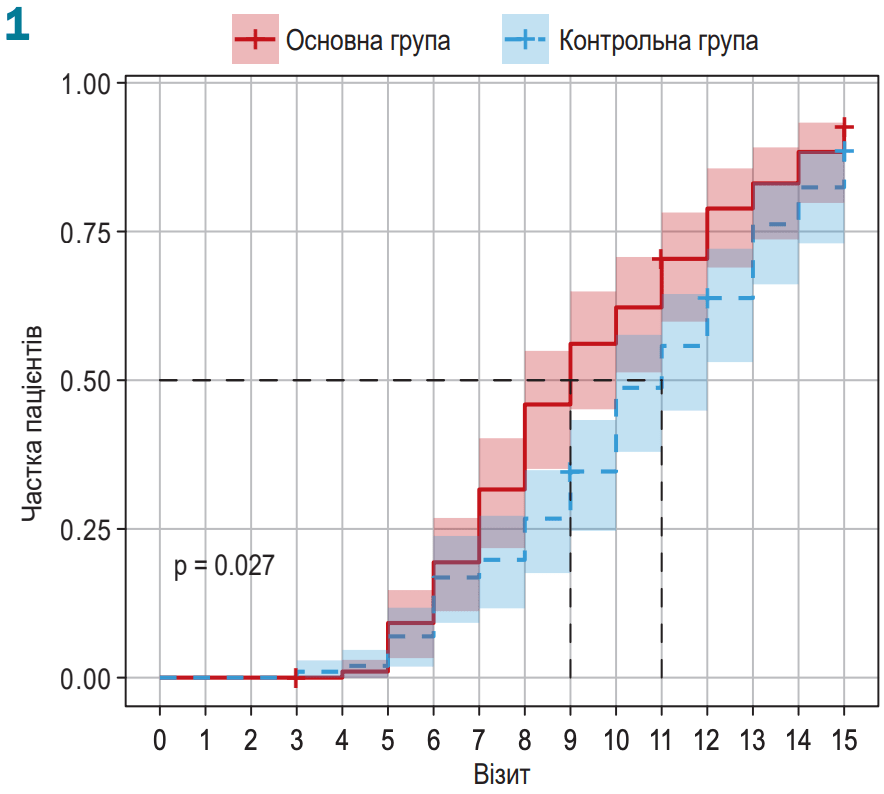
RCT 200 patients in Ukraine, 99 treated with IV quercetin/polyvinylirolidone followed by oral quercetin/pectin, showing improved recovery with treatment.
The paper states 'authors have no conflict of interest to declare.' However, author M. F. Pasichnyk is listed in the affiliations block as the 'General Director of PJSC SIC Borshchahivskiy CPP'. This entity is the Ukrainian pharmaceutical company that manufactures and holds the patents/trademarks for the proprietary intravenous and oral quercetin formulations (Corvitin/Quertin) evaluated in this study.
The study was unblinded (open-label). The treatment group received daily intravenous infusions for 10 days, while the control group only received 'basic therapy' without a placebo IV. Because primary measures of efficacy included subjective symptoms like 'general weakness evaluated by VAS' and 'cough,' the lack of blinding and uneven care administration introduces potential bias.
The study lacks a CONSORT flow diagram.
Mathematical discrepancies in text versus table data.: The text states that in the main group, the average increase in D-dimer at visit 16 was 149.6 ng/ml, but calculating the difference from Table 3 means (1147.0 at visit 16 minus 1004.2 at baseline) yields 142.8 ng/ml. Similar small discrepancies exist for the other visit calculations, suggesting a potential mix-up between 'mean of differences' and 'difference of means' or improper handling of missing data points.
Bioavailability. Quercetin has low bioavailability and studies typically use advanced formulations to improve bioavailability which may be required to reach therapeutic concentrations.
This is the 2nd of 9 COVID-19 RCTs for quercetin, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0018.
|
risk of no recovery, 29.4% lower, RR 0.71, p = 0.50, treatment 9 of 99 (9.1%), control 13 of 101 (12.9%), NNT 26.
|
|
recovery time, 18.2% lower, relative time 0.82, p = 0.03, treatment 99, control 101.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Zupanets et al., 1 Sep 2021, Randomized Controlled Trial, Ukraine, peer-reviewed, 14 authors.
Quercetin effectiveness in patients with COVID-19 associated pneumonia
Zaporozhye Medical Journal, doi:10.14739/2310-1210.2021.5.231714
The aim of this work was to evaluate the effectiveness of quercetin addition to the treatment regimen for patients with COVID-19 associated pneumonia.
Materials and methods. The effectiveness of two dosage forms of quercetin was studied in 200 patients, who were divided equally into the main and control groups. The main group patients received quercetin in addition to the basic therapy: intravenous drip of Quercetin/Polyvinylirolidone during the first 10 days followed by oral administration of Quercetin/Pectin over the next 10 days. Patients from the control group received only the basic therapy drugs. The study evaluated the dynamics of the disease symptoms (saturation level, respiratory rate, body temperature, cough, general weakness), as well as laboratory markers (C-reactive protein (CRP), ferritin, D-dimer). Results. Two dosage forms of quercetin consistently used in addition to the basic therapy improve pulmonary gas exchange and accelerate the lung function recovery. This is evidenced by a statistically significant majority of patients with positive dynamics in the symptoms of "Saturation level" and "Cough" as well as the meeting a complex indicator of the therapy effectiveness 2 days earlier than in the control group. The treatment regimen applied also helps to stabilize the level of D-dimer in the blood of the main group patients. Conclusions. The use of two dosage forms of quercetin in addition to the basic therapy accelerates the recovery of patients with coronavirus disease associated pneumonia and can help to prevent the progression of COVID-19 associated coagulopathy.
References
Ascierto, Fu, Wei, IL-6 modulation for COVID-19: the right patients at the right time?, Journal for Immuno-Therapy of Cancer, doi:10.1136/jitc-2020-002285
Ascierto, Fu, Wei, IL-6 modulation for COVID-19: the right patients at the right time?, Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer, doi:10.1136/jitc-2020-002285
Chornomydz, Kliniko-patohenetychne obgruntuvannia zastosuvannia kvertsytynu u kompleksnomu likuvanni ditei iz hostroiu pozalikarnianoiu pnevmoniieiu [Clinical and nosotropic ground of application of quercetin in complex treatment of children with acute extrahospital pneumonia
Fda, FDA Approves First Treatment for COVID-19
Fedortsiv, Ye, Chornomydz, Behosh, Klinichna efektyvnist vykorystannia kvertsetynu u kompleksnomu likuvanni ditei, khvorykh na pozalikarnianu pnevmoniiu [Clinical efficiency quercetin in complex treatment of children with community-acquired pneumonia
Griffiths, Guidelines on the management of acute respiratory distress syndrome / M, BMJ Open Respiratory Research, doi:10.1136/bmjresp-2019-000420
Griffiths, Mcauley, Perkins, Barrett, Blackwood et al., Guidelines on the management of acute respiratory distress syndrome, BMJ Open Respiratory Research, doi:10.1136/bmjresp-2019-000420
Marik, EVMS critical care COVID-19 management protocol
Marik, EVMS critical care COVID-19 management protocol
Metlay, Waterer, Treatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia During the Coronavirus Disease
Metlay, Waterer, Treatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pan, Annals of Internal Medicine, doi:10.7326/M20-2189
Ozgen, Kilinc, Selamoğlu, Antioxidant Activity of Quercetin: A Mechanistic Review, Turkish Journal of Agriculture -Food Science and Technology, doi:10.24925/turjaf.v4i12.1134-1138.1069
Ozgen, Kilinc, Selamoğlu, Antioxidant Activity of Quercetin: A Mechanistic Review, Turkish Journal of Agriculture -Food Science and Technology, doi:10.24925/turjaf.v4i12.1134-1138.1069
Parkhomenko, Kozhukhov, investigate the tolerability and efficacy of Corvitin® in patients with congestive heart failure and left ventricular systolic dysfunction
Shebeko, Chapter 27 -Effects of Quercetin and Its Combinations on Health, doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-813006-3.00027-1
Shebeko, Zupanets, Popov, Tarasenko, Shalamay, Chapter 27 -Effects of Quercetin and Its Combinations on Health, doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-813006-3.00027-1
Singh, Chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine for prevention and treatment of COVID-19, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013587.pub2
Singh, Ryan, Kredo, Chaplin, Fletcher, Chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine for prevention and treatment of COVID-19, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013587.pub2
Usenko, Zupanets, Tarasenko, Shebeko, Eksperymentalne doslidzhennia farmakokinetychnykh vlastyvostei kvertsetynu pry peroralnomu zastosuvanni z modyfikatoramy rozchynnosti [Experimental study of pharmacokinetic properties of quercetin at oral apрlication with modifiers of solubility, Medychna i klinichna khimiia
Varga, Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in COVID-19, The Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30937-5
Varga, Flammer, Steiger, Haberecker, Andermatt et al., Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in COVID-19, The Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30937-5
Xiao, Shi, Liu, Wang, Xie et al., Quercetin Suppresses Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression and Angiogenesis through Inactivation of P300 Signaling, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0022934
Zhang, Antioxidant Properties of Quercetin, doi:10.1007/978-1-4419-7756-4_38
Zhang, Swarts, Yin, Liu, Tian et al., Antioxidant Properties of Quercetin, doi:10.1007/978-1-4419-7756-4_38
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, The Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3
Zhoui, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, The Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3
Безугла, доцент каф. клінічної фармакології та клінічної фармації, Національний фармацевтичний університет, м. Харків, Україна
Відомості, Зупанець, р мед. наук, професор каф. клінічної фармакології та клінічної фармації, Національний фармацевтичний університет, м
Голубовська, Д-Р Мед. Наук, професор, зав. каф. інфекційних хвороб, Національний медичний університет імені
Максимчук, Рівне, MD, Infectious Disease Physician of the Department for Adults, Municipal Non-Commercial Enterprise
Мороз, Д-Р, мед. наук, професор каф. інфекційних хвороб з курсом епідеміології, Вінницький національний медичний університет імені М
Морочковский, врач-инфекционист инфекционного отделения, КНП «Ирпенская центральная городская больница» Ирпенского городского совета Киевской области, Украина. Список літератури
Пархоменко, Кожухов, Результаты открытого рандомизированного исследования по изучению переносимости и эффективности препарата Корвитин® у пациентов с застойной сердечной недостаточностью и систолической дисфункцией левого желудочка, Український медичний часопис
Пасічник, Наук, генеральний директор ПАТ НВЦ «Борщагівський ХФЗ
Тарасенко, доцент каф. клінічної фармакології та клінічної фармації, Національний фармацевтичний університет, м. Харків, Україна
Федорців, Чорномидз, Бегош, Клінічна ефективність використання кверцетину у комплексному лікуванні дітей, хворих на позалікарняну пневмонію. Актуальні питання педіатрії, акушерства та гінекології
Чорномидз, Клініко-патогенетичне обґрунтування застосування кверцитину у комплексному лікуванні дітей із гострою позалікарняною пневмонією, Вісник наукових досліджень
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.14739/2310-1210.2021.5.231714",
"ISSN": [
"2310-1210",
"2306-4145"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.14739/2310-1210.2021.5.231714",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The aim of this work was to evaluate the effectiveness of quercetin addition to the treatment regimen for patients with COVID-19 associated pneumonia.\nMaterials and methods. The effectiveness of two dosage forms of quercetin was studied in 200 patients, who were divided equally into the main and control groups. The main group patients received quercetin in addition to the basic therapy: intravenous drip of Quercetin/Polyvinylirolidone during the first 10 days followed by oral administration of Quercetin/Pectin over the next 10 days. Patients from the control group received only the basic therapy drugs. \nThe study evaluated the dynamics of the disease symptoms (saturation level, respiratory rate, body temperature, cough, general weakness), as well as laboratory markers (C-reactive protein (CRP), ferritin, D-dimer).\nResults. Two dosage forms of quercetin consistently used in addition to the basic therapy improve pulmonary gas exchange and accelerate the lung function recovery. This is evidenced by a statistically significant majority of patients with positive dynamics in the symptoms of “Saturation level” and “Cough” as well as the meeting a complex indicator of the therapy effectiveness 2 days earlier than in the control group. The treatment regimen applied also helps to stabilize the level of D-dimer in the blood of the main group patients.\nConclusions. The use of two dosage forms of quercetin in addition to the basic therapy accelerates the recovery of patients with coronavirus disease associated pneumonia and can help to prevent the progression of COVID-19 associated coagulopathy.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1253-9217",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zupanets",
"given": "I. A.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3455-8718",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Holubovska",
"given": "О. А.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8454-1829",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tarasenko",
"given": "O. O.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6420-2547",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bezuhla",
"given": "N. P.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pasichnyk",
"given": "M. F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karabynosh",
"given": "S. O.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9499-3733",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kopcha",
"given": "V. S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7111-3155",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Moroz",
"given": "L. V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maksymchuk",
"given": "H. V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kobrynska",
"given": "O. Ya.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fishchuk",
"given": "R. M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schulha",
"given": "D. I.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morochkovskyj",
"given": "R. S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zoshchak",
"given": "M. S.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Zaporozhye Medical Journal",
"container-title-short": "ZMJ",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-10T15:40:29Z",
"timestamp": 1641829229000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-10T15:41:33Z",
"timestamp": 1641829293000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-17T00:39:50Z",
"timestamp": 1700181590087
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 3,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
]
}
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://zmj.zsmu.edu.ua/article/download/231714/239305",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://zmj.zsmu.edu.ua/article/download/231714/239305",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "7452",
"original-title": [],
"page": "636-643",
"prefix": "10.14739",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
1
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Zaporozhye State Medical University",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://zmj.zsmu.edu.ua/article/view/231714"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Quercetin effectiveness in patients with COVID-19 associated pneumonia",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "23"
}