Effectiveness of the quercetin use in patients with COVID-19 with concomitant type 2 diabetes mellitus
et al., Wiadomości Lekarskie, doi:10.36740/WLek/191875, Dec 2024
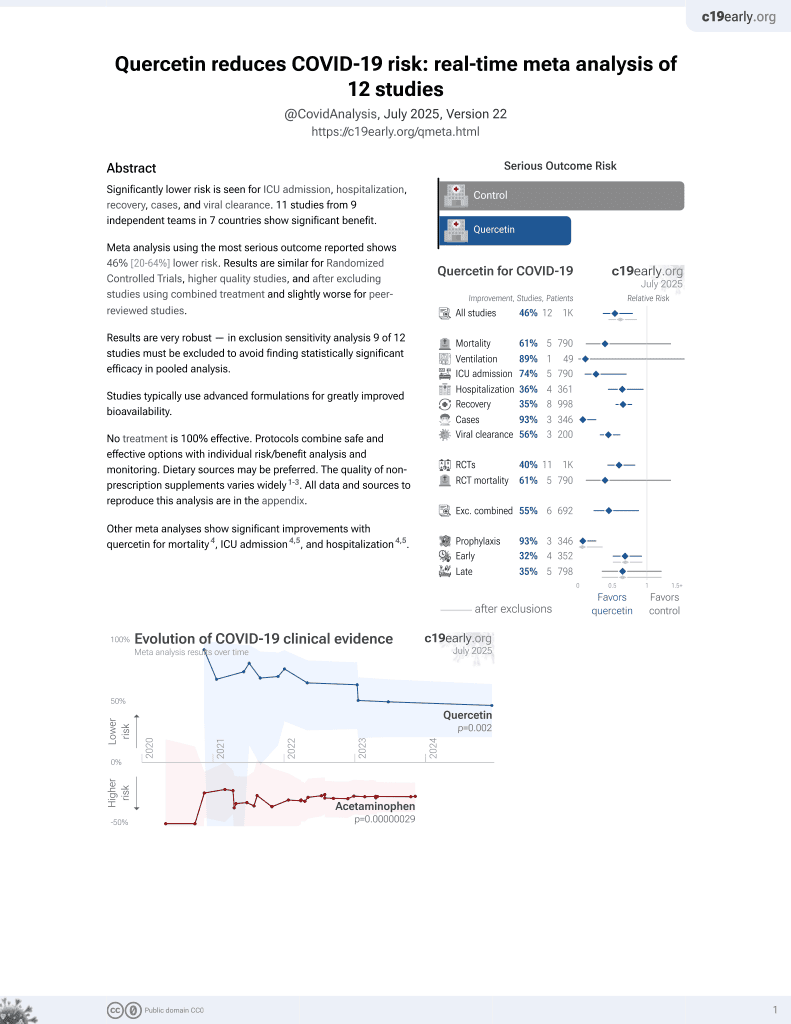
Quercetin for COVID-19
36th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2022, now with p = 0.0018 from 9 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 60 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes showing quercetin treatment decreased levels of inflammatory markers (interleukin-6, CRP, ferritin), reduced length of hospital stay, and improved capillaroscopy measures compared to standard care. Quercetin was administered at 0.5g intravenously once daily for 10 days. The authors hypothesize the benefits may be due to the anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and endothelium-protective effects of quercetin,
Authors explicitly used independent groups Chi-square (Pearson's) and independent groups Student's t-tests to evaluate paired before-and-after data within the exact same groups (e.g., saturation before vs after, χ² for edema before vs after).
Table 3 reports values as M±m. The reported t-test values in the text indicate 'm' was treated as the Standard Error of the Mean (SEM). However, the SEM values for the Main Group baseline parameters are very large (e.g., arterial capillary diameter 8.31 ± 1.93). For a sample size of 30, an SEM of 1.93 translates to a Standard Deviation of roughly 10.5. This suggests potential incorrect labeling or other error.
The paper provides an overall age and gender breakdown but fails to report baseline demographics per group.
Bioavailability. Quercetin has low bioavailability and studies typically use advanced formulations to improve bioavailability which may be required to reach therapeutic concentrations.
This is the 9th COVID-19 RCT for quercetin, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0018.
|
risk of no recovery, 40.0% lower, RR 0.60, p = 0.71, treatment 3 of 30 (10.0%), control 5 of 30 (16.7%), NNT 15, SpO2<90.
|
|
hospitalization time, 14.6% lower, relative time 0.85, p < 0.001, treatment mean 13.77 (±0.75) n=30, control mean 16.13 (±0.79) n=30.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Tylishchak et al., 6 Dec 2024, Randomized Controlled Trial, Ukraine, peer-reviewed, 7 authors.
Effectiveness of the quercetin use in patients with COVID-19 with concomitant type 2 diabetes mellitus
Wiadomości Lekarskie, doi:10.36740/wlek/191875
Aim: To conduct a comparative analysis of the effectiveness of basic therapy and basic therapy with the inclusion of quercetin in patients with COVID-19 with concomitant type 2 diabetes. Materials and Methods: There were examined 60 patients with COVID-19 with concomitant T2DM. Upon admission into the hospital and again after 10 days, serum levels of interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, ferritin, endothelin-1 were determined, and capillaroscopy of the nail plate was performed. Patients of the group I (30) against the background of protocol therapy received 0.5 g of quercetin intravenously once a day for 10 days. Patients of the group II (30) received to basic therapy. Results: After the treatment in patients of the group I general weakness decreased, body temperature normalized, improved saturation indicators, the level of acute-phase parameters (interleukin-6, CRP and ferritin) significantly decreased, a positive effect of quercetin on the level of D-dimer in blood serum was noted, indices of pericapillary edema and hemosiderin deposition significantly decreased, indices diameter of the arterial part of the capillary and capillary network density significantly increased. Conclusions: The use of quercetin against the background of basic therapy in patients with COVID-19 and concomitant T2DM reliably reduces the level of acute-phase indices, has an important clinical significance for reducing endothelial dysfunction and for preventing thrombotic complications.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST The Authors declare no conflict of interest
CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Oleksandr Boichuk Ivano-Frankivsk National Medical University 2 Halytska st, 76018 Ivano-Frankivsk, Ukraine e-mail: opboy@ukr.net ORCID AND CONTRIBUTIONSHIP Zoriana Tylishchak: 0000-0002-7891-2849 Oleksandra Pryshliak: 0000-0002-3256-5108 Oleksandr Boichuk: 0000-0003-0646-6533 Sergiy Fedorov: 0000-0002-2202-4279 Andrii Protsyk: 0000-0003-2041-5337 Taras Kobryn: 0000-0003-4381-6045 Ruslan Miziuk: 0000-0002-7829-9044
References
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7
Gómez-Pastora, Weigand, Kim, Hyperferritinemia in critically ill COVID-19 patients -Is ferritin the product of inflammation or a pathogenic mediator?, Clin Chim Acta, doi:10.1016/j.cca.2020.06.033
Hayden, Endothelial activation and dysfunction in metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes and coronavirus disease 2019, J Int Med Res, doi:10.1177/0300060520939746
Hryzhak, Pryshliak, Kobryn, Clinical and echocardiographic findings in patients with COVID-19 across different severity levels, JOURNAL of MEDICINE and LIFE, doi:10.25122/jml-2023-0206
Hua, Yang, Zou, COVID-19 and metabolic comorbidities: An update on emerging evidences for optimal therapies, Biomed Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111685
Kolotylo, Moskaliuk, Syrota, Evaluation of D-dimer level as a biomarker of disease severity and mortality in patients with COVID-19, Wiad Lek, doi:10.36740/WLek202307118
Lim, Bae, Kwon, COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: from pathophysiology to clinical management, Nat Rev Endocrinol, doi:10.1038/s41574-020-00435-4
Mahroum, Alghory, Kiyak, Ferritin -from iron, through inflammation and autoimmunity, to COVID-19, J Autoimmun, doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2021.102778
Natalello, Luca, Gigante, Nailfold capillaroscopy findings in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: Broadening the spectrum of COVID-19 microvascular involvement, Microvasc Res, doi:10.1016/j.mvr.2020.104071
Nykonenko, Podluzhniy, Koliada, Thrombotic conditions in patients with COVID-19: Dynamics of D-dimer and tactics of anticoagulant therapy, Ukrainskyi Zhurnal Sertsevo-Sudynnoi Khirurhii, doi:10.30702/ujcvs/22.30(01)/NP010-6470
Pryshliak, Marynchak, Kondryn, Clinical and laboratory characteristics of COVID-19 in pregnant women, JOURNAL of MEDICINE and LIFE, doi:10.25122/jml-2023-0044
Smith, Herrick, Ingegnoli, Standardisation of nailfold capillaroscopy for the assessment of patients with Raynaud' s phenomenon and systemic sclerosis, Autoimmun Rev, doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102458
Tylishchak, Peculiarities of endothelial dysfunction and capillary blood flow in patients with coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and accompanying type 2 diabetes mellitus, Bukovinian Medical Herald, doi:10.24061/2413-0737.27.1.105.2023.7
Tylishchak, Pryshliak, Skrypnyk, Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: clinical and laboratory peculiarities, Rom J Diabetes Nutr Metab Dis, doi:10.46389/rjd-2023-1224
Varga, Flammer, Steiger, Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in COVID-19, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30937-5
Wang, Hou, Luo, The laboratory tests and host immunity of COVID-19 patients with different severity of illness, JCI Insight, doi:10.1172/jci.insight-137799
Zhong, Wang, Zhang, Efficacy and safety of current therapeutic options for COVID-19 -lessons to be learnt from SARS and MERS epidemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Pharmacol Res, doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104872
Zupanets, Golubovska, Tarasenko, Effectiveness of quercetin in patients with pneumonia associated with coronavirus disease (COVID-19), Zaporozhye medical journal, doi:10.14739/2310-1210.2021.5.231714
Zupanets, Shebeko, Bezugla, Pathophysiological substantiation of the effectiveness of quercetine use in coronavirus disease (COVID-19) therapy, Pathologia, doi:10.14739/2310-1237.2020.1.203844
Çakmak, Demirbuga, Demirkol, Nailfold capillaroscopy: A sensitive method for evaluating microvascular involvement in children with SARS-CoV-2 infection, Microvasc Res, doi:10.1016/j.mvr.2021.104196
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.36740/wlek/191875",
"ISSN": [
"0043-5147",
"2719-342X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.36740/WLek/191875",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Aim</jats:title><jats:p>To conduct a comparative analysis of the effectiveness of basic therapy and basic therapy with the inclusion of quercetin in patients with COVID-19 with concomitant type 2 diabetes.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Material and methods</jats:title><jats:p>There were examined 60 patients with COVID-19 with concomitant T2DM. Upon admission into the hospital and again after 10 days, serum levels of interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, ferritin, endothelin-1 were determined, and capillaroscopy of the nail plate was performed. Patients of the group I (30) against the background of protocol therapy received 0.5 g of quercetin intravenously once a day for 10 days. Patients of the group II (30) received to basic therapy.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>After the treatment in patients of the group I general weakness decreased, body temperature normalized, improved saturation indicators, the level of acute-phase parameters (interleukin-6, CRP and ferritin) significantly decreased, a positive effect of quercetin on the level of D-dimer in blood serum was noted, indices of pericapillary edema and hemosiderin deposition significantly decreased, indices diameter of the arterial part of the capillary and capillary network density significantly increased.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>The use of quercetin against the background of basic therapy in patients with COVID-19 and concomitant T2DM reliably reduces the level of acute-phase indices, has an important clinical significance for reducing endothelial dysfunction and for preventing thrombotic complications.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"191875"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7891-2849",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tylishchak",
"given": "Zoriana",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3256-5108",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Pryshliak",
"given": "Oleksandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0646-6533",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Boichuk",
"given": "Oleksandr",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2202-4279",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Fedorov",
"given": "Sergiy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2041-5337",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Protsyk",
"given": "Andrii",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4381-6045",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kobryn",
"given": "Taras",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7829-9044",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Miziuk",
"given": "Ruslan",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Wiadomości Lekarskie",
"container-title-short": "Wiadomości Lekarskie",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-09T09:56:57Z",
"timestamp": 1733738217000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-09T09:57:10Z",
"timestamp": 1733738230000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-10T05:10:11Z",
"timestamp": 1733807411483,
"version": "3.30.1"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "10",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
6
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "10",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024
]
]
}
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.wiadomoscilekarskie.pl/pdf-191875-117367",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.wiadomoscilekarskie.pl/pdf-191875-117367",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "22436",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1962-1968",
"prefix": "10.36740",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
6
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "ALUNA",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.wiadomoscilekarskie.pl/Effectiveness-of-the-quercetin-use-in-patients-with-COVID-19-with-concomitant-type,191875,0,2.html"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effectiveness of the quercetin use in patients with COVID-19 with concomitant type 2 diabetes mellitus",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "77"
}