Treatment of COVID-19 patients with quercetin: a prospective, single center, randomized, controlled trial
et al., Turk. J. Biol., 45:518-529, Jan 2021 (preprint)
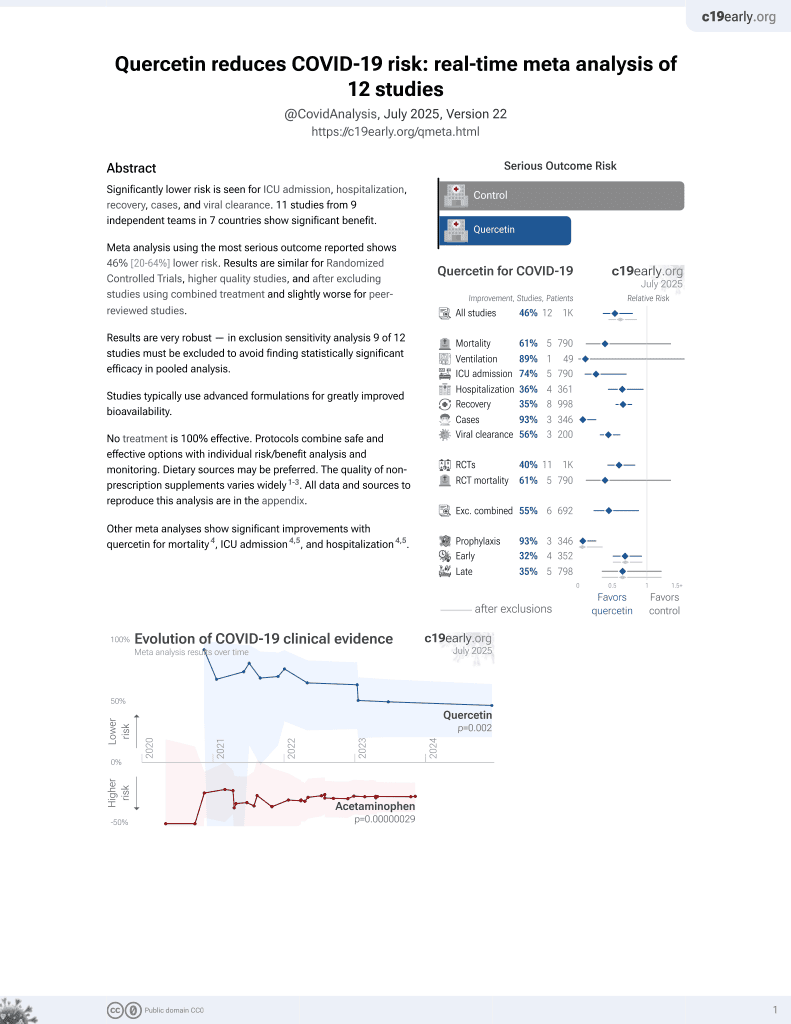
Quercetin for COVID-19
27th treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2021, now with p = 0.002 from 12 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 447 moderate-to-severe hospitalized patients in Turkey, 52 treated with quercetin, bromelain, and vitamin C, showing no statistically significant difference in clinical outcomes.
Bioavailability. Quercetin has low bioavailability and studies typically use advanced formulations to improve bioavailability which may be required to reach therapeutic concentrations.
This is the 2nd of 11 COVID-19 RCTs for quercetin, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0023.
This is the 2nd of 12 COVID-19 controlled studies for quercetin, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.002.
|
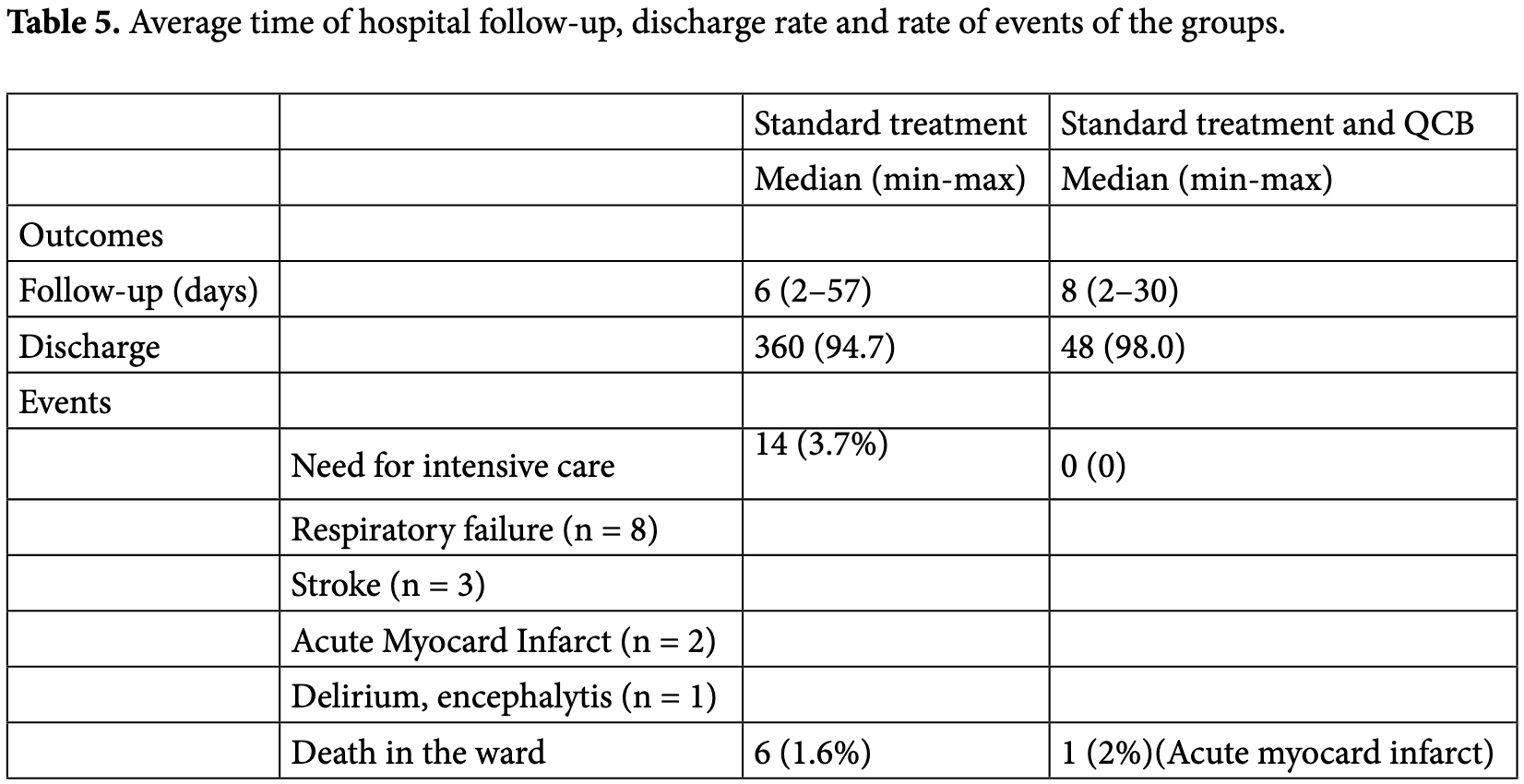
risk of death, 29.3% higher, RR 1.29, p = 0.57, treatment 1 of 49 (2.0%), control 6 of 380 (1.6%).
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 94.0% lower, RR 0.06, p = 0.39, treatment 0 of 49 (0.0%), control 14 of 380 (3.7%), NNT 27, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 77.8% lower, RR 0.22, p = 0.10, treatment 1 of 49 (2.0%), control 35 of 380 (9.2%), NNT 14.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Onal et al., 19 Jan 2021, Randomized Controlled Trial, Turkey, peer-reviewed, 10 authors, study period 7 May, 2020 - 8 July, 2020, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with bromelain and vitamin C) - results of individual treatments may vary.
Treatment of COVID-19 patients with quercetin: a prospective, single center, randomized, controlled trial
TURKISH JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY, doi:10.3906/biy-2104-16
Introduction Scientific research continues on new preventive and therapeutic strategies against severe acute respiratory syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). So far, there is no proven curative treatment for the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), and while vaccination is continuing worldwide, "wild" protocols based on "ancient" anti-inflammatory and anti-viral drugs are being offered. A valid and alternative therapeutic approach needs to be developed. Affecting the nasopharyngeal cells first, SARS-CoV-2 can target different tissues such as lung, vascular endothelium, kidney and nervous system at various degrees, and it can cause severe illness and death (Russo et al., 2017; Spagnuolo et al., 2018) . With the advantage of the lack of systemic toxicity, flavonoids, including quercetin are proven to potentialize the effects of routine drugs against coronavirus (Ferrer et al., 2008) . Flavonoids owe their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-viral properties against a wide range of DNA and RNA viruses, to their pleiotropic molecular structure that acts by targeting variable cells on multiple pathways
References
Ackermann, Verleden, Kuehnel, Haverich, Welte, Pulmonary vascular endothelialitis, thrombosis, and angiogenesis in Covid-19, New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2015432
Askari, Ghiasvand, Feizi, Ghanadian, Karimian, The effect of quercetin supplementation on selected markers of inflammation and oxidative stress, Journal of Research in Medical Sciences
Bindoli, Valente, Cavallini, Inhibitory action of quercetin on xanthine oxidase and xanthine dehydrogenase activity, Pharmacological Research Communications, doi:10.1016/0031-6989(85)90041-4
Boots, Haenen, Bast, Health effects of quercetin: from antioxidant to nutraceutical, European Journal of Pharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.03.008
Boots, Li, Schins, Duffin, Heemskerk, The quercetin paradox, Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.taap.2007.04.004
Bowles, Platton, Yartey, Lee, Lupus anticoagulant and abnormal coagulation tests in patients with Covid-19, New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2013656
Bösmüller, Traxler, Bitzer, Häberle, Raiser, The evolution of pulmonary pathology in fatal COVID-19 disease: an autopsy study with clinical correlation, Virchows Archiv, doi:10.1007/s00428-020-02881-x
Chen, Li, Luo, Liu, Xu, Binding interaction of quercetin-3-beta-galactoside and its synthetic derivatives with SARS-CoV 3CL(pro): structure-activity relationship studies reveal salient pharmacophore features, Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2006.09.014
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Qu, Gong, Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7
Conti, Ronconi, Caraffa, Gallenga, Ross, Induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1 and IL-6) and lung inflammation by Coronavirus-19 (COVI-19 or SARS-CoV-2): anti-inflammatory strategies, Journal of Biological Regulators and Homeostatic Agents, doi:10.23812/CONTI-E
Davis, Murphy, Carmichael, Effects of the dietary flavonoid quercetin upon performance and health, Current Sports Medicine Reports, doi:10.1249/JSR.0b013e3181ae8959
Evers, Chao, Wang, Zhang, Huong, Human cytomegalovirus-inhibitory flavonoids: studies on antiviral activity and mechanism of action, Antiviral Research, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2005.08.002
Fauvel, Weizman, Trimaille, Mika, Pommier, Pulmonary embolism in COVID-19 patients: a French multicentre cohort study, European Heart Journal, doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa500
Ferrer, Austin, Stewart, Noel, Structure and function of enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of phenylpropanoids, Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2007.12.009
Gormaz, Quintremil, Cardiovascular Disease: A Target for the Pharmacological Effects of Quercetin, Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, doi:10.2174/1568026615666150427124357
Graefe, Derendorf, Veit, Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of the flavonol quercetin in humans, Int Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
Hanley, Lucas, Youd, Swift, Osborn, Autopsy in suspected COVID-19 cases, Journal of Clinical Pathology, doi:10.1136/jclinpath-2020-206522
Harwood, Danielewska-Nikiel, Borzelleca, Flamm, Williams, A critical review of the data related to the safety of quercetin and lack of evidence of in vivo toxicity, including lack of genotoxic/carcinogenic properties, Food and Chemical Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.fct.2007.05.015
Hottz, Azevedo-Quintanilha, Palhinha, Teixeira, Barreto, Platelet activation and platelet-monocyte aggregate formation trigger tissue factor expression in patients with severe COVID-19, Blood, doi:10.1182/blood.2020007252
Hubbard, Stevens, Cicmil, Sage, Jordan, Quercetin inhibits collagen-stimulated platelet activation through inhibition of multiple components of the glycoprotein VI signaling pathway, Journal of Thrombosis Haemostasis, doi:10.1046/j.1538-7836.2003.00212.x
Ishitsuka, Ohsawa, Ohiwa, Umeda, Suhara, Antipicornavirus flavone Ro 09-0179, Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy Journal, doi:10.1128/AAC.22.4.611
Junior, Miggiolaro, Nagashima, De Paula, Baena, Mast Cells in Alveolar Septa of COVID-19 Patients: A Pathogenic Pathway That May Link Interstitial Edema to Immunothrombosis, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.574862
Karhausen, Choi, Maddipati, Mathew, Ma, Platelets trigger perivascular mast cell degranulation to cause inflammatory responses and tissue injury, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.aay6314
Kaul, Middleton, Ogra, Antiviral effect of flavonoids on human viruses, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.1890150110
Kim, Kim, Bae, Choi, Lim, Vitamin C Is an Essential Factor on the Anti-viral Immune Responses through the Production of Interferon-α/β at the Initial Stage of Influenza A Virus (H3N2) Infection, Immune Network, doi:10.4110/in.2013.13.2.70
Kumazawa, Kawaguchi, Takimoto, Immunomodulating effects of flavonoids on acute and chronic inflammatory responses caused by tumor necrosis factor alpha, Current Pharmaceutical Design, doi:10.2174/138161206778743565
Kuznetsova, Prange, Glass, De Winther, Transcriptional and epigenetic regulation of macrophages in atherosclerosis, Nature Reviews Cardiology, doi:10.1038/s41569-019-0265-3
Lei, Jiang, Su, Chen, Chen, Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients undergoing surgeries during the incubation period of COVID-19 infection, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100331
Li, Maeda, Beck, Vitamin C deficiency increases the lung pathology of influenza virus-infected gulo-/-mice, Journal of Nutrition, doi:10.1093/jn/136.10.2611
Loke, Proudfoot, Mckinley, Needs, Kroon, Quercetin and its in vivo metabolites inhibit neutrophil-mediated low-density lipoprotein oxidation, Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, doi:10.1021/jf8003042
Loke, Proudfoot, Stewart, Mckinley, Needs, Metabolic transformation has a profound effect on anti-inflammatory activity of flavonoids such as quercetin: lack of association between antioxidant and lipoxygenase inhibitory activity, Biochemical Pharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2007.11.002
Manach, Mazur, Scalbert, Polyphenols and prevention of cardiovascular diseases, Current Opinion in Lipidology, doi:10.1097/00041433-200502000-00013
Marchandot, Trimaille, Curtiaud, Matsushita, Jesel, Thromboprophylaxis: balancing evidence and experience during the COVID-19 pandemic, Journal of Thrombosis and Thrombolysis, doi:10.1007/s11239-020-02231-3
Mcfadyen, Stevens, Peter, The Emerging Threat of (Micro)Thrombosis in COVID-19 and Its Therapeutic Implications, Circulation Research, doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317447
Mendes, Gaspar, Conde, Mano, Duarte et al., Flavonoid-mediated immunomodulation of human macrophages involves key metabolites and metabolic pathways, Biopharmaceutics & Drug Disposition, doi:10.1038/s41598-019-51113
Nair, Kandaswami, Mahajan, Chadha, Chawda, The flavonoid, quercetin, differentially regulates Th-1 (IFNgamma) and Th-2 (IL4) cytokine gene expression by normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, doi:10.1016/s0167-4889(02)00328-2
Palma, Vliegen, Clercq, Neyts, Selective inhibitors of picornavirus replication, Medical Research Reviews, doi:10.1002/med.20125
Palmer, Bell, Fox, Brown, Design of second generation phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors, Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, doi:10.2174/156802607779941288
Pavan, Jain, Shraddha, Kumar, Properties and therapeutic application of bromelain: a review, Biotechnology Research International, doi:10.1155/2012/976203
Pearce, Befus, Bienenstock, Mucosal mast cells. III. Effect of quercetin and other flavonoids on antigeninduced histamine secretion from rat intestinal mast cells, Journal of Allergy Clinical Immunology, doi:10.1016/0091-6749(84)90453-6
Pignatelli, Santo, Carnevale, Violi, The polyphenols quercetin and catechin synergize in inhibiting platelet CD40L expression, Thrombosis and Haemostasis, doi:10.1160/TH05-04-0888
Potus, Mai, Lebret, Malenfant, Breton-Gagnon, Novel insights on the pulmonary vascular consequences of COVID-19, American Journal of Physiology Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology, doi:10.1152/ajplung.00195.2020
Puelles, Lütgehetmann, Lindenmeyer, Sperhake, Wong, Multiorgan and Renal Tropism of SARS-CoV-2, New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2011400
Ranucci, Ballotta, Dedda, Bayshnikova, Poli, The procoagulant pattern of patients with COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome, Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, doi:10.1111/jth.14854
Robaszkiewicz, Balcerczyk, Bartosz, Antioxidative and prooxidative effects of quercetin on A549 cells, Cell Biology International, doi:10.1016/j.cellbi.2007.04.009
Romero, Jiménez, Sánchez, López-Sepúlveda, Zarzuelo, Quercetin inhibits vascular superoxide production induced by endothelin-1: Role of NADPH oxidase, uncoupled eNOS and PKC, Atherosclerosis, doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2008.03.007
Ross, Kasum, Dietary flavonoids: bioavailability, metabolic effects, and safety, Annual Review of Nutrition, doi:10.1146/annurev.nutr.22.111401.144957
Rota, Oberste, Monroe, Nix, Campagnoli, Characterization of a novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome, Science, doi:10.1126/science.1085952
Russo, Tedesco, Spagnuolo, Russo, Antioxidant polyphenols in cancer treatment: Friend, foe or foil?, Seminars in Cancer Biology, doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.05.005
Salamanna, Maglio, Landini, Fini, Platelet functions and activities as potential hematologic parameters related to Coronavirus Disease 2019 (Covid-19), Platelets, doi:10.1080/09537104.2020.1762852
Shaik, Castellani, Perrella, Conti, Salini, Role of quercetin (a natural herbal compound) in allergy and inflammation, Journal of Biologic Regulators and Homeostatic Agents
Shukor, Camp, Gonzales, Staljanssens, Struijs, Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory effects by plant phenolic compounds: a study of structure activity relationships, Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, doi:10.1021/jf404641v
Smith, Smith, Repurposing Therapeutics for COVID-19: Supercomputer-Based Docking to the SARS-CoV-2 Viral Spike Protein and Viral Spike Protein-Human ACE2 Interface
Spagnuolo, Moccia, Russo, Anti-inflammatory effects of flavonoids in neurodegenerative disorders, European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.09.001
Uchide, Toyoda, Antioxidant therapy as a potential approach to severe influenza-associated complications, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules16032032
Valero, Mosquera, Alcocer, Bonilla, Salazar, Melatonin, minocycline and ascorbic acid reduce oxidative stress and viral titers and increase survival rate in experimental Venezuelan equine encephalitis, Brain Research, doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2015.06.034
Zandi, Teoh, Sam, Wong, At, Antiviral activity of four types of bioflavonoid against dengue virus type-2, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/1743-422X-8-560
Zhang, Lin, Sun, Curth, Drosten, Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 main protease provides a basis for design of improved α-ketoamide inhibitors, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abb3405
Zhang, Xiao, Zhang, Xia, Cao, Coagulopathy and Antiphospholipid Antibodies in Patients with Covid-19, New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2007575
Zwicker, Schlechter, Stopa, Liebman, Aggarwal, Targeting protein disulfide isomerase with the flavonoid isoquercetin to improve hypercoagulability in advanced cancer, JCI Insight, doi:10.1172/jci.insight.125851