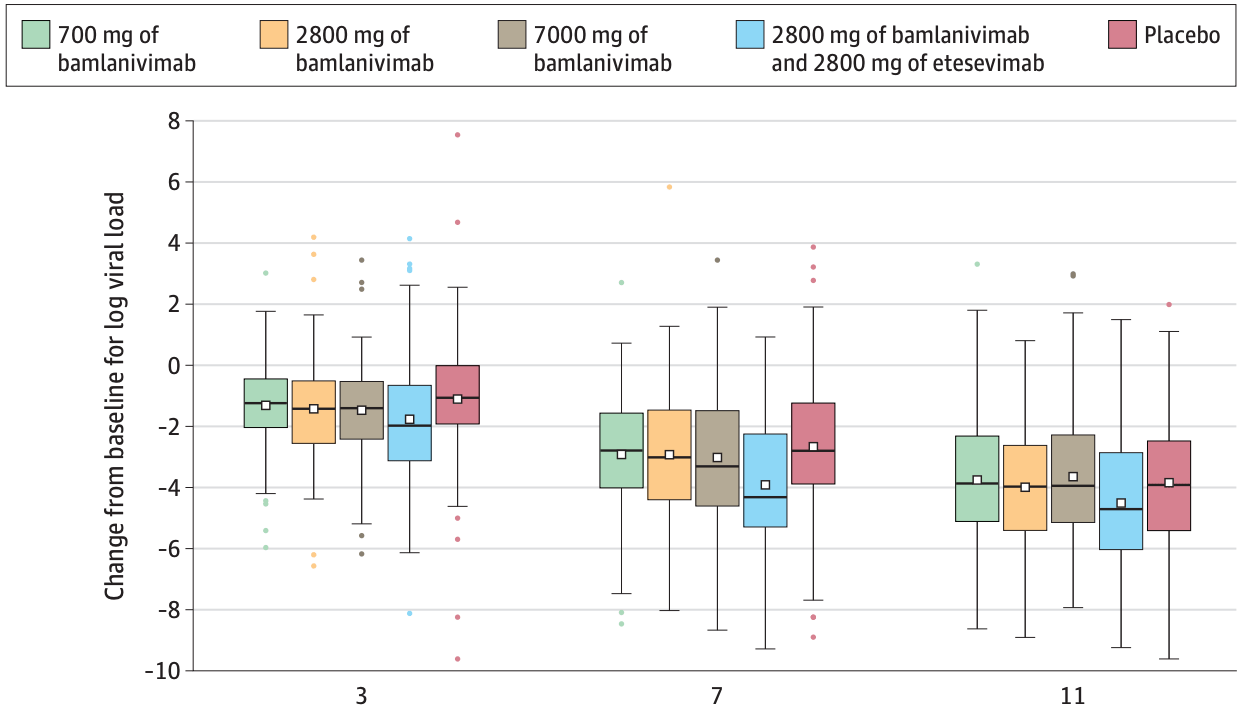
Effect of Bamlanivimab as Monotherapy or in Combination With Etesevimab on Viral Load in Patients With Mild to Moderate COVID-19
et al., JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2021.0202, Jan 2021
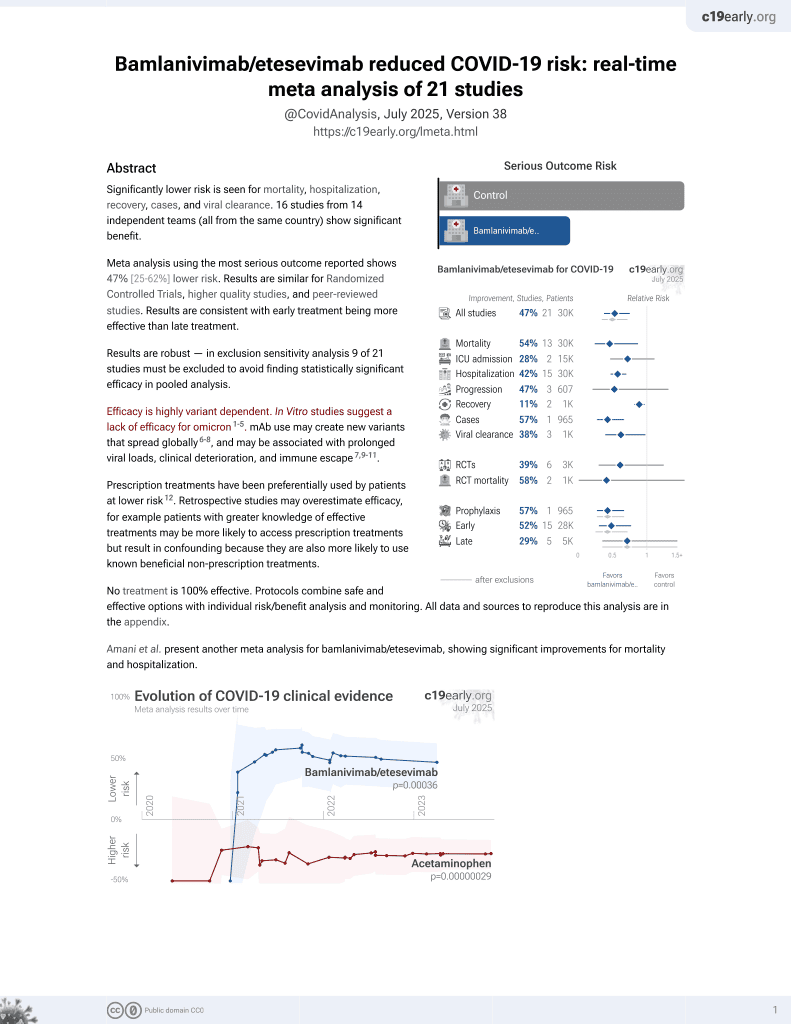
25th treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2021, now with p = 0.00049 from 22 studies, recognized in 11 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT for LY-CoV555 monotherapy and LY-CoV555/LY-CoV016 combination therapy with 592 patients showing lower hospitalization/ER visits with treatment.
For viral load at day 11, a statistically significant reduction was found with combination therapy but not monotherapy.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments6.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of hospitalization/ER, 70.6% lower, RR 0.29, p = 0.046, treatment 4 of 101 (4.0%), control 7 of 52 (13.5%), NNT 11, LY-CoV555 all dosages.
|
|
risk of hospitalization/ER, 79.9% lower, RR 0.20, p = 0.13, treatment 1 of 37 (2.7%), control 7 of 52 (13.5%), NNT 9.3, LY-CoV555 700mg.
|
|
risk of hospitalization/ER, 75.2% lower, RR 0.25, p = 0.25, treatment 1 of 30 (3.3%), control 7 of 52 (13.5%), NNT 9.9, LY-CoV555 2800mg.
|
|
risk of hospitalization/ER, 56.3% lower, RR 0.44, p = 0.31, treatment 2 of 34 (5.9%), control 7 of 52 (13.5%), NNT 13, LY-CoV555 7000mg.
|
|
risk of hospitalization/ER, 91.8% lower, RR 0.08, p = 0.04, treatment 0 of 31 (0.0%), control 7 of 52 (13.5%), NNT 7.4, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), LY-CoV555/LY-CoV016.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Liu et al., Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719.
2.
Sheward et al., Variable loss of antibody potency against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron), bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.19.473354.
3.
VanBlargan et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.472828.
4.
Pochtovyi et al., In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533.
Gottlieb et al., 21 Jan 2021, Randomized Controlled Trial, USA, peer-reviewed, 27 authors, study period 17 June, 2020 - 6 October, 2020, average treatment delay 4.0 days.
Effect of Bamlanivimab as Monotherapy or in Combination With Etesevimab on Viral Load in Patients With Mild to Moderate COVID-19
JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2021.0202
IMPORTANCE Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) continues to spread rapidly worldwide. Neutralizing antibodies are a potential treatment for COVID-19. OBJECTIVE To determine the effect of bamlanivimab monotherapy and combination therapy with bamlanivimab and etesevimab on severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) viral load in mild to moderate COVID-19.
DESIGN, SETTING, AND PARTICIPANTS The BLAZE-1 study is a randomized phase 2/3 trial at 49 US centers including ambulatory patients (N = 613) who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection and had 1 or more mild to moderate symptoms. Patients who received bamlanivimab monotherapy or placebo were enrolled first (June 17-August 21, 2020) followed by patients who received bamlanivimab and etesevimab or placebo (August 22-September 3). These are the final analyses and represent findings through October 6, 2020. INTERVENTIONS Patients were randomized to receive a single infusion of bamlanivimab (700 mg [n = 101], 2800 mg [n = 107], or 7000 mg [n = 101]), the combination treatment (2800 mg of bamlanivimab and 2800 mg of etesevimab [n = 112]), or placebo (n = 156). MAIN OUTCOMES AND MEASURES The primary end point was change in SARS-CoV-2 log viral load at day 11 (±4 days). Nine prespecified secondary outcome measures were evaluated with comparisons between each treatment group and placebo, and included 3 other measures of viral load, 5 on symptoms, and 1 measure of clinical outcome (the proportion of patients with a COVID-19-related hospitalization, an emergency department [ED] visit, or death at day 29). RESULTS Among the 577 patients who were randomized and received an infusion (mean age, 44.7 [SD, 15.7] years; 315 [54.6%] women), 533 (92.4%) completed the efficacy evaluation period (day 29). The change in log viral load from baseline at day 11 was -3.72 for 700 mg, -4.08 for 2800 mg, -3.49for7000mg,-4.37forcombinationtreatment,and-3.80forplacebo.Comparedwithplacebo, the differences in the change in log viral load at day 11 were 0.09 (95% CI, -0.35 to 0.52; P = .69)for 700 mg, -0.27 (95% CI, -0.71 to 0.16; P = .21) for 2800 mg, 0.31 (95% CI, -0.13 to 0.76; P = .16) for 7000 mg, and -0.57 (95% CI, -1.00 to -0.14; P = .01) for combination treatment. Among the secondary outcome measures, differences between each treatment group vs the placebo group werestatisticallysignificantfor10of84endpoints.TheproportionofpatientswithCOVID-19-related hospitalizationsorEDvisitswas5.8%(9events)forplacebo,1.0%(1event)for700mg,1.9%(2events) for 2800 mg, 2.0% (2 events) for 7000 mg, and 0.9% (1 event) for combination treatment. Immediate hypersensitivity reactions were reported in 9 patients (6 bamlanivimab, 2 combination treatment, and 1 placebo). No deaths occurred during the study treatment. CONCLUSIONS AND RELEVANCE Among nonhospitalized patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 illness, treatment with bamlanivimab and etesevimab, compared with placebo, was associated with a statistically significant..
References
Baum, Fulton, Wloga, Antibody cocktail to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein prevents rapid mutational escape seen with individual antibodies, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abd0831
Berlin, Gulick, Martinez, Severe Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMcp2009575
Chen, Nirula, Heller, for the BLAZE-1
Garg, Kim, Whitaker, Hospitalization rates and characteristics of patients hospitalized with laboratory-confirmed coronavirus disease 2019-COVID-NET, 14 States, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Golub, Md, None
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Investigators, SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody LY-CoV555 in outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med. Published online, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2029849
Jones, Brown-Augsburger, Corbett, LY-CoV555, a rapidly isolated potent neutralizing antibody, provides protection in a non-human primate model of SARS-CoV-2 infection. bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.09.30.318972
Joyner, Wright, Fairweather, Early safety indicators of COVID-19 convalescent plasma in 5000 patients, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI140200
Ko, Danielson, Town, Risk factors for COVID-19-associated hospitalization: COVID-19-associated hospitalization surveillance network and behavioral risk factor surveillance system, Clin Infect Dis. Published online, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1419
Petrilli, Jones, Yang, Factors associated with hospital admission and critical illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York City: prospective cohort study, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m1966
Preeti, Malani, Md, Msj, None
Shi, Shan, Duan, A human neutralizing antibody targets the receptor-binding site of SARS-CoV-2, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2381-y
Williamson, Walker, Bhaskaran, Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2521-4
Wu, Chen, Cai, Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994?utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jama.2021.0202
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.0202",
"ISSN": [
"0098-7484"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.0202",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Baylor University Medical Center and Baylor Scott and White Research Institute, Dallas, Texas"
}
],
"family": "Gottlieb",
"given": "Robert L.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, Indiana"
}
],
"family": "Nirula",
"given": "Ajay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Women’s Guild Lung Institute, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California"
}
],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Peter",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Vitalink Research, Union, South Carolina"
}
],
"family": "Boscia",
"given": "Joseph",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Long Beach Clinical Trials, Long Beach, California"
}
],
"family": "Heller",
"given": "Barry",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Imperial Health, Lake Charles, Louisiana"
}
],
"family": "Morris",
"given": "Jason",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Cook County Health, Chicago, Illinois"
}
],
"family": "Huhn",
"given": "Gregory",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Indago Research, Hialeah, Florida"
}
],
"family": "Cardona",
"given": "Jose",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Las Vegas Medical Research Center, Las Vegas, Nevada"
}
],
"family": "Mocherla",
"given": "Bharat",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University, Chicago, Illinois"
}
],
"family": "Stosor",
"given": "Valentina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Franciscan Health, Greenwood, Indiana"
}
],
"family": "Shawa",
"given": "Imad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Georgetown University, Washington, DC"
}
],
"family": "Kumar",
"given": "Princy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, Indiana"
}
],
"family": "Adams",
"given": "Andrew C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, Indiana"
}
],
"family": "Van Naarden",
"given": "Jacob",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, Indiana"
}
],
"family": "Custer",
"given": "Kenneth L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, Indiana"
}
],
"family": "Durante",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, Indiana"
}
],
"family": "Oakley",
"given": "Gerard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, Indiana"
}
],
"family": "Schade",
"given": "Andrew E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, Indiana"
}
],
"family": "Holzer",
"given": "Timothy R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, Indiana"
}
],
"family": "Ebert",
"given": "Philip J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, Indiana"
}
],
"family": "Higgs",
"given": "Richard E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, Indiana"
}
],
"family": "Kallewaard",
"given": "Nicole L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, Indiana"
}
],
"family": "Sabo",
"given": "Janelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, Indiana"
}
],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Dipak R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, Indiana"
}
],
"family": "Klekotka",
"given": "Paul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, Indiana"
}
],
"family": "Shen",
"given": "Lei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, Indiana"
}
],
"family": "Skovronsky",
"given": "Daniel M.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "JAMA",
"container-title-short": "JAMA",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-21T17:00:13Z",
"timestamp": 1611248413000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-19T04:02:22Z",
"timestamp": 1613707342000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-09T11:19:50Z",
"timestamp": 1712661590289
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 770,
"issue": "7",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
16
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "7",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
16
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/articlepdf/2775647/jama_gottlieb_2021_oi_210002_1613412631.85755.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "10",
"original-title": [],
"page": "632",
"prefix": "10.1001",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
16
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
16
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Medical Association (AMA)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMcp2009575",
"article-title": "Severe Covid-19.",
"author": "Berlin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2451",
"issue": "25",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "joi210002r1",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994",
"article-title": "Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China.",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "934",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "joi210002r2",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2521-4",
"article-title": "Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY.",
"author": "Williamson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "430",
"issue": "7821",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "joi210002r3",
"volume": "584",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9",
"article-title": "Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial.",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1569",
"issue": "10236",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "joi210002r4",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19—final report.",
"author": "Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1813",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "joi210002r5",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.16747",
"article-title": "Corticosteroids in COVID-19 ARDS: evidence and hope during the pandemic.",
"author": "Prescott",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1292",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "joi210002r6",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.10044",
"article-title": "Effect of convalescent plasma therapy on time to clinical improvement in patients with severe and life-threatening COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial.",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "460",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "joi210002r7",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tips.2020.07.004",
"article-title": "Fruitful neutralizing antibody pipeline brings hope to defeat SARS-Cov-2.",
"author": "Renn",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "815",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Trends Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "joi210002r8",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody LY-CoV555 in outpatients with Covid-19.",
"author": "Chen",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "joi210002r9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2381-y",
"article-title": "A human neutralizing antibody targets the receptor-binding site of SARS-CoV-2.",
"author": "Shi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "120",
"issue": "7819",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "joi210002r14",
"volume": "584",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abd0831",
"article-title": "Antibody cocktail to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein prevents rapid mutational escape seen with individual antibodies.",
"author": "Baum",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1014",
"issue": "6506",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "joi210002r15",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China.",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "497",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "joi210002r16",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm6915e3",
"article-title": "Hospitalization rates and characteristics of patients hospitalized with laboratory-confirmed coronavirus disease 2019—COVID-NET, 14 States, March 1-30, 2020.",
"author": "Garg",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "458",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "joi210002r17",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1966",
"article-title": "Factors associated with hospital admission and critical illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York City: prospective cohort study.",
"author": "Petrilli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "m1966",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "joi210002r18",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Risk factors for COVID-19-associated hospitalization: COVID-19-associated hospitalization surveillance network and behavioral risk factor surveillance system.",
"author": "Ko",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "joi210002r19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI140200",
"article-title": "Early safety indicators of COVID-19 convalescent plasma in 5000 patients.",
"author": "Joyner",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4791",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "joi210002r20",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "joi210002r10",
"unstructured": "US Food and Drug Administration. FDA issues Emergency Use Authorization for convalescent plasma as potential promising COVID–19 treatment, another achievement in administration’s fight against pandemic. Published August 23, 2020. Accessed December 22, 2020. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-issues-emergency-use-authorization-convalescent-plasma-potential-promising-covid-19-treatment?"
},
{
"key": "joi210002r11",
"unstructured": "US Food and Drug Administration. Coronavirus (COVID-19) update: FDA authorizes monoclonal antibody for treatment of COVID-19. Published November 9, 2020. Accessed December 22, 2020. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-monoclonal-antibody-treatment-covid-19?"
},
{
"key": "joi210002r12",
"unstructured": "US Food and Drug Administration. Coronavirus (COVID-19) update: FDA authorizes monoclonal antibodies for treatment of COVID-19. Published November 21, 2020. Accessed December 22, 2020. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-monoclonal-antibodies-treatment-covid-19?"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.09.30.318972",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "joi210002r13",
"unstructured": "Jones? BE, Brown-Augsburger? PL, Corbett? KS, . LY-CoV555, a rapidly isolated potent neutralizing antibody, provides protection in a non-human primate model of SARS-CoV-2 infection.? bioRxiv. Published online October 9, 2020. doi:10.1101/2020.09.30.318972?"
}
],
"reference-count": 20,
"references-count": 20,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2775647"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [
"A Randomized Clinical Trial"
],
"title": "Effect of Bamlanivimab as Monotherapy or in Combination With Etesevimab on Viral Load in Patients With Mild to Moderate COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "325"
}