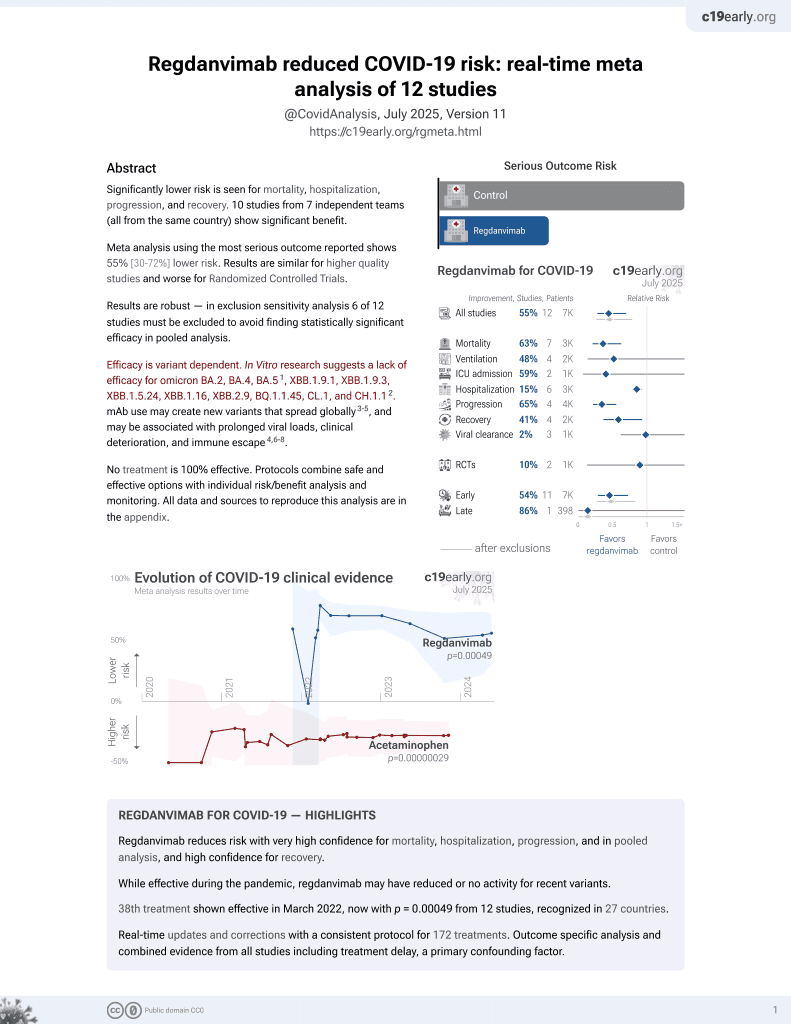
Effectiveness of regdanvimab on clinical outcomes in COVID-19 infected patients on hemodialysis
et al., Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation, doi:10.1093/ndt/gfae069.1573, May 2024
39th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2022, now with p = 0.00049 from 12 studies, recognized in 27 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 230 hemodialysis patients with COVID-19, showing lower mortality with regdanvimab. Details of the adjusted results are not provided.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro research suggests a lack of efficacy for omicron BA.2, BA.4, BA.51, ХВВ.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5.24, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.9, BQ.1.1.45, CL.1, and CH.1.12.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
minimal details provided.
|
risk of death, 59.4% lower, RR 0.41, p = 0.002, treatment 10 of 77 (13.0%), control 49 of 153 (32.0%), NNT 5.3, unadjusted.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Lee et al., 23 May 2024, retrospective, South Korea, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, study period 1 December, 2020 - 30 November, 2021.
Abstract: Abstracts | i2507
Abstract citation ID: gfae069.1573
#616
Effectiveness of regdanvimab on clinical outcomes in
COVID-19 infected patients on hemodialysis
Young-Ki Lee1 , Youn Kyung Kee2 , Hayne Cho Park1 , Ajin Cho1 , Do Hyoung Kim1 and Jong-Woo Yoon3
1
Hallym University College of Medicine, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Republic of South Korea
Hallym University College of Medicine, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Republic of South Korea
3
Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Republic of South Korea
2
Method: We conducted a retrospective study of 230 HD patients hospitalized with COVID-19 infection between December 1, 2020 and
November 30, 2021. Of these, 77 (33.5%) were treated with regdanvimab alone or in combination with dexamethasone or remdesivir
during hospitalization (regdanvimab group), and 153 (66.5%) did not treat with regdanvimab (non-regdanvimab group). We compared
in-hospital mortality rate according to the use of regdanvimab and investigated the factors associated with mortality.
Results: The mean age of the patients was 67.9 ± 12.1 years, with 214 (93%) patients aged 50 years or older. There were no significant
differences in demographics and comorbidity between the regdanvimab and non-regdanvimab groups. Fifty-nine deaths occurred
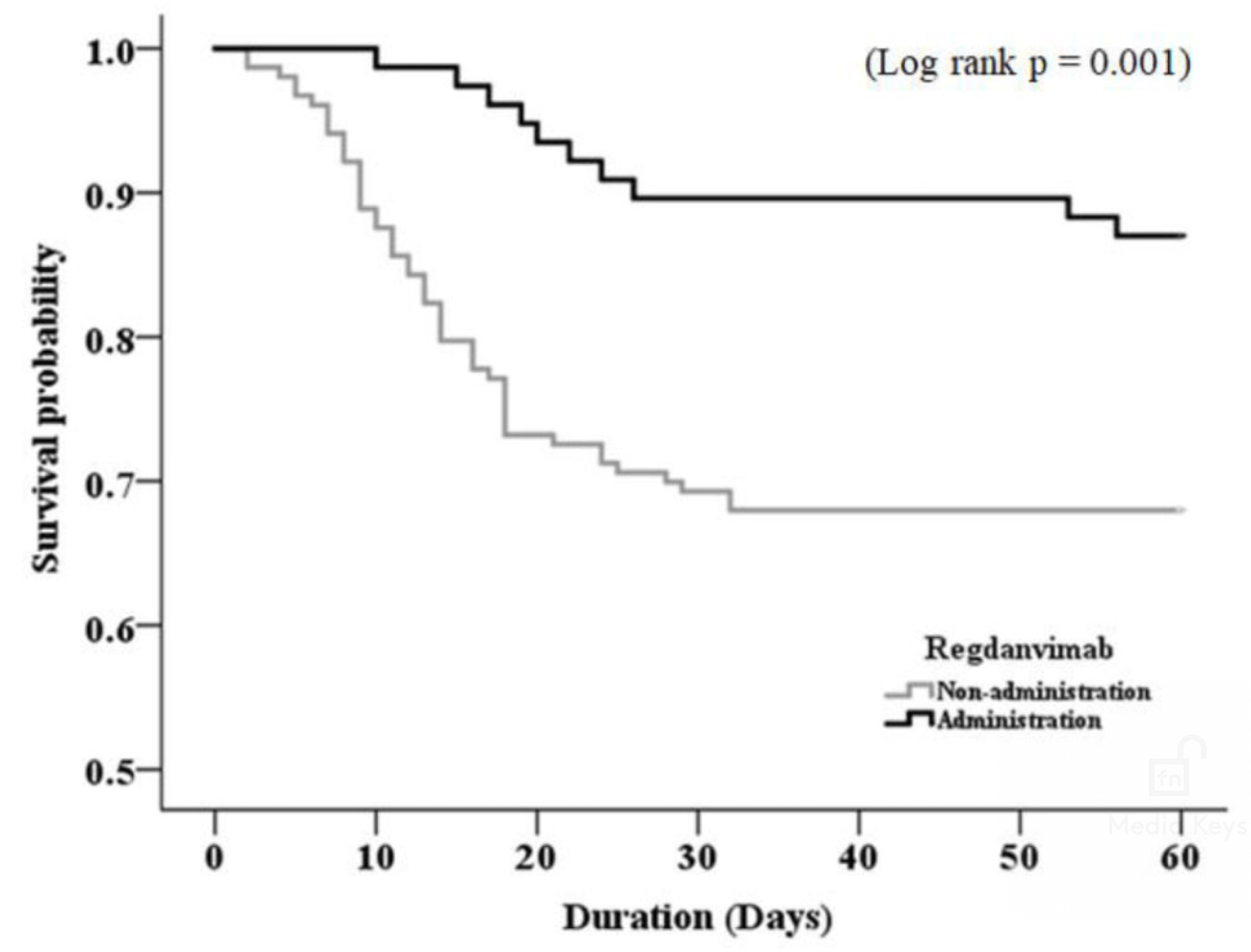
during hospitalization, 49 (32%) in the non-regdanvimab group and 10 (13%) in the regdanvimab group, and mortality rate was significantly higher in the non-regdanvimab group than that in the regdanvimab group (P=0.001, Fig.). Multivariate Cox regression analysis
showed that malignancy (P=0.001), low oxygen saturation<95% at admission (P=0.003), and administration of antibiotics and regdanvimab (P=0.007 and P=0.002, respectively) were significantly associated factors with mortality.
Conclusion: Regdanvimab administration is beneficial in improving prognosis in hospitalized COVID-19 patients on HD. Considering
the vulnerability of ESKD patients to infection, regdanvimab may be considered as a therapeutic option in COVID-19 patients on HD.
Figure:
Background and Aims: Although several therapeutic agents have been evaluated for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019
(COVID-19), there are lack of effective and proven treatments for the COVID-19 patients with end-stage kidney disease (ESKD). The
present study aims to evaluate the effectiveness of regdanvimab on clinical outcomes in COVID-19-infected patients on hemodialysis
(HD).