Spike protein genetic evolution in patients at high-risk of severe COVID-19 treated by monoclonal antibodies
et al., The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiad523, NCT04885452, Nov 2023
42nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
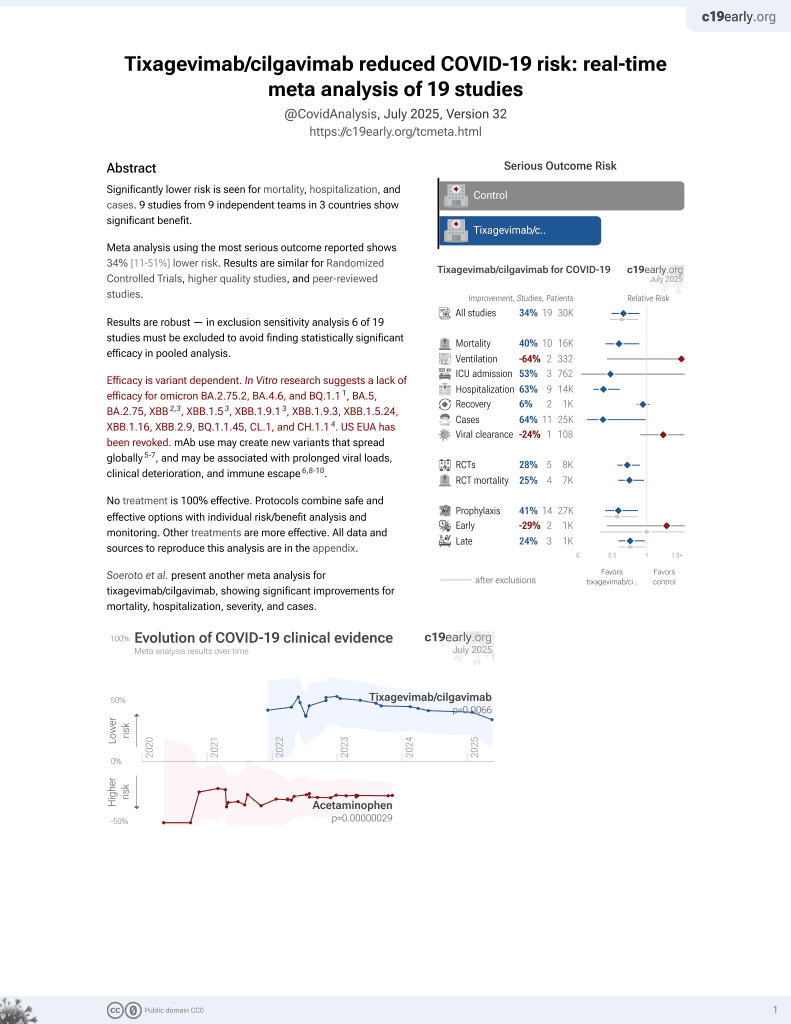
May 2022, now with p = 0.0066 from 19 studies, recognized in 33 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
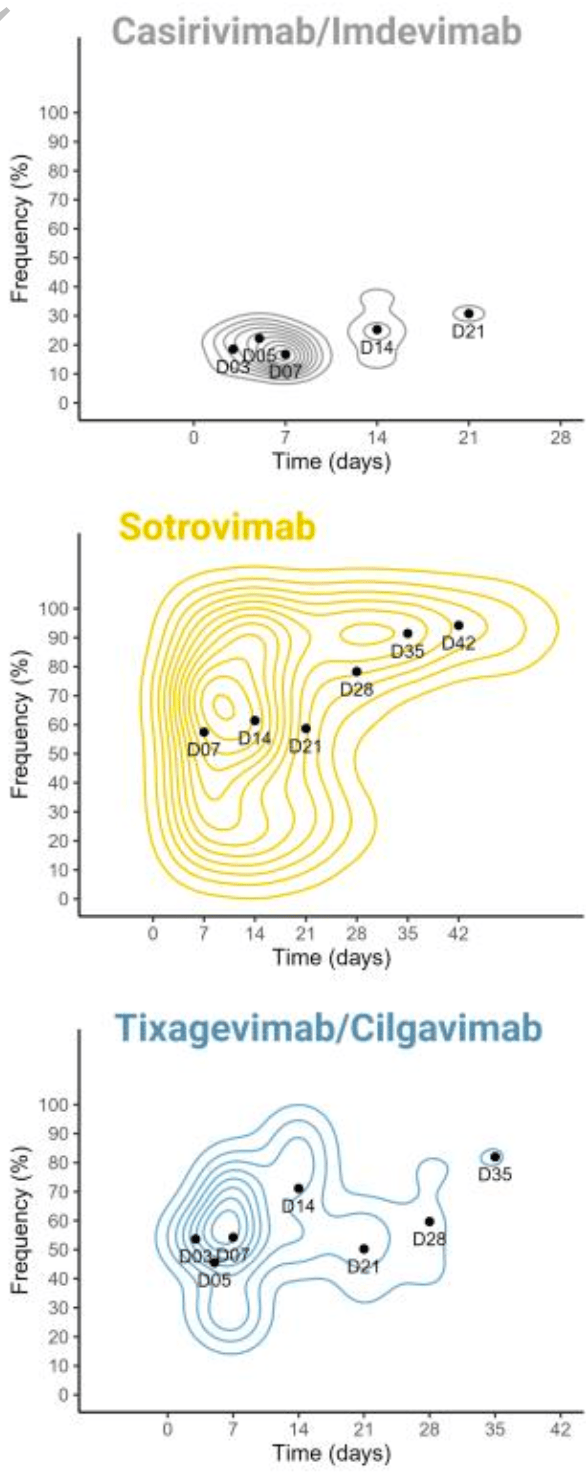
Prospective study of 264 high-risk COVID-19 patients treated with monoclonal antibodies. Tixagevimab/cilgavimab was associated with 5 times higher risk of emergence of mutations. Treatment with sotrovimab was linked to mutations associated with higher viral loads. Mutations associated with tixagevimab/cilgavimab have been identified in multiple SARS-CoV-2 lineages, including BQ.1 and XBB. Authors conclude that using mAbs in treating high-risk COVID-19 patients could drive the genetic evolution of the virus, potentially leading to treatment resistance.
Authors recommend bi-therapies and mAbs with Fc-effector functions and emphasize the need to assess the impact of mAb treatments on the broader evolutionary trajectory of SARS-CoV-2.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro research suggests a lack of efficacy for omicron BA.2.75.2, BA.4.6, BQ.1.11, BA.5, BA.2.75, XBB2,3, XBB.1.53, ХВВ.1.9.13, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5.24, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.9, BQ.1.1.45, CL.1, and CH.1.14.
Study covers tixagevimab/cilgavimab, casirivimab/imdevimab, and sotrovimab.
1.
Planas et al., Resistance of Omicron subvariants BA.2.75.2, BA.4.6 and BQ.1.1 to neutralizing antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.11.17.516888.
2.
Haars et al., Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Sublineages and Spike Protein Mutations Conferring Resistance against Monoclonal Antibodies in a Swedish Cohort during 2022–2023, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11102417.
Leducq et al., 23 Nov 2023, prospective, France, peer-reviewed, 169 authors, study period August 2021 - December 2022, trial NCT04885452 (history).
Contact: valentin.leducq@sorbonneuniversite.fr.
Spike protein genetic evolution in patients at high-risk of severe COVID-19 treated by monoclonal antibodies
The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiad523
Background High-risk patients, often immunocompromised and not responding to vaccine, continue to experience severe COVID-19 and death. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) were shown effective to prevent severe COVID-19 for these patients. Nevertheless, concerns about the emergence of resistance mutations were raised.
Methods We conducted a multicentric prospective cohort study, including 264 patients with mildto moderate COVID-19 at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19 and treated early with Casirivimab/Imdevimab, Sotrovimab or Tixagevimab/Cilgavimab. We sequenced the SARS-CoV-2 genome during follow-up and searched for emerging Spike mutations.
DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiad523 9 Together, these data suggest that mAb monotherapy, without Fc-effector functions, is highly sensitive to the emergence of mutations located in the targeted epitope reducing neutralizing activity and may explain the higher risk of mutation emergence with Tixagevimab/Cilgavimab. In conclusion, our analysis highlights how using mAbs to treat high-risk COVID-19 patients can drive genetic evolution of SARS-CoV-2, potentially leading to treatment resistance through the rapid and frequent acquisition of mutations in Spike protein in immunocompromised patients. To mitigate this risk, our findings suggest that employing bi-therapies and mAbs featuring Fc-effector functions may be beneficial. Moreover, we have identified these resistance mutations across multiple SARS-CoV-2 lineages, including various VOCs, emphasizing the need to assess the impact of mAb treatments on SARS-CoV-2 evolution more broadly within the population.
Author contributions
Conceptualization
References
Andrés, González-Sánchez, Jiménez, Márquez-Algaba, Piñana et al., Emergence of Delta and Omicron variants carrying resistance-associated mutations in immunocompromised patients undergoing sotrovimab treatment with long-term viral excretion, Clin Microbiol Infect
Barnes, Jette, Abernathy, Dam, Esswein et al., SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody structures inform therapeutic strategies, Nature
Baum, Fulton, Wloga, Copin, Pascal et al., Antibody cocktail to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein prevents rapid mutational escape seen with individual antibodies, Science
Bruel, Hadjadj, Maes, Planas, Seve et al., Serum neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sublineages BA.1 and BA.2 in patients receiving monoclonal antibodies, Nat Med
Bruel, Stéfic, Nguyen, Toniutti, Staropoli et al., Longitudinal analysis of serum neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2, BA.4, and BA.5 in patients receiving monoclonal antibodies, Cell Rep Med
Bruel, Vrignaud, Porrot, Staropoli, Planas et al., Antiviral activities of sotrovimab against BQ.1.1 and XBB.1.5 in sera of treated patients, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.05.25.23290512v1
Cameroni, Bowen, Rosen, Saliba, Zepeda et al., Broadly neutralizing antibodies overcome SARS-CoV-2 Omicron antigenic shift, Nature
Cao, Jian, Wang, Yu, Song et al., Imprinted SARS-CoV-2 humoral immunity induces convergent Omicron RBD evolution, Nature
Cheminant, Chavarot (hôpital, Necker, Paris, Chauvin et al., Hôpital de la Pitié Salpêtrière
Chen, Zhao, Zhou, Zhu, Jiang et al., Broadly neutralizing antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 and other human coronaviruses, Nat Rev Immunol
Copin, Baum, Wloga, Pascal, Giordano et al., The monoclonal antibody combination REGEN-COV protects against SARS-CoV-2 mutational escape in preclinical and human studies, Cell
Cui, Liu, Wang, Wang, Fan et al., Structural and functional characterizations of infectivity and immune evasion of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron, Cell
Ema, COVID-19 medicines
Focosi, Casadevall, A Critical Analysis of the Use of Cilgavimab plus Tixagevimab Monoclonal Antibody Cocktail (Evusheld TM ) for COVID-19 Prophylaxis and Treatment, Viruses
Focosi, Quiroga, Mcconnell, Johnson, Casadevall, Convergent Evolution in SARS-CoV-2 Spike Creates a Variant Soup from Which New COVID-19 Waves Emerge, Int J Mol Sci
Fratev, R346K Mutation in the Mu Variant of SARS-CoV-2 Alters the Interactions with Monoclonal Antibodies from Class 2: A Free Energy Perturbation Study, J Chem Inf Model
Ghotloo, Maghsood, Golsaz-Shirazi, Amiri, Moog et al., Epitope mapping of neutralising anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies: Implications for immunotherapy and vaccine design, Rev Med Virol
Huang, Han, Yan, Structure-based neutralizing mechanisms for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, Emerg Microbes Infect
Iketani, Liu, Guo, Liu, Chan et al., Antibody evasion properties of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sublineages, Nature
Jana, Bhattacharya, Mayilsamy, Banerjee, Bhattacharje et al., Targeting an evolutionarily conserved 'E-L-L' motif in the spike protein to develop a small molecule fusion inhibitor against SARS-CoV-2, BioRxiv Prepr Serv Biol
Jian, Yu, Song, Yisimayi, Yu et al., Further humoral immunity evasion of emerging SARS-CoV-2 BA.4 and BA.5 subvariants, Lancet Infect Dis
Keam, Tixagevimab + Cilgavimab: First Approval, Drugs
Li, Liao, Meng, Li, Han et al., Structural basis of human ACE2 higher binding affinity to currently circulating Omicron SARS-CoV-2 sub-variants BA, 2 and BA
Lin, Chen, Chen, Lee, Wu, Glycan Masking of Epitopes in the NTD and RBD of the Spike Protein Elicits Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies Against SARS-CoV-2 Variants, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.795741
Liu, Iketani, Guo, Chan, Wang et al., Striking antibody evasion manifested by the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2, Nature
Liu, Vanblargan, Bloyet, Rothlauf, Chen et al., Identification of SARS-CoV-2 spike mutations that attenuate monoclonal and serum antibody neutralization, Cell Host Microbe
Mader, Tydykov, Glück, Bertok, Weidlich et al., Omicron's binding to sotrovimab, casirivimab, imdevimab, CR3022, and sera from previously infected or vaccinated individuals, iScience
Martin-Blondel, Marcelin, Soulié, Kaisaridi, Lusivika-Nzinga et al., Outcome of very high-risk patients treated by Sotrovimab for mild-to-moderate COVID-19 Omicron, a prospective cohort study (the ANRS 0003S COCOPREV study), J Infect
Martin-Blondel, Marcelin, Soulié, Kaisaridi, Lusivika-Nzinga et al., Sotrovimab to prevent severe COVID-19 in high-risk patients infected with Omicron BA.2, J Infect
Mccallum, Czudnochowski, Rosen, Zepeda, Bowen et al., Structural basis of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron immune evasion and receptor engagement, Science
Ortega, Pujol, Jastrzebska, Rangel, Mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein modulate the virus affinity to the human ACE2 receptor, an in silico analysis, EXCLI J
Pinto, Park, Beltramello, Walls, Tortorici et al., Cross-neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 by a human monoclonal SARS-CoV antibody, Nature
Planas, Saunders, Maes, Guivel-Benhassine, Planchais et al., Considerable escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron to antibody neutralization, Nature
Ragonnet-Cronin, Nutalai, Huo, Dijokaite-Guraliuc, Das et al., Generation of SARS-CoV-2 escape mutations by monoclonal antibody therapy, Nat Commun
Rockett, Basile, Maddocks, Fong, Agius et al., Resistance Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Delta Variant after Sotrovimab Use, N Engl J Med
Roe, Brady, Schuko, Nguyen, Beloor et al., Molecular Characterization of AZD7442 (Tixagevimab-Cilgavimab) Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Subvariants, Microbiol Spectr
Shafin, Pesout, Chang, Nattestad, Kolesnikov et al., Haplotype-aware variant calling with PEPPER-Margin-DeepVariant enables high accuracy in nanopore long-reads, Nat Methods
Soeroto, Yanto, Kurniawan, Hariyanto, Efficacy and safety of tixagevimabcilgavimab as pre-exposure prophylaxis for COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Rev Med Virol
Takashita, Yamayoshi, Simon, Van Bakel, Sordillo et al., Efficacy of Antibodies and Antiviral Drugs against Omicron BA.2.12.1, BA.4, and BA.5 Subvariants, N Engl J Med
Tao, Tzou, Pond, Ioannidis, Shafer, Susceptibility of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variants to Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis, Microbiol Spectr
Vellas, Kamar, Izopet, Resistance mutations in SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant after tixagevimab-cilgavimab treatment, J Infect
Vellas, Trémeaux, Bello, Latour, Ranger, Resistance mutations in SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant in patients treated with sotrovimab, Clin Microbiol Infect Off Publ Eur Soc Clin Microbiol Infect Dis
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, Ali, Gao et al., REGEN-COV Antibody Combination and Outcomes in Outpatients with Covid -19, N Engl J Med
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, Ali, Gao et al., REGN-COV2, a Neutralizing Antibody Cocktail, in Outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiad523",
"ISSN": [
"0022-1899",
"1537-6613"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiad523",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>High-risk patients, often immunocompromised and not responding to vaccine, continue to experience severe COVID-19 and death. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) were shown effective to prevent severe COVID-19 for these patients. Nevertheless, concerns about the emergence of resistance mutations were raised.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We conducted a multicentric prospective cohort study, including 264 patients with mild-to moderate COVID-19 at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19 and treated early with Casirivimab/Imdevimab, Sotrovimab or Tixagevimab/Cilgavimab. We sequenced the SARS-CoV-2 genome during follow-up and searched for emerging Spike mutations.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Immunocompromised patients have a 6-fold increased risk of developing mutations, which are associated with a prolonged duration of viral clearance but no clinical worsening. Emerging P337S/R/L/H, E340D/K/A/Q/V/G and K356T/R substitutions in patients treated with Sotrovimab are associated with higher viral RNA loads for up to 14 days post-treatment initiation. Tixagevimab/Cilgavimab is associated with a 5-fold increased risk of developing mutations. R346K/I/T/S and K444R/N/M substitutions associated with Tixagevimab/Cilgavimab have been identified in multiple SARS-CoV-2 lineages, including BQ.1 and XBB.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In conclusion, the probability of emerging mutations arising in response to mAbs is significant, emphasizing the crucial need to investigate these mutations thoroughly and assess their impact on patients and the evolutionary trajectory of the SARS-CoV-2.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6817-6227",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Sorbonne Université, INSERM, Institut Pierre Louis d'Epidémiologie et de Santé Publique, AP-HP, Hôpitaux Universitaires Pitié-Salpêtrière - Charles Foix, Laboratoire de Virologie , Paris , France"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Leducq",
"given": "Valentin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Sorbonne Université, INSERM, Institut Pierre Louis d'Epidémiologie et de Santé Publique, AP-HP, Hôpitaux Universitaires Pitié-Salpêtrière - Charles Foix, Laboratoire de Virologie , Paris , France"
}
],
"family": "Zafilaza",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Sorbonne Université, INSERM, Institut Pierre Louis d'Epidémiologie et de Santé Publique, AP-HP, Hôpitaux Universitaires Pitié-Salpêtrière - Charles Foix, Laboratoire de Virologie , Paris , France"
}
],
"family": "Fauchois",
"given": "Antoine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Sorbonne Université, INSERM, Institut Pierre Louis d'Epidémiologie et de Santé Publique, AP-HP, Hôpitaux Universitaires Pitié-Salpêtrière - Charles Foix, Laboratoire de Virologie , Paris , France"
}
],
"family": "Ghidaoui",
"given": "Emna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Sorbonne Université, INSERM, Institut Pierre Louis d'Epidémiologie et de Santé Publique, AP-HP, Hôpitaux Universitaires Pitié-Salpêtrière - Charles Foix, Laboratoire de Virologie , Paris , France"
}
],
"family": "Sayon",
"given": "Sophie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Sorbonne Université, INSERM, Institut Pierre Louis d'Epidémiologie et de Santé Publique , Paris , France"
}
],
"family": "Dorival",
"given": "Céline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Sorbonne Université, INSERM, Institut Pierre Louis d'Epidémiologie et de Santé Publique , Paris , France"
}
],
"family": "Meledje",
"given": "Marie-Laure",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Sorbonne Université, INSERM, Institut Pierre Louis d'Epidémiologie et de Santé Publique , Paris , France"
}
],
"family": "Lusivika-Nzinga",
"given": "Clovis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Sorbonne Université, Hôpital Saint Antoine, Service d'Accueil des Urgences, INSERM, Institut Pierre Louis d'Epidémiologie et de Santé Publique , Paris , France"
}
],
"family": "Yordanov",
"given": "Youri",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Service des Maladies Infectieuses et Tropicales, CHU de Toulouse, France, Institut Toulousain des Maladies Infectieuses et Inflammatoires (Infinity) INSERM, Université Toulouse III. , Toulouse , France"
}
],
"family": "Martin-Blondel",
"given": "Guillaume",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8672-7918",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Sorbonne Université, INSERM, Institut Pierre Louis d'Epidémiologie et de Santé Publique, Unité de Santé Publique, AP-HP, Hôpital Saint-Antoine , Paris , France"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Carrat",
"given": "Fabrice",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Sorbonne Université, INSERM, Institut Pierre Louis d'Epidémiologie et de Santé Publique, AP-HP, Hôpitaux Universitaires Pitié-Salpêtrière - Charles Foix, Laboratoire de Virologie , Paris , France"
}
],
"family": "Marcelin",
"given": "Anne-Geneviève",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Sorbonne Université, INSERM, Institut Pierre Louis d'Epidémiologie et de Santé Publique, AP-HP, Hôpitaux Universitaires Pitié-Salpêtrière - Charles Foix, Laboratoire de Virologie , Paris , France"
}
],
"family": "Soulie",
"given": "Cathia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Garcia",
"given": "Magali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Giraud",
"given": "Valentin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Metais",
"given": "Agathe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cazenave-Roblot",
"given": "France",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martellosio",
"given": "Jean-Philippe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ronchetti",
"given": "Anne-Marie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gabas",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Had- jadj",
"given": "Naima",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Salanoubat",
"given": "Célia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chabrol",
"given": "Amélie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Housset",
"given": "Pierre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Par- don",
"given": "Agathe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Faucon",
"given": "Anne-Laure",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Caudwell",
"given": "Valérie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hanafi",
"given": "Latifa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alric",
"given": "Laurent",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pugnet",
"given": "Grégory",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mourguet",
"given": "Mor- gane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bories",
"given": "Eva",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bonnet",
"given": "Delphine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Charpentier",
"given": "Sandrine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Delobel",
"given": "Pierre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Debard",
"given": "Alexa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beck",
"given": "Colleen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boumaza",
"given": "Xavier",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rousset",
"given": "Stella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lanternier",
"given": "Fanny",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Delage",
"given": "Claire",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pires",
"given": "Elisabete Gomes",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cheminant",
"given": "Morgane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chavarot",
"given": "Nathalie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chauvin",
"given": "Anthony",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eyer",
"given": "Xavier",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Delcey",
"given": "Véronique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bessis",
"given": "Simon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gueneau",
"given": "Romain",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thibaut",
"given": "Pelagie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nadal",
"given": "Marine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Siguier",
"given": "Mar- tin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bachir",
"given": "Marwa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Palacios",
"given": "Christia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pourcher",
"given": "Valérie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Faycal",
"given": "Antoine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Berot",
"given": "Vincent",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brin",
"given": "Cécile",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Djebara",
"given": "Siham",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zafilaza",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marot",
"given": "Stephane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sayon",
"given": "Sophie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leducq",
"given": "Valentin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lacombe",
"given": "Karine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aad",
"given": "Yasmine Abi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chiarabini",
"given": "Thibault",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Feliho",
"given": "Raynald",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Valin",
"given": "Nadia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brigant",
"given": "Fabien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boize",
"given": "Julien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thiébaud",
"given": "Pierre-Clément",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moreau",
"given": "Marie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Billard",
"given": "Charlotte",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "De Castro",
"given": "Nathalie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liégeon",
"given": "Geoffroy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Denis",
"given": "Blandine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Molina",
"given": "Jean-Michel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Etheve",
"given": "Lucia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cabié",
"given": "André",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abel",
"given": "Sylvie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cabras",
"given": "Ornella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guitteaud",
"given": "Karine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pierre-François",
"given": "Sandrine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dubee",
"given": "Vincent",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ndiaye",
"given": "Diama",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pehlivan",
"given": "Jonathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phelippeau",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahieu",
"given": "Rafael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cazanave",
"given": "Charles",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duvignaud",
"given": "Alexandre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pistone",
"given": "Thierry",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Desclaux",
"given": "Arnaud",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Neau",
"given": "Didier",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Faucher",
"given": "Jean-François",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Festou",
"given": "Benjamin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dupuy-Grasset",
"given": "Magali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Loustaud-Ratti",
"given": "Véronique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chainier",
"given": "Delphine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peiffer-Smadja",
"given": "Nathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Da Conceicao",
"given": "Olivia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thy",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Collas",
"given": "Lio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Godard",
"given": "Cindy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bouzid",
"given": "Donia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ing",
"given": "Vittiaroat",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pereira",
"given": "Laurent",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pavlowsky",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ravaut",
"given": "Camille",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Asquier-Khati",
"given": "Antoine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boutoille",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chauveau",
"given": "Marie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Deschanvres",
"given": "Colin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raffi",
"given": "François",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Le Bot",
"given": "Audrey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cailleaux",
"given": "Marine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Benezit",
"given": "François",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maillard",
"given": "Anne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hue",
"given": "Benoit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tattevin",
"given": "Pierre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coustilleres",
"given": "François",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schneider",
"given": "Claudia Carvalho-",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jamard",
"given": "Simon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Petit",
"given": "Laetitia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stefic",
"given": "Karl",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mrozek",
"given": "Natacha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Theis",
"given": "Clement",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vidal",
"given": "Magali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sauvat",
"given": "Leo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martineau",
"given": "Delphine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lefèvre",
"given": "Benjamin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baronnet",
"given": "Guillaume",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Didier",
"given": "Agnès",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ader",
"given": "Florence",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Perpoint",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Conrad",
"given": "Anne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chabert",
"given": "Paul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chauvelot",
"given": "Pierre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "Aurélie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Loubet",
"given": "Paul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mazet",
"given": "Julien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Larcher",
"given": "Romaric",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Laureillard",
"given": "Didier",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "De- vaux",
"given": "Mathilde",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Frey",
"given": "Jérôme",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woerlen",
"given": "Amos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Remillon",
"given": "Aline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Absensur-Vuillaume",
"given": "Laure",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bouquet",
"given": "Pauline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trinh-Duc",
"given": "Albert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rispal",
"given": "Patrick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Petua",
"given": "Philippe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carillo",
"given": "Julien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Perrot",
"given": "Aurore",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Delavigne",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cougoul",
"given": "Pierre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dion",
"given": "Jérémie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rauzy",
"given": "Odile",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yazdanpanah",
"given": "Yazdan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Petrov-Sanchez",
"given": "Ventzislava",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Diallo",
"given": "Alpha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Le Mestre",
"given": "Soizic",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Le Meut",
"given": "Guillaume",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goderel",
"given": "Isabelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chau",
"given": "Frédéric",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Soltana",
"given": "Brahim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tang",
"given": "Jessica Chane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guedj",
"given": "Jeremie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Caille",
"given": "Yvanie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "COCOPREV Study Group",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-21T16:45:08Z",
"timestamp": 1700585108000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-23T20:55:15Z",
"timestamp": 1700772915000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-24T04:40:13Z",
"timestamp": 1700800813872
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
23
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/pages/standard-publication-reuse-rights",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-23T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1700697600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/infdis/jiad523/53711860/jiad523.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/infdis/jiad523/53711860/jiad523.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
23
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
23
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/infdis/jiad523/7444950"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Immunology and Allergy"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Spike protein genetic evolution in patients at high-risk of severe COVID-19 treated by monoclonal antibodies",
"type": "journal-article"
}