Regdanvimab for patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study and subgroup analysis of patients with the Delta variant
et al., International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035, Jan 2023
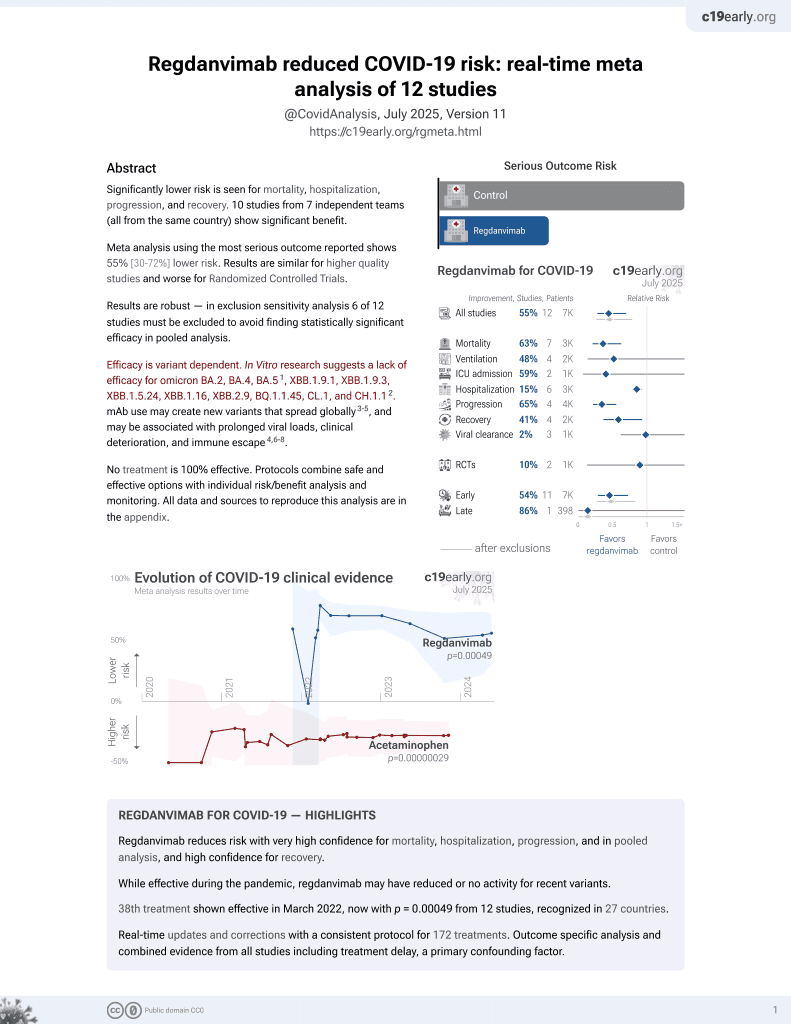
39th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2022, now with p = 0.00049 from 12 studies, recognized in 27 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 722 hospitalized mild-to-moderate COVID-19 patients in Korea showing lower risk of disease progression with regdanvimab treatment.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro research suggests a lack of efficacy for omicron BA.2, BA.4, BA.51, ХВВ.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5.24, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.9, BQ.1.1.45, CL.1, and CH.1.12.
|
risk of death, 70.4% lower, RR 0.30, p = 0.42, treatment 0 of 418 (0.0%), control 1 of 304 (0.3%), NNT 304, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
hospitalization time, 12.1% lower, relative time 0.88, p < 0.001, treatment mean 10.27 (±2.94) n=418, control mean 11.69 (±4.71) n=304.
|
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 48.5% lower, RR 0.51, p < 0.001, treatment 92 of 418 (22.0%), control 130 of 304 (42.8%), NNT 4.8.
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 67.8% lower, RR 0.32, p < 0.001, treatment 31 of 418 (7.4%), control 70 of 304 (23.0%), NNT 6.4.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Jang et al., 6 Jan 2023, retrospective, South Korea, peer-reviewed, 3 authors, study period September 2020 - October 2021.
Contact: kjykey@icmc.or.kr.
Regdanvimab for patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study and subgroup analysis of patients with the Delta variant
International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035
Objectives: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of regdanvimab, a neutralizing antibody, in patients with mild-to-moderate SARS-CoV-2 including against the Delta variant. Methods: A single-center, retrospective, observational cohort study in adults with confirmed COVID-19. The primary end point was the proportion of patients deteriorating with peripheral oxygen saturation < 90% in room air, requiring supplemental oxygen therapy above high flow, or experiencing mortality due to COVID-19 up to day 28. Results: A total of 722 patients were eligible; 418 received regdanvimab and 304 received standard of care (SoC), of whom 71.1% (297/418, regdanvimab) and 37.8% (115/304, SoC) were infected with the Delta variant. The proportion of patients with a primary end point event was significantly lower with regdanvimab than SoC (3.1% vs 9.9%; difference: -6.8 [95% confidence interval: -10.9, -2.8]; P = 0.0 0 02). A similar trend was observed in the Delta variant subgroup (regdanvimab, 2.7% vs SoC, 7.0%; difference -4.3 [95% confidence interval: -10.8, 0.2]; P = 0.0827). The secondary efficacy end points supported the primary analysis findings in the overall cohort and Delta variant subgroup. No new safety signals were identified. Conclusion: Regdanvimab demonstrated clinical efficacy in the overall cohort and may provide a clinical benefit for patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 infected with the Delta variant.
Author contributions YRJ, YJO, and JYK were jointly responsible for the acquisition/interpretation of data, conception, and design of the study. Statistical analysis was conducted by Celltrion, Inc. All authors contributed to manuscript development and approved the final version.
Supplementary materials Supplementary material associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035 .
References
Baral, Yin, James, Treatment and prevention strategies for the COVID 19 pandemic: a review of immunotherapeutic approaches for neutralizing SARS-CoV-2, Int J Biol Macromol, doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.07.013
Bierle, Ganesh, Razonable, Breakthrough COVID-19 and casirivimabimdevimab treatment during a SARS-CoV-2 B1.617.2 (Delta) surge, J Clin Virol, doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2021.105026
Corti, Purcell, Snell, Veesler, Tackling COVID-19 with neutralizing monoclonal antibodies, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.05.005
Dougan, Nirula, Azizad, Mocherla, Gottlieb et al., Bamlanivimab plus etesevimab in mild or moderate Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2102685
Gupta, Gonzalez-Rojas, Juarez, Casal, Moya et al., Early treatment for Covid-19 with SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody sotrovimab, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2107934
Gupta, Kaur, Yadav, Mukhopadhyay, Sahay et al., Clinical characterization and genomic analysis of samples from COVID-19 breakthrough infections during the second wave among the various states of India, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13091782
Harder, Külper-Schiek, Reda, Treskova-Schwarzbach, Koch et al., Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 infection with the Delta (B.1.617.2) variant: second interim results of a living systematic review and meta-analysis, 1 January to 25, Euro Surveill, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.41.2100920
Kim, Jang, Hong, Jung, Park et al., Safety, virologic efficacy, and pharmacokinetics of CT-P59, a neutralizing monoclonal antibody against SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding protein: two randomized, placebo-controlled, phase I studies in healthy individuals and patients with mild SARS-CoV-2 infection, Clin Ther, doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2021.08.009
Kim, Ryu, Lee, Kim, Seo et al., A therapeutic neutralizing antibody targeting receptor binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-20602-5
Kumar, Banu, Sasikala, Parsa, Sowpati et al., Effectiveness of REGEN-COV antibody cocktail against the B.1.617.2 (delta) variant of SARS-CoV-2: a cohort study, J Intern Med, doi:10.1111/joim.13408
Lee, Lee, Lee, Kim, Lee et al., Regdanvimab in patients with mild-to-moderate SARS-CoV-2 infection: a propensity scorematched retrospective cohort study, Int Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108570
Liu, Huuskonen, Laitinen, Redchuk, Bogacheva et al., SARS-CoV-2-host proteome interactions for antiviral drug discovery, Mol Syst Biol, doi:10.15252/msb.202110396
Mahase, Delta variant: what is happening with transmission, hospital admissions, and restrictions, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.n1513
O'horo, Challener, Speicher, Bosch, Seville et al., Effectiveness of monoclonal antibodies in preventing severe COVID-19 with emergence of the delta variant, Mayo Clin Proc, doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.12.002
Park, Kim, Lee, Rhee, Kim et al., Update 2021 status and characteristics of COVID-19 variant virus outbreak in the Republic of Korea
Planas, Veyer, Baidaliuk, Staropoli, Guivel-Benhassine et al., Reduced sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 variant Delta to antibody neutralization, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03777-9
Ryu, Kang, Noh, Woo, Lee et al., The in vitro and in vivo efficacy of CT-P59 against Gamma, Delta and its associated variants of SARS-CoV-2, Biochem Biophys Res Commun, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.09.023
Sheikh, Mcmenamin, Taylor, Cpublic, Health Scotland and the EAVE II Collaborators. SARS-CoV-2 Delta VOC in Scotland: demographics, risk of hospital admission, and vaccine effectiveness, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01358-1
Streinu-Cercel, Preotescu, Kim, Kim, Cheon, Efficacy and safety of regdanvimab (CT-P59): a phase 2/3 randomized, doubleblind, placebo-controlled trial in outpatients with mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease 2019, Open Forum Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofac053
Syed, Regdanvimab: first approval, Drugs, doi:10.1007/s40265-021-01626-7
Taylor, Patel, Pham, Whitaker, Anglin et al., Severity of disease among adults hospitalized with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 before and during the period of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 (Delta) predominance -COVID-NET, 14 states, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep, doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7043e1
Tian, Sun, Zhou, Ye, The global epidemic of the SARS-CoV-2 delta variant, key spike mutations and immune escape, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.751778
Twohig, Nyberg, Zaidi, Thelwall, Sinnathamby et al., Hospital admission and emergency care attendance risk for SARS-CoV-2 delta (B.1.617.2) compared with alpha (B.1.1.7) variants of concern: a cohort study, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00475-8
Venkatesan, Repurposing drugs for treatment of COVID-19, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00270-8
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, Ali, Gao et al., REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2035002
Zhao, Huang, Zhang, Chen, Gao et al., The global transmission of new coronavirus variants, Environ Res, doi:10.1016/j.envres.2021.112240
Zhu, Zhang, Li, Yang, Song, A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001017
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035",
"ISSN": [
"1201-9712"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035",
"alternative-id": [
"S1201971222006749"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Regdanvimab for patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study and subgroup analysis of patients with the Delta variant"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "International Journal of Infectious Diseases"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd on behalf of International Society for Infectious Diseases."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jang",
"given": "Young Rock",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oh",
"given": "Yoon Ju",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Jin Yong",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"container-title-short": "International Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"ijidonline.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-07T01:17:23Z",
"timestamp": 1673054243000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-07T03:37:46Z",
"timestamp": 1680838666000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100018592",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Celltrion"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-25T05:53:15Z",
"timestamp": 1698213195785
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 3,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1682899200000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-26T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1672012800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1201971222006749?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1201971222006749?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "94-100",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"article-title": "A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "727",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0001",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.envres.2021.112240",
"article-title": "The global transmission of new coronavirus variants",
"author": "Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Environ Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0002",
"volume": "206",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n1513",
"article-title": "Delta variant: what is happening with transmission, hospital admissions, and restrictions?",
"author": "Mahase",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "n1513",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0003",
"volume": "373",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.751778",
"article-title": "The global epidemic of the SARS-CoV-2 delta variant, key spike mutations and immune escape",
"author": "Tian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0004",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01358-1",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Delta VOC in Scotland: demographics, risk of hospital admission, and vaccine effectiveness",
"author": "Sheikh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2461",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0005",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7043e1",
"article-title": "Severity of disease among adults hospitalized with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 before and during the period of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 (Delta) predominance - COVID-NET, 14 states, January–August 2021",
"author": "Taylor",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1513",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0006",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0007",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Weekly epidemiological update on COVID-19 –26 October 2021, https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on-covid-19—26-october-2021; 2021 [accessed 01 November 2021]."
},
{
"article-title": "Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 infection with the Delta (B.1.617.2) variant: second interim results of a living systematic review and meta-analysis, 1 January to 25 August 2021",
"author": "Harder",
"journal-title": "Euro Surveill",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0008",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13091782",
"article-title": "Clinical characterization and genomic analysis of samples from COVID-19 breakthrough infections during the second wave among the various states of India",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1782",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0009",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/msb.202110396",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2-host proteome interactions for antiviral drug discovery",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e10396",
"journal-title": "Mol Syst Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0010",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00270-8",
"article-title": "Repurposing drugs for treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Venkatesan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e63",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0011",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.07.013",
"article-title": "Treatment and prevention strategies for the COVID 19 pandemic: a review of immunotherapeutic approaches for neutralizing SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Baral",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "490",
"journal-title": "Int J Biol Macromol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0012",
"volume": "186",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.05.005",
"article-title": "Tackling COVID-19 with neutralizing monoclonal antibodies",
"author": "Corti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3086",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0013",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-20602-5",
"article-title": "A therapeutic neutralizing antibody targeting receptor binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "288",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0014",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.09.023",
"article-title": "The in vitro and in vivo efficacy of CT-P59 against Gamma, Delta and its associated variants of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Ryu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "91",
"journal-title": "Biochem Biophys Res Commun",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0015",
"volume": "578",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clinthera.2021.08.009",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1706",
"journal-title": "Clin Ther",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0016",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0017",
"unstructured": "European Medicines Agency. Regkirona: EPAR - Public assessment report, https://www.ema.europa.eu/documents/product-information/regkirona-epar-product-information_en.pdf; 2021 [accessed 31 January 2022]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40265-021-01626-7",
"article-title": "Regdanvimab: first approval",
"author": "Syed",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2133",
"journal-title": "Drugs",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0018",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108570",
"article-title": "Regdanvimab in patients with mild-to-moderate SARS-CoV-2 infection: a propensity score–matched retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Int Immunopharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0019",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofac053",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of regdanvimab (CT-P59): a phase 2/3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in outpatients with mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Streinu-Cercel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "ofac053",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0020",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2102685",
"article-title": "Bamlanivimab plus etesevimab in mild or moderate Covid-19",
"author": "Dougan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1382",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0021",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2107934",
"article-title": "Early treatment for Covid-19 with SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody sotrovimab",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1941",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0022",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2035002",
"article-title": "REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with Covid-19",
"author": "Weinreich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "238",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0023",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0024",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Clinical management of COVID-19 patients: living guidance, https://app.magicapp.org/#/guideline/j1WBYn/section/L0bmdE; 2021 [accessed 01 February 2022]."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0025",
"unstructured": "Park AKK, I-H., Kim J-M, Lee N-J, Rhee JE, Kim E-J, Kim J, Kim JY, Gwak J, Kim E-K, Kim Y-M, Lee S-E, Park YJ. [COVID-19 special report]. Update 2021 status and characteristics of COVID-19 variant virus outbreak in the Republic of Korea, https://nih.go.kr/filepath/boardDownload.es?bid=0034&list_no=713840&seq=1; 2021 [accessed 14 February 2022]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00475-8",
"article-title": "Hospital admission and emergency care attendance risk for SARS-CoV-2 delta (B.1.617.2) compared with alpha (B.1.1.7) variants of concern: a cohort study",
"author": "Twohig",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "35",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0026",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03777-9",
"article-title": "Reduced sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 variant Delta to antibody neutralization",
"author": "Planas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "276",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0027",
"volume": "596",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13408",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of REGEN-COV antibody cocktail against the B.1.617.2 (delta) variant of SARS-CoV-2: a cohort study",
"author": "Kumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "380",
"journal-title": "J Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0028",
"volume": "291",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2021.105026",
"article-title": "Breakthrough COVID-19 and casirivimab-imdevimab treatment during a SARS-CoV-2 B1.617.2 (Delta) surge",
"author": "Bierle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Clin Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0029",
"volume": "145",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.12.002",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of monoclonal antibodies in preventing severe COVID-19 with emergence of the delta variant",
"author": "O'Horo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "327",
"journal-title": "Mayo Clin Proc",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0030",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0031",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Tracking SARS-CoV-2 variants, https://www.who.int/en/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants/; 2022 [accessed 02 August 2022]."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0032",
"unstructured": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The possibility of COVID-19 after vaccination: breakthrough infections, https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/effectiveness/why-measure-effectiveness/breakthrough-cases.html; 2021 [accessed 01 February 2022]."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0033",
"unstructured": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim clinical considerations for use of COVID-19 vaccines currently approved or authorized in the United States, https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/covid-19/clinical-considerations/covid-19-vaccines-us.html; 2022 [accessed 14 February 2022]."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035_bib0034",
"series-title": "Bioethics and Safety Act",
"year": "2014"
}
],
"reference-count": 34,
"references-count": 34,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1201971222006749"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Regdanvimab for patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study and subgroup analysis of patients with the Delta variant",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "130"
}