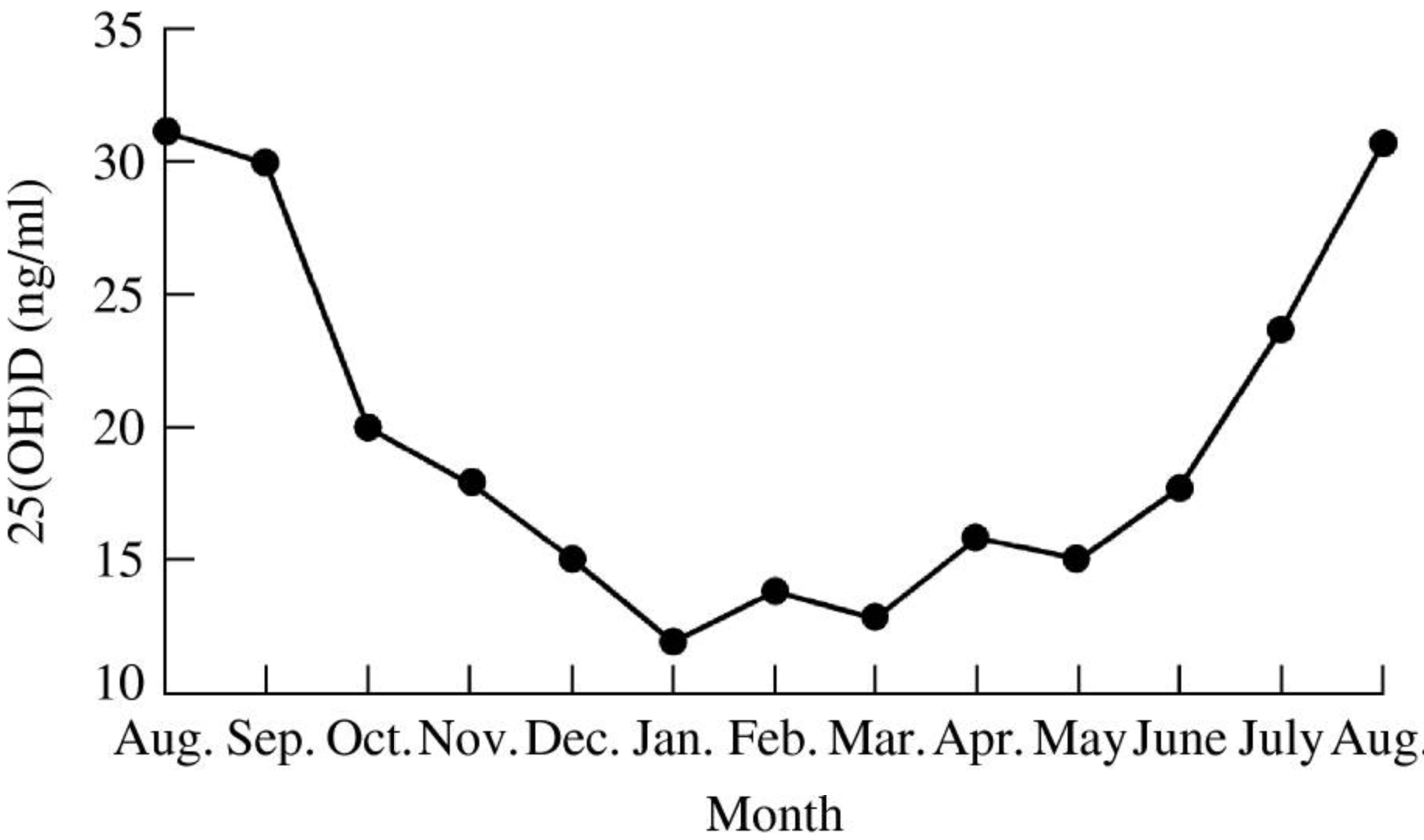
Epidemic influenza and vitamin D
et al., Epidemiol Infect., 2006, 134:6. 1129-40, doi:10.1017/S0950268806007175, Sep 2006
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Review article on the mechanisms of action and seasonality of vitamin D levels, concluding that varying vitamin D levels may be the reason for the seasonality of epidemic influenza.
1.
Jaurrieta-Largo et al., A Machine Learning Approach to Understanding the Genetic Role in COVID-19 Prognosis: The Influence of Gene Polymorphisms Related to Inflammation, Vitamin D, and ACE2, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms26167975.
2.
Al-Khrasani et al., Do vitamins halt the COVID-19-evoked pro-inflammatory cytokines involved in the development of neuropathic pain?, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2025.118346.
3.
Kow et al., Vitamin D and COVID‐19: How much more evidence do we need?, Nutrition in Clinical Practice, doi:10.1002/ncp.11349.
4.
Bigman et al., A Comprehensive Scoping Review on Diet and Nutrition in Relation to Long COVID-19 Symptoms and Recovery, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17111802.
5.
Hewison, M., COVID-19 and our understanding of vitamin D and immune function, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2025.106710.
6.
Wimalawansa, S., Vitamin D Deficiency Meets Hill’s Criteria for Causation in SARS-CoV-2 Susceptibility, Complications, and Mortality: A Systematic Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17030599.
7.
Sanduzzi Zamparelli et al., Immune-Boosting and Antiviral Effects of Antioxidants in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Therapeutic Perspective, Life, doi:10.3390/life15010113.
8.
Fazli et al., Possible Link between Gut Microbiota, Diet, and COVID-19 Infection, Journal of Medical Bacteriology, 12:4, jmb.tums.ac.ir/index.php/jmb/article/view/525.
9.
Wojciulik et al., The impact of genetic polymorphism on course and severity of the SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease, Przeglad Epidemiologiczny, doi:10.32394/pe/194862.
10.
Wimalawansa (B), S., Unveiling the Interplay—Vitamin D and ACE-2 Molecular Interactions in Mitigating Complications and Deaths from SARS-CoV-2, Biology, doi:10.3390/biology13100831.
11.
Santa et al., Comparative analysis of COVID-19 responses in Japan and Africa: diet, phytochemicals, vitamin D, and gut microbiota in reducing mortality—A systematic review and meta-analysis, Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1465324.
12.
Kaushal, A., Nutraceuticals and pharmacological to balance the transitional microbiome to extend immunity during COVID-19 and other viral infections, Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12967-024-05587-9.
13.
Mu et al., Anti-inflammatory and Nutritional Interventions Against SARS-CoV-2: A Comprehensive Review, Journal of Agriculture and Food Research, doi:10.1016/j.jafr.2024.101422.
14.
Wimalawansa (C), S., Unlocking Insights: Navigating COVID-19 Challenges and Emulating Future Pandemic Resilience Strategies with Strengthening Natural Immunity, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34691.
15.
Imran et al., Therapeutic Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19 Patients, Clinical Nutrition Open Science, doi:10.1016/j.nutos.2024.07.004.
16.
Grant, W., Vitamin D and viral infections: Infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases, and cancers, Advances in Food and Nutrition Research, doi:10.1016/bs.afnr.2023.12.007.
17.
Polonowita et al., Molecular Quantum and Logic Process of Consciousness—Vitamin D Big-Data in COVID-19—A Case for Incorporating Machine Learning In Medicine, European Journal of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical sciences, doi:10.5281/zenodo.10435649.
18.
Gomaa et al., Pharmacological evaluation of vitamin D in COVID-19 and long COVID-19: recent studies confirm clinical validation and highlight metformin to improve VDR sensitivity and efficacy, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01383-x.
19.
Gotelli et al., Understanding the immune-endocrine effects of vitamin D in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a role in protecting against neurodamage?, Neuroimmunomodulation, doi:10.1159/000533286.
20.
Cutolo et al., Involvement of the secosteroid vitamin D in autoimmune rheumatic diseases and COVID-19, Nature Reviews Rheumatology, doi:10.1038/s41584-023-00944-2.
21.
Schloss et al., Nutritional deficiencies that may predispose to long COVID, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01183-3.
22.
Arora et al., Global Dietary and Herbal Supplement Use during COVID-19—A Scoping Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15030771.
23.
Nicoll et al., COVID-19 Prevention: Vitamin D Is Still a Valid Remedy, Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm11226818.
24.
Foshati et al., Antioxidants and clinical outcomes of patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A systematic review of observational and interventional studies, Food Science & Nutrition, doi:10.1002/fsn3.3034.
25.
Quesada-Gomez et al., Vitamin D Endocrine System and COVID-19: Treatment with Calcifediol, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14132716.
26.
DiGuilio et al., Micronutrient Improvement of Epithelial Barrier Function in Various Disease States: A Case for Adjuvant Therapy, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms23062995.
27.
Grant (B) et al., A Narrative Review of the Evidence for Variations in Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentration Thresholds for Optimal Health, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14030639.
28.
Shah Alam et al., The role of vitamin D in reducing SARS-CoV-2 infection: An update, International Immunopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107686.
29.
Griffin et al., Perspective: Vitamin D supplementation prevents rickets and acute respiratory infections when given as daily maintenance but not as intermittent bolus: implications for COVID-19, Clinical Medicine, doi:10.7861/clinmed.2021-0035.
30.
Kohlmeier et al., When Mendelian randomisation fails, BMJ Nutrition, Prevention & Health, doi:10.1136/bmjnph-2021-000265.
31.
Brenner, H., Vitamin D Supplementation to Prevent COVID-19 Infections and Deaths—Accumulating Evidence from Epidemiological and Intervention Studies Calls for Immediate Action, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13020411.
32.
Mercola et al., Evidence Regarding Vitamin D and Risk of COVID-19 and Its Severity, Nutrients 2020, 12:11, 3361, doi:10.3390/nu12113361.
33.
Basha et al., Is the shielding effect of cholecalciferol in SARS CoV-2 infection dependable? An evidence based unraveling, Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health, doi:10.1016/j.cegh.2020.10.005.
34.
Xu et al., The importance of vitamin d metabolism as a potential prophylactic, immunoregulatory and neuroprotective treatment for COVID-19, Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12967-020-02488-5.
35.
Alexander et al., Early Nutritional Interventions with Zinc, Selenium and Vitamin D for Raising Anti-Viral Resistance Against Progressive COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12082358.
36.
Andrade et al., Vitamin A and D deficiencies in the prognosis of respiratory tract infections: A systematic review with perspectives for COVID-19 and a critical analysis on supplementation, SciELO preprints, doi:10.1590/SciELOPreprints.839.
37.
Grant (C) et al., Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients, 12:4, 988, doi:10.3390/nu12040988.
38.
McCullough et al., Daily oral dosing of vitamin D3 using 5000 TO 50,000 international units a day in long-term hospitalized patients: Insights from a seven year experience, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.12.010.
39.
EFSA, Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to vitamin D and normal function of the immune system and inflammatory response (ID 154, 159), maintenance of normal muscle function (ID 155) and maintenance of normal cardiovascular function (ID 159) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (E, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1468.
40.
EFSA (B), Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of a health claim related to vitamin D and contribution to the normal function of the immune system pursuant to Article 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2015.4096.
Cannell et al., 7 Sep 2006, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
Epidemic influenza and vitamin D
Epidemiology and Infection, doi:10.1017/s0950268806007175
In 1981, R. Edgar Hope-Simpson proposed that a 'seasonal stimulus ' intimately associated with solar radiation explained the remarkable seasonality of epidemic influenza. Solar radiation triggers robust seasonal vitamin D production in the skin ; vitamin D deficiency is common in the winter, and activated vitamin D, 1,25(OH) 2 D, a steroid hormone, has profound effects on human immunity. 1,25(OH) 2 D acts as an immune system modulator, preventing excessive expression of inflammatory cytokines and increasing the 'oxidative burst ' potential of macrophages. Perhaps most importantly, it dramatically stimulates the expression of potent anti-microbial peptides, which exist in neutrophils, monocytes, natural killer cells, and in epithelial cells lining the respiratory tract where they play a major role in protecting the lung from infection. Volunteers inoculated with live attenuated influenza virus are more likely to develop fever and serological evidence of an immune response in the winter. Vitamin D deficiency predisposes children to respiratory infections. Ultraviolet radiation (either from artificial sources or from sunlight) reduces the incidence of viral respiratory infections, as does cod liver oil (which contains vitamin D). An interventional study showed that vitamin D reduces the incidence of respiratory infections in children. We conclude that vitamin D, or lack of it, may be Hope-Simpson's 'seasonal stimulus '.
DECLARATION OF INTEREST Dr Cannell heads the non-profit educational group, ' The Vitamin D Council '.
References
Abu-Amer, Bar-Shavit, Impaired bone marrowderived macrophage differentiation in vitamin D deficiency, Cellular Immunology
Adams, Vitamin-D synthesis and metabolism after ultraviolet irradiation of normal and vitamin-D-deficient subjects, New England Journal of Medicine
Aloia, A randomized controlled trial of vitamin D3 supplementation in African American women, Archives of Internal Medicine
Alvensleben, Influenza according to Hoyle, Nature
Amento, Vitamin D and the immune system, Steroids
Andrewes, The Common Cold
Arias, from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National vital statistics reports
Aylin, Temperature, housing, deprivation and their relationship to excess winter mortality in Great Britain, 1986-1996, International Journal of Epidemiology
Banajeh, Sunbali, Sanahani, Clinical characteristics and outcome of children aged under 5 years hospitalized with severe pneumonia in Yemen, Annals of Tropical Paediatrics
Barger-Lux, Vitamin D and its major metabolites : serum levels after graded oral dosing in healthy men, Osteoporosis International
Beigel, Avian influenza A (H5N1) infection in humans, New England Journal of Medicine
Beisswenger, Bals, Antimicrobial peptides in lung inflammation, Chemical Immunology and Allergy
Beser, Cakmakci, Factors affecting the morbidity of vitamin D deficiency rickets and primary protection, East African Medical Journal
Bischoff-Ferrari, Higher 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are associated with better lowerextremity function in both active and inactive persons aged >or=60, American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
Brammer, Influenza surveillance -United States, 1992-93 and 1993-94. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, CDC Surveillance Summaries
Burns, Paterson, Single dose vitamin D treatment for osteomalacia in the elderly, British Medical Journal
Chan, Proinflammatory cytokine responses induced by influenza A (H5N1) viruses in primary human alveolar and bronchial epithelial cells, Respiratory Research
Cheung, Induction of proinflammatory cytokines in human macrophages by influenza A (H5N1) viruses : a mechanism for the unusual severity of human disease ?, Lancet
Cohen, 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 activates secretion of hydrogen peroxide by human monocytes, Journal of Immunology
Crighton, Influenza and pneumonia hospitalizations in Ontario : a time-series analysis, Epidemiology and Infection
Csato, Jablonski, Tronnier, Effect of ultraviolet irradiation on granulocyte chemotaxis and nitroblue tetrazolium reduction activity in healthy individuals, British Journal of Dermatology
Curwen, Excess winter mortality in England and Wales with special reference to the effects of temperature and influenza
Daher, Selsted, Lehrer, Direct inactivation of viruses by human granulocyte defensins, Journal of Virology
Diamond, Annual intramuscular injection of a megadose of cholecalciferol for treatment of vitamin D deficiency : efficacy and safety data, Medical Journal of Australia
Dowell, Mortality from pneumonia in children in the United States, 1939 through 1996, New England Journal of Medicine
Ebi, Association of normal weather periods and El Nino events with hospitalization for viral pneumonia in females : California, 1983-1998, American Journal of Public Health
Eccles, An explanation for the seasonality of acute upper respiratory tract viral infections, Acta Otolaryngologica
El-Radhi, High incidence of rickets in children with wheezy bronchitis in a developing country, Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine
Fox, Influenzavirus infections in Seattle families, 1975-1979. I. Study design, methods and the occurrence of infections by time and age, American Journal of Epidemiology
Ganz, Defensins : antimicrobial peptides of innate immunity, Nature Reviews. Immunology
Gigineishvili, The use of UV irradiation to correct the immune system and decrease morbidity in athletes
Glantz, Currents of Change : impacts of El Nino and La Nina on climate and society
Gombart, Borregaard, Koeffler, Human cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) gene is a direct target of the vitamin D receptor and is strongly up-regulated in myeloid cells by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, FASEB Journal
Gray, Robert Edgar Hope-Simpson, British Medical Journal
Hanley, Davison, Vitamin D insufficiency in North America, Journal of Nutrition
Hanneman, Cooper, Baron, Ultraviolet immunosuppression : mechanisms and consequences, Dermatology Clinics
Hayes, The immunological functions of the vitamin D endocrine system, Cellular and Molecular Biology
Heaney, Calcium absorption varies within the reference range for serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D, Journal of the American College of Nutrition
Heaney, The Vitamin D requirement in health and disease, Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
Helming, 1a,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is a potent suppressor of interferon c-mediated macrophage activation, Blood
Hewison, Vitamin D and barrier function : a novel role for extra-renal 1 alpha-hydroxylase, Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology
Hiemstra, Antimicrobial peptides: mediators of innate immunity as templates for the development of novel anti-infective and immune therapeutics, Current Pharmaceutical Design
Hirani, Primatesta, Vitamin D concentrations among people aged 65 years and over living in private households and institutions in England : population survey, Age and Ageing
Holick, High prevalence of vitamin D inadequacy and implications for health, Mayo Clinic Proceedings
Holick, McCollum Award Lecture, 1994: vitamin D -new horizons for the 21st century, American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
Holick, Photosynthesis of vitamin D in the skin: effect of environmental and life-style variables, Federation Proceedings
Holick, The vitamin D epidemic and its health consequences, Journal of Nutrition
Holmes, Vitamins aid reduction of lost time in industry, Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry
Homes, Cod liver oil -a five-year study of its value for reducing industrial absenteeism caused by colds and respiratory diseases, Industrial Medicine
Hope-Simpson, Sunspots and flu: a correlation, Nature
Hope-Simpson, The Transmission of Epidemic Influenza
Hope-Simpson, The nature of herpes zoster : a long-term study and a new hypothesis, Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine
Hope-Simpson, The role of season in the epidemiology of influenza, Journal of Hygiene
Horgan, Space invaders. Extra ! Extra ! Flu linked to sunspots!, Scientific American
Hoyle, Wickramasinghe, Sunspots and influenza, Nature
Johnson, Eccles, Acute cooling of the feet and the onset of common cold symptoms, Family Practice
Kobasa, Enhanced virulence of influenza A viruses with the haemagglutinin of the 1918 pandemic virus, Nature
Kochanek, from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National vital statistics reports
Kohn, Three summertime outbreaks of influenza type A, Journal of Infectious Diseases
Krause, Suberythemal UV-irradiation increases immunological capacity in children with frequent cold
Laake, Sverre, Winter excess mortality : a comparison between Norway and England plus Wales, Age and Ageing
Leino, Systemic suppression of human peripheral blood phagocytic leukocytes after whole-body UVB irradiation, Journal of Leukocyte Biology
Leung, Lui, Swaminathan, Vitamin D status of Hong Kong Chinese infants, Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica
Levis, Vitamin D deficiency and seasonal variation in an adult South Florida population, Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism
Lieberman, Lieberman, Friger, Seasonal variation in hospital admissions for communityacquired pneumonia : a 5-year study, Journal of Infection
Linday, Effect of daily cod liver oil and a multivitamin-mineral supplement with selenium on upper respiratory tract pediatric visits by young, innercity, Latino children : randomized pediatric sites, Annals of Otology, Rhinology, and Laryngology
Lips, A global study of vitamin D status and parathyroid function in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis : baseline data from the multiple outcomes of raloxifene evaluation clinical trial, Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism
Liu, Toll-like receptor triggering of a vitamin D-mediated human antimicrobial response, Science
Mariam, Sterky, Severe rickets in infancy and childhood in Ethiopia, Journal of Pediatrics
Marrie, Huang, Epidemiology of communityacquired pneumonia in Edmonton, Alberta: an emergency department-based study, Canadian Respiratory Journal: Journal of the Canadian Thoracic Society
Maxwell, Seasonal variation in vitamin D, Proceedings of the Nutrition Society
Mckenna, Differences in vitamin D status between countries in young adults and the elderly, American Medical Journal
Miller, Pereira, Clarke, Epidemiology of the Hong Kong-68 variant of influenza A2 in Britain, British Medical Journal
Minino, from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National vital statistics reports
Monto, Kioumehr, The Tecumseh Study of Respiratory Illness. IX. Occurence of influenza in the community, 1966-1971, American Journal of Epidemiology
Mosekilde, Vitamin D and the elderly, Clinical Endocrinology
Muhe, Case-control study of the role of nutritional rickets in the risk of developing pneumonia in Ethiopian children, Lancet
Najada, Habashneh, Khader, The frequency of nutritional rickets among hospitalized infants and its relation to respiratory diseases, Journal of Tropical Pediatrics
Noah, Cyclical patterns and predictability in infection, Epidemiology and Infection
Patwari, Pulmonary changes in rickets in children, Indian Pediatrics
Pitrez, Brennan, Sly, Inflammatory profile in nasal secretions of infants hospitalized with acute lower airway tract infections, Respirology
Poskitt, Cole, Lawson, Diet, sunlight, and 25-hydroxy vitamin D in healthy children and adults, British Medical Journal
Reddy, Yedery, Aranha, Antimicrobial peptides: premises and promises, International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents
Rehman, Sub-clinical rickets and recurrent infection, Journal of Tropical Pediatrics
Reichert, Influenza and the winter increase in mortality in the United States, 1959-1999, American Journal of Epidemiology
Rogan, Antimicrobial proteins and polypeptides in pulmonary innate defence, Respiratory Research, doi:10.1186/1465-9921-7-29
Rozema, Toward solving the UV puzzle, Science
Saynajakangas, Keistinen, Tuuponen, Seasonal fluctuations in hospitalisation for pneumonia in Finland, International Journal of Circumpolar Health
Scharla, Prevalence of subclinical vitamin D deficiency in different European countries, Osteoporosis International
Schutte, Pb, b-defensins in lung host defense, Annual Review of Physiology
Scragg, Seasonal variation of mortality in Queensland, Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health (Community Health Studies
Semba, Vitamin A as ' anti-infective ' therapy, 1920-1940, Journal of Nutrition
Shadrin, Marinich, Taros, Experimental and epidemiological estimation of seasonal and climatogeographical features of non-specific resistance of the organism to influenza, Journal of Hygiene, Epidemiology, Microbiology, and Immunology
Shek, Lee, Epidemiology and seasonality of respiratory tract virus infections in the tropics, Paediatric Respiratory Review
Shindell, Solar cycle variability, ozone, and climate, Science
Siddiqui, Rai, Presentation and predisposing factors of nutritional rickets in children of Hazara Division, Journal of Ayub Medical College
Sprenger, Impact of influenza on mortality in relation to age and underlying disease, 1967-1989, International Journal of Epidemiology
Sprenger, Influenza mortality and excess deaths in the elderly, 1967-82, Epidemiology and Infection
Termorshuizen, A review of studies on the effects of ultraviolet irradiation on the resistance to infections : evidence from rodent infection models and verification by experimental and observational human studies, International Immunopharmacology
Termorshuizen, Exposure to solar ultraviolet radiation and respiratory tract symptoms in 1-year-old children, Photodermatology, Photoimmunology and Photomedicine
Thacker, The persistence of influenza A in human populations, Epidemiology Reviews
Thomas, Hypovitaminosis D in medical inpatients, New England Journal of Medicine
Thompson, Influenza-associated hospitalizations in the United States, Journal of the American Medical Association
Van Der Wielen, Serum vitamin D concentrations among elderly people in Europe, Lancet
Viboud, Association of influenza epidemics with global climate variability, European Journal of Epidemiology
Vieth, Enzyme kinetics hypothesis to explain the U-shaped risk curve for prostate cancer vs. 25-hydroxyvitamin D in nordic countries, International Journal of Cancer
Vieth, Randomized comparison of the effects of the vitamin D3 adequate intake versus 100 mcg (4000 IU) per day on biochemical responses and the wellbeing of patients, Nutrition Journal
Vieth, Vitamin D supplementation, 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations, and safety, American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
Vieth, Wintertime vitamin D insufficiency is common in young Canadian women, and their vitamin D intake does not prevent it, European Journal of Clinical Nutrition
Wang, Cutting edge : 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is a direct inducer of antimicrobial peptide gene expression, Journal of Immunology
Wayse, Association of subclinical vitamin D deficiency with severe acute lower respiratory infection in Indian children under 5, European Journal of Clinical Nutrition
Webb, Kline, Holick, Influence of season and latitude on the cutaneous synthesis of vitamin D3 : exposure to winter sunlight in Boston and Edmonton will not promote vitamin D3 synthesis in human skin, Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism
Ws, A study of illness in a group of Cleveland families. XVII. The occurrence of Asian influenza, American Journal of Hygiene
Wu, Efficacy of an oral, 10-day course of high-dose calciferol in correcting vitamin D deficiency, New Zealand Medical Journal
Zadshir, The prevalence of hypovitaminosis D among US adults : data from the NHANES III, Ethnicity and Disease
Zittermann, Vitamin D in preventive medicine: are we ignoring the evidence ?, British Journal of Nutrition
Zykov, Sosunov, Vaccination activity of live influenza vaccine in different seasons of the year, Journal of Hygiene, Epidemiology, Microbiology, and Immunology
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1017/s0950268806007175",
"ISSN": [
"0950-2688",
"1469-4409"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0950268806007175",
"abstract": "<jats:p>In 1981, R. Edgar Hope-Simpson proposed that a ‘seasonal stimulus’ intimately associated with solar radiation explained the remarkable seasonality of epidemic influenza. Solar radiation triggers robust seasonal vitamin D production in the skin; vitamin D deficiency is common in the winter, and activated vitamin D, 1,25(OH)<jats:sub>2</jats:sub>D, a steroid hormone, has profound effects on human immunity. 1,25(OH)<jats:sub>2</jats:sub>D acts as an immune system modulator, preventing excessive expression of inflammatory cytokines and increasing the ‘oxidative burst’ potential of macrophages. Perhaps most importantly, it dramatically stimulates the expression of potent anti-microbial peptides, which exist in neutrophils, monocytes, natural killer cells, and in epithelial cells lining the respiratory tract where they play a major role in protecting the lung from infection. Volunteers inoculated with live attenuated influenza virus are more likely to develop fever and serological evidence of an immune response in the winter. Vitamin D deficiency predisposes children to respiratory infections. Ultraviolet radiation (either from artificial sources or from sunlight) reduces the incidence of viral respiratory infections, as does cod liver oil (which contains vitamin D). An interventional study showed that vitamin D reduces the incidence of respiratory infections in children. We conclude that vitamin D, or lack of it, may be Hope-Simpson's ‘seasonal stimulus’.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"S0950268806007175"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "CANNELL",
"given": "J. J.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "VIETH",
"given": "R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "UMHAU",
"given": "J. C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "HOLICK",
"given": "M. F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "GRANT",
"given": "W. B.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "MADRONICH",
"given": "S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "GARLAND",
"given": "C. F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "GIOVANNUCCI",
"given": "E.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Epidemiology and Infection",
"container-title-short": "Epidemiol. Infect.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2006,
9,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2006-09-07T14:30:16Z",
"timestamp": 1157639416000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2019,
5,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2019-05-02T19:30:49Z",
"timestamp": 1556825449000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-14T18:41:13Z",
"timestamp": 1715712073149
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 719,
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2006,
9,
7
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2006,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.cambridge.org/core/terms",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2006,
9,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2006-09-07T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1157587200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.cambridge.org/core/services/aop-cambridge-core/content/view/S0950268806007175",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "56",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1129-1140",
"prefix": "10.1017",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2006,
9,
7
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2006,
9,
7
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2006,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cambridge University Press (CUP)",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.cambridge.org/core/product/identifier/S0950268806007175/type/journal_article"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Epidemic influenza and vitamin D",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "134"
}
