Vitamin A and D deficiencies in the prognosis of respiratory tract infections: A systematic review with perspectives for COVID-19 and a critical analysis on supplementation
et al., SciELO preprints, doi:10.1590/SciELOPreprints.839, Jun 2020
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Systematic review showing deficiencies of vitamins A and D negatively affecting the prognosis of respiratory tract infections.
Review covers vitamin D and vitamin A.
1.
Jaurrieta-Largo et al., A Machine Learning Approach to Understanding the Genetic Role in COVID-19 Prognosis: The Influence of Gene Polymorphisms Related to Inflammation, Vitamin D, and ACE2, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms26167975.
2.
Al-Khrasani et al., Do vitamins halt the COVID-19-evoked pro-inflammatory cytokines involved in the development of neuropathic pain?, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2025.118346.
3.
Kow et al., Vitamin D and COVID‐19: How much more evidence do we need?, Nutrition in Clinical Practice, doi:10.1002/ncp.11349.
4.
Bigman et al., A Comprehensive Scoping Review on Diet and Nutrition in Relation to Long COVID-19 Symptoms and Recovery, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17111802.
5.
Hewison, M., COVID-19 and our understanding of vitamin D and immune function, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2025.106710.
6.
Wimalawansa, S., Vitamin D Deficiency Meets Hill’s Criteria for Causation in SARS-CoV-2 Susceptibility, Complications, and Mortality: A Systematic Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17030599.
7.
Sanduzzi Zamparelli et al., Immune-Boosting and Antiviral Effects of Antioxidants in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Therapeutic Perspective, Life, doi:10.3390/life15010113.
8.
Fazli et al., Possible Link between Gut Microbiota, Diet, and COVID-19 Infection, Journal of Medical Bacteriology, 12:4, jmb.tums.ac.ir/index.php/jmb/article/view/525.
9.
Wojciulik et al., The impact of genetic polymorphism on course and severity of the SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease, Przeglad Epidemiologiczny, doi:10.32394/pe/194862.
10.
Wimalawansa (B), S., Unveiling the Interplay—Vitamin D and ACE-2 Molecular Interactions in Mitigating Complications and Deaths from SARS-CoV-2, Biology, doi:10.3390/biology13100831.
11.
Santa et al., Comparative analysis of COVID-19 responses in Japan and Africa: diet, phytochemicals, vitamin D, and gut microbiota in reducing mortality—A systematic review and meta-analysis, Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1465324.
12.
Kaushal, A., Nutraceuticals and pharmacological to balance the transitional microbiome to extend immunity during COVID-19 and other viral infections, Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12967-024-05587-9.
13.
Mu et al., Anti-inflammatory and Nutritional Interventions Against SARS-CoV-2: A Comprehensive Review, Journal of Agriculture and Food Research, doi:10.1016/j.jafr.2024.101422.
14.
Wimalawansa (C), S., Unlocking Insights: Navigating COVID-19 Challenges and Emulating Future Pandemic Resilience Strategies with Strengthening Natural Immunity, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34691.
15.
Imran et al., Therapeutic Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19 Patients, Clinical Nutrition Open Science, doi:10.1016/j.nutos.2024.07.004.
16.
Grant, W., Vitamin D and viral infections: Infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases, and cancers, Advances in Food and Nutrition Research, doi:10.1016/bs.afnr.2023.12.007.
17.
Polonowita et al., Molecular Quantum and Logic Process of Consciousness—Vitamin D Big-Data in COVID-19—A Case for Incorporating Machine Learning In Medicine, European Journal of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical sciences, doi:10.5281/zenodo.10435649.
18.
Gomaa et al., Pharmacological evaluation of vitamin D in COVID-19 and long COVID-19: recent studies confirm clinical validation and highlight metformin to improve VDR sensitivity and efficacy, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01383-x.
19.
Gotelli et al., Understanding the immune-endocrine effects of vitamin D in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a role in protecting against neurodamage?, Neuroimmunomodulation, doi:10.1159/000533286.
20.
Cutolo et al., Involvement of the secosteroid vitamin D in autoimmune rheumatic diseases and COVID-19, Nature Reviews Rheumatology, doi:10.1038/s41584-023-00944-2.
21.
Schloss et al., Nutritional deficiencies that may predispose to long COVID, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01183-3.
22.
Arora et al., Global Dietary and Herbal Supplement Use during COVID-19—A Scoping Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15030771.
23.
Nicoll et al., COVID-19 Prevention: Vitamin D Is Still a Valid Remedy, Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm11226818.
24.
Foshati et al., Antioxidants and clinical outcomes of patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A systematic review of observational and interventional studies, Food Science & Nutrition, doi:10.1002/fsn3.3034.
25.
Quesada-Gomez et al., Vitamin D Endocrine System and COVID-19: Treatment with Calcifediol, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14132716.
26.
DiGuilio et al., Micronutrient Improvement of Epithelial Barrier Function in Various Disease States: A Case for Adjuvant Therapy, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms23062995.
27.
Grant (B) et al., A Narrative Review of the Evidence for Variations in Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentration Thresholds for Optimal Health, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14030639.
28.
Shah Alam et al., The role of vitamin D in reducing SARS-CoV-2 infection: An update, International Immunopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107686.
29.
Griffin et al., Perspective: Vitamin D supplementation prevents rickets and acute respiratory infections when given as daily maintenance but not as intermittent bolus: implications for COVID-19, Clinical Medicine, doi:10.7861/clinmed.2021-0035.
30.
Kohlmeier et al., When Mendelian randomisation fails, BMJ Nutrition, Prevention & Health, doi:10.1136/bmjnph-2021-000265.
31.
Brenner, H., Vitamin D Supplementation to Prevent COVID-19 Infections and Deaths—Accumulating Evidence from Epidemiological and Intervention Studies Calls for Immediate Action, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13020411.
32.
Mercola et al., Evidence Regarding Vitamin D and Risk of COVID-19 and Its Severity, Nutrients 2020, 12:11, 3361, doi:10.3390/nu12113361.
33.
Basha et al., Is the shielding effect of cholecalciferol in SARS CoV-2 infection dependable? An evidence based unraveling, Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health, doi:10.1016/j.cegh.2020.10.005.
34.
Xu et al., The importance of vitamin d metabolism as a potential prophylactic, immunoregulatory and neuroprotective treatment for COVID-19, Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12967-020-02488-5.
35.
Alexander et al., Early Nutritional Interventions with Zinc, Selenium and Vitamin D for Raising Anti-Viral Resistance Against Progressive COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12082358.
36.
Andrade et al., Vitamin A and D deficiencies in the prognosis of respiratory tract infections: A systematic review with perspectives for COVID-19 and a critical analysis on supplementation, SciELO preprints, doi:10.1590/SciELOPreprints.839.
37.
Grant (C) et al., Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients, 12:4, 988, doi:10.3390/nu12040988.
38.
McCullough et al., Daily oral dosing of vitamin D3 using 5000 TO 50,000 international units a day in long-term hospitalized patients: Insights from a seven year experience, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.12.010.
39.
EFSA, Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to vitamin D and normal function of the immune system and inflammatory response (ID 154, 159), maintenance of normal muscle function (ID 155) and maintenance of normal cardiovascular function (ID 159) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (E, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1468.
40.
EFSA (B), Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of a health claim related to vitamin D and contribution to the normal function of the immune system pursuant to Article 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2015.4096.
Andrade et al., 24 Jun 2020, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
Vitamin A and D deficiencies in the prognosis of respiratory tract infections: A systematic review with perspectives for COVID-19 and a critical analysis on supplementation Vitamin A and D deficiencies: Perspectives for COVID-19
Individual Collaboration: Maria Izabel Siqueira de Andrade: study design, bibliographic search, database construction, data analysis, interpretation of results, writing, review and approval of the final version of the manuscript. Patrícia Fortes Cavalcanti de Macêdo: study design, bibliographic search, database construction, data analysis, interpretation of results, writing, review and approval of the final version of the manuscript. Tafnes Laís Pereira Santos de Oliveira: study design, bibliographic search, database construction, data analysis, interpretation of results, writing, review and approval of the final version of the manuscript. Niedja Maria da Silva Lima: study design, bibliographic search, database construction, data analysis, review and approval of the final version. Isabella da Costa Ribeiro: data analysis, writing, review and approval of the final version of the manuscript. Thayná Menezes Santos: bibliographic search, data analysis, review and approval of the final version.
References
Aglipay, Birken, Parkin, Loeb, Thorpe et al., Effect of high-dose vs standard-dose wintertime vitamin D supplementation on viral upper respiratory tract infections in young healthy children, Jama
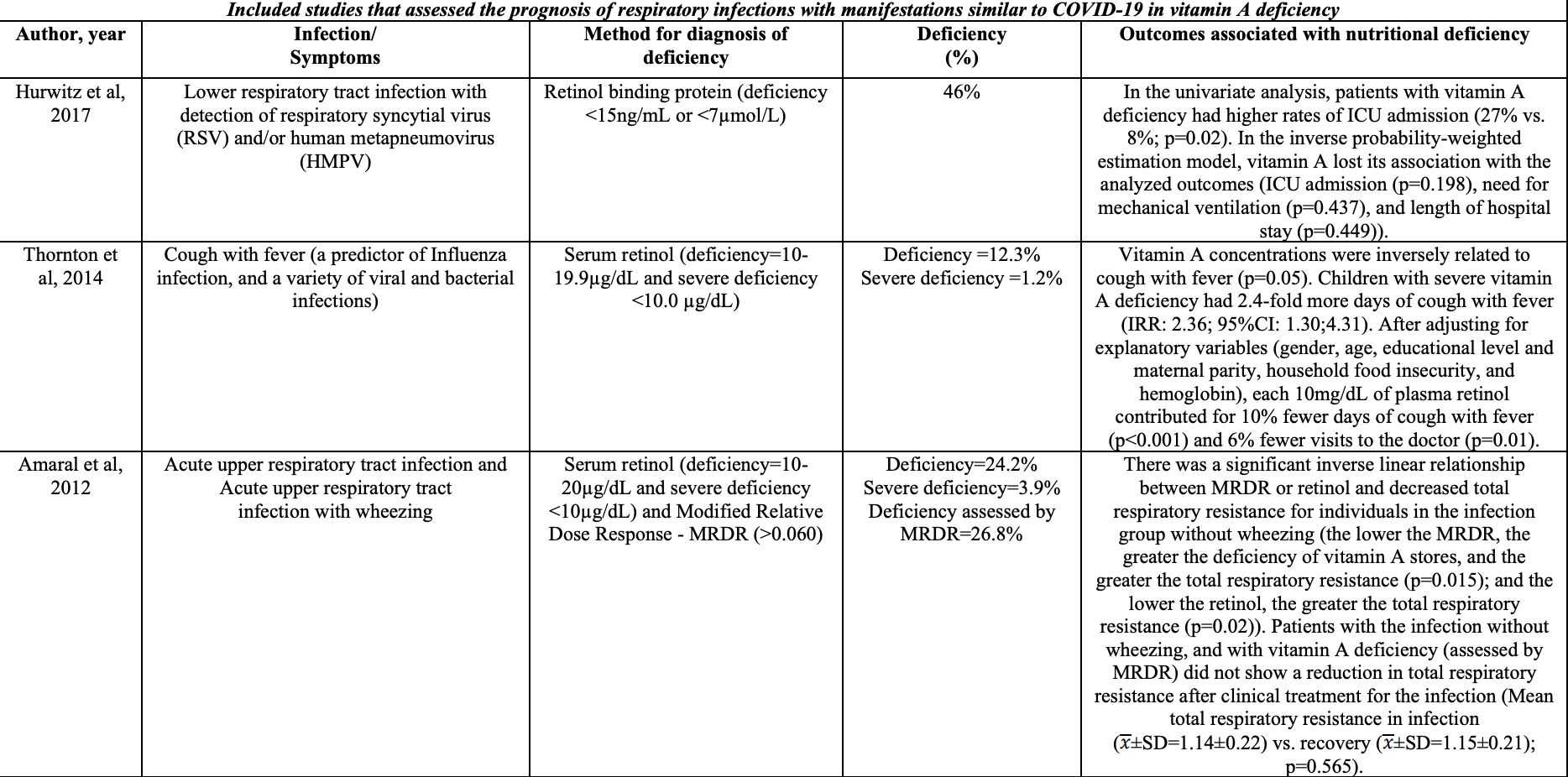
Amaral, Pontes, Maciel, Bezerra, Triesta et al., Vitamin A deficiency alters airway resistance in children with acute upper respiratory infection, Pediatr Pulmonol
Bailey, Jr, Black, The epidemiology of global micronutrient deficiencies, Ann Nutr Metab
Barbosa, Cunha, Jr, Weffort, Cunha, Transient decreased retinol serum levels in children with pneumonia and acute phase response, J Pediatr
Brance, Miljevic, Tizziani, Taberna, Grossi, Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in hospitalized adults with community-acquired pneumonia, Clin Respir J
Calder, Carr, Gombart, Eggersdorfer, Optimal nutritional status for a well-functioning immune system is an important factor to protect against viral infections, Nutrients
Cebey-López, Pardo-Seco, Gómez-Carballa, Martinón-Torres, Rivero-Calle et al., Role of vitamin D in hospitalized children with lower tract acute respiratory infections, J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr
Chen, Zhuo, Yuan, Wang, Wu, Vitamin A for preventing acute lower respiratory tract infections in children up to seven years of age, Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Childs, Calder, Miles, Diet and Immune Function, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu11081933
Choudhary, Gupta, Vitamin D supplementation for severe pneumonia-a randomized controlled trial, Indian Pediatr
Darnton-Hill, Public Health Aspects in the Prevention and Control of Vitamin Deficiencies, Curr Dev Nutr
De Carvalho, De Almeida Fonsêca, Priore, Franceschini, Do et al., Food consumption and nutritional adequacy in Brazilian children: a systematic review, Rev Paul Pediatr
Dong, Li, Bai, Liu, Zhou et al., Epidemiological characteristics of confirmed COVID-19 cases in Tianjin. Zhonghua liu Xing Bing xue, za zhi= Zhonghua Liuxingbingxue Zazhi
Gombart, Pierre, Maggini, A Review of Micronutrients and the Immune System-Working in Harmony to Reduce the Risk of Infection, Nutrients
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients
Guillin, Vindry, Ohlmann, Chavatte, Selenium, Selenoproteins and Viral Infection, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu11092101
Health Organization, Assessing the iron status of populations: report of a Joint World Health Organization/Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Technical Consultation on the Assessment of Iron Status at the Population Level
Huang, Lu, Li, Wang, Does comorbidity increase the risk of patients with COVID-19: evidence from meta-analysis, Aging
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Hurwitz, Jones, Penkert, Gansebom, Sun et al., Low retinol-binding protein and vitamin D levels are associated with severe outcomes in children hospitalized with lower respiratory tract infection and respiratory syncytial virus or human metapneumovirus detection, J Pediatr
Inamo, Hasegawa, Saito, Hayashi, Ishikawa et al., Serum vitamin D concentrations and associated severity of acute lower respiratory tract infections in Japanese hospitalized children, Pediatr Int
Kim, Jang, Hong, Park, Choi, Relationship between serum vitamin D concentrations and clinical outcome of community-acquired pneumonia, Int J Tuberc Lung Dis
Liberati, Altman, Tetzlaff, Mulrow, Gøtzsche et al., The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration, Ann Intern Med
Loeb, Dang, Thiem, Thanabalan, Wang et al., Effect of vitamin D supplementation to reduce respiratory infections in children and adolescents in Vietnam: a randomized controlled trial, Influenza Other Respi Viruses
Malta, Cardoso, Bastos, Magnanini, Silva et al., STROBE initiative: guidelines on reporting observational studies, Rev Saude Publica
Mamani, Muceli, Basir, Vasheghani, Poorolajal, Association between serum concentration of 25-hydroxyvitamin D and community-acquired pneumonia: A case-control study, Int J Gen Med
Manaseki-Holland, Qader, Masher, Bruce, Mughal et al., Effects of vitamin D supplementation to children diagnosed with pneumonia in Kabul: a randomised controlled trial, Trop Med Int Heal
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ
Mawson, Role of Fat-Soluble Vitamins A and D in the Pathogenesis of Influenza: A New Perspective, ISRN Infect Dis
Ministério, da Saúde. Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde. Centro de Operações em, New Coronavirus Disease
Naja, Hamadeh, Nutrition amid the COVID-19 pandemic: a multi-level framework for action, Eur J Clin Nutr
Qi, Niu, Zhu, Zhao, Yang et al., Relationship between deficiencies in vitamin A and E and occurrence of infectious diseases among children, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci
Saghazadeh, Rezaei, Immune-epidemiological parameters of the novel coronavirus-a perspective, Expert Rev Clin Immunol
Thornton, Mora-Plazas, Marín, Villamor, Vitamin A deficiency is associated with gastrointestinal and respiratory morbidity in school-age children, J Nutr
Thurnham, Mccabe, Clewes, Nestel, Effects of subclinical infection on plasma retinol concentrations and assessment of prevalence of vitamin A deficiency: meta-analysis, Lancet
Urashima, Segawa, Okazaki, Kurihara, Wada et al., Randomized trial of vitamin D supplementation to prevent seasonal influenza A in schoolchildren, Am J Clin Nutr
Xu, Fang, Perera, Kam, Ng et al., Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Was Not Associated with Influenza Virus Infection in Children and Adults in Hong Kong, 2009-2010, J Nutr, doi:10.3945/jn.116.234856
Xu, Fang, Perera, Kam, Ng et al., Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Was Not Associated with Influenza Virus Infection in Children and Adults in Hong Kong, 2009-2010, J Nutr, doi:10.3945/jn.116.234856
Zhang, Liu, Potential interventions for novel coronavirus in China: a systemic review, J Med Virol
Zhu, Wang, Huang, Liu, Zhao et al., Clinical characteristics of a case series of children with coronavirus disease 2019, Pediatr Pulmonol
Zhu, Zhang, Li, Yang, Song, A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019, N Engl J Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1590/scielopreprints.839",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/SciELOPreprints.839",
"abstract": "<jats:p>OBJECTIVE: Considering the rapid spread of COVID-19, the scientific community has been looking for ways to recognize factors that may interfere with the outcome of viral infection. Despite the lack of studies with the new coronavirus, it is known that adequate serum levels of micronutrients are essential for the organic response to infectious diseases. Thus, we aim to review the effects of vitamin A, D, iron, zinc, or folate deficiency on the prognosis of patients with respiratory infections with manifestations similar to COVID-19 and discuss about supplementation of the nutrients analyzed in this review. METHODS: The search was conducted in the databases PubMed, Lilacs, and SciELO, including observational studies published between 2010-2020, with results for individuals with respiratory tract infections with manifestations similar to COVID-19. RESULTS: Six articles met the inclusion criteria, all of which were related to deficiencies of vitamins A and D. In general, vitamin A deficiency was associated with cough, fever, and greater total respiratory resistance. Regarding vitamin D, the lack of this nutrient led to higher rates of ICU admission, the need for mechanical ventilation, and mortality. Evidence linking specific relationships between nutritional deficiencies and COVID-19 remain lacking due to the small number of studies and heterogeneities in population subgroups. CONCLUSION: In conclusion, deficiencies of vitamins A and D seem to negatively affect the prognosis of respiratory tract infections. Supplementation of these nutrients for prevention or treatment of patients diagnosed with COVID-19 should respect serum levels, nutritional status and housing conditions (e.g.,endemic location) of individuals.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1087-1320",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Andrade",
"given": "Maria Izabel Siqueira de",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2728-0431",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Macêdo",
"given": "Patrícia Fortes Cavalcanti de",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5904-8557",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Oliveira",
"given": "Tafnes Laís Pereira Santos de",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5185-1636",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Lima",
"given": "Niedja Maria da Silva",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3817-2073",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ribeiro",
"given": "Isabella da Costa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2920-2373",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Santos",
"given": "Thayná Menezes",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2020-06-24T19:29:12Z",
"timestamp": 1593026952000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-20T19:21:01Z",
"timestamp": 1642706461000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-16T07:36:17Z",
"timestamp": 1692171377110
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 2,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
28
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2020-06-28T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1593302400000
}
}
],
"member": "530",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
28
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1590",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
28
]
]
},
"publisher": "FapUNIFESP (SciELO)",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://preprints.scielo.org/index.php/scielo/preprint/view/839/version/913"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Vitamin A and D deficiencies in the prognosis of respiratory tract infections: A systematic review with perspectives for COVID-19 and a critical analysis on supplementation",
"type": "posted-content"
}
