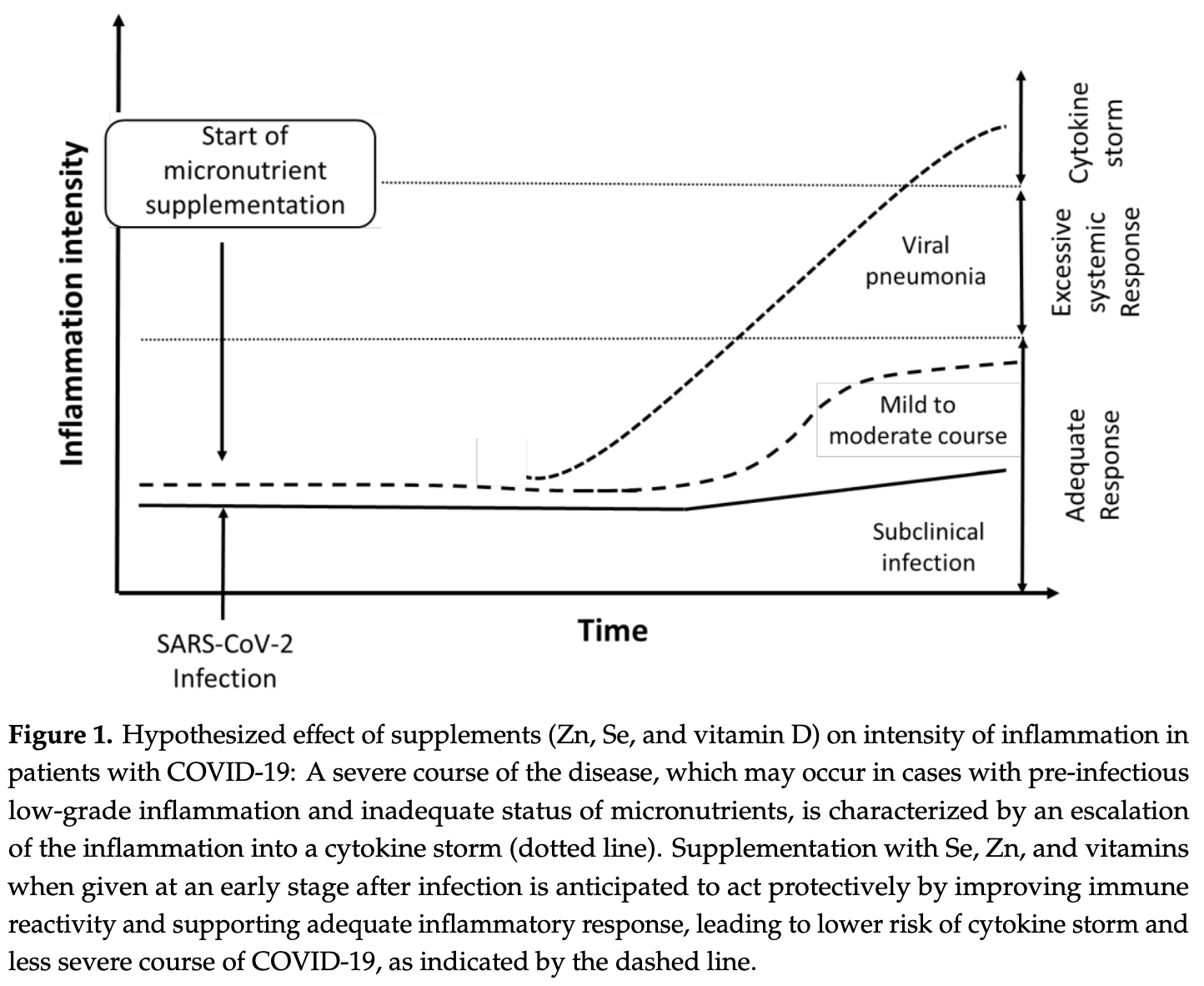
Early Nutritional Interventions with Zinc, Selenium and Vitamin D for Raising Anti-Viral Resistance Against Progressive COVID-19
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12082358, Aug 2020
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Review exploring the potential of early nutritional intervention with zinc, selenium and vitamin D to prevent progression of COVID-19, based on the importance of these micronutrients for anti-viral resistance and reduced inflammation. Authors recommend early initiation of supplementation in high-risk areas and soon after suspected infection, particularly for high-risk groups, based on previous research showing the importance of these micronutrients for other respiratory infections and inflammatory conditions.
1.
Jaurrieta-Largo et al., A Machine Learning Approach to Understanding the Genetic Role in COVID-19 Prognosis: The Influence of Gene Polymorphisms Related to Inflammation, Vitamin D, and ACE2, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms26167975.
2.
Al-Khrasani et al., Do vitamins halt the COVID-19-evoked pro-inflammatory cytokines involved in the development of neuropathic pain?, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2025.118346.
3.
Kow et al., Vitamin D and COVID‐19: How much more evidence do we need?, Nutrition in Clinical Practice, doi:10.1002/ncp.11349.
4.
Bigman et al., A Comprehensive Scoping Review on Diet and Nutrition in Relation to Long COVID-19 Symptoms and Recovery, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17111802.
5.
Hewison, M., COVID-19 and our understanding of vitamin D and immune function, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2025.106710.
6.
Wimalawansa, S., Vitamin D Deficiency Meets Hill’s Criteria for Causation in SARS-CoV-2 Susceptibility, Complications, and Mortality: A Systematic Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17030599.
7.
Sanduzzi Zamparelli et al., Immune-Boosting and Antiviral Effects of Antioxidants in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Therapeutic Perspective, Life, doi:10.3390/life15010113.
8.
Fazli et al., Possible Link between Gut Microbiota, Diet, and COVID-19 Infection, Journal of Medical Bacteriology, 12:4, jmb.tums.ac.ir/index.php/jmb/article/view/525.
9.
Wojciulik et al., The impact of genetic polymorphism on course and severity of the SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease, Przeglad Epidemiologiczny, doi:10.32394/pe/194862.
10.
Wimalawansa (B), S., Unveiling the Interplay—Vitamin D and ACE-2 Molecular Interactions in Mitigating Complications and Deaths from SARS-CoV-2, Biology, doi:10.3390/biology13100831.
11.
Santa et al., Comparative analysis of COVID-19 responses in Japan and Africa: diet, phytochemicals, vitamin D, and gut microbiota in reducing mortality—A systematic review and meta-analysis, Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1465324.
12.
Kaushal, A., Nutraceuticals and pharmacological to balance the transitional microbiome to extend immunity during COVID-19 and other viral infections, Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12967-024-05587-9.
13.
Mu et al., Anti-inflammatory and Nutritional Interventions Against SARS-CoV-2: A Comprehensive Review, Journal of Agriculture and Food Research, doi:10.1016/j.jafr.2024.101422.
14.
Wimalawansa (C), S., Unlocking Insights: Navigating COVID-19 Challenges and Emulating Future Pandemic Resilience Strategies with Strengthening Natural Immunity, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34691.
15.
Imran et al., Therapeutic Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19 Patients, Clinical Nutrition Open Science, doi:10.1016/j.nutos.2024.07.004.
16.
Grant, W., Vitamin D and viral infections: Infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases, and cancers, Advances in Food and Nutrition Research, doi:10.1016/bs.afnr.2023.12.007.
17.
Polonowita et al., Molecular Quantum and Logic Process of Consciousness—Vitamin D Big-Data in COVID-19—A Case for Incorporating Machine Learning In Medicine, European Journal of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical sciences, doi:10.5281/zenodo.10435649.
18.
Gomaa et al., Pharmacological evaluation of vitamin D in COVID-19 and long COVID-19: recent studies confirm clinical validation and highlight metformin to improve VDR sensitivity and efficacy, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01383-x.
19.
Gotelli et al., Understanding the immune-endocrine effects of vitamin D in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a role in protecting against neurodamage?, Neuroimmunomodulation, doi:10.1159/000533286.
20.
Cutolo et al., Involvement of the secosteroid vitamin D in autoimmune rheumatic diseases and COVID-19, Nature Reviews Rheumatology, doi:10.1038/s41584-023-00944-2.
21.
Schloss et al., Nutritional deficiencies that may predispose to long COVID, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01183-3.
22.
Arora et al., Global Dietary and Herbal Supplement Use during COVID-19—A Scoping Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15030771.
23.
Nicoll et al., COVID-19 Prevention: Vitamin D Is Still a Valid Remedy, Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm11226818.
24.
Foshati et al., Antioxidants and clinical outcomes of patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A systematic review of observational and interventional studies, Food Science & Nutrition, doi:10.1002/fsn3.3034.
25.
Quesada-Gomez et al., Vitamin D Endocrine System and COVID-19: Treatment with Calcifediol, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14132716.
26.
DiGuilio et al., Micronutrient Improvement of Epithelial Barrier Function in Various Disease States: A Case for Adjuvant Therapy, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms23062995.
27.
Grant (B) et al., A Narrative Review of the Evidence for Variations in Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentration Thresholds for Optimal Health, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14030639.
28.
Shah Alam et al., The role of vitamin D in reducing SARS-CoV-2 infection: An update, International Immunopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107686.
29.
Griffin et al., Perspective: Vitamin D supplementation prevents rickets and acute respiratory infections when given as daily maintenance but not as intermittent bolus: implications for COVID-19, Clinical Medicine, doi:10.7861/clinmed.2021-0035.
30.
Kohlmeier et al., When Mendelian randomisation fails, BMJ Nutrition, Prevention & Health, doi:10.1136/bmjnph-2021-000265.
31.
Brenner, H., Vitamin D Supplementation to Prevent COVID-19 Infections and Deaths—Accumulating Evidence from Epidemiological and Intervention Studies Calls for Immediate Action, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13020411.
32.
Mercola et al., Evidence Regarding Vitamin D and Risk of COVID-19 and Its Severity, Nutrients 2020, 12:11, 3361, doi:10.3390/nu12113361.
33.
Basha et al., Is the shielding effect of cholecalciferol in SARS CoV-2 infection dependable? An evidence based unraveling, Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health, doi:10.1016/j.cegh.2020.10.005.
34.
Xu et al., The importance of vitamin d metabolism as a potential prophylactic, immunoregulatory and neuroprotective treatment for COVID-19, Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12967-020-02488-5.
35.
Alexander et al., Early Nutritional Interventions with Zinc, Selenium and Vitamin D for Raising Anti-Viral Resistance Against Progressive COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12082358.
36.
Andrade et al., Vitamin A and D deficiencies in the prognosis of respiratory tract infections: A systematic review with perspectives for COVID-19 and a critical analysis on supplementation, SciELO preprints, doi:10.1590/SciELOPreprints.839.
37.
Grant (C) et al., Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients, 12:4, 988, doi:10.3390/nu12040988.
38.
McCullough et al., Daily oral dosing of vitamin D3 using 5000 TO 50,000 international units a day in long-term hospitalized patients: Insights from a seven year experience, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.12.010.
39.
EFSA, Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to vitamin D and normal function of the immune system and inflammatory response (ID 154, 159), maintenance of normal muscle function (ID 155) and maintenance of normal cardiovascular function (ID 159) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (E, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1468.
40.
EFSA (B), Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of a health claim related to vitamin D and contribution to the normal function of the immune system pursuant to Article 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2015.4096.
Alexander et al., 7 Aug 2020, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
Contact: urban.alehagen@liu.se (corresponding author), jan.alexander@fhi.no, tinkov.a.a@gmail.com, skalny3@gmail.com, jaol-aas@online.no, tors@me.com.
Early Nutritional Interventions with Zinc, Selenium and Vitamin D for Raising Anti-Viral Resistance Against Progressive COVID-19
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12082358
Objectives: The novel coronavirus infection (COVID-19) conveys a serious threat globally to health and economy because of a lack of vaccines and specific treatments. A common factor for conditions that predispose for serious progress is a low-grade inflammation, e.g., as seen in metabolic syndrome, diabetes, and heart failure, to which micronutrient deficiencies may contribute. The aim of the present article was to explore the usefulness of early micronutrient intervention, with focus on zinc, selenium, and vitamin D, to relieve escalation of COVID-19. Methods: We conducted an online search for articles published in the period 2010-2020 on zinc, selenium, and vitamin D, and corona and related virus infections. Results: There were a few studies providing direct evidence on associations between zinc, selenium, and vitamin D, and COVID-19. Adequate supply of zinc, selenium, and vitamin D is essential for resistance to other viral infections, immune function, and reduced inflammation. Hence, it is suggested that nutrition intervention securing an adequate status might protect against the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome -coronavirus-2) and mitigate the course of COVID-19. Conclusion: We recommended initiation of adequate supplementation in high-risk areas and/or soon after the time of suspected infection with SARS-CoV-2. Subjects in high-risk groups should have high priority as regards this nutritive adjuvant therapy, which should be started prior to administration of specific and supportive medical measures.
Author Contributions: J.A. (Jan Aaseth) and J.A. (Jan Alexander) searched the literature and prepared the first draft. All authors contributed equally to writing additional text, review and editing of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest: One of the authors (U.A.) received support from Pharma Nord ApS, Denmark for a previous study. Authors J.A. (Jan Alexander), A.T., T.A.S., A.S., and J.A. (Jan Aaseth) declare no conflicts of interests. Author Contributions: J.A. (Jan Aaseth) and J.A. (Jan Alexander) searched the literature and prepared the first draft. All authors contributed equally to writing additional text, review and editing of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest: One of the authors (U.A.) received support from Pharma Nord ApS, Denmark for a previous study. Authors J.A. (Jan Alexander), A.T., T.A.S., A.S., and J.A. (Jan Aaseth) declare no conflicts of interests.
References
Alehagen, Alexander, Aaseth, Larsson, Decrease in inflammatory biomarker concentration by intervention with selenium and coenzyme Q10: A subanalysis of osteopontin, osteoprotergerin, TNFr1, TNFr2 and TWEAK, J. Inflamm, doi:10.1186/s12950-019-0210-6
Alehagen, Alexander, Aaseth, Supplementation with Selenium and Coenzyme Q10 Reduces Cardiovascular Mortality in Elderly with Low Selenium Status. A Secondary Analysis of a Randomised Clinical Trial, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0157541
Alehagen, Johansson, Bjornstedt, Rosen, Post et al., Relatively high mortality risk in elderly Swedish subjects with low selenium status, Eur. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1038/ejcn.2015.92
Alehagen, Lindahl, Aaseth, Svensson, Johansson, Levels of sP-selectin and hs-CRP Decrease with Dietary Intervention with Selenium and Coenzyme Q10 Combined: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0137680
Arabi, Fowler, Hayden, Critical care management of adults with community-acquired severe respiratory viral infection, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-020-05943-5
Arabi, Fowler, Hayden, Critical care management of adults with community-acquired severe respiratory viral infection, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30317-2
Avery, Hoffmann, Selenium, Selenoproteins, and Immunity, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu10091203
Barnett, Hamer, Meydani, Low zinc status: A new risk factor for pneumonia in the elderly?, Nutr. Rev, doi:10.1111/j.1753-4887.2009.00253.x
Basnet, Mathisen, Strand, Oral zinc and common childhood infections-An update, J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2014.05.006
Beck, Matthews, Micronutrients and host resistance to viral infection, Proc. Nutr. Soc, doi:10.1017/S0029665100000823
Beck, Nelson, Shi, Van Dael, Schiffrin et al., Selenium deficiency increases the pathology of an influenza virus infection, FASEB J, doi:10.1096/fj.00-0721fje
Beck, Selenium as an antiviral agent
Bernheim, Mei, Huang, Yang, Fayad et al., Chest CT Findings in Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19): Relationship to Duration of Infection, Radiology, doi:10.1148/radiol.2020200463
Bhatnagar, Wadhwa, Aneja, Lodha, Kabra et al., Zinc as adjunct treatment in infants aged between 7 and 120 days with probable serious bacterial infection: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60477-2
Bjorklund, Dadar, Pivina, Dosa, Semenova et al., The role of zinc and copper in insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus, Curr. Med. Chem, doi:10.2174/0929867326666190902122155
Bonaventura, Benedetti, Albarede, Miossec, Zinc and its role in immunity and inflammation, Autoimmun Rev, doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2014.11.008
Brockman-Schneider, Pickles, Gern, Effects of vitamin D on airway epithelial cell morphology and rhinovirus replication, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0086755
Broman, Bernardson, Bursell, Wernerman, Flaring et al., Serum selenium in critically ill patients: Profile and supplementation in a depleted region, Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand, doi:10.1111/aas.13573
Caccialanza, Laviano, Lobascio, Montagna, Bruno et al., Early nutritional supplementation in non-critically ill patients hospitalized for the 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19): Rationale and feasibility of a shared pragmatic protocol, Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2020.110835
Calder, Carr, Gombart, Eggersdorfer, Optimal Nutritional Status for a Well-Functioning Immune System Is an Important Factor to Protect against Viral Infections, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12041181
Chang, Ding, Freund, Johnson, Schwarz et al., Prior diagnoses and medications as risk factors for COVID-19 in a Los Angeles Health System, doi:10.1101/2020.07.03.20145581
Chaves, Mansego, Blesa, Gonzalez-Albert, Jimenez et al., Inadequate cytoplasmic antioxidant enzymes response contributes to the oxidative stress in human hypertension, Am. J. Hypertens, doi:10.1016/j.amjhyper.2006.06.006
Chen, Liu, Guo, Emerging coronaviruses: Genome structure, replication, and pathogenesis, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.25681
Chen, Liu, Guo, Emerging coronaviruses: Genome structure, replication, and pathogenesis, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.25681
Conti, Ronconi, Caraffa, Gallenga, Ross et al., Induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1 and IL-6) and lung inflammation by Coronavirus-19 (COVI-19 or SARS-CoV-2): Anti-inflammatory strategies, J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents, doi:10.23812/CONTI-E
Conti, Ronconi, Caraffa, Gallenga, Ross et al., Induction of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1 and IL-6) and lung inflammation by Coronavirus-19 (COVI-19 or SARS-CoV-2): Anti-inflammatory strategies, J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents, doi:10.1007/s00134-020-05943-5
Dancer, Parekh, Lax, Souza, Zheng et al., Vitamin D deficiency contributes directly to the acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), Thorax, doi:10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-206680
De Haan, Groeneveld, De Geus, Egal, Struijs, Vitamin D deficiency as a risk factor for infection, sepsis and mortality in the critically ill: Systematic review and meta-analysis, Crit. Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-014-0660-4
Fairweather-Tait, Bao, Broadley, Collings, Ford et al., Selenium in human health and disease, Antioxid Redox Signal, doi:10.1089/ars.2010.3275
Farrokhian, Bahmani, Taghizadeh, Mirhashemi, Aarabi et al., Selenium Supplementation Affects Insulin Resistance and Serum hs-CRP in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Coronary Heart Disease, Horm. Metab. Res, doi:10.1055/s-0035-1569276
Finzi, Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 with high dose oral zinc salts: A report on four patients, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.06.006
Gordon, Jang, Bouhaddou, Xu, Obernier et al., A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9
Grundy, Metabolic syndrome: Connecting and reconciling cardiovascular and diabetes worlds, J. Am. Coll. Cardiol, doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2005.11.046
Guillin, Vindry, Ohlmann, Chavatte, Selenium, Selenoproteins and Viral Infection, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu11092101
Haider, Lassi, Ahmed, Bhutta, Zinc supplementation as an adjunct to antibiotics in the treatment of pneumonia in children 2 to 59 months of age, Cochrane Database Syst Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007368.pub2
Hansdottir, Monick, Lovan, Powers, Gerke et al., Vitamin D decreases respiratory syncytial virus induction of NF-kappaB-linked chemokines and cytokines in airway epithelium while maintaining the antiviral state, J. Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0902840
Harthill, Review: Micronutrient selenium deficiency influences evolution of some viral infectious diseases, Biol. Trace Elem. Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-011-8977-1
Hemila, Chalker, Vitamin C as a Possible Therapy for COVID-19, Infect. Chemother, doi:10.3947/ic.2020.52.2.222
Hemila, Vitamin C and Infections, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu9040339
Hemila, Zinc lozenges may shorten the duration of colds: A systematic review, Open Respir. Med. J, doi:10.2174/1874306401105010051
Hoffman, Micronutrient deficiencies in the elderly-Could ready meals be part of the solution?, J. Nutr. Sci, doi:10.1017/jns.2016.42
Holick, The vitamin D deficiency pandemic: Approaches for diagnosis, treatment and prevention, Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord, doi:10.1007/s11154-017-9424-1
Holmberg, Rignell-Hydbom, Lindh, Jonsson, Thelin et al., High levels of vitamin D associated with less ischemic heart disease-A nested case-control study among rural men in Sweden, Ann. Agric. Environ. Med, doi:10.5604/12321966.1235176
Holter, Ueland, Norseth, Brunborg, Froland et al., Vitamin D Status and Long-Term Mortality in Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Secondary Data Analysis from a Prospective Cohort, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0158536
Horowitz, Freeman, Bruzzese, Efficacy of glutathione therapy in relieving dyspnea associated with COVID-19 pneumonia: A report of 2 cases, Respir Med. Case Rep, doi:10.1016/j.rmcr.2020.101063
Hughes, Norton, Vitamin D and respiratory health, Clin. Exp. Immunol, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.04001.x
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality, Aging Clin. Exp. Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8
Ingels, Vanhorebeek, Van Cromphaut, Wouters, Derese et al., Effect of Intravenous 25OHD Supplementation on Bone Turnover and Inflammation in Prolonged Critically Ill Patients, Horm. Metab. Res, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2012.2813
Ivory, Prieto, Spinks, Armah, Goldson et al., Selenium supplementation has beneficial and detrimental effects on immunity to influenza vaccine in older adults, Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2015.12.003
Iyigundogdu, Demir, Asutay, Sahin, Developing Novel Antimicrobial and Antiviral Textile Products, Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol, doi:10.1007/s12010-016-2275-5
Kafai, Ganji, Sex, age, geographical location, smoking, and alcohol consumption influence serum selenium concentrations in the USA: Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Kalen, Appelkvist, Dallner, Age-related changes in the lipid compositions of rat and human tissues, Lipids, doi:10.1007/BF02535072
Khomich, Kochetkov, Bartosch, Ivanov, Redox Biology of Respiratory Viral Infections, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v10080392
Ko, Guo, Hsu, Chiou, Yeh et al., The effect of zinc supplementation on the treatment of chronic hepatitis C patients with interferon and ribavirin, Clin. Biochem, doi:10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2005.04.003
Kulik, Maywald, Kloubert, Wessels, Rink, Zinc deficiency drives Th17 polarization and promotes loss of Treg cell function, J. Nutr. Biochem, doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.09.011
Lai, Ng, Osburga Chan, Wong, Cheng, High-dose N-acetylcysteine therapy for novel H1N1 influenza pneumonia, Ann. Intern. Med, doi:10.7326/0003-4819-152-10-201005180-00017
Lang, Mills, Mastropaolo, Liu, Blood glutathione decreases in chronic diseases, J. Lab. Clin. Med, doi:10.1067/mlc.2000.105977
Lang, Naryshkin, Schneider, Mills, Lindeman, Low blood glutathione levels in healthy aging adults, J. Lab. Clin. Med
Lassi, Moin, Bhutta, Zinc supplementation for the prevention of pneumonia in children aged 2 months to 59 months, Cochrane Database Syst Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005978.pub3
Lazzerini, Wanzira, Oral zinc for treating diarrhoea in children, Cochrane Database Syst Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005436.pub5
Lew, Kwek, Tai, Earnest, Loo et al., Acute respiratory distress syndrome in critically ill patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.290.3.374
Li, Chen, Cao, Zhu, Zheng et al., Extraordinary GU-rich single-strand RNA identified from SARS coronavirus contributes an excessive innate immune response, Microbes Infect, doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2012.10.008
Li, Chen, Cao, Zhu, Zheng et al., Extraordinary GU-rich single-strand RNA identified from SARS coronavirus contributes an excessive innate immune response, Microbes Infect, doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2012.10.008
Lipsitch, Swerdlow, Finelli, Defining the Epidemiology of Covid-19-Studies Needed, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMp2002125
Liu, Voors, Van Veldhuisen, Van Der Veer, Belonje et al., Vitamin D status and outcomes in heart failure patients, Eur. J. Heart Fail, doi:10.1093/eurjhf/hfr032
Long, Liu, Zhou, He, Dietary Serine Supplementation Regulates Selenoprotein Transcription and Selenoenzyme Activity in Pigs, Biol. Trace Elem. Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-020-02117-8
Lu, Zhang, Ma, Yue, Zou et al., Link between community-acquired pneumonia and vitamin D levels in older patients, Z. Gerontol. Geriatr, doi:10.1007/s00391-017-1237-z
Maares, Haase, Zinc and immunity: An essential interrelation, Arch. Biochem. Biophys, doi:10.1016/j.abb.2016.03.022
Maggini, Pierre, Calder, Immune Function and Micronutrient Requirements Change over the Life Course, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu10101531
Manzanares, Lemieux, Elke, Langlois, Bloos et al., High-dose intravenous selenium does not improve clinical outcomes in the critically ill: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Crit. Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-016-1529-5
Mariani, Cattini, Neri, Malavolta, Mocchegiani et al., Simultaneous evaluation of circulating chemokine and cytokine profiles in elderly subjects by multiplex technology: Relationship with zinc status, Biogerontology, doi:10.1007/s10522-006-9060-8
Mendy, Apewokin, Wells, Morrow, Factors Associated with Hospitalization and Disease Severity in a Racially and Ethnically Diverse Population of COVID-19 Patients, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.06.25.20137323
Moghaddam, Heller, Sun, Seelig, Cherkezov et al., Selenium Deficiency Is Associated with Mortality Risk from COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12072098
Panagiotou, Tee, Ihsan, Athar, Marchitelli et al., Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels in patients hospitalised with COVID-19 are associated with greater disease severity, Clin. Endocrinol, doi:10.1111/cen.14276
Pearson, Clarke, Abbott, Knight, Cyranoski, SARS: What have we learned, Nature, doi:10.1038/424121a
Ramirez, Wongtrakool, Welch, Steinmeyer, Zugel et al., Vitamin D inhibition of pro-fibrotic effects of transforming growth factor beta1 in lung fibroblasts and epithelial cells, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2009.11.004
Remmelts, Spoorenberg, Oosterheert, Bos, De Groot et al., The role of vitamin D supplementation in the risk of developing pneumonia: Three independent case-control studies, Thorax, doi:10.1136/thoraxjnl-2013-203623
Remmelts, Van De Garde, Meijvis, Peelen, Damoiseaux et al., Addition of vitamin D status to prognostic scores improves the prediction of outcome in community-acquired pneumonia, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/cis751
Rhodes, Subramanian, Laird, Kenny, Low population mortality from COVID-19 in countries south of latitude 35 degrees North supports vitamin D as a factor determining severity, Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther, doi:10.1111/apt.15777
Russell, Millar, Baillie, Clinical evidence does not support corticosteroid treatment for 2019-nCoV lung injury, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30317-2
Russell, Millar, Baillie, Clinical evidence does not support corticosteroid treatment for 2019-nCoV lung injury, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30317-2
Sanada, Taniyama, Muratsu, Otsu, Shimizu et al., Source of Chronic Inflammation in Aging, Front. Cardiovasc Med, doi:10.3389/fcvm.2018.00012
Sattar, Connerney, Rauf, Saini, Ullah et al., Three Cases of COVID-19 Disease With Colonic Manifestations, Am. J. Gastroenterol, doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000000692
Schogler, Muster, Kieninger, Casaulta, Tapparel et al., Vitamin D represses rhinovirus replication in cystic fibrosis cells by inducing LL-37, Eur. Respir. J, doi:10.1183/13993003.00665-2015
Science, Johnstone, Roth, Guyatt, Loeb, Zinc for the treatment of the common cold: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, CMAJ, doi:10.1503/cmaj.111990
Seale, Torres, Berry, Pitts, A role for selenium-dependent GPX1 in SARS-CoV-2 virulence, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqaa177
Shetty, Udupa, Mutalik, Kulkarni, Rao, Mechanisms and Therapeutics of N-acetylcysteine: A Recent Update, Res. J. Pharm. Technol, doi:10.5958/0974-360X.2019.00434.7
Shimabukuro-Vornhagen, Godel, Subklewe, Stemmler, Schlosser et al., Cytokine release syndrome, J. Immunother. Cancer, doi:10.1186/s40425-018-0343-9
Shimabukuro-Vornhagen, Godel, Subklewe, Stemmler, Schlosser et al., Cytokine release syndrome, J. Immunother. Cancer, doi:10.1186/s40425-018-0343-9
Shojadoost, Kulkarni, Yitbarek, Laursen, Taha-Abdelaziz et al., Dietary selenium supplementation enhances antiviral immunity in chickens challenged with low pathogenic avian influenza virus subtype H9N2, Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol, doi:10.1016/j.vetimm.2018.12.002
Sies, Parnham, Potential therapeutic use of ebselen for COVID-19 and other respiratory viral infections, Free Radic. Biol. Med, doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.06.032
Skalny, Rink, Ajsuvakova, Aschner, Gritsenko et al., Zinc and respiratory tract infections: Perspectives for COVID19 (Review), Int. J. Mol. Med, doi:10.3892/ijmm.2020.4575
Steinbrenner, Al-Quraishy, Dkhil, Wunderlich, Sies, Dietary selenium in adjuvant therapy of viral and bacterial infections, Adv. Nutr, doi:10.3945/an.114.007575
Tainer, Getzoff, Richardson, Richardson, Structure and mechanism of copper, zinc superoxide dismutase, Nature, doi:10.1038/306284a0
Tangpricha, Pearce, Chen, Holick, Vitamin D insufficiency among free-living healthy young adults, Am. J. Med, doi:10.1016/S0002-9343(02)01091-4
Telcian, Zdrenghea, Edwards, Laza-Stanca, Mallia et al., Vitamin D increases the antiviral activity of bronchial epithelial cells in vitro, Antiviral Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.11.004
Thickett, Moromizato, Litonjua, Amrein, Quraishi et al., Association between prehospital vitamin D status and incident acute respiratory failure in critically ill patients: A retrospective cohort study, BMJ Open Respir Res, doi:10.1136/bmjresp-2014-000074
Trace, None, Elem. Med. Biol, doi:10.1016/S0946-672X(03)80040-8
Tuerk, Fazel, Zinc, Deficiency, None, Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol, doi:10.1097/MOG.0b013e328321b395
Vavougios, Selenium-Associated gene signatures within the SARS-CoV-2-Host genomic interaction interface, Free Radic. Biol. Med, doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.07.014
Velthuis, Van Den Worm, Sims, Baric, Snijder et al., Zn(2+) inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176
Vogt, Richie, Jr, Glutathione depletion and recovery after acute ethanol administration in the aging mouse, Biochem. Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2007.01.033
Weiss, Murdoch, Clinical course and mortality risk of severe COVID-19, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30633-4
Yang, Li, Zhang, Zhang, Cheung et al., Mental health services for older adults in China during the COVID-19 outbreak, Lancet Psychiatry, doi:10.1016/S2215-0366(20)30079-1
Yu, Sun, Nan, Zhu, Protection from H1N1 influenza virus infections in mice by supplementation with selenium: A comparison with selenium-deficient mice, Biol. Trace Elem. Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-010-8726-x
Zhai, Bo, Lu, Liu, Zhang, Effects of Coenzyme Q10 on Markers of Inflammation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0170172
Zhang, Liu, Potential interventions for novel coronavirus in China: A systematic review, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.25707
Zhang, Taylor, Bennett, Saad, Rayman, Association between regional selenium status and reported outcome of COVID-19 cases in China, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqaa095
Zheng, Ma, Zhang, Xie, COVID-19 and the cardiovascular system, Nat. Rev. Cardiol, doi:10.1038/s41569-020-0360-5
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12082358",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu12082358",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Objectives: The novel coronavirus infection (COVID-19) conveys a serious threat globally to health and economy because of a lack of vaccines and specific treatments. A common factor for conditions that predispose for serious progress is a low-grade inflammation, e.g., as seen in metabolic syndrome, diabetes, and heart failure, to which micronutrient deficiencies may contribute. The aim of the present article was to explore the usefulness of early micronutrient intervention, with focus on zinc, selenium, and vitamin D, to relieve escalation of COVID-19. Methods: We conducted an online search for articles published in the period 2010–2020 on zinc, selenium, and vitamin D, and corona and related virus infections. Results: There were a few studies providing direct evidence on associations between zinc, selenium, and vitamin D, and COVID-19. Adequate supply of zinc, selenium, and vitamin D is essential for resistance to other viral infections, immune function, and reduced inflammation. Hence, it is suggested that nutrition intervention securing an adequate status might protect against the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome - coronavirus-2) and mitigate the course of COVID-19. Conclusion: We recommended initiation of adequate supplementation in high-risk areas and/or soon after the time of suspected infection with SARS-CoV-2. Subjects in high-risk groups should have high priority as regards this nutritive adjuvant therapy, which should be started prior to administration of specific and supportive medical measures.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu12082358"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6381-5720",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infection Control and Environment Health, Norwegian Institute of Public Health, P.O. Box 222 Skøyen, 0213 Oslo, Norway"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Alexander",
"given": "Jan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Biotechnology and Bioelementology, Yaroslavl State University, Sovetskaya Str. 14, Yaroslavl 150000, Russia"
},
{
"name": "IM Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University (Sechenov University), Bolshaya Pirogovskaya St., Moscow 119146, Russia"
}
],
"family": "Tinkov",
"given": "Alexey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4038-151X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centre for International Health, University of Bergen, P.O. Box 7804, 5020 Bergen, Norway"
},
{
"name": "Research Department, Innlandet Hospital Trust, P.O. Box 104, 2381 Brumunddal, Norway"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Strand",
"given": "Tor A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, Department of Medical and Health Sciences, Linköping University, SE-58185 Linköping, Sweden"
}
],
"family": "Alehagen",
"given": "Urban",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Biotechnology and Bioelementology, Yaroslavl State University, Sovetskaya Str. 14, Yaroslavl 150000, Russia"
},
{
"name": "IM Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University (Sechenov University), Bolshaya Pirogovskaya St., Moscow 119146, Russia"
}
],
"family": "Skalny",
"given": "Anatoly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7518-5703",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "IM Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University (Sechenov University), Bolshaya Pirogovskaya St., Moscow 119146, Russia"
},
{
"name": "Research Department, Innlandet Hospital Trust, P.O. Box 104, 2381 Brumunddal, Norway"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Aaseth",
"given": "Jan",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
8,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2020-08-07T13:30:54Z",
"timestamp": 1596807054000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-02T00:12:44Z",
"timestamp": 1719879164000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-02T00:40:19Z",
"timestamp": 1719880819356
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 165,
"issue": "8",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
8,
7
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "8",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
8
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
8,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2020-08-07T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1596758400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/12/8/2358/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "2358",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
8,
7
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
8,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25681",
"article-title": "Emerging coronaviruses: Genome structure, replication, and pathogenesis",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "418",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.micinf.2012.10.008",
"article-title": "Extraordinary GU-rich single-strand RNA identified from SARS coronavirus contributes an excessive innate immune response",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "88",
"journal-title": "Microbes Infect.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40425-018-0343-9",
"article-title": "Cytokine release syndrome",
"author": "Godel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "56",
"journal-title": "J. Immunother. Cancer",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"key": "ref_4",
"unstructured": "Conti, P., Ronconi, G., Caraffa, A., Gallenga, C.E., Ross, R., Frydas, I., and Kritas, S.K. (2020). Induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1 and IL-6) and lung inflammation by Coronavirus-19 (COVI-19 or SARS-CoV-2): Anti-inflammatory strategies. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents, 34."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-05943-5",
"article-title": "Critical care management of adults with community-acquired severe respiratory viral infection",
"author": "Arabi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "315",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30317-2",
"article-title": "Clinical evidence does not support corticosteroid treatment for 2019-nCoV lung injury",
"author": "Russell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "473",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.290.3.374",
"article-title": "Acute respiratory distress syndrome in critically ill patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome",
"author": "Lew",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "374",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "290",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30633-4",
"article-title": "Clinical course and mortality risk of severe COVID-19",
"author": "Weiss",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1014",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41569-020-0360-5",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and the cardiovascular system",
"author": "Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "259",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Cardiol.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2215-0366(20)30079-1",
"article-title": "Mental health services for older adults in China during the COVID-19 outbreak",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e19",
"journal-title": "Lancet Psychiatry",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/jns.2016.42",
"article-title": "Micronutrient deficiencies in the elderly—Could ready meals be part of the solution?",
"author": "Hoffman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2",
"journal-title": "J. Nutr. Sci.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMp2002125",
"article-title": "Defining the Epidemiology of Covid-19—Studies Needed",
"author": "Lipsitch",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1194",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/0929867326666190902122155",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_13",
"unstructured": "Bjorklund, G., Dadar, M., Pivina, L., Dosa, M.D., Semenova, Y., and Aaseth, J. (2019). The role of zinc and copper in insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus. Curr. Med. Chem."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-0035-1569276",
"article-title": "Selenium Supplementation Affects Insulin Resistance and Serum hs-CRP in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Coronary Heart Disease",
"author": "Farrokhian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "263",
"journal-title": "Horm. Metab. Res.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5604/12321966.1235176",
"article-title": "High levels of vitamin D associated with less ischemic heart disease—A nested case-control study among rural men in Sweden",
"author": "Holmberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "288",
"journal-title": "Ann. Agric. Environ. Med.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jacc.2005.11.046",
"article-title": "Metabolic syndrome: Connecting and reconciling cardiovascular and diabetes worlds",
"author": "Grundy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1093",
"journal-title": "J. Am. Coll. Cardiol.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcvm.2018.00012",
"article-title": "Source of Chronic Inflammation in Aging",
"author": "Sanada",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12",
"journal-title": "Front. Cardiovasc Med.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10101531",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_18",
"unstructured": "Maggini, S., Pierre, A., and Calder, P.C. (2018). Immune Function and Micronutrient Requirements Change over the Life Course. Nutrients, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/306284a0",
"article-title": "Structure and mechanism of copper, zinc superoxide dismutase",
"author": "Tainer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "284",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "306",
"year": "1983"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.abb.2016.03.022",
"article-title": "Zinc and immunity: An essential interrelation",
"author": "Maares",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "58",
"journal-title": "Arch. Biochem. Biophys",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "611",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MOG.0b013e328321b395",
"article-title": "Zinc deficiency",
"author": "Tuerk",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "136",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1753-4887.2009.00253.x",
"article-title": "Low zinc status: A new risk factor for pneumonia in the elderly?",
"author": "Barnett",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "30",
"journal-title": "Nutr. Rev.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2014.11.008",
"article-title": "Zinc and its role in immunity and inflammation",
"author": "Bonaventura",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "277",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun Rev.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.09.011",
"article-title": "Zinc deficiency drives Th17 polarization and promotes loss of Treg cell function",
"author": "Kulik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "J. Nutr. Biochem.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10522-006-9060-8",
"article-title": "Simultaneous evaluation of circulating chemokine and cytokine profiles in elderly subjects by multiplex technology: Relationship with zinc status",
"author": "Mariani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "449",
"journal-title": "Biogerontology",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.06.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_26",
"unstructured": "Finzi, E. (2020). Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 with high dose oral zinc salts: A report on four patients. Int. J. Infect. Dis."
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000000692",
"article-title": "Three Cases of COVID-19 Disease With Colonic Manifestations",
"author": "Sattar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "948",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Gastroenterol.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Oral zinc for treating diarrhoea in children",
"author": "Lazzerini",
"first-page": "CD005436",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "Zinc and respiratory tract infections: Perspectives for COVID19 (Review)",
"author": "Skalny",
"first-page": "17",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Med.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Zinc supplementation for the prevention of pneumonia in children aged 2 months to 59 months",
"author": "Lassi",
"first-page": "CD005978",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD007368.pub2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_31",
"unstructured": "Haider, B.A., Lassi, Z.S., Ahmed, A., and Bhutta, Z.A. (2011). Zinc supplementation as an adjunct to antibiotics in the treatment of pneumonia in children 2 to 59 months of age. Cochrane Database Syst Rev."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60477-2",
"article-title": "Zinc as adjunct treatment in infants aged between 7 and 120 days with probable serious bacterial infection: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Bhatnagar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2072",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "379",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1503/cmaj.111990",
"article-title": "Zinc for the treatment of the common cold: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Science",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E551",
"journal-title": "CMAJ",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1874306401105010051",
"article-title": "Zinc lozenges may shorten the duration of colds: A systematic review",
"author": "Hemila",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "51",
"journal-title": "Open Respir. Med. J.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jtemb.2014.05.006",
"article-title": "Oral zinc and common childhood infections—An update",
"author": "Basnet",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "163",
"journal-title": "J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2005.04.003",
"article-title": "The effect of zinc supplementation on the treatment of chronic hepatitis C patients with interferon and ribavirin",
"author": "Ko",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "614",
"journal-title": "Clin. Biochem.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_37",
"unstructured": "te Velthuis, A.J., van den Worm, S.H., Sims, A.C., Baric, R.S., Snijder, E.J., and van Hemert, M.J. (2010). Zn(2+) inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture. PLoS Pathog., 6."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12010-016-2275-5",
"article-title": "Developing Novel Antimicrobial and Antiviral Textile Products",
"author": "Iyigundogdu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1155",
"journal-title": "Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25707",
"article-title": "Potential interventions for novel coronavirus in China: A systematic review",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "479",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref_40",
"unstructured": "EU Scientific Committee on Food (2003). Opinion of the Scientific Committee on Food on the Tolerable Upper Intake Level of Zinc, European Commission."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/ars.2010.3275",
"article-title": "Selenium in human health and disease",
"author": "Bao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1337",
"journal-title": "Antioxid Redox Signal.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0029665100000823",
"article-title": "Micronutrients and host resistance to viral infection",
"author": "Beck",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "581",
"journal-title": "Proc. Nutr. Soc.",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-020-02117-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_43",
"unstructured": "Long, J., Liu, Y., Zhou, X., and He, L. (2020). Dietary Serine Supplementation Regulates Selenoprotein Transcription and Selenoenzyme Activity in Pigs. Biol. Trace Elem. Res."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/nqaa095",
"article-title": "Association between regional selenium status and reported outcome of COVID-19 cases in China",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1297",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "111",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20944/preprints202007.0113.v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_45",
"unstructured": "Moghaddam, A., Heller, R.A., Sun, Q., Seelig, J., Cherkezov, A., Seibert, L., Hackler, J., Seemann, P., Diegmann, J., and Pilz, M. (2020). Selenium Deficiency Is Associated with Mortality Risk from COVID-19. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9",
"article-title": "A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing",
"author": "Gordon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "459",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "583",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/nqaa177",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_47",
"unstructured": "Seale, L.A., Torres, D.J., Berry, M.J., and Pitts, M.W. (2020). A role for selenium-dependent GPX1 in SARS-CoV-2 virulence. Am. J. Clin. Nutr."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.06.032",
"article-title": "Potential therapeutic use of ebselen for COVID-19 and other respiratory viral infections",
"author": "Sies",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "107",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Biol. Med.",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "156",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.07.014",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_49",
"unstructured": "Vavougios, G.D. (2020). Selenium—Associated gene signatures within the SARS-CoV-2—Host genomic interaction interface. Free Radic. Biol. Med."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11092101",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_50",
"unstructured": "Guillin, O.M., Vindry, C., Ohlmann, T., and Chavatte, L. (2019). Selenium, Selenoproteins and Viral Infection. Nutrients, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/424121a",
"article-title": "SARS: What have we learned?",
"author": "Pearson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "121",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_51",
"volume": "424",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-011-8977-1",
"article-title": "Review: Micronutrient selenium deficiency influences evolution of some viral infectious diseases",
"author": "Harthill",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1325",
"journal-title": "Biol. Trace Elem. Res.",
"key": "ref_52",
"volume": "143",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12950-019-0210-6",
"article-title": "Decrease in inflammatory biomarker concentration by intervention with selenium and coenzyme Q10: A subanalysis of osteopontin, osteoprotergerin, TNFr1, TNFr2 and TWEAK",
"author": "Alehagen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5",
"journal-title": "J. Inflamm.",
"key": "ref_53",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10091203",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_54",
"unstructured": "Avery, J.C., and Hoffmann, P.R. (2018). Selenium, Selenoproteins, and Immunity. Nutrients, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.00-0721fje",
"article-title": "Selenium deficiency increases the pathology of an influenza virus infection",
"author": "Beck",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1481",
"journal-title": "FASEB J.",
"key": "ref_55",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-1-4615-1609-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_56",
"unstructured": "Hatfield, D.L. (2001). Selenium as an antiviral agent. Selenium. Its Molecular Biology and Role in Human Health, Kluwer Academic Publishers."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-010-8726-x",
"article-title": "Protection from H1N1 influenza virus infections in mice by supplementation with selenium: A comparison with selenium-deficient mice",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "254",
"journal-title": "Biol. Trace Elem. Res.",
"key": "ref_57",
"volume": "141",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vetimm.2018.12.002",
"article-title": "Dietary selenium supplementation enhances antiviral immunity in chickens challenged with low pathogenic avian influenza virus subtype H9N2",
"author": "Shojadoost",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "62",
"journal-title": "Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol.",
"key": "ref_58",
"volume": "207",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnu.2015.12.003",
"article-title": "Selenium supplementation has beneficial and detrimental effects on immunity to influenza vaccine in older adults",
"author": "Ivory",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "407",
"journal-title": "Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_59",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/an.114.007575",
"article-title": "Dietary selenium in adjuvant therapy of viral and bacterial infections",
"author": "Steinbrenner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "73",
"journal-title": "Adv. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_60",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0946-672X(03)80040-8",
"article-title": "Sex, age, geographical location, smoking, and alcohol consumption influence serum selenium concentrations in the USA: Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–1994",
"author": "Kafai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "13",
"journal-title": "J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol.",
"key": "ref_61",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ejcn.2015.92",
"article-title": "Relatively high mortality risk in elderly Swedish subjects with low selenium status",
"author": "Alehagen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "91",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_62",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bcp.2007.01.033",
"article-title": "Glutathione depletion and recovery after acute ethanol administration in the aging mouse",
"author": "Vogt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1613",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_63",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"article-title": "Low blood glutathione levels in healthy aging adults",
"author": "Lang",
"first-page": "720",
"journal-title": "J. Lab. Clin. Med.",
"key": "ref_64",
"volume": "120",
"year": "1992"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1067/mlc.2000.105977",
"article-title": "Blood glutathione decreases in chronic diseases",
"author": "Lang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "402",
"journal-title": "J. Lab. Clin. Med.",
"key": "ref_65",
"volume": "135",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjhyper.2006.06.006",
"article-title": "Inadequate cytoplasmic antioxidant enzymes response contributes to the oxidative stress in human hypertension",
"author": "Chaves",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "62",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Hypertens.",
"key": "ref_66",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v10080392",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_67",
"unstructured": "Khomich, O.A., Kochetkov, S.N., Bartosch, B., and Ivanov, A.V. (2018). Redox Biology of Respiratory Viral Infections. Viruses, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.5958/0974-360X.2019.00434.7",
"article-title": "Mechanisms and Therapeutics of N-acetylcysteine: A Recent Update",
"author": "Shetty",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2584",
"journal-title": "Res. J. Pharm. Technol.",
"key": "ref_68",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-152-10-201005180-00017",
"article-title": "High-dose N-acetylcysteine therapy for novel H1N1 influenza pneumonia",
"author": "Lai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "687",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_69",
"volume": "152",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.rmcr.2020.101063",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_70",
"unstructured": "Horowitz, R.I., Freeman, P.R., and Bruzzese, J. (2020). Efficacy of glutathione therapy in relieving dyspnea associated with COVID-19 pneumonia: A report of 2 cases. Respir Med. Case Rep."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0137680",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_71",
"unstructured": "Alehagen, U., Lindahl, T.L., Aaseth, J., Svensson, E., and Johansson, P. (2015). Levels of sP-selectin and hs-CRP Decrease with Dietary Intervention with Selenium and Coenzyme Q10 Combined: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. PLoS ONE, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0157541",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_72",
"unstructured": "Alehagen, U., Alexander, J., and Aaseth, J. (2016). Supplementation with Selenium and Coenzyme Q10 Reduces Cardiovascular Mortality in Elderly with Low Selenium Status. A Secondary Analysis of a Randomised Clinical Trial. PLoS ONE, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0170172",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_73",
"unstructured": "Zhai, J., Bo, Y., Lu, Y., Liu, C., and Zhang, L. (2017). Effects of Coenzyme Q10 on Markers of Inflammation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF02535072",
"article-title": "Age-related changes in the lipid compositions of rat and human tissues",
"author": "Kalen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "579",
"journal-title": "Lipids",
"key": "ref_74",
"volume": "24",
"year": "1989"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/aas.13573",
"article-title": "Serum selenium in critically ill patients: Profile and supplementation in a depleted region",
"author": "Broman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "803",
"journal-title": "Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand.",
"key": "ref_75",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-016-1529-5",
"article-title": "High-dose intravenous selenium does not improve clinical outcomes in the critically ill: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Manzanares",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "356",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care",
"key": "ref_76",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"key": "ref_77",
"unstructured": "EU Scientific Committee on Food (2000). Opinion of the Scientific Committee on Food on the Tolerable Upper Intake Level of Selenium, European Commission."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/eurjhf/hfr032",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status and outcomes in heart failure patients",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "619",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Heart Fail.",
"key": "ref_78",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0002-9343(02)01091-4",
"article-title": "Vitamin D insufficiency among free-living healthy young adults",
"author": "Tangpricha",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "659",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_79",
"volume": "112",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11154-017-9424-1",
"article-title": "The vitamin D deficiency pandemic: Approaches for diagnosis, treatment and prevention",
"author": "Holick",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "153",
"journal-title": "Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord.",
"key": "ref_80",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8",
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality",
"author": "Ilie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1195",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin. Exp. Res.",
"key": "ref_81",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apt.15777",
"article-title": "Editorial: Low population mortality from COVID-19 in countries south of latitude 35 degrees North supports vitamin D as a factor determining severity",
"author": "Rhodes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1434",
"journal-title": "Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther.",
"key": "ref_82",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.07.03.20145581",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_83",
"unstructured": "Chang, T.S., Ding, Y., Freund, M.K., Johnson, R., Schwarz, T., Yabu, J.M., Hazlett, C., Chiang, J.N., Wulf, A., and Geschwind, D.H. (2020). Prior diagnoses and medications as risk factors for COVID-19 in a Los Angeles Health System. medRxiv."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.06.21.20136903",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_84",
"unstructured": "Panagiotou, G., Tee, S.A., Ihsan, Y., Athar, W., Marchitelli, G., Kelly, D., Boot, C.S., Stock, N., Macfarlane, J., and Martineau, A.R. (2020). Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels in patients hospitalised with COVID-19 are associated with greater disease severity. Clin. Endocrinol."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.06.25.20137323",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_85",
"unstructured": "Mendy, A., Apewokin, S., Wells, A.A., and Morrow, A.L. (2020). Factors Associated with Hospitalization and Disease Severity in a Racially and Ethnically Diverse Population of COVID-19 Patients. medRxiv."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.04001.x",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and respiratory health",
"author": "Hughes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20",
"journal-title": "Clin. Exp. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_86",
"volume": "158",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-014-0660-4",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency as a risk factor for infection, sepsis and mortality in the critically ill: Systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Groeneveld",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "660",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care",
"key": "ref_87",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00391-017-1237-z",
"article-title": "Link between community-acquired pneumonia and vitamin D levels in older patients",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "435",
"journal-title": "Z. Gerontol. Geriatr.",
"key": "ref_88",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/cis751",
"article-title": "Addition of vitamin D status to prognostic scores improves the prediction of outcome in community-acquired pneumonia",
"author": "Remmelts",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1488",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_89",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0158536",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_90",
"unstructured": "Holter, J.C., Ueland, T., Norseth, J., Brunborg, C., Froland, S.S., Husebye, E., Aukrust, P., and Heggelund, L. (2016). Vitamin D Status and Long-Term Mortality in Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Secondary Data Analysis from a Prospective Cohort. PLoS ONE, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-206680",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency contributes directly to the acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)",
"author": "Dancer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "617",
"journal-title": "Thorax",
"key": "ref_91",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjresp-2014-000074",
"article-title": "Association between prehospital vitamin D status and incident acute respiratory failure in critically ill patients: A retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Thickett",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e000074",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open Respir Res.",
"key": "ref_92",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.11.004",
"article-title": "Vitamin D increases the antiviral activity of bronchial epithelial cells in vitro",
"author": "Telcian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "93",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res.",
"key": "ref_93",
"volume": "137",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.00665-2015",
"article-title": "Vitamin D represses rhinovirus replication in cystic fibrosis cells by inducing LL-37",
"author": "Schogler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "520",
"journal-title": "Eur. Respir. J.",
"key": "ref_94",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0086755",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_95",
"unstructured": "Brockman-Schneider, R.A., Pickles, R.J., and Gern, J.E. (2014). Effects of vitamin D on airway epithelial cell morphology and rhinovirus replication. PLoS ONE, 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.0902840",
"article-title": "Vitamin D decreases respiratory syncytial virus induction of NF-kappaB-linked chemokines and cytokines in airway epithelium while maintaining the antiviral state",
"author": "Hansdottir",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "965",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_96",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1148/radiol.2020200463",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_97",
"unstructured": "Bernheim, A., Mei, X., Huang, M., Yang, Y., Fayad, Z.A., Zhang, N., Diao, K., Lin, B., Zhu, X., and Li, K. (2020). Chest CT Findings in Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19): Relationship to Duration of Infection. Radiology."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2009.11.004",
"article-title": "Vitamin D inhibition of pro-fibrotic effects of transforming growth factor beta1 in lung fibroblasts and epithelial cells",
"author": "Ramirez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "142",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "ref_98",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thoraxjnl-2013-203623",
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D supplementation in the risk of developing pneumonia: Three independent case-control studies",
"author": "Remmelts",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "990",
"journal-title": "Thorax",
"key": "ref_99",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/a-1114-6072",
"article-title": "Effect of Intravenous 25OHD Supplementation on Bone Turnover and Inflammation in Prolonged Critically Ill Patients",
"author": "Ingels",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "168",
"journal-title": "Horm. Metab. Res.",
"key": "ref_100",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref_101",
"unstructured": "(2012). Scientific Opinion on the Tolerable Upper Intake Level of vitamin D. EFSA J., 10, 2813."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12041181",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_102",
"unstructured": "Calder, P.C., Carr, A.C., Gombart, A.F., and Eggersdorfer, M. (2020). Optimal Nutritional Status for a Well-Functioning Immune System Is an Important Factor to Protect against Viral Infections. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3947/ic.2020.52.2.222",
"article-title": "Vitamin C as a Possible Therapy for COVID-19",
"author": "Hemila",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "222",
"journal-title": "Infect. Chemother",
"key": "ref_103",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu9040339",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_104",
"unstructured": "Hemila, H. (2017). Vitamin C and Infections. Nutrients, 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.110835",
"article-title": "Early nutritional supplementation in non-critically ill patients hospitalized for the 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19): Rationale and feasibility of a shared pragmatic protocol",
"author": "Caccialanza",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110835",
"journal-title": "Nutrition",
"key": "ref_105",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 105,
"references-count": 105,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/12/8/2358"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Early Nutritional Interventions with Zinc, Selenium and Vitamin D for Raising Anti-Viral Resistance Against Progressive COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "12"
}
alexander2
