A Machine Learning Approach to Understanding the Genetic Role in COVID-19 Prognosis: The Influence of Gene Polymorphisms Related to Inflammation, Vitamin D, and ACE2
et al., International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms26167975, Aug 2025
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 338 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Spain showing that genetic polymorphisms in inflammation, vitamin D, and ACE2-related genes can predict COVID-19 pneumonia, mortality, and rehospitalization with high accuracy.
1.
Jaurrieta-Largo et al., A Machine Learning Approach to Understanding the Genetic Role in COVID-19 Prognosis: The Influence of Gene Polymorphisms Related to Inflammation, Vitamin D, and ACE2, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms26167975.
2.
Al-Khrasani et al., Do vitamins halt the COVID-19-evoked pro-inflammatory cytokines involved in the development of neuropathic pain?, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2025.118346.
3.
Kow et al., Vitamin D and COVID‐19: How much more evidence do we need?, Nutrition in Clinical Practice, doi:10.1002/ncp.11349.
4.
Bigman et al., A Comprehensive Scoping Review on Diet and Nutrition in Relation to Long COVID-19 Symptoms and Recovery, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17111802.
5.
Hewison, M., COVID-19 and our understanding of vitamin D and immune function, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2025.106710.
6.
Wimalawansa, S., Vitamin D Deficiency Meets Hill’s Criteria for Causation in SARS-CoV-2 Susceptibility, Complications, and Mortality: A Systematic Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17030599.
7.
Sanduzzi Zamparelli et al., Immune-Boosting and Antiviral Effects of Antioxidants in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Therapeutic Perspective, Life, doi:10.3390/life15010113.
8.
Fazli et al., Possible Link between Gut Microbiota, Diet, and COVID-19 Infection, Journal of Medical Bacteriology, 12:4, jmb.tums.ac.ir/index.php/jmb/article/view/525.
9.
Wojciulik et al., The impact of genetic polymorphism on course and severity of the SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease, Przeglad Epidemiologiczny, doi:10.32394/pe/194862.
10.
Wimalawansa (B), S., Unveiling the Interplay—Vitamin D and ACE-2 Molecular Interactions in Mitigating Complications and Deaths from SARS-CoV-2, Biology, doi:10.3390/biology13100831.
11.
Santa et al., Comparative analysis of COVID-19 responses in Japan and Africa: diet, phytochemicals, vitamin D, and gut microbiota in reducing mortality—A systematic review and meta-analysis, Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1465324.
12.
Kaushal, A., Nutraceuticals and pharmacological to balance the transitional microbiome to extend immunity during COVID-19 and other viral infections, Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12967-024-05587-9.
13.
Mu et al., Anti-inflammatory and Nutritional Interventions Against SARS-CoV-2: A Comprehensive Review, Journal of Agriculture and Food Research, doi:10.1016/j.jafr.2024.101422.
14.
Wimalawansa (C), S., Unlocking Insights: Navigating COVID-19 Challenges and Emulating Future Pandemic Resilience Strategies with Strengthening Natural Immunity, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34691.
15.
Imran et al., Therapeutic Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19 Patients, Clinical Nutrition Open Science, doi:10.1016/j.nutos.2024.07.004.
16.
Grant, W., Vitamin D and viral infections: Infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases, and cancers, Advances in Food and Nutrition Research, doi:10.1016/bs.afnr.2023.12.007.
17.
Polonowita et al., Molecular Quantum and Logic Process of Consciousness—Vitamin D Big-Data in COVID-19—A Case for Incorporating Machine Learning In Medicine, European Journal of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical sciences, doi:10.5281/zenodo.10435649.
18.
Gomaa et al., Pharmacological evaluation of vitamin D in COVID-19 and long COVID-19: recent studies confirm clinical validation and highlight metformin to improve VDR sensitivity and efficacy, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01383-x.
19.
Gotelli et al., Understanding the immune-endocrine effects of vitamin D in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a role in protecting against neurodamage?, Neuroimmunomodulation, doi:10.1159/000533286.
20.
Cutolo et al., Involvement of the secosteroid vitamin D in autoimmune rheumatic diseases and COVID-19, Nature Reviews Rheumatology, doi:10.1038/s41584-023-00944-2.
21.
Schloss et al., Nutritional deficiencies that may predispose to long COVID, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01183-3.
22.
Arora et al., Global Dietary and Herbal Supplement Use during COVID-19—A Scoping Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15030771.
23.
Nicoll et al., COVID-19 Prevention: Vitamin D Is Still a Valid Remedy, Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm11226818.
24.
Foshati et al., Antioxidants and clinical outcomes of patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A systematic review of observational and interventional studies, Food Science & Nutrition, doi:10.1002/fsn3.3034.
25.
Quesada-Gomez et al., Vitamin D Endocrine System and COVID-19: Treatment with Calcifediol, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14132716.
26.
DiGuilio et al., Micronutrient Improvement of Epithelial Barrier Function in Various Disease States: A Case for Adjuvant Therapy, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms23062995.
27.
Grant (B) et al., A Narrative Review of the Evidence for Variations in Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentration Thresholds for Optimal Health, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14030639.
28.
Shah Alam et al., The role of vitamin D in reducing SARS-CoV-2 infection: An update, International Immunopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107686.
29.
Griffin et al., Perspective: Vitamin D supplementation prevents rickets and acute respiratory infections when given as daily maintenance but not as intermittent bolus: implications for COVID-19, Clinical Medicine, doi:10.7861/clinmed.2021-0035.
30.
Kohlmeier et al., When Mendelian randomisation fails, BMJ Nutrition, Prevention & Health, doi:10.1136/bmjnph-2021-000265.
31.
Brenner, H., Vitamin D Supplementation to Prevent COVID-19 Infections and Deaths—Accumulating Evidence from Epidemiological and Intervention Studies Calls for Immediate Action, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13020411.
32.
Mercola et al., Evidence Regarding Vitamin D and Risk of COVID-19 and Its Severity, Nutrients 2020, 12:11, 3361, doi:10.3390/nu12113361.
33.
Basha et al., Is the shielding effect of cholecalciferol in SARS CoV-2 infection dependable? An evidence based unraveling, Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health, doi:10.1016/j.cegh.2020.10.005.
34.
Xu et al., The importance of vitamin d metabolism as a potential prophylactic, immunoregulatory and neuroprotective treatment for COVID-19, Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12967-020-02488-5.
35.
Alexander et al., Early Nutritional Interventions with Zinc, Selenium and Vitamin D for Raising Anti-Viral Resistance Against Progressive COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12082358.
36.
Andrade et al., Vitamin A and D deficiencies in the prognosis of respiratory tract infections: A systematic review with perspectives for COVID-19 and a critical analysis on supplementation, SciELO preprints, doi:10.1590/SciELOPreprints.839.
37.
Grant (C) et al., Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients, 12:4, 988, doi:10.3390/nu12040988.
38.
McCullough et al., Daily oral dosing of vitamin D3 using 5000 TO 50,000 international units a day in long-term hospitalized patients: Insights from a seven year experience, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.12.010.
39.
EFSA, Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to vitamin D and normal function of the immune system and inflammatory response (ID 154, 159), maintenance of normal muscle function (ID 155) and maintenance of normal cardiovascular function (ID 159) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (E, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1468.
40.
EFSA (B), Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of a health claim related to vitamin D and contribution to the normal function of the immune system pursuant to Article 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2015.4096.
Jaurrieta-Largo et al., 18 Aug 2025, Spain, peer-reviewed, 9 authors.
Contact: joseluis.perez@uva.es (corresponding author), sofia.jaurrieta@uva.es, jpmiramontes@uva.es, luis.corral@uva.es, miriam.gabella@uva.es, sofia.perez.arroyo@estudiantes.uva.es, ana.torres@uclm.es, jorge.mateo@uclm.es, ricardo.usategui@uva.es.
A Machine Learning Approach to Understanding the Genetic Role in COVID-19 Prognosis: The Influence of Gene Polymorphisms Related to Inflammation, Vitamin D, and ACE2
International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms26167975
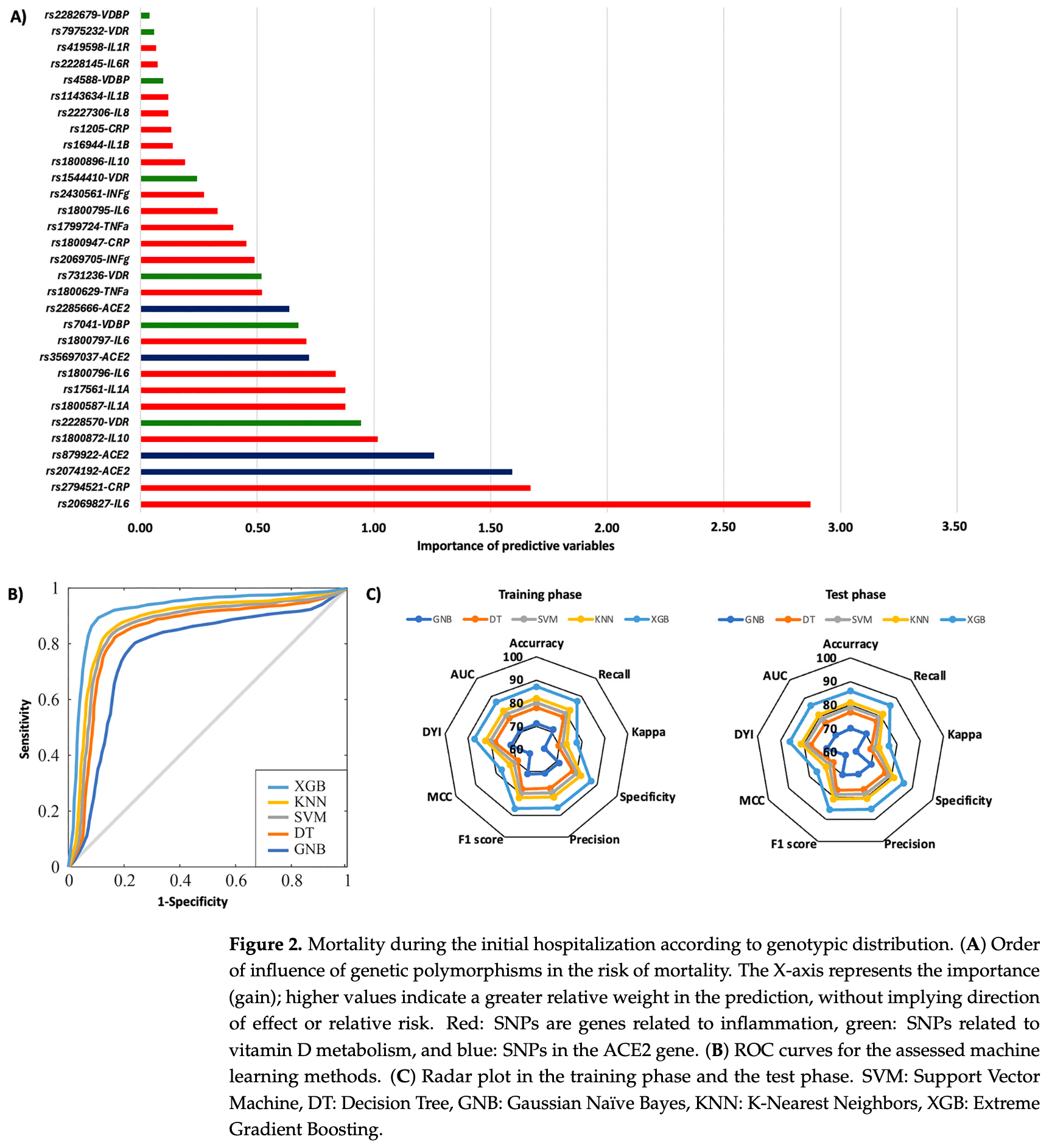
The genetic background influences the outcomes of COVID-19. This study aimed to evaluate the incidence of polymorphisms in genes linked to the RAAS system, cytokine production, and vitamin D on COVID-19 severity, with the goal of gaining a deeper understanding of the genetic etiology related to COVID-19. This study involved 338 COVID-19 patients and employed machine learning methods to identify the genetic variants that most significantly affect COVID-19 severity. The results revealed that polymorphisms in the IL6, IL6R, IL1α, IL1R, IFNγ, TNFα, CRP, VDR, VDBP, and ACE2 genes are the most significant genetic factors influencing COVID-19 prognosis, particularly in terms of the risks of COVID-19 pneumonia, mortality, rehospitalization, and associated mortality. The machine learning methods achieved an AUC of 0.86 for predicting COVID-19 pneumonia, mortality, and mortality related to rehospitalization, as well as an AUC of 0.85 for rehospitalization within the first year. These results confirm the crucial role of genetic background in COVID-19 prognosis, facilitating the identification of patients at increased risk. In summary, this research demonstrates that genetics-driven machine learning models can pinpoint patients at heightened risk by primarily focusing on genetic variants associated with ACE2, inflammation, and vitamin D.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
Abobaker, Nagib, Alsoufi, The impact of certain genetic variants (single nucleotide polymorphisms) on incidence and severity of COVID-19, J. Gene Med, doi:10.1002/jgm.3310
Ampomah, Nyame, Qin, Addo, Gyamfi et al., Stock Market Prediction with Gaussian Naïve Bayes Machine Learning Algorithm, Informatica, doi:10.31449/inf.v45i2.3407
Annoni, Orbegozo, Rahmania, Irazabal, Mendoza et al., Angiotensin-converting enzymes in acute respiratory distress syndrome, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-019-05600-6
Bischoff-Ferrari, Dawson-Hughes, Stöcklin, Sidelnikov, Willett et al., Oral supplementation with 25(OH)D 3 versus vitamin D3: Effects on 25(OH)D levels, lower extremity function, blood pressure, and markers of innate immunity, J. Bone Miner. Res, doi:10.1002/jbmr.551
Bouillon, Bikle, Vitamin D Metabolism Revised: Fall of Dogmas, J. Bone Miner. Res, doi:10.1002/jbmr.3884
Camps-Vilaró, Pinsach-Abuin, Degano, Ramos, Martí-Lluch et al., Genetic characteristics involved in COVID-19 severity. The CARGENCORS case-control study and meta-analysis, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.29404
Cervantes, Garcia-Lamont, Rodríguez-Mazahua, Lopez, A comprehensive survey on support vector machine classification: Applications, challenges and trends, Neurocomputing, doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2019.10.118
Charbuty, Abdulazeez, Classification Based on Decision Tree Algorithm for Machine Learning, J. Appl. Sci. Technol. Trends, doi:10.38094/jastt20165
Chen, Benesty, Khotilovich, Tang, Cho et al., Xgboost: Extreme gradient boosting, Sci. Res
Chen, Dewi, Huang, Caraka, Selecting critical features for data classification based on machine learning methods, J. Big Data, doi:10.1186/s40537-020-00327-4
Colotta, Jansson, Bonelli, Modulation of inflammatory and immune responses by vitamin D, J. Autoimmun, doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2017.07.007
Cools, Goemaere, Baetens, Raes, Desloovere et al., Calcium and bone homeostasis in heterozygous carriers of CYP24A1 mutations: A cross-sectional study, Bone, doi:10.1016/j.bone.2015.06.018
Cubillos, Wøhlk, Wulff, A bi-objective k-nearest-neighbors-based imputation method for multilevel data, Expert Syst. Appl, doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2022.117298
Darbeheshti, Mahdiannasser, Uhal, Ogino, Gupta et al., Interindividual immunogenic variants: Susceptibility to coronavirus, respiratory syncytial virus and influenza virus, Rev. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2234
Dobrijevic, Robajac, Gligorijevic, Šunderic, Penezic et al., The association of ACE1, ACE2, TMPRSS2, IFITM3 and VDR polymorphisms with COVID-19 severity: A systematic review and meta-analysis, EXCLI J
Feurer, Hutter, Hyperparameter Optimization, doi:10.1007/978-3-030-05318-5_1
Fu, Wang, Yuan, Chen, Ao et al., Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis, J. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.041
Gong, Song, Hu, Che, Guo et al., Natural and socio-environmental factors in the transmission of COVID-19: A comprehensive analysis of epidemiology and mechanisms, BMC Public Health, doi:10.1186/s12889-024-19749-3
Guan, Ni, Hu, Liang, Ou et al., Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2002032
Gustine, Jones, Immunopathology of Hyperinflammation in COVID-19, Am. J. Pathol, doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.08.009
Gómez, Albaiceta, García-Clemente, López-Larrea, Amado-Rodríguez et al., Angiotensin-converting enzymes (ACE, ACE2) gene variants and COVID-19 outcome, Gene, doi:10.1016/j.gene.2020.145102
Handelman, Kok, Chandra, Razavi, Lee et al., eDoctor: Machine learning and the future of medicine, J. Intern. Med, doi:10.1111/joim.12822
Herland, Khoshgoftaar, Wald, A review of data mining using big data in health informatics, J. Big Data
Imai, Kuba, Rao, Huan, Guo et al., Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protects from severe acute lung failure, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature03712
Ingraham, Barakat, Reilkoff, Bezdicek, Schacker et al., Understanding the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-SARS-CoV axis: A comprehensive review, Eur. Respir. J, doi:10.1183/13993003.00912-2020
Jiang, Chi, Sun, Li, Vitamin D Binding Protein: A Potential Factor in Geriatric COVID-19 Acute Lung Injury, J. Inflamm. Res, doi:10.2147/JIR.S470097
Jose, Manuel, COVID-19 cytokine storm: The interplay between inflammation and coagulation, Lancet Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30216-2
Karcıo Glu Batur, Dokur, Koç, Karabay, Akcay et al., Investigation of the Relationship between Vitamin D Deficiency and Vitamin D-Binding Protein Polymorphisms in Severe COVID-19 Patients, Diagnostics, doi:10.3390/diagnostics14171941
Kuan, Martineau, Griffiths, Hyppönen, Walton, DHCR7 mutations linked to higher vitamin D status allowed early human migration to Northern latitudes, BMC Evol. Biol, doi:10.1186/1471-2148-13-144
Kuba, Imai, Rao, Gao, Guo et al., A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/nm1267
Litmanovich, Chung, Kirkbride, Kicska, Kanne, Review of Chest Radiograph Findings of COVID-19 Pneumonia and Suggested Reporting Language, J. Thorac. Imaging, doi:10.1097/RTI.0000000000000541
Malmberg, Hanel, Taipale, Heikkinen, Carlberg, Vitamin D Treatment Sequence Is Critical for Transcriptome Modulation of Immune Challenged Primary Human Cells, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.754056
Manousaki, Dudding, Haworth, Hsu, Liu et al., Low-Frequency Synonymous Coding Variation in CYP2R1 Has Large Effects on Vitamin D Levels and Risk of Multiple Sclerosis, Am. J. Hum. Genet, doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2017.06.014
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., Consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0
Merad, Blish, Sallusto, Iwasaki, The immunology and immunopathology of COVID-19, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abm8108
Minton, Vitamin D shuts down T cell-mediated inflammation, Nat. Rev. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-021-00663-3
Mohan, Cherian, Sharma, Exploring links between vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1008874
Niemi, Daly, Ganna, The human genetic epidemiology of COVID-19, Nat. Rev. Genet, doi:10.1038/s41576-022-00478-5
Radujkovic, Hippchen, Tiwari-Heckler, Dreher, Boxberger et al., Vitamin D Deficiency and Outcome of COVID-19 Patients, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092757
Ren, Lin, Huang, Xu, Luo et al., Association of genetic polymorphisms with COVID-19 infection and outcomes: An updated meta-analysis based on 62 studies, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23662
Sabater Molina, Nicolás Rocamora, Bendicho, Vázquez, Zorio et al., Polymorphisms in ACE, ACE2, AGTR1 genes and severity of COVID-19 disease, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0263140
Saccone, Asani, Bornman, Regulation of the vitamin D receptor gene by environment, genetics and epigenetics, Gene, doi:10.1016/j.gene.2015.02.024
Saengsiwaritt, Jittikoon, Chaikledkaew, Udomsinprasert, Genetic polymorphisms of ACE1, ACE2, and TMPRSS2 associated with COVID-19 severity: A systematic review with meta-analysis, Rev. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2323
Sanders, Monogue, Jodlowski, Cutrell, Pharmacologic Treatments for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.6019
Sarker, Machine Learning: Algorithms, Real-World Applications and Research Directions, SN Comput. Sci, doi:10.1007/s42979-021-00592-x
Scazzone, Agnello, Bivona, Lo Sasso, Ciaccio, Vitamin D and Genetic Susceptibility to Multiple Sclerosis, Biochem. Genet, doi:10.1007/s10528-020-10010-1
Schleinitz, Distefano, Kovacs, Targeted SNP genotyping using the TaqMan® assay
Shang, Ye, Shi, Wan, Luo et al., Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2179-y
Tan, Komarasamy, Balasubramaniam, Hyperinflammatory Immune Response and COVID-19: A Double Edged Sword, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.742941
Tentolouris, Achilla, Anastasiou, Eleftheriadou, Tentolouris et al., The Association of Vitamin D Receptor Polymorphisms with COVID-19 Severity, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16050727
Velavan, Pallerla, Rüter, Augustin, Kremsner et al., Host genetic factors determining COVID-19 susceptibility and severity, eBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103629
Vogi, Haschka, Forer, Schwendinger, Petzer et al., Severe COVID-19 disease is associated with genetic factors affecting plasma ACE2 receptor and CRP concentrations, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-89306-4
Waring, Lindvall, Umeton, Automated machine learning: Review of the state-of-the-art and opportunities for healthcare, Artif. Intell. Med, doi:10.1016/j.artmed.2020.101822
Weir, Thenappan, Bhargava, Chen, Does vitamin D deficiency increase the severity of COVID-19?, Clin. Med, doi:10.7861/clinmed.2020-0301
Yan, Zhang, Li, Xia, Guo et al., Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abb2762
Yip, Oo, Ng, Chin, Tan et al., The role of inflammatory gene polymorphisms in severe COVID-19: A review, Virol. J, doi:10.1186/s12985-024-02597-3
Zdrenghea, Makrinioti, Bagacean, Bush, Johnston et al., Vitamin D modulation of innate immune responses to respiratory viral infections, Rev. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.1909
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms26167975",
"ISSN": [
"1422-0067"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167975",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The genetic background influences the outcomes of COVID-19. This study aimed to evaluate the incidence of polymorphisms in genes linked to the RAAS system, cytokine production, and vitamin D on COVID-19 severity, with the goal of gaining a deeper understanding of the genetic etiology related to COVID-19. This study involved 338 COVID-19 patients and employed machine learning methods to identify the genetic variants that most significantly affect COVID-19 severity. The results revealed that polymorphisms in the IL6, IL6R, IL1α, IL1R, IFNγ, TNFα, CRP, VDR, VDBP, and ACE2 genes are the most significant genetic factors influencing COVID-19 prognosis, particularly in terms of the risks of COVID-19 pneumonia, mortality, rehospitalization, and associated mortality. The machine learning methods achieved an AUC of 0.86 for predicting COVID-19 pneumonia, mortality, and mortality related to rehospitalization, as well as an AUC of 0.85 for rehospitalization within the first year. These results confirm the crucial role of genetic background in COVID-19 prognosis, facilitating the identification of patients at increased risk. In summary, this research demonstrates that genetics-driven machine learning models can pinpoint patients at heightened risk by primarily focusing on genetic variants associated with ACE2, inflammation, and vitamin D.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"ijms26167975"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pneumonology, University Clinical Hospital of Valladolid, 47003 Valladolid, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Jaurrieta-Largo",
"given": "Sofía",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2247-9679",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Río Hortega University Hospital, 47012 Valladolid, Spain"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University of Valladolid, 47003 Valladolid, Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Miramontes-González",
"given": "José Pablo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Río Hortega University Hospital, 47012 Valladolid, Spain"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University of Valladolid, 47003 Valladolid, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Corral-Gudino",
"given": "Luis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Río Hortega University Hospital, 47012 Valladolid, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Gabella-Martín",
"given": "Miriam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Río Hortega University Hospital, 47012 Valladolid, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Pérez-Arroyo",
"given": "Sofía",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4603-9034",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Analysis Expert Group, Castilla-La Mancha Institute of Health Research (IDISCAM), 45071 Toledo, Spain"
},
{
"name": "Medical Analysis Expert Group, Institute of Technology, University of Castilla-La Mancha, 16071 Cuenca, Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Torres",
"given": "Ana M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Analysis Expert Group, Castilla-La Mancha Institute of Health Research (IDISCAM), 45071 Toledo, Spain"
},
{
"name": "Medical Analysis Expert Group, Institute of Technology, University of Castilla-La Mancha, 16071 Cuenca, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Mateo",
"given": "Jorge",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1723-217X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Río Hortega University Hospital, 47012 Valladolid, Spain"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University of Valladolid, 47003 Valladolid, Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Pérez-Castrillón",
"given": "José Luis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7699-4388",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Cell Biology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Valladolid, 47005 Valladolid, Spain"
},
{
"name": "Unit of Excellence IOBA, University of Valladolid, 47005 Valladolid, Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Usategui-Martín",
"given": "Ricardo",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Molecular Sciences",
"container-title-short": "IJMS",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-18T16:22:33Z",
"timestamp": 1755534153000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-19T07:57:35Z",
"timestamp": 1755590255000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"GRS 2255/A/20",
"GRS COVID91/A/20"
],
"name": "Gerencia Regional de Salud, Castilla y León, Spain"
},
{
"name": "Institute of Technology"
},
{
"name": "Chair of Artificial Intelligence"
},
{
"name": "Castilla-La Mancha Institute of Health Research"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-19T08:10:09Z",
"timestamp": 1755591009166,
"version": "3.43.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "16",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
18
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "16",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-18T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1755475200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/26/16/7975/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "7975",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
18
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
18
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"article-title": "Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China",
"author": "Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1708",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12889-024-19749-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_2",
"unstructured": "Gong, Z., Song, T., Hu, M., Che, Q., Guo, J., Zhang, H., Li, H., Wang, Y., Liu, B., and Shi, N. (2024). Natural and socio-environmental factors in the transmission of COVID-19: A comprehensive analysis of epidemiology and mechanisms. BMC Public Health, 24."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.00912-2020",
"article-title": "Understanding the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-SARS-CoV axis: A comprehensive review",
"author": "Ingraham",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2000912",
"journal-title": "Eur. Respir. J.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb2762",
"article-title": "Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1444",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "367",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2179-y",
"article-title": "Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Shang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "221",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "581",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature03712",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protects from severe acute lung failure",
"author": "Imai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "112",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "436",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-019-05600-6",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-converting enzymes in acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Annoni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1159",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm1267",
"article-title": "A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus–induced lung injury",
"author": "Kuba",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "875",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression",
"author": "Mehta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1033",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30216-2",
"article-title": "COVID-19 cytokine storm: The interplay between inflammation and coagulation",
"author": "Jose",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e46",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.08.009",
"article-title": "Immunopathology of Hyperinflammation in COVID-19",
"author": "Gustine",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Pathol.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "191",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.742941",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_12",
"unstructured": "Tan, L.Y., Komarasamy, T.V., and Balasubramaniam, V.R. (2021). Hyperinflammatory Immune Response and COVID-19: A Double Edged Sword. Front. Immunol., 12, Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2021.742941/full."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-021-00663-3",
"article-title": "Vitamin D shuts down T cell-mediated inflammation",
"author": "Minton",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaut.2017.07.007",
"article-title": "Modulation of inflammatory and immune responses by vitamin D",
"author": "Colotta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "78",
"journal-title": "J. Autoimmun.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "85",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.1909",
"article-title": "Vitamin D modulation of innate immune responses to respiratory viral infections",
"author": "Zdrenghea",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1909",
"journal-title": "Rev. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1008874",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_16",
"unstructured": "Mohan, M., Cherian, J.J., and Sharma, A. (2020). Exploring links between vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19. PLoS Pathog., 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.7861/clinmed.2020-0301",
"article-title": "Does vitamin D deficiency increase the severity of COVID-19?",
"author": "Weir",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e107",
"journal-title": "Clin. Med.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092757",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_18",
"unstructured": "Radujkovic, A., Hippchen, T., Tiwari-Heckler, S., Dreher, S., Boxberger, M., and Merle, U. (2020). Vitamin D Deficiency and Outcome of COVID-19 Patients. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.041",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Fu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "656",
"journal-title": "J. Infect.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.29404",
"article-title": "Genetic characteristics involved in COVID-19 severity. The CARGENCORS case-control study and meta-analysis",
"author": "Degano",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e29404",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103629",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_21",
"unstructured": "Velavan, T.P., Pallerla, S.R., Rüter, J., Augustin, Y., Kremsner, P.G., Krishna, S., and Meyer, C.G. (2021). Host genetic factors determining COVID-19 susceptibility and severity. eBioMedicine, 72, Available online: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/ebiom/article/PIIS2352-3964(21)00422-9/fulltext."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41576-022-00478-5",
"article-title": "The human genetic epidemiology of COVID-19",
"author": "Niemi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "533",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Genet.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.artmed.2020.101822",
"article-title": "Automated machine learning: Review of the state-of-the-art and opportunities for healthcare",
"author": "Waring",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101822",
"journal-title": "Artif. Intell. Med.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "104",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.12822",
"article-title": "eDoctor: Machine learning and the future of medicine",
"author": "Handelman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "603",
"journal-title": "J. Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "284",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s42979-021-00592-x",
"article-title": "Machine Learning: Algorithms, Real-World Applications and Research Directions",
"author": "Sarker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "160",
"journal-title": "SN Comput. Sci.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jgm.3310",
"article-title": "The impact of certain genetic variants (single nucleotide polymorphisms) on incidence and severity of COVID-19",
"author": "Abobaker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e3310",
"journal-title": "J. Gene Med.",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23662",
"article-title": "Association of genetic polymorphisms with COVID-19 infection and outcomes: An updated meta-analysis based on 62 studies",
"author": "Ren",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e23662",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.gene.2020.145102",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-converting enzymes (ACE, ACE2) gene variants and COVID-19 outcome",
"author": "Albaiceta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "145102",
"journal-title": "Gene",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "762",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2323",
"article-title": "Genetic polymorphisms of ACE1, ACE2, and TMPRSS2 associated with COVID-19 severity: A systematic review with meta-analysis",
"author": "Saengsiwaritt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2323",
"journal-title": "Rev. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0263140",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_30",
"unstructured": "Sabater Molina, M., Nicolás Rocamora, E., Bendicho, A.I., Vázquez, E.G., Zorio, E., Rodriguez, F.D., Gil Ortuño, C., Rodríguez, A.I., Sánchez-López, A.J., and Jara Rubio, R. (2022). Polymorphisms in ACE, ACE2, AGTR1 genes and severity of COVID-19 disease. PLoS ONE, 17."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abm8108",
"article-title": "The immunology and immunopathology of COVID-19",
"author": "Merad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1122",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "375",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Pharmacologic Treatments for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review",
"author": "Sanders",
"first-page": "1824",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2234",
"article-title": "Interindividual immunogenic variants: Susceptibility to coronavirus, respiratory syncytial virus and influenza virus",
"author": "Darbeheshti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2234",
"journal-title": "Rev. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-024-02597-3",
"article-title": "The role of inflammatory gene polymorphisms in severe COVID-19: A review",
"author": "Yip",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "327",
"journal-title": "Virol. J.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-025-89306-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_35",
"unstructured": "Vogi, V., Haschka, D., Forer, L., Schwendinger, S., Petzer, V., Coassin, S., Tancevski, I., Sonnweber, T., Löffler-Ragg, J., and Puchhammer-Stöckl, E. (2025). Severe COVID-19 disease is associated with genetic factors affecting plasma ACE2 receptor and CRP concentrations. Sci. Rep., 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jbmr.551",
"article-title": "Oral supplementation with 25(OH)D3 versus vitamin D3: Effects on 25(OH)D levels, lower extremity function, blood pressure, and markers of innate immunity",
"author": "Sidelnikov",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "160",
"journal-title": "J. Bone Miner. Res.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.754056",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_37",
"unstructured": "Malmberg, H.-R., Hanel, A., Taipale, M., Heikkinen, S., and Carlberg, C. (2021). Vitamin D Treatment Sequence Is Critical for Transcriptome Modulation of Immune Challenged Primary Human Cells. Front. Immunol., 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jbmr.3884",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Metabolism Revised: Fall of Dogmas",
"author": "Bouillon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1985",
"journal-title": "J. Bone Miner. Res.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajhg.2017.06.014",
"article-title": "Low-Frequency Synonymous Coding Variation in CYP2R1 Has Large Effects on Vitamin D Levels and Risk of Multiple Sclerosis",
"author": "Manousaki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "227",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Hum. Genet.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10528-020-10010-1",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and Genetic Susceptibility to Multiple Sclerosis",
"author": "Scazzone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Genet.",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bone.2015.06.018",
"article-title": "Calcium and bone homeostasis in heterozygous carriers of CYP24A1 mutations: A cross-sectional study",
"author": "Cools",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "89",
"journal-title": "Bone",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2148-13-144",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_42",
"unstructured": "Kuan, V., Martineau, A.R., Griffiths, C.J., Hyppönen, E., and Walton, R. (2013). DHCR7 mutations linked to higher vitamin D status allowed early human migration to Northern latitudes. BMC Evol. Biol., 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.gene.2015.02.024",
"article-title": "Regulation of the vitamin D receptor gene by environment, genetics and epigenetics",
"author": "Saccone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "171",
"journal-title": "Gene",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "561",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/diagnostics14171941",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_44",
"unstructured": "Karcıoğlu Batur, L., Dokur, M., Koç, S., Karabay, M., Akcay, Z.N., Gunger, E., and Hekim, N. (2024). Investigation of the Relationship between Vitamin D Deficiency and Vitamin D-Binding Protein Polymorphisms in Severe COVID-19 Patients. Diagnostics, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/JIR.S470097",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Binding Protein: A Potential Factor in Geriatric COVID-19 Acute Lung Injury",
"author": "Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4419",
"journal-title": "J. Inflamm. Res.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"article-title": "The association of ACE1, ACE2, TMPRSS2, IFITM3 and VDR polymorphisms with COVID-19 severity: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Dobrijevic",
"first-page": "818",
"journal-title": "EXCLI J.",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu16050727",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_47",
"unstructured": "Tentolouris, N., Achilla, C., Anastasiou, I.A., Eleftheriadou, I., Tentolouris, A., Basoulis, D., Kosta, O., Lambropoulos, A., Yavropoulou, M.P., and Chatzikyriakidou, A. (2024). The Association of Vitamin D Receptor Polymorphisms with COVID-19 Severity. Nutrients, 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/RTI.0000000000000541",
"article-title": "Review of Chest Radiograph Findings of COVID-19 Pneumonia and Suggested Reporting Language",
"author": "Litmanovich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "354",
"journal-title": "J. Thorac. Imaging",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-1-61737-954-3_6",
"article-title": "Targeted SNP genotyping using the TaqMan® assay",
"author": "Schleinitz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "77",
"journal-title": "Disease Gene Identification: Methods and Protocols",
"key": "ref_49",
"volume": "Volume 700",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"article-title": "Xgboost: Extreme gradient boosting",
"author": "Chen",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci. Res.",
"key": "ref_50",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.neucom.2019.10.118",
"article-title": "A comprehensive survey on support vector machine classification: Applications, challenges and trends",
"author": "Cervantes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "189",
"journal-title": "Neurocomputing",
"key": "ref_51",
"volume": "408",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.38094/jastt20165",
"article-title": "Classification Based on Decision Tree Algorithm for Machine Learning",
"author": "Charbuty",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20",
"journal-title": "J. Appl. Sci. Technol. Trends",
"key": "ref_52",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.31449/inf.v45i2.3407",
"article-title": "Stock Market Prediction with Gaussian Naïve Bayes Machine Learning Algorithm",
"author": "Ampomah",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3407",
"journal-title": "Informatica",
"key": "ref_53",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eswa.2022.117298",
"article-title": "A bi-objective k-nearest-neighbors-based imputation method for multilevel data",
"author": "Cubillos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "117298",
"journal-title": "Expert Syst. Appl.",
"key": "ref_54",
"volume": "204",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "ref_55",
"unstructured": "(2025, April 23). MATLAB Runtime—MATLAB Compiler. Available online: https://es.mathworks.com/products/compiler/matlab-runtime.html."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-3-030-05318-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_56",
"unstructured": "Hutter, F., Kotthoff, L., and Vanschoren, J. (2019). Hyperparameter Optimization. Automated Machine Learning: Methods, Systems, Challenges, Springer International Publishing."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40537-020-00327-4",
"article-title": "Selecting critical features for data classification based on machine learning methods",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "52",
"journal-title": "J. Big Data",
"key": "ref_57",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/2196-1115-1-2",
"article-title": "A review of data mining using big data in health informatics",
"author": "Herland",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2",
"journal-title": "J. Big Data",
"key": "ref_58",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2014"
}
],
"reference-count": 58,
"references-count": 58,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/26/16/7975"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "A Machine Learning Approach to Understanding the Genetic Role in COVID-19 Prognosis: The Influence of Gene Polymorphisms Related to Inflammation, Vitamin D, and ACE2",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "26"
}
