Vitamin D Deficiency and Outcome of COVID-19 Patients
et al., Nutrients 2020, 12:9, 2757, doi:10.3390/nu12092757, Sep 2020
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
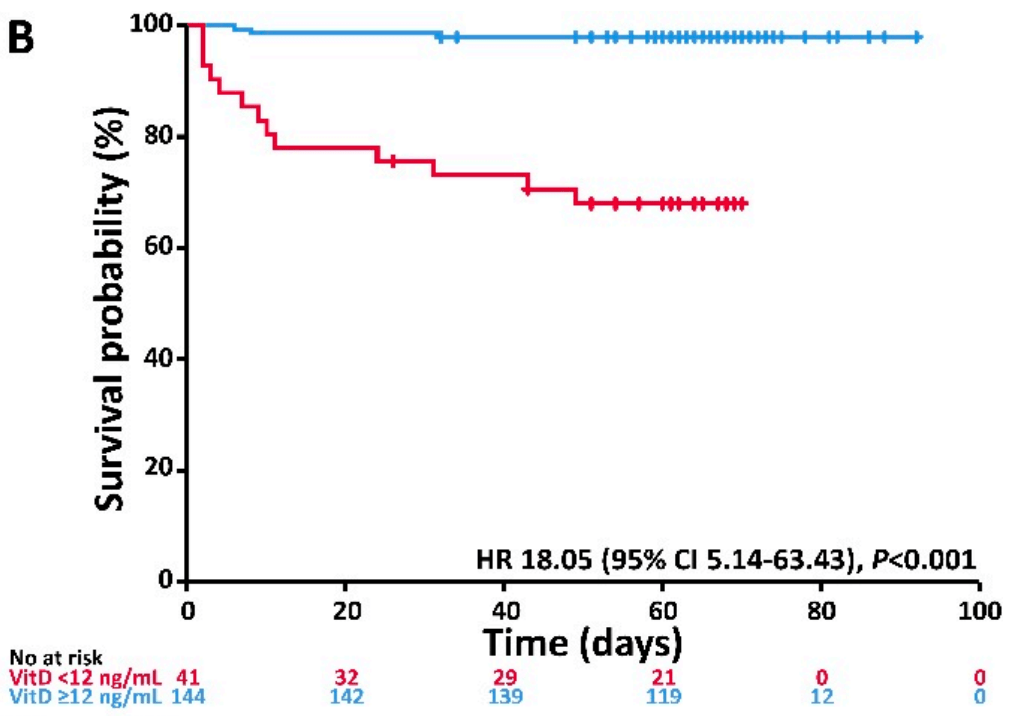
Observational study 185 patients in Germany shows an association between vitamin D status and severity and mortality. Adjusted hazard ratio of vitamin D sufficiency for combined mechanical ventilation and death was HR 0.16, p < 0.001, and for death HR 0.068, p < 0.001.
This is the 14th of 228 COVID-19 sufficiency studies for vitamin D, which collectively show higher levels reduce risk with p<0.0000000001.
|
risk of death, 93.2% lower, HR 0.07, p = 0.001, high D levels 144, low D levels 12, >30nmol/L.
|
|
risk of death/intubation, 84.0% lower, HR 0.16, p < 0.001, high D levels 144, low D levels 12, >30nmol/L.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Radujkovic et al., 10 Sep 2020, prospective, Germany, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
Vitamin D Deficiency and Outcome of COVID-19 Patients
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092757
Infection with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) poses an enormous challenge to health care systems throughout the world. Without causal treatment, identification of modifiable prognostic factors may help to improve outcomes. To explore possible associations of vitamin D (VitD) status with disease severity and survival, we studied 185 patients diagnosed with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and treated at our center. VitD status at first presentation was assessed retrospectively using accredited laboratory methods. VitD deficiency was defined as serum total 25-hydroxyvitamin D level < 12 ng/mL (<30 nM). Primary endpoint was severe course of disease (i.e., need for invasive mechanical ventilation and/or death, IMV/D). Within a median observation period of 66 days (range 2-92), 23 patients required IMV. A total of 28 patients had IMV/D, including 16 deaths. Ninety-three (50%) patients required hospitalization (inpatient subgroup). A total of 41 (22%) patients were VitD deficient. When adjusted for age, gender, and comorbidities, VitD deficiency was associated with higher risk of IMV/D and death (HR 6.12, 95% CI 2.79-13.42, p < 0.001 and HR 14.73, 95% CI 4.16-52.19, p < 0.001, respectively). Similar correlations were observed in the inpatient subgroup. Our study demonstrates an association between VitD deficiency and severity/mortality of COVID-19, highlighting the need for interventional studies on VitD supplementation in SARS-CoV-2 infected individuals.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no competing financial interest. Appendix A
References
Arboleda, Urcuqui-Inchima, Vitamin, Supplementation: A Potential Approach for Coronavirus/COVID-19 Therapeutics? Front, Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01523
Charoenngam, Holick, Immunologic Effects of Vitamin D on Human Health and Disease, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12072097
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Qu, Gong et al., Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7
D'avolio, Avataneo, Manca, Cusato, De Nicolò et al., 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations Are Lower in Patients with Positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12051359
Dong, Du, Gardner, An interactive web-based dashboard to track COVID-19 in real time, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30120-1
Faul, Kerley, Love, O'neill, Cody et al., Vitamin D Deficiency and ARDS after SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Ir. Med. J
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12040988
Hippchen, Kräusslich, Merle, Coronataxi brings outpatient care to covid-19 patients, Ann. Emerg. Med, doi:10.1016/j.annemergmed.2020.06.001
Holick, Vitamin, Deficiency, None, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMra070553
Isaia, Medico, Associations between hypovitaminosis D and COVID-19: A narrative review, Aging Clin. Exp. Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01650-9
Jakovac, COVID-19 and vitamin D-Is there a link and an opportunity for intervention?, Am. J. Physiol. Metab, doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00138.2020
Marik, Kory, Varon, Does vitamin D status impact mortality from SARS-CoV-2 infection?, Med. Drug Discov, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100041
Martineau, Forouhi, Vitamin D for COVID-19: A case to answer?, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30268-0
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: Systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.i6583
Mitchell, Vitamin-D and COVID-19: Do deficient risk a poorer outcome?, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30183-2
Munshi, Hussein, Toraih, Elshazli, Jardak et al., Vitamin D insufficiency as a potential culprit in critical COVID-19 patients, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26360
Rabenberg, Scheidt-Nave, Busch, Rieckmann, Hintzpeter et al., Vitamin D status among adults in Germany-results from the German Health Interview and Examination Survey for Adults (DEGS1), BMC Public Health, doi:10.1186/s12889-015-2016-7
Rhodes, Subramanian, Laird, Kenny, Editorial: Low population mortality from COVID-19 in countries south of latitude 35 degrees North supports vitamin D as a factor determining severity, Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther, doi:10.1111/apt.15777
Schemper, Smith, A note on quantifying follow-up in studies of failure time, Control. Clin. Trials, doi:10.1016/0197-2456(96)00075-X
Shi, Yu, Zhao, Wang, Zhao et al., Host susceptibility to severe COVID-19 and establishment of a host risk score: Findings of 487 cases outside Wuhan, Crit. Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-2833-7
Verity, Okell, Dorigatti, Winskill, Whittaker et al., Estimates of the severity of coronavirus disease 2019: A model-based analysis, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30243-7
Yang, Zheng, Gou, Pu, Chen et al., Prevalence of comorbidities and its effects in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.03.017
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092757",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu12092757",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Infection with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) poses an enormous challenge to health care systems throughout the world. Without causal treatment, identification of modifiable prognostic factors may help to improve outcomes. To explore possible associations of vitamin D (VitD) status with disease severity and survival, we studied 185 patients diagnosed with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and treated at our center. VitD status at first presentation was assessed retrospectively using accredited laboratory methods. VitD deficiency was defined as serum total 25-hydroxyvitamin D level < 12 ng/mL (<30 nM). Primary endpoint was severe course of disease (i.e., need for invasive mechanical ventilation and/or death, IMV/D). Within a median observation period of 66 days (range 2–92), 23 patients required IMV. A total of 28 patients had IMV/D, including 16 deaths. Ninety-three (50%) patients required hospitalization (inpatient subgroup). A total of 41 (22%) patients were VitD deficient. When adjusted for age, gender, and comorbidities, VitD deficiency was associated with higher risk of IMV/D and death (HR 6.12, 95% CI 2.79–13.42, p < 0.001 and HR 14.73, 95% CI 4.16–52.19, p < 0.001, respectively). Similar correlations were observed in the inpatient subgroup. Our study demonstrates an association between VitD deficiency and severity/mortality of COVID-19, highlighting the need for interventional studies on VitD supplementation in SARS-CoV-2 infected individuals.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu12092757"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Radujkovic",
"given": "Aleksandar",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hippchen",
"given": "Theresa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tiwari-Heckler",
"given": "Shilpa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dreher",
"given": "Saida",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boxberger",
"given": "Monica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1386-3350",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Merle",
"given": "Uta",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-10T13:10:09Z",
"timestamp": 1599743409000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-10T13:30:33Z",
"timestamp": 1599744633000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-08T18:36:22Z",
"timestamp": 1712601382441
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 297,
"issue": "9",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
10
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "9",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1599696000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/12/9/2757/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "2757",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
10
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30120-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.03.017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-2833-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12072097",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMra070553",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100041",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30183-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apt.15777",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01650-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpendo.00138.2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01523",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"key": "ref15",
"unstructured": "Hinweise zu Erkennung, Diagnostik und Therapie von Patienten mit COVID-19https://www.rki.de/DE/Content/Kommissionen/Stakob/Stellungnahmen/Stellungnahme-Covid-19_Therapie_Diagnose.html"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30243-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.annemergmed.2020.06.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0197-2456(96)00075-X",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"article-title": "Institute of Medicine (US) Committee to Review Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin D and Calcium",
"key": "ref19",
"series-title": "Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30268-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12051359",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26360",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D Deficiency and ARDS after SARS-CoV-2 Infection",
"author": "Faul",
"first-page": "84",
"journal-title": "Ir. Med. J.",
"key": "ref23",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12889-015-2016-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24"
}
],
"reference-count": 24,
"references-count": 24,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/12/9/2757"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Food Science",
"Nutrition and Dietetics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Vitamin D Deficiency and Outcome of COVID-19 Patients",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "12"
}
