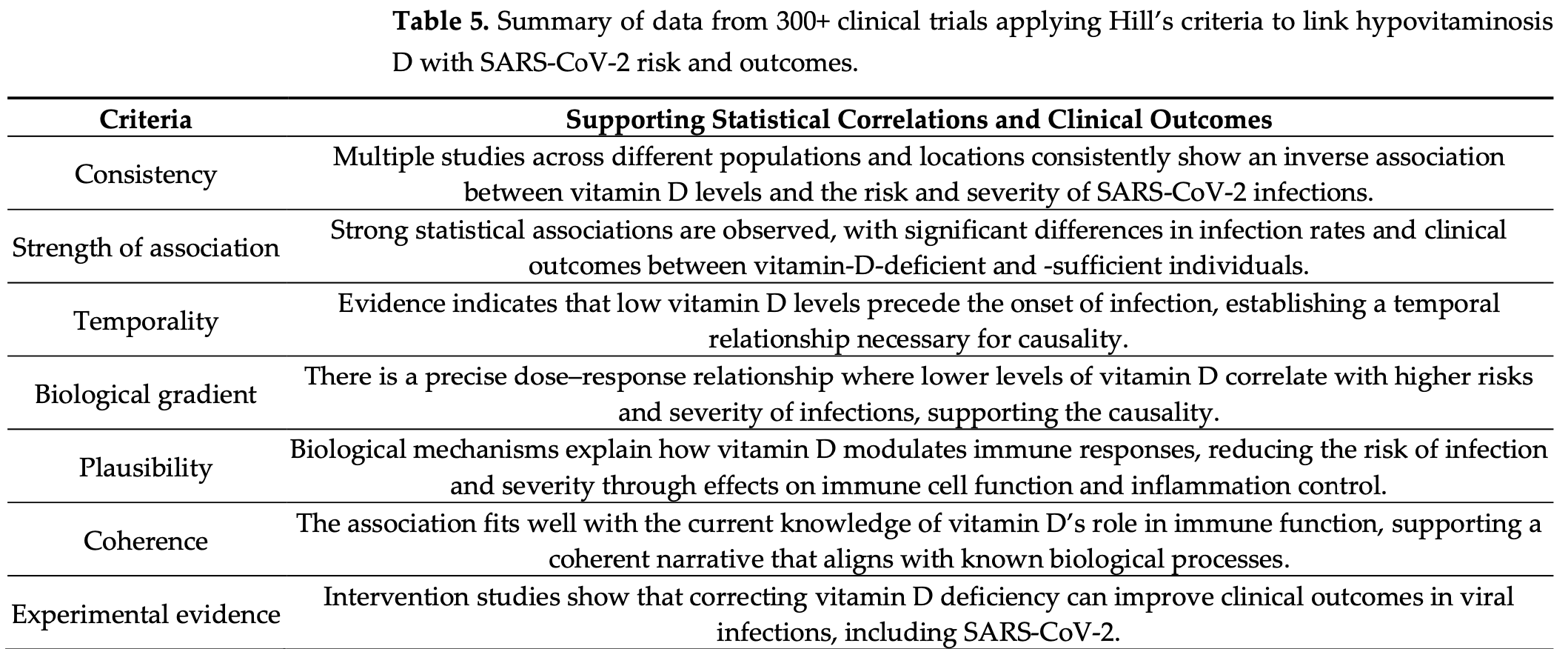
Vitamin D Deficiency Meets Hill’s Criteria for Causation in SARS-CoV-2 Susceptibility, Complications, and Mortality: A Systematic Review
, S., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17030599, Feb 2025
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Systematic review examining the evidence for vitamin D deficiency as a causative factor in COVID-19 susceptibility, complications, and mortality, evaluated using Bradford Hill's criteria for causality. Author analyzed 294 studies, finding a strong inverse relationship between serum vitamin D levels and COVID-19 severity, with optimal protection suggested at concentrations >50 ng/mL, associated with ~50% reduction in hospitalization and death. Clinical trials using cholecalciferol or calcifediol demonstrated significant benefits, particularly when administered early, with calcifediol showing faster onset of action. The review notes that 97% of trials reported positive effects, while 11 studies that showed no benefit had major design flaws, such as very late-stage intervention and insufficient dosing. Vitamin D supplementation, estimated at $2 per patient, was highlighted as a cost-effective intervention compared to hospitalization. Author criticizes health agencies for not integrating vitamin D into protocols despite over 300 studies supporting its role in immune resilience, antiviral defense, and cytokine regulation.
1.
Jaurrieta-Largo et al., A Machine Learning Approach to Understanding the Genetic Role in COVID-19 Prognosis: The Influence of Gene Polymorphisms Related to Inflammation, Vitamin D, and ACE2, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms26167975.
2.
Al-Khrasani et al., Do vitamins halt the COVID-19-evoked pro-inflammatory cytokines involved in the development of neuropathic pain?, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2025.118346.
3.
Kow et al., Vitamin D and COVID‐19: How much more evidence do we need?, Nutrition in Clinical Practice, doi:10.1002/ncp.11349.
4.
Bigman et al., A Comprehensive Scoping Review on Diet and Nutrition in Relation to Long COVID-19 Symptoms and Recovery, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17111802.
5.
Hewison, M., COVID-19 and our understanding of vitamin D and immune function, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2025.106710.
6.
Wimalawansa, S., Vitamin D Deficiency Meets Hill’s Criteria for Causation in SARS-CoV-2 Susceptibility, Complications, and Mortality: A Systematic Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17030599.
7.
Sanduzzi Zamparelli et al., Immune-Boosting and Antiviral Effects of Antioxidants in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Therapeutic Perspective, Life, doi:10.3390/life15010113.
8.
Fazli et al., Possible Link between Gut Microbiota, Diet, and COVID-19 Infection, Journal of Medical Bacteriology, 12:4, jmb.tums.ac.ir/index.php/jmb/article/view/525.
9.
Wojciulik et al., The impact of genetic polymorphism on course and severity of the SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease, Przeglad Epidemiologiczny, doi:10.32394/pe/194862.
10.
Wimalawansa (B), S., Unveiling the Interplay—Vitamin D and ACE-2 Molecular Interactions in Mitigating Complications and Deaths from SARS-CoV-2, Biology, doi:10.3390/biology13100831.
11.
Santa et al., Comparative analysis of COVID-19 responses in Japan and Africa: diet, phytochemicals, vitamin D, and gut microbiota in reducing mortality—A systematic review and meta-analysis, Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1465324.
12.
Kaushal, A., Nutraceuticals and pharmacological to balance the transitional microbiome to extend immunity during COVID-19 and other viral infections, Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12967-024-05587-9.
13.
Mu et al., Anti-inflammatory and Nutritional Interventions Against SARS-CoV-2: A Comprehensive Review, Journal of Agriculture and Food Research, doi:10.1016/j.jafr.2024.101422.
14.
Wimalawansa (C), S., Unlocking Insights: Navigating COVID-19 Challenges and Emulating Future Pandemic Resilience Strategies with Strengthening Natural Immunity, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34691.
15.
Imran et al., Therapeutic Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19 Patients, Clinical Nutrition Open Science, doi:10.1016/j.nutos.2024.07.004.
16.
Grant, W., Vitamin D and viral infections: Infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases, and cancers, Advances in Food and Nutrition Research, doi:10.1016/bs.afnr.2023.12.007.
17.
Polonowita et al., Molecular Quantum and Logic Process of Consciousness—Vitamin D Big-Data in COVID-19—A Case for Incorporating Machine Learning In Medicine, European Journal of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical sciences, doi:10.5281/zenodo.10435649.
18.
Gomaa et al., Pharmacological evaluation of vitamin D in COVID-19 and long COVID-19: recent studies confirm clinical validation and highlight metformin to improve VDR sensitivity and efficacy, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01383-x.
19.
Gotelli et al., Understanding the immune-endocrine effects of vitamin D in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a role in protecting against neurodamage?, Neuroimmunomodulation, doi:10.1159/000533286.
20.
Cutolo et al., Involvement of the secosteroid vitamin D in autoimmune rheumatic diseases and COVID-19, Nature Reviews Rheumatology, doi:10.1038/s41584-023-00944-2.
21.
Schloss et al., Nutritional deficiencies that may predispose to long COVID, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01183-3.
22.
Arora et al., Global Dietary and Herbal Supplement Use during COVID-19—A Scoping Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15030771.
23.
Nicoll et al., COVID-19 Prevention: Vitamin D Is Still a Valid Remedy, Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm11226818.
24.
Foshati et al., Antioxidants and clinical outcomes of patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A systematic review of observational and interventional studies, Food Science & Nutrition, doi:10.1002/fsn3.3034.
25.
Quesada-Gomez et al., Vitamin D Endocrine System and COVID-19: Treatment with Calcifediol, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14132716.
26.
DiGuilio et al., Micronutrient Improvement of Epithelial Barrier Function in Various Disease States: A Case for Adjuvant Therapy, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms23062995.
27.
Grant (B) et al., A Narrative Review of the Evidence for Variations in Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentration Thresholds for Optimal Health, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14030639.
28.
Shah Alam et al., The role of vitamin D in reducing SARS-CoV-2 infection: An update, International Immunopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107686.
29.
Griffin et al., Perspective: Vitamin D supplementation prevents rickets and acute respiratory infections when given as daily maintenance but not as intermittent bolus: implications for COVID-19, Clinical Medicine, doi:10.7861/clinmed.2021-0035.
30.
Kohlmeier et al., When Mendelian randomisation fails, BMJ Nutrition, Prevention & Health, doi:10.1136/bmjnph-2021-000265.
31.
Brenner, H., Vitamin D Supplementation to Prevent COVID-19 Infections and Deaths—Accumulating Evidence from Epidemiological and Intervention Studies Calls for Immediate Action, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13020411.
32.
Mercola et al., Evidence Regarding Vitamin D and Risk of COVID-19 and Its Severity, Nutrients 2020, 12:11, 3361, doi:10.3390/nu12113361.
33.
Basha et al., Is the shielding effect of cholecalciferol in SARS CoV-2 infection dependable? An evidence based unraveling, Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health, doi:10.1016/j.cegh.2020.10.005.
34.
Xu et al., The importance of vitamin d metabolism as a potential prophylactic, immunoregulatory and neuroprotective treatment for COVID-19, Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12967-020-02488-5.
35.
Alexander et al., Early Nutritional Interventions with Zinc, Selenium and Vitamin D for Raising Anti-Viral Resistance Against Progressive COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12082358.
36.
Andrade et al., Vitamin A and D deficiencies in the prognosis of respiratory tract infections: A systematic review with perspectives for COVID-19 and a critical analysis on supplementation, SciELO preprints, doi:10.1590/SciELOPreprints.839.
37.
Grant (C) et al., Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients, 12:4, 988, doi:10.3390/nu12040988.
38.
McCullough et al., Daily oral dosing of vitamin D3 using 5000 TO 50,000 international units a day in long-term hospitalized patients: Insights from a seven year experience, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.12.010.
39.
EFSA, Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to vitamin D and normal function of the immune system and inflammatory response (ID 154, 159), maintenance of normal muscle function (ID 155) and maintenance of normal cardiovascular function (ID 159) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (E, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1468.
40.
EFSA (B), Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of a health claim related to vitamin D and contribution to the normal function of the immune system pursuant to Article 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2015.4096.
Wimalawansa et al., 6 Feb 2025, peer-reviewed, 1 author.
Contact: suniljw@hotmail.com.
Vitamin D Deficiency Meets Hill’s Criteria for Causation in SARS-CoV-2 Susceptibility, Complications, and Mortality: A Systematic Review
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17030599
Clinical trials consistently demonstrate an inverse correlation between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D; calcifediol] levels and the risk of symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 disease, complications, and mortality. This systematic review (SR), guided by Bradford Hill's causality criteria, analyzed 294 peer-reviewed manuscripts published between December 2019 and November 2024, focusing on plausibility, consistency, and biological gradient. Evidence confirms that cholecalciferol (D3) and calcifediol significantly reduce symptomatic disease, complications, hospitalizations, and mortality, with optimal effects above 50 ng/mL. While vitamin D requires 3-4 days to act, calcifediol shows effects within 24 h. Among 329 trials, only 11 (3%) showed no benefit due to flawed designs. At USD 2/patient, D3 supplementation is far cheaper than hospitalization costs and more effective than standard interventions. This SR establishes a strong inverse relationship between 25(OH)D levels and SARS-CoV-2 vulnerability, meeting Hill's criteria. Vitamin D3 and calcifediol reduce infections, complications, hospitalizations, and deaths by ~50%, outperforming all patented, FDA-approved COVID-19 therapies. With over 300 trials confirming these findings, waiting for further studies is unnecessary before incorporating them into clinical protocols. Health agencies and scientific societies must recognize the significance of these results and incorporate D3 and calcifediol for prophylaxis and early treatment protocols of SARS-CoV-2 and similar viral infections. Promoting safe sun exposure and adequate vitamin D3 supplementation within communities to maintain 25(OH)D levels above 40 ng/mL (therapeutic range: 40-80 ng/mL) strengthens immune systems, reduces hospitalizations and deaths, and significantly lowers healthcare costs. When serum 25(OH)D levels exceed 70 ng/mL, taking vitamin K2 (100 µg/day or 800 µg/week) alongside vitamin D helps direct any excess calcium to bones. The recommended vitamin D dosage (approximately 70 IU/kg of body weight for a non-obese adult) to maintain 25(OH)D levels between 50-100 ng/mL is safe and cost-effective for disease prevention, ensuring optimal health outcomes.
Conflicts of Interest: The author has no competing interests to declare.
References
Akbar, Wibowo, Pranata, Setiabudiawan, Low Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (Vitamin D) Level Is Associated With Susceptibility to COVID-19, Severity, and Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Front. Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.660420.195
Akhtar, Neupane, Singh, Khan, Radiological Association Between Multiple Sclerosis Lesions and Serum Vitamin D Levels, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.31824.252
Al Sulaiman, Korayem, Aljuhani, Altebainawi, Shawaqfeh et al., Survival implications vs. complications: Unraveling the impact of vitamin D adjunctive use in critically ill patients with COVID-19-A multicenter cohort study, Front Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1237903
Al-Khalil, High-dose vitamin D-No benefit for postmenopausal women, Praxis, doi:10.1024/1661-8157/a002192.156
Alcala-Diaz, Limia-Perez, Gomez-Huelgas, Martin-Escalante, Cortes-Rodriguez et al., Calcifediol treatment and hospital mortality due to COVID-19: A cohort study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13061760
Alexander, Tinkov, Strand, Alehagen, Skalny et al., Early nutritional interventions with zinc, selenium and vitamin D for raising anti-viral resistance against progressive COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12082358.229
Alloubani, Akhu-Zaheya, Samara, Abdulhafiz, Saleh et al., Relationship between vitamin D deficiency, diabetes, and obesity, Diabetes Metab. Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2019.02.021
Alsafar, Grant, Hijazi, Uddin, Alkaabi et al., COVID-19 disease severity and death in relation to vitamin D status among SARS-CoV-2-positive UAE residents, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13051714
Amrein, Scherkl, Hoffmann, Neuwersch-Sommeregger, Kostenberger et al., Vitamin D deficiency 2.0: An update on the current status worldwide, Eur. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1038/s41430-020-0558-y
Annweiler, Beaudenon, Gautier, Gonsard, Boucher et al., High-dose versus standard-dose vitamin D supplementation in older adults with COVID-19 (COVIT-TRIAL): A multicenter, open-label, randomized controlled superiority trial, PLoS Med, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1003999
Annweiler, Corvaisier, Gautier, Dubee, Legrand et al., Vitamin D supplementation associated to better survival in hospitalized frail elderly COVID-19 patients: The GERIA-COVID Quasi-Experimental Study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113377.259
Annweiler, Hanotte, Grandin De L'eprevier, Sabatier, Lafaie et al., Vitamin D and survival in COVID-19 patients: A quasi-experimental study, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105771.291
Argano, Mallaci Bocchio, Natoli, Scibetta, Lo Monaco et al., Protective effect of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19-related intensive care hospitalization and mortality: Sefinitive evidence from meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph16010130.130
Asaduzzaman; Alam, Bari, Alam, Chakraborty, Ferdousi, Clinical Characteristics and Predictors of Mortality in Elderly Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19 in Bangladesh: A Multicenter, Retrospective Study Interdiscip, Perspect Infect Dis, doi:10.1155/2022/5904332.119
Ashique, Gupta, Gupta, Vitamin D-A prominent immunomodulator to prevent COVID-19 infection, Int. J. Rheum. Dis, doi:10.1111/1756-185X.14477.128
Athanassiou, Kostoglou-Athanassiou, Koutsilieris, Shoenfeld, Vitamin D and autoimmune rheumatic diseases, Biomolecules, doi:10.3390/biom13040709.110
Azem, Daou, Bassil, Anvari, Taliercio et al., Serum magnesium, mortality and disease progression in chronic kidney disease, J. Psychol. Med, doi:10.1186/s12882-020-1713-3.205
Baktash, Hosack, Patel, Shah, Kandiah et al., Vitamin D status and outcomes for hospitalised older patients with COVID-19, Postgrad. Med. J, doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-138712
Barker-Davies, O'sullivan, Senaratne, Baker, Cranley et al., The Stanford Hall consensus statement for post-COVID-19 rehabilitation, Br. J. Sports Med, doi:10.1136/bjsports-2020-102596.100
Barrea, Verde, Grant, Frias-Toral, Sarno et al., Vitamin D: A role also in long COVID-19?, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14081625.191
Barrett, Youssef, Shah, Ioana, Lawati et al., Vitamin D status and mortality from SARS CoV-2: A prospective study of unvaccinated caucasian adults, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14163252.293
Bayrak, Ozturk, Bolat, Unay, Association between vitamin D levels and COVID-19 infection in children: A casecontrol study, Turk. Arch. Pediatr, doi:10.5152/TurkArchPediatr.2023.22217
Bekele, Gebreselassie, Ashenafi, Kassa, Aseffa et al., Daily adjunctive therapy with vitamin D(3) and phenylbutyrate supports clinical recovery from pulmonary tuberculosis: A randomized controlled trial in Ethiopia, J. Intern. Med, doi:10.1111/joim.12767.125
Beltran-Garcia, Osca-Verdegal, Pallardo, Ferreres, Rodriguez et al., Oxidative stress and Inflammation in COVID-19-associated sepsis: The potential role of anti-oxidant therapy in avoiding disease progression, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox9100936.237
Ben Mohamed, Zouari, Ketata, Nabli, Blel et al., Myoclonus status revealing COVID 19 infection, Seizure, doi:10.1016/j.seizure.2022.11.010.192
Ben-Eltriki, Hopefl, Wright, Deb, Association between vitamin D status and risk of developing severe COVID-19 infection: A meta-analysis of observational studies, J. Am. Coll. Nutr, doi:10.1080/07315724.2021.1951891.178
Bergman, Lindh, Bjorkhem-Bergman, Lindh, Vitamin D and Respiratory Tract Infections: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0065835.155
Bianconi, Mannarino, Figorilli, Cosentini, Batori et al., Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and its prognostic impact on patients hospitalized with COVID-19, Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2021.111408
Bilezikian, Bikle, Hewison, Lazaretti-Castro, Formenti et al., Mechanisums in Endocrinology: Vitamin D and COVID-19, Eur. J. Endocrinol, doi:10.1530/EJE-20-0665.184
Bischoff-Ferrari, Vellas, Rizzoli, Kressig, Da Silva et al., Effect of vitamin D supplementation, omega-3 fatty acid supplementation, or a strength-training exercise program on clinical outcomes in older adults: The DO-HEALTH randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.16909.289
Bishop, Ismailova, Dimeloe, Hewison, White, Vitamin D and immune regulation: Antibacterial, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, JBMR Plus, doi:10.1002/jbm4.10405.186
Borsche, Glauner, Von Mendel, COVID-19 mortality risk correlates inversely with vitamin D3 status, and a mortality rate close to zero could theoretically be achieved at 50 ng/mL 25(OH)D3: Results of a systematic review and meta-analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13103596
Brenner, Kuznia, Laetsch, Niedermaier, Schottker, Prevention of advanced cancer by vitamin D(3) supplementation: Interaction by body mass index revisited, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13051408
Brown, Sakar, Vitamin D deficiency: A factor in COVID-19, progression, severity and mortality?-An urgent call for research
Brustad, Yousef, Stokholm, Bonnelykke, Bisgaard et al., Safety of high-dose vitamin D supplementation among children aged 0 to 6 years: A systematic review and meta-analysis, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.7410.220
Buechner, Constantine, Gjelsvik, John Snow and the Broad Street pump: 150 years of epidemiology, Med. Health R. I
Caccialanza, Laviano, Lobascio, Montagna, Bruno et al., Early nutritional supplementation in non-critically ill patients hospitalized for the 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19): Rationale and feasibility of a shared pragmatic protocol, Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2020.110835.230
Cadranel, Garabedian, Milleron, Guillozzo, Valeyre et al., Vitamin D metabolism by alveolar immune cells in tuberculosis: Correlation with calcium metabolism and clinical manifestations, Eur. Respir. J
Cancela, Nemere, Norman, 1 alpha,25(OH)2 vitamin D3: A steroid hormone capable of producing pleiotropic receptor-mediated biological responses by both genomic and nongenomic mechanisms, J. Steroid Biochem, doi:10.1016/0022-4731(88)90073-8
Cannata-Andia, Diaz-Sottolano, Fernandez, Palomo-Antequera, Herrero-Puente et al., A single-oral bolus of 100,000 IU of cholecalciferol at hospital admission did not improve outcomes in the COVID-19 disease: The COVID-VIT-D-a randomised multicentre international clinical trial, BMC Med, doi:10.1186/s12916-022-02290-8
Carrubba, Veronese, Di Bella, Cusumano, Di Prazza et al., Prognostic Value of Magnesium in COVID-19: Findings from the COMEPA Study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15040830.221
Castano, Madariaga, Grau, Garcia-Castano, 25(OH)Vitamin D deficiency and calcifediol treatment in pediatrics, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14091854.225
Castillo, Entrenas Costa, Vaquero Barrios, Alcala Diaz, Lopez Miranda et al., Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751.142
Cauley, Lacroix, Wu, Horwitz, Danielson et al., Serum 25 hydroxyvitamin D concentrations and the risk of hip Fractures: The women's health initiative, Ann. Intern. Med
Cervero, Lopez-Wolf, Casado, Novella-Mena, Ryan-Murua et al., Beneficial effect of short-term supplementation of high dose of vitamin D(3) in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A multicenter, single-blinded, prospective randomized pilot clinical trial, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.863587.216
Chandler, Chen, Ajala, Hazra, Cook et al., Effect of vitamin D3 supplements on development of advanced cancer: A secondary analysis of the VITAL randomized clinical trial, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.25850.159
Charoenngam, Holick, Immunologic effects of vitamin D on human health and sisease, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12072097
Charoenngam, Shirvani, Holick, Vitamin D and Its Potential Benefit for the COVID-19 Pandemic, Endocr. Pr, doi:10.1016/j.eprac.2021.03.006
Charoenngam, Shirvani, Reddy, Vodopivec, Apovian et al., Association of Vitamin D Status With Hospital Morbidity and Mortality in Adult Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19, Endocr. Pr, doi:10.1016/j.eprac.2021.02.013
Charoenngam, Sriussadaporn, Darker skin color measured by Von Luschan Chromatic Scale and increased sunlight exposure time are independently associated with decreased odds of vitamin D deficiency in Thai ambulatory patients, J. Nutr. Metab, doi:10.1155/2021/8899931
Charoenporn, Tungsukruthai, Teacharushatakit, Hanvivattanakul, Sriyakul et al., Effects of an 8-week high-dose vitamin D supplementation on fatigue and neuropsychiatric manifestations in post-COVID syndrome: A randomized controlled trial, Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci, doi:10.1111/pcn.13716.151
Charpy, The clinical treatment of tuberculosis lupus and certain tuberculosis by vitamin D 2 (calciferol), Med. Cir. Farm
Chauss, Freiwald, Mcgregor, Yan, Wang et al., Autocrine vitamin D signaling switches off pro-inflammatory programs of TH1 cells, Nat. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41590-021-01080-3.105
Chiodini, Gatti, Soranna, Merlotti, Mingiano et al., Vitamin D Status and SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Clinical Outcomes, Front Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2021.736665
Cicero, Fogacci, Borghi, Vitamin D supplementation and COVID-19 outcomes: Mounting evidence and fewer doubts, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14173584.132
Cosentino, Vernocchi, Martini, Marino, Allasino et al., Early outpatient treatment of COVID-19: A retrospective analysis of 392 cases in Italy, J. Clin. Med, doi:10.3390/jcm11206138.231
D'ecclesiis, Gavioli, Martinoli, Raimondi, Chiocca et al., Vitamin D and SARS-CoV2 infection, severity and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0268396.181
Dai, Zhu, Manson, Song, Li et al., Magnesium status and supplementation influence vitamin D status and metabolism: Results from a randomized trial, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqy274.264
Dancer, Parekh, Lax, Souza, Zheng et al., Vitamin D deficiency contributes directly to the acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), Thorax, doi:10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-206680.189
Davies, Mazess, Benskin, Letter to the editor in response to the article: "Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK biobank, Diabetes Metab. Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.02.016.145
Dayem Ullah, Sivapalan, Kocher, Chelala, COVID-19 in patients with hepatobiliary and pancreatic diseases: A single-centre cross-sectional study in East London, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-045077.218
De Sire, Andrenelli, Negrini, Lazzarini, Patrini et al., Rehabilitation and COVID-19: The Cochrane Rehabilitation 2020 rapid living systematic review. Update as of, Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med, doi:10.23736/S1973-9087.20.06614-9.101
Demay, Pittas, Bikle, Diab, Kiely et al., Vitamin D for the prevention of disease: An endocrine society clinical practice guideline, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgae290
Desouza, Chatterjee, Vickery, Nelson, Johnson et al., The effect of vitamin D supplementation on cardiovascular risk in patients with prediabetes: A secondary analysis of the D2d study, J. Diabetes Its Complicat, doi:10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2022.108230
Diani, Leonardi, Cavezzi, Ferrari, Iacono et al., SARS-CoV-2-The role of natural immunity: A narrative review, J. Clin. Med, doi:10.3390/jcm11216272
Dilokpattanamongkol, Yan, Jayanama, Ngamjanyaporn, Sungkanuparph et al., Impact of vitamin D supplementation on the clinical outcomes of COVID-19 pneumonia patients: A single-center randomized controlled trial, BMC Complement. Med. Ther, doi:10.1186/s12906-024-04393-6.260
Doll, Hill, Mortality in relation to smoking: Ten years' observations of british doctors, Br. Med. J, doi:10.1136/bmj.1.5395.1399.269
Doll, Peto, Mortality in relation to smoking: 20 years' observations on male British doctors, Br. Med. J, doi:10.1136/bmj.2.6051.1525.268
Donati, Palmini, Aurilia, Falsetti, Miglietta et al., Rapid Nontranscriptional Effects of Calcifediol and Calcitriol, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14061291.226.FAES-Pharma
Dror, Morozov, Daoud, Namir, Yakir et al., Preinfection 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 levels and association with severity of COVID-19 illness, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0263069
Dudenkov, Yawn, Oberhelman, Fischer, Singh et al., Changing incidence of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D values above 50 ng/mL: A 10-year population-based study, Mayo Clin. Proc, doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2015.02.012.129
Ebrahimzadeh, Mohseni, Narimani, Ebrahimzadeh, Kazemi et al., Association between vitamin D status and risk of covid-19 in-hospital mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr, doi:10.1080/10408398.2021.2012419.143
Essalim, Tachet, Demingo, Bruel, Gagneux-Brunon et al., Vaccination during febrile illness, what do we know? A systematic-narrative hybrid review of the literature and international recommendations, Vaccine, doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2024.126473
Euser, Zoccali, Jager, Dekker, Cohort studies: Prospective versus retrospective, Nephron Clin. Pr, doi:10.1159/000235241.285
Evans, Heaney, Guidelines for optimizing design and analysis of clinical studies of nutrient effects, J. Exp. Stroke Transl. Med, doi:10.6030/1939-067x-3.1
Evans, Lewis, Antony, Crowley, Guthrie et al., Breaking new frontiers: Assessment and reevaluation of clinical trial design for nutraceuticals, Front. Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.958753.158
Fairfield, Murray, Anzalone, Beasley, Khodaverdi et al., Association of vitamin D prescribing and clinical outcomes in adults hospitalized with COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14153073.217
Fernandes De Souza, Fonseca, Sartori, COVID-19 and Multiple Sclerosis: A Complex Relationship Possibly Aggravated by Low Vitamin D Levels, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells12050684.251
Fernandez, Ramirez-Mejia, Castillo, Urcuqui-Inchima, Vitamin D modulates expression of antimicrobial peptides and proinflammatory cytokines to restrict Zika virus infection in macrophages, Int. Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110232.114
Fletcher, Brown, Hewison, Swift, Cooper, Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and modifiable risk factors in patients with Crohn's disease: A prospective observational study, J. Adv. Nurs, doi:10.1111/jan.15476.224
Fouda Mbarga, Abubakari, Aminde, Morgan, Seatbelt use and risk of major injuries sustained by vehicle occupants during motor-vehicle crashes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies, BMC Public. Health, doi:10.1186/s12889-018-6280-1.276
Fu, Wu, Zhang, Chen, Li et al., Preoperative vitamin D deficiency is associated with increased one-year mortality in Chinese geriatric hip fracture patients-A propensity score matching study, Clin. Interv. Aging, doi:10.2147/CIA.S395228.127
Gallelli, Mannino, Luciani, De Sire, Mancuso et al., Vitamin D serum Levels in subjects tested for SARS-CoV-2: What are the differences among acute, healed, and negative COVID-19 patients? A multicenter real-practice study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13113932.150
Gan, You, Ying, Mu, The association between serum vitamin D levels and urinary tract infection risk in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15122690.120
Garg, Al-Ani, Mitchell, Hendy, Christensen, Editorial: Low population mortality from COVID-19 in countries south of latitude 35 degrees North-supports vitamin D as a factor determining severity. Authors' reply, Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther, doi:10.1111/apt.15796
Garland, Gorham, Mohr, Garland, Vitamin D for cancer prevention: Global perspective, Ann. Epidemiol, doi:10.1016/j.annepidem.2009.03.021.212
Georgakopoulou, Gkoufa, Tsakanikas, Makrodimitri, Karamanakos et al., Predictors of COVID-19-associated mortality among hospitalized elderly patients with dementia, Exp. Ther. Med
Ghanaati, Choukroun, Volz, Hueber, Mourão et al., One Hundred Years after Vitamin D Discovery: Is There Clinical Evidence for Supplementation Doses?, Int. J. Growth Factors Stem Cells Dent, doi:10.4103/GFSC.GFSC_4_20.197
Gonen, Alaylioglu, Durcan, Ozdemir, Sahin et al., Rapid and effective vitamin D supplementation may present better clinical outcomes in COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) patients by altering serum INOS1, IL1B, IFNg, cathelicidin-LL37, and ICAM1, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13114047.133
Gospodarska, Ghosh Dastidar, Carlberg, Intervention Approaches in Studying the Response to Vitamin D(3) Supplementation, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15153382.198
Grant, Al Anouti, Boucher, Dursun, Gezen-Ak et al., A Narrative Review of the Evidence for Variations in Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentration Thresholds for Optimal Health, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14030639.164
Grant, Al Anouti, Boucher, Fakhoury, Moukayed et al., Evidence That Increasing Serum 25(OH)D Concentrations to 30 ng/mL in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates Could Greatly Improve Health Outcomes, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines11040994
Grant, Al Anouti, Moukayed, Targeted 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration measurements and vitamin D3 supplementation can have important patient and public health benefits, Eur. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1038/s41430-020-0564-0.223
Grant, Boucher, Are Hill's criteria for causality satisfied for vitamin D and periodontal disease?, Dermatoendocrinol, doi:10.4161/derm.2.1.12488.177
Grant, Boucher, Bhattoa, Lahore, Why vitamin D clinical trials should be based on 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.08.009
Grant, Boucher, Pludowski, Wimalawansa, The emerging evidence for non-skeletal health benefits of vitamin D supplementation in adults, Nat. Rev. Endocrinol, doi:10.1038/s41574-022-00646-x.208
Grant, Boucher, Randomized controlled trials of vitamin D and cancer incidence: A modeling study, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0176448.162
Grant, Boucher, Why secondary analyses in vitamin D clinical trials are important and how to improve vitamin D clinical trial outcome analyses-A momment on "extra-skeletal effects of vitamin D, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu11092182.222
Grant, How strong is the evidence that solar ultraviolet B and vitamin D reduce the risk of cancer?: An examination using Hill's criteria for causality, Dermatoendocrinol, doi:10.4161/derm.1.1.7388.248
Grant, The Institute of Medicine did not find the vitamin D-cancer link because it ignored UV-B dose studies, Public. Health Nutr, doi:10.1017/S1368980011000267.207
Grant, Vitamin D Acceptance Delayed by Big Pharma Following the Disinformation Playbook
Grant, Wimalawansa, Pludowski, Cheng, Vitamin D: Evidence-based health benefits and recommendations for population guidelines, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17020277
Grasselli, Zangrillo, Zanella, Antonelli, Cabrini et al., Baseline Characteristics and Outcomes of 1591 Patients Infected With SARS-CoV-2 Admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.5394.228
Greiller, Martineau, Modulation of the immune response to respiratory viruses by vitamin D, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu7064240.131
Guo, Huang, Fan, Hong, Zhao et al., Association between vitamin D supplementation and cancer incidence and mortality: A trial sequential meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr, doi:10.1080/10408398.2022.2056574.247
Guo, Li, Geng, Song, Xie et al., Vitamin D receptor involves in the protection of intestinal epithelial barrier function via up-regulating SLC26A3, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2022.106231.103
Guven, Gultekin, The effect of high-dose parenteral vitamin D(3) on COVID-19-related inhospital mortality in critical COVID-19 patients during intensive care unit admission: An observational cohort study, Eur. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1038/s41430-021-00984-5.215
Haines, Kempton, Seymour, Bosse, Churchill et al., The effect of a single early high-dose vitamin D supplement on fracture union in patients with hypovitaminosis D: A prospective randomised trial, Bone Jt. J, doi:10.1302/0301-620X.99B11.BJJ-2017-0271.R1.157
Hanwell, Banwell, Assessment of evidence for a protective role of vitamin D in multiple sclerosis, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.07.017.176
Hardy, Commentary: Bread and alum, syphilis and sunlight: Rickets in the nineteenth century, Int. J. Epidemiol, doi:10.1093/ije/dyg175
Hastie, Mackay, Ho, Celis-Morales, Katikireddi et al., Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank, Diabetes Metab. Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.050.148
Hastie, Pell, Sattar, Vitamin D and COVID-19 infection and mortality in UK Biobank, Eur. J. Nutr, doi:10.1007/s00394-020-02372-4.146
Heath, Hodge, Ebeling, Kvaskoff, Eyles et al., Circulating 25hydroxyvitamin D concentration and cause-specific mortality in the Melbourne Collaborative Cohort Study, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105612.163
Hewison, Vitamin D and immune function: Autocrine, paracrine or endocrine?, Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. . Suppl, doi:10.3109/00365513.2012.682862.255
Hewison, Vitamin D and innate and adaptive immunity, Vitam. Horm, doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-386960-9.00002-2.185
Hii, Ferrante, The non-genomic actions of vitamin D, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu8030135.107
Hill, The environment and disease: Association or causation?, Proc. R. Soc. Med
Holick, Binkley, Bischoff-Ferrari, Gordon, Hanley et al., treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: An Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1210/jc.2011-0385
Holick, Resurrection of vitamin D deficiency and rickets, J. Clin. Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI29449.283
Holick, Revisiting vitamin D guidelines: A critical appraisal of the literature, Endocr. Pr, doi:10.1016/j.eprac.2024.10.011
Holick, The vitamin D epidemic and its health consequences, J. Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/135.11.2739S.232
Hollis, Marshall, Savage, Garrett-Mayer, Kindy et al., Vitamin D3 supplementation, lowrisk prostate cancer, and health disparities, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2012.11.012.214
Hong, Xiong, Huang, Wu, Lin et al., Association of vitamin D supplementation with respiratory tract infection in infants, Matern. Child. Nutr, doi:10.1111/mcn.12987.138
Hosseini, El Abd, Ducharme, Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation on COVID-19 Related Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14102134.182
Huang, Wang, Liu, Cao, Han et al., Vitamin D deficiency and the risk of tuberculosis: A meta-analysis, Drug Des. Dev. Ther, doi:10.2147/DDDT.S79870.124
Infante, Ricordi, Baidal, Alejandro, Lanzoni et al., VITAL study: An incomplete picture?, Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci, doi:10.26355/eurrev_201904_17599
Islamoska, Petersen, Benfield, Norredam, Socioeconomic and demographic risk factors in COVID-19 hospitalization among immigrants and ethnic minorities, Eur. J. Public. Health, doi:10.1093/eurpub/ckab186
Ismailova, White, Vitamin, infections and immunity, Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord, doi:10.1007/s11154-021-09679-5
Jain, Chaurasia, Sengar, Singh, Mahor et al., Analysis of vitamin D level among asymptomatic and critically ill COVID-19 patients and its correlation with inflammatory markers, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-77093-z.258
Jaun, Boesing, Luthi-Corridori, Abig, Makhdoomi et al., High-dose vitamin D substitution in patients with COVID-19: Study protocol for a randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled, multi-center study-VitCov Trial, Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-022-06016-2
Jodar, Campusano, De Jongh, Holick, Calcifediol: A review of its pharmacological characteristics and clinical use in correcting vitamin D deficiency, Eur. J. Nutr, doi:10.1007/s00394-023-03103-1.168
Jolliffe, Camargo, Jr, Sluyter, Aglipay et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data from randomised controlled trials, Lancet. Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00051-6.134
Jolliffe, Griffiths, Martineau, Vitamin D in the prevention of acute respiratory infection: Systematic review of clinical studies, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2012.11.017.136
Jomova, Raptova, Alomar, Alwasel, Nepovimova et al., Reactive oxygen species, toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: Chronic diseases and aging, Arch. Toxicol, doi:10.1007/s00204-023-03562-9.106
Jukes, The prevention and conquest of scurvy, beri-beri, and pellagra, Prev. Med, doi:10.1016/0091-7435(89)90023-6.280
Kalantari, Sepidarkish, Ghaffari, Rostami-Mansoor, Does vitamin D reduce the mortality rate of Plasmodium infection?: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Malar. J, doi:10.1186/s12936-023-04612-4.115
Kaufman, Niles, Kroll, Bi, Holick, SARS-CoV-2 positivity rates associated with circulating 25hydroxyvitamin D levels, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0239252
Kaya, Pamukcu, Yakar, The role of vitamin D deficiency on COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies, Epidemiol. Health, doi:10.4178/epih.e2021074.179
Kazemi, Mohammadi, Aghababaee, Golzarand, Clark et al., Association of vitamin D status with SARS-CoV-2 infection or COVID-19 severity: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Adv. Nutr, doi:10.1093/advances/nmab012
Khan, Kunutsor, Franco, Chowdhury, Vitamin D, type 2 diabetes and other metabolic outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies, Proc. Nutr. Soc, doi:10.1017/S0029665112002765.211
Khan, Kurnik-Lucka, Latacz, Gil, Systematic-narrative hybrid lterature review: Crosstalk between gastrointestinal renin-angiotensin and dopaminergic systems in the regulation of intestinal permeability by tight junctions, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms25105566
Klebanoff, Snowden, Historical (retrospective) cohort studies and other epidemiologic study designs in perinatal research, Am. J. Obs. Gynecol, doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2018.08.044.290
Lappe, Heaney, Why randomized controlled trials of calcium and vitamin D sometimes fail, Dermatoendocrinol, doi:10.4161/derm.19833.161
Ledderose, Bao, Zhang, Junger, Novel method for real-time monitoring of ATP release reveals multiple phases of autocrine purinergic signalling during immune cell activation, Acta Physiol, doi:10.1111/apha.12435.104
Lee, Flaherty, Blanchard, Agarwal, Council On Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention. Helmet use in preventing head injuries in bicycling, snow sports, and other recreational activities and sports, Pediatrics, doi:10.1542/peds.2022-058877.275
Lemen, Chrysotile asbestos as a cause of mesothelioma: Application of the Hill causation model, Int. J. Occup. Env. Health, doi:10.1179/oeh.2004.10.2.233.175
Leung, Muo, Liu, Chan, Vitamin D3 Intake Dose and Common Cancer: A Population-Based Case Control Study in a Chinese Population, J. Cancer, doi:10.7150/jca.16505.213
Li, Zhou, Vitamin D deficiency, obesity and diabetes, Cell Mol. Biol
Ling, Broad, Murphy, Pappachan, Pardesi-Newton et al., High-dose cholecalciferol booster therapy is associated with a reduced risk of mortality in patients with COVID-19: A cross-sectional multi-centre observational study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12123799.141
Liu, Meng, Hou, Characterization of the autocrine/paracrine function of vitamin D in human gingival fibroblasts and periodontal ligament cells, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0039878.256
Lopez-Caleya, Ortega-Valin, Fernandez-Villa, Delgado-Rodriguez, Martin-Sanchez et al., The role of calcium and vitamin D dietary intake on risk of colorectal cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis of case-control studies, Cancer Causes Control, doi:10.1007/s10552-021-01512-3.266
Lopez-Leon, Wegman-Ostrosky, Perelman, Sepulveda, Rebolledo et al., More than 50 longterm effects of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-95565-8.180
Luong, Nguyen, Impact of vitamin D in the treatment of tuberculosis, Am. J. Med. Sci, doi:10.1097/MAJ.0b013e3182070f47.239
Maghbooli, Sahraian, Jamalimoghadamsiahkali, Asadi, Zarei et al., Treatment With 25-hydroxyvitamin D(3) (calcifediol) is associated with a reduction in the blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio marker of disease severity in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A pilot multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded clinical trial, Endocr. Pr, doi:10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016
Malinverni, Ochogavia, Lecrenier, Scorpinniti, Preiser et al., Severe vitamin D deficiency in patients admitted to the emergency department with severe sepsis is associated with an increased 90-day mortality, Emerg. Med. J, doi:10.1136/emermed-2021-211973
Manson, Bassuk, Lee, Cook, Albert et al., The VITamin D and OmegA-3 TriaL (VITAL): Rationale and design of a large randomized controlled trial of vitamin D and marine omega-3 fatty acid supplements for the primary prevention of cancer and cardiovascular disease, Contemp. Clin. Trials, doi:10.1016/j.cct.2011.09.009
Manson, Cook, Lee, Christen, Bassuk et al., Marine n-3 Fatty Acids and Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1811403
Manson, Cook, Lee, Christen, Bassuk et al., Vitamin D Supplements and Prevention of Cancer and Cardiovascular Disease, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1809944
Mariani, Antonietti, Tajer, Ferder, Inserra et al., High-dose vitamin D versus placebo to prevent complications in COVID-19 patients: Multicentre randomized controlled clinical trial, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0267918
Martineau, Hanifa, Witt, Barnes, Hooper et al., Double-blind randomised controlled trial of vitamin D3 supplementation for the prevention of acute respiratory infection in older adults and their carers (ViDiFlu), Thorax, doi:10.1136/thoraxjnl-2015-206996
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: Systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.i6583.135
Mcdonnell, Baggerly, Baggerly, Aliano, French et al., Maternal 25(OH)D concentrations >/=40 ng/mL associated with 60% lower preterm birth risk among general obstetrical patients at an urban medical center, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0180483
Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French, Baggerly, Garland et al., Serum 25hydroxyvitamin D concentrations >/=40 ng/ml are associated with >65% lower cancer risk: Pooled analysis of randomized trial and prospective cohort study, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0152441
Mcgregor, Chauss, Freiwald, Yan, Wang et al., An autocrine Vitamin D-driven Th1 shutdown program can be exploited for COVID-19, doi:10.1101/2020.07.18.210161v1
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of vitamin D deficiency and treatment with COVID-19 incidence, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.05.08.20095893.292
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of vitamin D status and other clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722.243
Merzon, Tworowski, Gorohovski, Vinker, Golan Cohen et al., Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: An Israeli population-based study, FEBS J, doi:10.1111/febs.15495
Moher, Liberati, Tetzlaff, Altman, Group, Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement, PLoS Med, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Moher, Shamseer, Clarke, Ghersi, Liberati et al., Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement, Syst. Rev, doi:10.1186/2046-4053-4-1
Mohr, Gorham, Alcaraz, Kane, Macera et al., Does the evidence for an inverse relationship between serum vitamin D status and breast cancer risk satisfy the Hill criteria?, Dermatoendocrinol, doi:10.4161/derm.20449.249
Molloy, Murphy, Vitamin, Covid-19 and Children, Ir. Med. J
Morris, Anderson, Autocrine and paracrine actions of vitamin d, Clin. Biochem. Rev
Murai, Fernandes, Sales, Pinto, Goessler et al., Effect of a Single High Dose of Vitamin D3 on Hospital Length of Stay in Patients With Moderate to Severe COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.26848
Nafilyan, Bermingham, Ward, Morgan, Zaccardi et al., Risk of death following COVID-19 vaccination or positive SARS-CoV-2 test in young people in England, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-023-36494-0
National, Heart, Blood Institute, Ginde, Brower et al., Early high-dose vitamin D3 for critically ill, vitamin D-deficient patients, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1911124
Neale, Baxter, Romero, Mcleod, English et al., The D-Health Trial: A randomised controlled trial of the effect of vitamin D on mortality, Lancet. Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00345-4
Nhanes, Analytical Note for 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Data Analysis Using NHANES III (1988-1994)
Nielsen, Junker, Boelt, Cohen, Munger et al., Vitamin D status and severity of COVID-19, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-21513-9.242
Nik, Zulkeflee, Ab Rahim, Tuan Ismail, Association of vitamin D and magnesium with insulin sensitivity and their influence on glycemic control, World J. Diabetes, doi:10.4239/wjd.v14.i1.26.262
Nnoaham, Clarke, Low serum vitamin D levels and tuberculosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Int. J. Epidemiol, doi:10.1093/ije/dym247.240
Nogués, Od; Quesada-Gomez, Bouillon, Calcifediol treatment and COVID-19-related outcomes, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab405.169
Olivier, Boufous, Grzebieta, The impact of bicycle helmet legislation on cycling fatalities in Australia, Int. J. Epidemiol, doi:10.1093/ije/dyz003.274
Pender, CD8+ T-cell deficiency, Epstein-Barr virus infection, vitamin D deficiency, and steps to autoimmunity: A unifying hypothesis, Autoimmune Dis, doi:10.1155/2012/189096.112
Pereira, Dantas Damascena, Galvao Azevedo, De Almeida Oliveira, Da Mota Santana, Vitamin D deficiency aggravates COVID-19: Systematic review and meta-analysis, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr, doi:10.1080/10408398.2020.1841090.183
Perez-Castrillon, Duenas-Laita, Brandi, Jodar, Del Pino-Montes et al., Calcifediol is superior to cholecalciferol in improving vitamin D status in postmenopausal women: A randomized trial, J. Bone Min. Res, doi:10.1002/jbmr.4387.172
Pilz, Trummer, Theiler-Schwetz, Grubler, Verheyen et al., Critical appraisal of large vitamin D randomized controlled trials, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14020303.160
Pittas, Dawson-Hughes, Li, Van Dam, Willett et al., Vitamin D and calcium intake in relation to type 2 diabetes in women, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/diacare.29.03.06.dc05-1961.284
Pittas, Dawson-Hughes, Sheehan, Ware, Knowler et al., Vitamin D supplementation and prevention of type 2 diabetes, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1900906.286
Pludowski, Marcinowska-Suchowierska, Togizbayev, Belaya, Grant et al., High Doses" of Cholecalciferol for the Prevention and Treatment of Vitamin D Deficiency for Obese or Multi-Morbidity and Multi-Treatment Patients Requiring Multi-Drugs-A Narrative Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16152541
Polonowita, Wimalawansa, Molecular quantum and logic process of consciousness-Vitamin D big-data in COVID-19-A case for incorporating machine learning in medicine, Euro. J. Biomed. Pharma. Sci, doi:10.5281/zenodo.10435649
Polonowita, Wimalawansa, The impact of withholding cost-effective early treatments, such as vitamin D, on COVID-19: An analysis using an innovative logical paradigm, World J. Adv. Pharma Life Sci, doi:10.53346/wjapls.2023.5.2.0080
Quesada-Gomez, Lopez-Miranda, Entrenas-Castillo, Casado-Diaz, Nogues et al., Vitamin D endocrine system and COVID-19: Treatment with calcifediol, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14132716
Quraishi, Bittner, Blum, Hutter, Camargo et al., Association between preoperative 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and hospital-acquired infections following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery, JAMA Surg, doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2013.3176
Quraishi, Bittner, Blum, Mccarthy, Bhan et al., Prospective study of vitamin D status at initiation of care in critically ill surgical patients and risk of 90-day mortality, Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000000210.113
Quraishi, De Pascale, Needleman, Nakazawa, Kaneki et al., Effect of cholecalciferol supplementation on vitamin D status and cathelicidin levels in sepsis: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial, Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000001148
Rachman, Rahmaniyah, Khomeini, Iriani, The association between vitamin D deficiency and the clinical outcomes of hospitalized COVID-19 patients, F1000Res, doi:10.12688/f1000research.132214.3.261
Radujkovic, Hippchen, Tiwari-Heckler, Dreher, Boxberger et al., Vitamin D deficiency and outcome of COVID-19 patients, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092757
Raisi-Estabragh, Mccracken, Bethell, Cooper, Cooper et al., Greater risk of severe COVID-19 in Black, Asian and Minority Ethnic populations is not explained by cardiometabolic, socioeconomic or behavioural factors, or by 25(OH)-vitamin D status: Study of 1326 cases from the UK Biobank, J. Public Health, doi:10.1093/pubmed/fdaa095.147
Raju, Luthra, Shahbaz, Almatooq, Foucambert et al., Role of vitamin D deficiency in increased susceptibility to respiratory infections among children: A systematic review, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.29205.121
Ramezani-Jolfaie, Eftekhar, Dadinasab, Hesarooeyeh, Pakdaman et al., The effect of vitamin D and magnesium supplementation on clinical symptoms and serum inflammatory and oxidative stress markers in patients with COVID-19: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial, Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-023-07107-4.238
Rastogi, Bhansali, Khare, Suri, Yaddanapudi et al., Short term, high-dose vitamin D supplementation for COVID-19 disease: A randomised, placebo-controlled, study (SHADE study), Postgrad. Med. J, doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-139065.219
Razzaque, Wimalawansa, Minerals and Human Health: From Deficiency to Toxicity, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17030454
Rhodes, Evans, Alhazzani, Levy, Antonelli et al., Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock: 2016, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-017-4683-6
Rudd, Johnson, Agesa, Shackelford, Tsoi et al., Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990-2017: Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32989-7
Rustecka, Maret, Drab, Leszczynska, Tomaszewska et al., The Impact of COVID-19 pandemic during 2020-2021 on the vitamin D serum levels in the paediatric population in Warsaw, Poland, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13061990
Salahuddin, Ali, Hasan, Rao, Aqeel et al., Vitamin D accelerates clinical recovery from tuberculosis: Results of the SUCCINCT Study [Supplementary Cholecalciferol in recovery from tuberculosis]. A randomized, placebocontrolled, clinical trial of vitamin D supplementation in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis, BMC Infect. Dis, doi:10.1186/1471-2334-13-22.126
Sami, Abrahamsen, The latest evidence from vitamin D intervention trials for skeletal and non-skeletal outcomes, Calcif. Tissue Int, doi:10.1007/s00223-019-00616-y.253
Sarau, Rachabattuni, Gadde, Daruvuri, Marusca et al., Exploring the preventive potential of vitamin D against respiratory infections in preschool-age children: A cross-sectional study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16111595
Sarwahi, Atlas, Galina, Satin, Dowling et al., Seatbelts save Lives, and spines, in motor vehicle accidents: A review of the national trauma data bank in the pediatric population, Spine, doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000004072.277
Sciscent, Eisele, Ho, King, Jain et al., COVID-19 reinfection: The role of natural immunity, vaccines, and variants, J. Community Hosp. Intern. Med. Perspect, doi:10.1080/20009666.2021.1974665
Scragg, Khaw, Toop, Sluyter, Lawes et al., Monthly high-dose vitamin D supplementation and cancer risk: A post hoc analysis of the vitamin D assessment randomized clinical trial, JAMA Oncol, doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.2178.288
Scragg, Overview of results from the Vitamin D Assessment (ViDA) study, J. Endocrinol. Invest, doi:10.1007/s40618-019-01056-z
Selvaraj, Vitamin D, vitamin D receptor, and cathelicidin in the treatment of tuberculosis, Vitam. Horm, doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-386960-9.00013-7.241
Sempos, Durazo-Arvizu, Binkley, Jones, Merkel et al., Developing vitamin D dietary guidelines and the lack of 25-hydroxyvitamin D assay standardization: The ever-present past, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2015.08.027
Shah, Varna, Sharma, Mavalankar, Does vitamin D supplementation reduce COVID-19 severity?: A systematic review, QJM, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcac040.267
Shahini, Pesce, Argentiero, Solimando, Can vitamin D status influence seroconversion to SARS-COV2 vaccines? Front, Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.1038316.187
Shamseer, Moher, Clarke, Ghersi, Liberati et al., Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: Elaboration and explanation, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.g7647
Sharma, Kumar, Dutta, Vitamin D Supplementation, Insulin Resistance, and Cardiovascular Risk Factors: Who are Likely to Benefit the Most? Indian, J. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.4103/ijem.IJEM_594_19.210
Shiravi, Saadatkish, Abdollahi, Miar, Khanahmad et al., Vitamin D can be effective on the prevention of COVID-19 complications: A narrative review on molecular aspects, Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res, doi:10.1024/0300-9831/a000676
Shoemaker, Huynh, Smith, Mustad, Duarte et al., Immunomodulatory effects of vitamin D and prevention of respiratory tract infections and COVID-19, Top. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1097/TIN.0000000000000284
Singh, Bateman, Viswanath, Klaire, Mahmud et al., Risk of COVID-19 hospital admission and COVID-19 mortality during the first COVID-19 wave with a special emphasis on ethnic minorities: An observational study of a single, deprived, multiethnic UK health economy, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-046556
Sirbe, Rednic, Grama, Pop, An update on the effects of vitamin D on the immune system and autoimmune diseases, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms23179784.196
Slominski, Slominski, Goepfert, Kim, Holick et al., Can vitamin D prevent or manage COVID-19 illness?, Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00348.2020.166
Smaha, Jackuliak, Kuzma, Max, Binkley et al., Vitamin D deficiency prevalence in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 significantly decreased during the pandemic in Slovakia from 2020 to 2022 Which Was associated with decreasing mortality, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15051132
Smaha, Kuzma, Brazdilova, Nachtmann, Jankovsky et al., Patients with COVID-19 pneumonia with 25(OH)D levels lower than 12 ng/ml are at increased risk of death, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2022.01.044.200
Smolders, Torkildsen, Camu, Holmoy, An update on vitamin D and disease activity in multiple sclerosis, CNS Drugs, doi:10.1007/s40263-019-00674-8.294
Sobczak, Pawliczak, Effect of vitamin D3 supplementation on severe COVID-19: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16101402.245
Song, Shi, Zhang, Ivermectin for treatment of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27647.234
Sposito, Pennington, David, Duggan, Northey et al., Age-differential CD13 and interferon expression in airway epithelia affect SARS-CoV-2 infection-Effects of vitamin D, Mucosal Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.mucimm.2023.08.002.116
Stagi, Rigante, Lepri, Matucci Cerinic, Falcini, Severe vitamin D deficiency in patients with Kawasaki disease: A potential role in the risk to develop heart vascular abnormalities?, Clin. Rheumatol, doi:10.1007/s10067-015-2970-6.170
Stohs, Aruoma, Vitamin D and Wellbeing beyond Infections: COVID-19 and Future Pandemics, J. Am. Coll. Nutr, doi:10.1080/07315724.2020.1786302.140
Sun, Arbesman, Piliang, Vitamin D, autoimmunity and immune-related adverse events of immune checkpoint inhibitors, Arch. Dermatol. Res, doi:10.1007/s00403-020-02094-x.109
Tanaka, Ao, Kuwabara, Insufficiency of B vitamins with its possible clinical implications, J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr, doi:10.3164/jcbn.20-56.281
Tenali, Babu, A systematic literature review and future perspectives for handling big data analytics in COVID-19 diagnosis, New Gener. Comput, doi:10.1007/s00354-023-00211-8
Trecarichi, Mazzitelli, Serapide, Pelle, Tassone et al., Clinical characteristics and predictors of mortality associated with COVID-19 in elderly patients from a long-term care facility, Sci. Rep
Tulchinski, Snow, cholera, the Broad Street pump; Waterborne diseases then and now, Case Stud. Public. Health, doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-804571-8.00017-2.271
Ulitsky, Ananthakrishnan, Naik, Skaros, Zadvornova et al., Vitamin D deficiency in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: Association with disease activity and quality of life, JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr, doi:10.1177/0148607110381267.154
Underwood, White, Baker, Law, Moore-Gillon, Contact tracing and population screening for tuberculosis--who should be assessed?, J. Public. Health Med, doi:10.1093/pubmed/fdg012.272
Uwitonze, Razzaque, Role of magnesium in vitamin D activation and function, J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc, doi:10.7556/jaoa.2018.037.204
Verstuyf, Carmeliet, Bouillon, Mathieu, Vitamin, A pleiotropic hormone, Kidney Int, doi:10.1038/ki.2010.17
Virtanen, Nurmi, Aro, Bertone-Johnson, Hypponen et al., Vitamin D supplementation and prevention of cardiovascular disease and cancer in the Finnish vitamin D trial: A randomized controlled trial, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqab419.287
Wacker, Holick, Sunlight and Vitamin D: A global perspective for health, Derm. Endocrinol, doi:10.4161/derm.24494
Wald, Folic acid and neural tube defects: Discovery, debate and the need for policy change, J. Med. Screen, doi:10.1177/09691413221102321.282
Walsh, Mccartney, Laird, Mccarroll, Byrne et al., Title: Understanding a Low Vitamin D State in the Context of COVID-19, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.835480
Watkins, Yamshchikov, Lemonovich, Salata, The role of vitamin D deficiency in sepsis and potential therapeutic implications, J. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2011.07.002
Welch, Petticrew, Tugwell, Moher, O'neill et al., PRISMA-Equity 2012 extension: Reporting guidelines for systematic reviews with a focus on health equity, PLoS Med, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1001333
Werneke, Gaughran, Taylor, Vitamin D in the time of the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic -a clinical review from a public health and public mental health perspective, Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol, doi:10.1177/20451253211027699.188
Weyland, Grant, Howie-Esqauivel, Does sufficient evidence exist to support a causal association between vitamin D status and cardiovascular disease risk? An assessment using Hill's criteria for causality, Nutrients
White, Regulation of intracrine production of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D and its role in innate immune defense against infection, Arch. Biochem. Biophys, doi:10.1016/j.abb.2011.11.006.254
Wilding, Cardiovascular disease, statins and vitamin D, Br. J. Nurs, doi:10.12968/bjon.2012.21.4.214.153
Wimalawansa, Achieving population vitamin D sufficiency will markedly reduce healthcare costs, EJBPS
Wimalawansa, Biology of vitamin D, J. Steroids Horm. Sci, doi:10.24105/2157-7536.10.198
Wimalawansa, Controlling chronic diseases and acute Infections with vitamin D sufficiency, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15163623.167
Wimalawansa, Decoding the paradox: Understanding elevated hospitalization and reduced mortality in SARS-CoV-2 variants, Int. J. Front. Sci. Technol. Res, doi:10.53294/ijfstr.2024.6.2.0031
Wimalawansa, Dissanayake, Factors Affecting the Environmentally Induced, Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Aetiology in Dry Zonal Regions in Tropical Countries-Novel Findings, Environments
Wimalawansa, Dissanayake, Nanocrystal-induced chronic tubular-nephropathy in tropical countries: Diagnosis, mitigation, and eradication, Eur. J. Med. Res, doi:10.1186/s40001-023-01162-y.279
Wimalawansa, Enhancing the design of nutrient clinical trials for disease prevention: A focus on vitamin D: A systematic review, Nutr. Rev, doi:10.1093/nutrit/nuae164.(inpress
Wimalawansa, Infections and Autoimmunity-The Immune System and Vitamin D: A Systematic Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15173842
Wimalawansa, Maintaining optimum health requires longer-term stable vitamin D concentrations, Int. J. Regenr Med, doi:10.31487/j.RGM.2020.03.03.173
Wimalawansa, Non-musculoskeletal benefits of vitamin D, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.09.016
Wimalawansa, Overcoming infections including COVID-19, by maintaining circulating 25(OH)D concentrations above 50 ng/mL, Pathol. Lab. Med. Int, doi:10.2147/PLMI.S373617
Wimalawansa, Part 4: How does one determine the right amount and type of vitamin D to take? Available online
Wimalawansa, Physiological Basis for Using Vitamin D to Improve Health, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines11061542
Wimalawansa, Physiology of Vitamin D-Focusing on Disease Prevention, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16111666
Wimalawansa, Polonowita, Boosting immunity with vitamin D for preventing complications and deaths from COVID-19
Wimalawansa, Prophylactic use of vitamin D to maintain a robust immune system against infections like SARS-CoV-2, Glob. J. Endocrinol. Metab. GJEM, doi:10.31031/GJEM.2023.03.000571.199
Wimalawansa, Rapidly Increasing Serum 25(OH)D Boosts the Immune System, against Infections-Sepsis and COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14142997
Wimalawansa, Unlocking insights: Navigating COVID-19 challenges and Emulating future pandemic Resilience strategies with strengthening natural immunity, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34691
Wimalawansa, Unveiling the interplay-vitamin D and ACE-2 molecular interactions in mitigating complications and deaths from SARS-CoV-2, Biology, doi:10.3390/biology13100831
Wimalawansa, Vitamin, An essential component for skeletal health, Ann. N. Y Acad. Sci, doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06374.x.209
Wimalawansa, Weiss, Hollis, Integrating Endocrine, Genomic, and Extra-Skeletal Benefits of Vitamin D into National and Regional Clinical Guidelines, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16223969
Wimalawansa, Whittle, Vitamin D: A single initial dose is not bogus if followed by an appropriate maintenance intake, JBMR Plus, doi:10.1002/jbm4.10606.235
Wobke, Sorg, Steinhilber, Vitamin D in inflammatory diseases, Front. Physiol, doi:10.3389/fphys.2014.00244.152
Wolf, Trapani, Magnesium and vitamin D in long COVID syndrome; do they help?, Magnes. Res, doi:10.1684/mrh.2024.0521.263
Wortham, Li, Althomsons, Kammerer, Haddad et al., Tuberculosis genotype clusters and transmission in the U.S., 2009-2018, Am. J. Prev. Med, doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2021.02.006.273
Xu, Baylink, Chen, Reeves, Xiao et al., The importance of vitamin D metabolism as a potential prophylactic, immunoregulatory and neuroprotective treatment for COVID-19, J. Transl. Med, doi:10.1186/s12967-020-02488-5.171
Xu, Yang, Chen, Luo, Zhang et al., Vitamin D alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via regulation of the renin-angiotensin system, Mol. Med. Rep, doi:10.3892/mmr.2017.7546.193
Yu, Lin, Dai, Xu, Liu, Association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and osteoarthritis: A national populationbased analysis of NHANES 2001-2018, Front Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2023.1016809
Zangeneh, Valeh, Sharifi, Survival analysis based on body mass index in patients with Covid-19 admitted to the intensive care unit of Amir Al-Momenin Hospital in Arak-2021, Obes. Med, doi:10.1016/j.obmed.2022.100420
Zdrenghea, Makrinioti, Bagacean, Bush, Johnston et al., Vitamin D modulation of innate immune responses to respiratory viral infections, Rev. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.1909.190
Zhang, Shen, Petryk, Tang, Chen et al., English disease": Historical notes on rickets, the bone-lung link and child neglect issues, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu8110722
Zhang, Wu, Role of vitamin D in immune responses and autoimmune diseases, with emphasis on its role in multiple sclerosis, Neurosci. Bull, doi:10.1007/s12264-010-0731-8.111
Zhang, Zhang, Liu, Pei, Xu et al., Association between Vitamin D Supplementation and Cancer Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Cancers, doi:10.3390/cancers14153717.246
Zhang, Zhou, Hua, Li, Wu et al., Vitamin D receptor (VDR) on the cell membrane of mouse macrophages participates in the formation of lipopolysaccharide tolerance: mVDR is related to the effect of artesunate to reverse LPS tolerance, Cell Commun. Signal, doi:10.1186/s12964-023-01137-w.102
Zhong, Zhao, Zhao, Xia, High-dose vitamin D supplementation in patients with COVID-19: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Food Sci. Nutr, doi:10.1002/fsn3.3875.233
Zhuang, Zhu, Chi, Zhou, Peng et al., Efficacy of intermittent versus daily vitamin D supplementation on improving circulating 25(OH)D concentration: A Bayesian network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Front. Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2023.1168115.137
Zittermann, Ernst, Prokop, Fuchs, Dreier et al., Effect of vitamin D on all-cause mortality in heart failure (EVITA): A 3-year randomized clinical trial with 4000 IU vitamin D daily, Eur Heart J, doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehx235
Zmijewski, Nongenomic activities of vitamin D, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14235104.108
Zurita-Cruz, Fonseca-Tenorio, Villasis-Keever, Lopez-Alarcon, Parra-Ortega et al., Efficacy and safety of vitamin D supplementation in hospitalized COVID-19 pediatric patients: A randomized controlled trial, Front. Pediatr, doi:10.3389/fped.2022.943529.203
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu17030599",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu17030599",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Clinical trials consistently demonstrate an inverse correlation between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D; calcifediol] levels and the risk of symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 disease, complications, and mortality. This systematic review (SR), guided by Bradford Hill’s causality criteria, analyzed 294 peer-reviewed manuscripts published between December 2019 and November 2024, focusing on plausibility, consistency, and biological gradient. Evidence confirms that cholecalciferol (D3) and calcifediol significantly reduce symptomatic disease, complications, hospitalizations, and mortality, with optimal effects above 50 ng/mL. While vitamin D requires 3–4 days to act, calcifediol shows effects within 24 h. Among 329 trials, only 11 (3%) showed no benefit due to flawed designs. At USD 2/patient, D3 supplementation is far cheaper than hospitalization costs and more effective than standard interventions. This SR establishes a strong inverse relationship between 25(OH)D levels and SARS-CoV-2 vulnerability, meeting Hill’s criteria. Vitamin D3 and calcifediol reduce infections, complications, hospitalizations, and deaths by ~50%, outperforming all patented, FDA-approved COVID-19 therapies. With over 300 trials confirming these findings, waiting for further studies is unnecessary before incorporating them into clinical protocols. Health agencies and scientific societies must recognize the significance of these results and incorporate D3 and calcifediol for prophylaxis and early treatment protocols of SARS-CoV-2 and similar viral infections. Promoting safe sun exposure and adequate vitamin D3 supplementation within communities to maintain 25(OH)D levels above 40 ng/mL (therapeutic range: 40–80 ng/mL) strengthens immune systems, reduces hospitalizations and deaths, and significantly lowers healthcare costs. When serum 25(OH)D levels exceed 70 ng/mL, taking vitamin K2 (100 µg/day or 800 µg/week) alongside vitamin D helps direct any excess calcium to bones. The recommended vitamin D dosage (approximately 70 IU/kg of body weight for a non-obese adult) to maintain 25(OH)D levels between 50–100 ng/mL is safe and cost-effective for disease prevention, ensuring optimal health outcomes.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu17030599"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1096-8595",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Endocrinology and Human Nutrition, CardioMetabolic & Endocrine Institute, North Brunswick, NJ 08902, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Wimalawansa",
"given": "Sunil",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-06T16:32:32Z",
"timestamp": 1738859552000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-06T16:39:30Z",
"timestamp": 1738859970000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-06T17:10:02Z",
"timestamp": 1738861802987,
"version": "3.37.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
6
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1738800000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/17/3/599/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "599",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
6
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/17/3/599"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Vitamin D Deficiency Meets Hill’s Criteria for Causation in SARS-CoV-2 Susceptibility, Complications, and Mortality: A Systematic Review",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "17"
}
