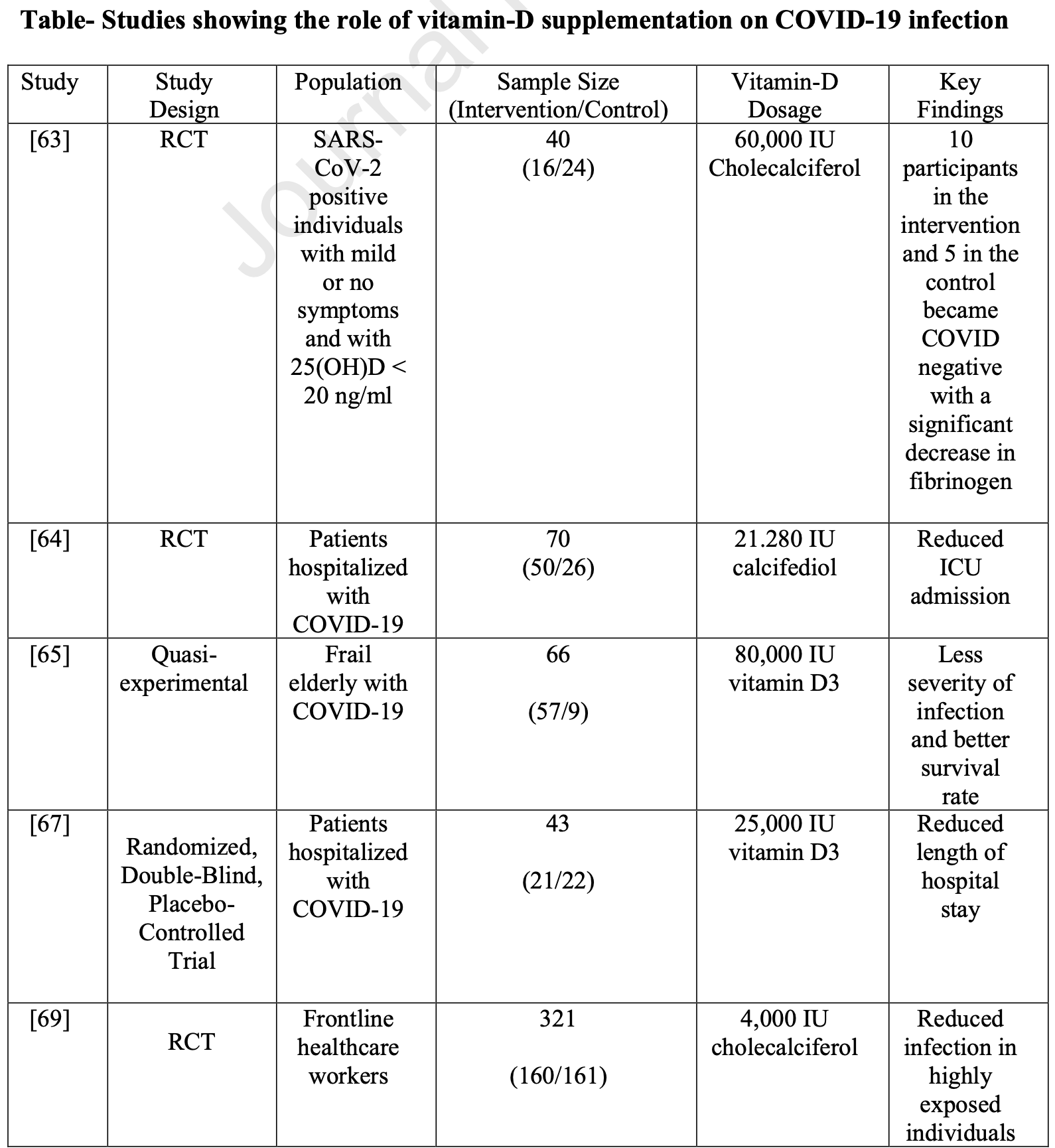
Therapeutic Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19 Patients
et al., Clinical Nutrition Open Science, doi:10.1016/j.nutos.2024.07.004, Jul 2024
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Review of vitamin D for COVID-19. Low vitamin D levels have been associated with increased susceptibility to and severity of COVID-19. Vitamin D plays an essential role in modulating the immune response and reducing inflammation, with proposed mechanisms including regulation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, production of antimicrobial peptides, and suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Clinical studies have shown that vitamin D supplementation may reduce disease severity, mortality, and complications in COVID-19 patients. Authors recommend maintaining adequate vitamin D levels through sun exposure and/or supplementation, as deficiency is common and linked to poor COVID-19 outcomes.
1.
Jaurrieta-Largo et al., A Machine Learning Approach to Understanding the Genetic Role in COVID-19 Prognosis: The Influence of Gene Polymorphisms Related to Inflammation, Vitamin D, and ACE2, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms26167975.
2.
Al-Khrasani et al., Do vitamins halt the COVID-19-evoked pro-inflammatory cytokines involved in the development of neuropathic pain?, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2025.118346.
3.
Kow et al., Vitamin D and COVID‐19: How much more evidence do we need?, Nutrition in Clinical Practice, doi:10.1002/ncp.11349.
4.
Bigman et al., A Comprehensive Scoping Review on Diet and Nutrition in Relation to Long COVID-19 Symptoms and Recovery, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17111802.
5.
Hewison, M., COVID-19 and our understanding of vitamin D and immune function, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2025.106710.
6.
Wimalawansa, S., Vitamin D Deficiency Meets Hill’s Criteria for Causation in SARS-CoV-2 Susceptibility, Complications, and Mortality: A Systematic Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17030599.
7.
Sanduzzi Zamparelli et al., Immune-Boosting and Antiviral Effects of Antioxidants in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Therapeutic Perspective, Life, doi:10.3390/life15010113.
8.
Fazli et al., Possible Link between Gut Microbiota, Diet, and COVID-19 Infection, Journal of Medical Bacteriology, 12:4, jmb.tums.ac.ir/index.php/jmb/article/view/525.
9.
Wojciulik et al., The impact of genetic polymorphism on course and severity of the SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease, Przeglad Epidemiologiczny, doi:10.32394/pe/194862.
10.
Wimalawansa (B), S., Unveiling the Interplay—Vitamin D and ACE-2 Molecular Interactions in Mitigating Complications and Deaths from SARS-CoV-2, Biology, doi:10.3390/biology13100831.
11.
Santa et al., Comparative analysis of COVID-19 responses in Japan and Africa: diet, phytochemicals, vitamin D, and gut microbiota in reducing mortality—A systematic review and meta-analysis, Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1465324.
12.
Kaushal, A., Nutraceuticals and pharmacological to balance the transitional microbiome to extend immunity during COVID-19 and other viral infections, Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12967-024-05587-9.
13.
Mu et al., Anti-inflammatory and Nutritional Interventions Against SARS-CoV-2: A Comprehensive Review, Journal of Agriculture and Food Research, doi:10.1016/j.jafr.2024.101422.
14.
Wimalawansa (C), S., Unlocking Insights: Navigating COVID-19 Challenges and Emulating Future Pandemic Resilience Strategies with Strengthening Natural Immunity, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34691.
15.
Imran et al., Therapeutic Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19 Patients, Clinical Nutrition Open Science, doi:10.1016/j.nutos.2024.07.004.
16.
Grant, W., Vitamin D and viral infections: Infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases, and cancers, Advances in Food and Nutrition Research, doi:10.1016/bs.afnr.2023.12.007.
17.
Polonowita et al., Molecular Quantum and Logic Process of Consciousness—Vitamin D Big-Data in COVID-19—A Case for Incorporating Machine Learning In Medicine, European Journal of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical sciences, doi:10.5281/zenodo.10435649.
18.
Gomaa et al., Pharmacological evaluation of vitamin D in COVID-19 and long COVID-19: recent studies confirm clinical validation and highlight metformin to improve VDR sensitivity and efficacy, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01383-x.
19.
Gotelli et al., Understanding the immune-endocrine effects of vitamin D in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a role in protecting against neurodamage?, Neuroimmunomodulation, doi:10.1159/000533286.
20.
Cutolo et al., Involvement of the secosteroid vitamin D in autoimmune rheumatic diseases and COVID-19, Nature Reviews Rheumatology, doi:10.1038/s41584-023-00944-2.
21.
Schloss et al., Nutritional deficiencies that may predispose to long COVID, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01183-3.
22.
Arora et al., Global Dietary and Herbal Supplement Use during COVID-19—A Scoping Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15030771.
23.
Nicoll et al., COVID-19 Prevention: Vitamin D Is Still a Valid Remedy, Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm11226818.
24.
Foshati et al., Antioxidants and clinical outcomes of patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A systematic review of observational and interventional studies, Food Science & Nutrition, doi:10.1002/fsn3.3034.
25.
Quesada-Gomez et al., Vitamin D Endocrine System and COVID-19: Treatment with Calcifediol, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14132716.
26.
DiGuilio et al., Micronutrient Improvement of Epithelial Barrier Function in Various Disease States: A Case for Adjuvant Therapy, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms23062995.
27.
Grant (B) et al., A Narrative Review of the Evidence for Variations in Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentration Thresholds for Optimal Health, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14030639.
28.
Shah Alam et al., The role of vitamin D in reducing SARS-CoV-2 infection: An update, International Immunopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107686.
29.
Griffin et al., Perspective: Vitamin D supplementation prevents rickets and acute respiratory infections when given as daily maintenance but not as intermittent bolus: implications for COVID-19, Clinical Medicine, doi:10.7861/clinmed.2021-0035.
30.
Kohlmeier et al., When Mendelian randomisation fails, BMJ Nutrition, Prevention & Health, doi:10.1136/bmjnph-2021-000265.
31.
Brenner, H., Vitamin D Supplementation to Prevent COVID-19 Infections and Deaths—Accumulating Evidence from Epidemiological and Intervention Studies Calls for Immediate Action, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13020411.
32.
Mercola et al., Evidence Regarding Vitamin D and Risk of COVID-19 and Its Severity, Nutrients 2020, 12:11, 3361, doi:10.3390/nu12113361.
33.
Basha et al., Is the shielding effect of cholecalciferol in SARS CoV-2 infection dependable? An evidence based unraveling, Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health, doi:10.1016/j.cegh.2020.10.005.
34.
Xu et al., The importance of vitamin d metabolism as a potential prophylactic, immunoregulatory and neuroprotective treatment for COVID-19, Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12967-020-02488-5.
35.
Alexander et al., Early Nutritional Interventions with Zinc, Selenium and Vitamin D for Raising Anti-Viral Resistance Against Progressive COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12082358.
36.
Andrade et al., Vitamin A and D deficiencies in the prognosis of respiratory tract infections: A systematic review with perspectives for COVID-19 and a critical analysis on supplementation, SciELO preprints, doi:10.1590/SciELOPreprints.839.
37.
Grant (C) et al., Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients, 12:4, 988, doi:10.3390/nu12040988.
38.
McCullough et al., Daily oral dosing of vitamin D3 using 5000 TO 50,000 international units a day in long-term hospitalized patients: Insights from a seven year experience, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.12.010.
39.
EFSA, Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to vitamin D and normal function of the immune system and inflammatory response (ID 154, 159), maintenance of normal muscle function (ID 155) and maintenance of normal cardiovascular function (ID 159) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (E, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1468.
40.
EFSA (B), Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of a health claim related to vitamin D and contribution to the normal function of the immune system pursuant to Article 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2015.4096.
Imran et al., 16 Jul 2024, peer-reviewed, 13 authors.
Contact: chaudharyimran39@gmail.com, sanabilquees1@gmail.com, usamaiqbalfts@gmail.com, imaryamaly@gmail.com, aliahsan514@gmail.com, ramnazia1010@gmail.com, drsaim3@gmail.com, kiraniqbal24@gmail.com, asad869@gmail.com, itsjawaria@gmail.com, chahmed1622@gmail.com, zahrakalim@yahoo.com, sajjad.ullah@mlt.uol.edu.pk.
Therapeutic Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19 Patients
Clinical Nutrition Open Science, doi:10.1016/j.nutos.2024.07.004
SARS-CoV-2 has had a significant worldwide impact, leading to widespread illness and mortality. With the lack of specific antiviral treatments, there is a growing interest in exploring the potential therapeutic effects of various nutritional supplements, including vitamin D. Vitamin D plays an essential role in health, has been implicated in modulating the immune response and reducing inflammation, which may have implications in the prevention and management of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Patients having low level of vitamin D are predisposed to severe consequences. Vitamin D and COVID-19 have shown an inverse relationship. This review is an understanding of the remedial effects of vitamin D in J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f COVID-19, including its potential mechanism of action, evidence from clinical studies, and recommendations for supplementation of vitamin D in patients suffering from COVID-19.
Conflict of Interest Statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest related to the research, authorship, and publication of this article. No financial, personal, or professional interests have influenced the content and findings presented in this review on the therapeutic role of vitamin D in COVID-19 patients. The authors have no affiliations, financial involvement, or funding sources that could potentially bias their interpretation of the available evidence or impact the objectivity of this work. This review is solely intended to contribute to the scientific understanding of the subject matter and does not reflect any competing interests. J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f
References
Ahmadpoor, Rostaing, Why the immune system fails to mount an adaptive immune response to a Covid-19 infection, Transplant International
Ahsan, Shabbir, Qadeer, Rafiq, Yaseen et al., Comparison of Rapid Antigen Test with RT-PCR for COVID-19 Diagnosis: Performance and Limitation
Alshahawey, A genetic insight into vitamin D binding protein and COVID-19, Medical Hypotheses
Annweiler, Hanotte, De L'eprevier, Sabatier, Lafaie et al., Vitamin D and survival in COVID-19 patients: A quasi-experimental study, The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology
Argano, Bocchio, Natoli, Scibetta, Monaco et al., Protective effect of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19-related intensive care hospitalization and mortality: definitive evidence from meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis, Pharmaceuticals
Bae, Choe, Holick, Lim, Association of vitamin D status with COVID-19 and its severity: Vitamin D and COVID-19: A narrative review, Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders
Behl, Shah, Kaur, Yadav, Kanwar et al., Role of ACE 2 and vitamin D: the two players in global fight against COVID-19 pandemic, Annals of the National Academy of Medical Sciences
Berry, Hesketh, Power, Hyppönen, Vitamin D status has a linear association with seasonal infections and lung function in British adults, British Journal of Nutrition
Bhaskar, Sinha, Banach, Mittoo, Weissert et al., Cytokine storm in COVID-19-immunopathological mechanisms, clinical considerations, and therapeutic approaches: the REPROGRAM consortium position paper, Frontiers in immunology
Bikle, Schwartz, Vitamin D binding protein, total and free vitamin D levels in different physiological and pathophysiological conditions, Front Endocrinol
Bikle, Schwartz, Vitamin D binding protein, total and free vitamin D levels in different physiological and pathophysiological conditions, Frontiers in endocrinology
Bollag, Gonzales, Phosphatidylglycerol and surfactant: A potential treatment for COVID-19?, Medical Hypotheses
Boonstra, Barrat, Crain, Heath, Savelkoul et al., 1α, 25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 has a direct effect on naive CD4+ T cells to enhance the development of Th2 cells, The Journal of Immunology
Brenner, Holleczek, Schöttker, Vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency and mortality from respiratory diseases in a cohort of older adults: potential for limiting the death toll during and beyond the COVID-19 pandemic?, Nutrients
Cannell, Vieth, Umhau, Holick, Grant et al., Epidemic influenza and vitamin D, Epidemiology & Infection
Castillo, Costa, Barrios, Díaz, Miranda et al., Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study, The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology
Charoenngam, Holick, Immunologic effects of vitamin D on human health and disease, Nutrients
Chu, Tsang, Tang, Lam, Lai et al., Acute renal impairment in coronavirus-associated severe acute respiratory syndrome, Kidney international
D'avolio, Avataneo, Manca, Cusato, Nicolò et al., 25-Hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are lower in patients with positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2, Nutrients
Dalan, Bornstein, El-Armouche, Rodionov, Markov et al., The ACE-2 in COVID-19: foe or friend?, Hormone and Metabolic Research
Di Filippo, Frara, Terenzi, Nannipieri, Locatelli et al., Lack of vitamin D predicts impaired long-term immune response to COVID-19 vaccination, Endocrine
Di Filippo, Terenzi, Ienno, Trasciatti, Bonaretti, Novel protective circulating miRNA are associated with preserved vitamin D levels in patients with mild COVID-19 presentation at hospital admission not progressing into severe disease, Endocrine
Farzi, Aghbash, Eslami, Azadi, Shamekh et al., The role of antigen-presenting cells in the pathogenesis of COVID-19, Pathology-Research and Practice
Filippo, Uygur, Locatelli, Nannipieri, Frara et al., Low vitamin D levels predict outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with both severe and non-severe disease at hospitalization, Endocrine
Findlay, Currie, Davidson, Cationic host defence peptides: potential as antiviral therapeutics, BioDrugs
Ghelani, Alesi, Mousa, Vitamin D and COVID-19: An overview of recent evidence, International Journal of Molecular Sciences
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients
Greiller, Martineau, Modulation of the immune response to respiratory viruses by vitamin D, Nutrients
Hall, Control of blood pressure by the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, Clinical cardiology
J O U R N A L P R E -P R O O F 25, Hanff, Harhay, Brown, Cohen et al., Is there an association between COVID-19 mortality and the renin-angiotensin system? A call for epidemiologic investigations, Clinical Infectious Diseases
J O U R N A L P R E, None
J O U R N A L P R E, None
J O U R N A L P R E, None
J O U R N A L P R E, None
Kara, Ekiz, Ricci, Kara, Chang et al., Scientific Strabismus' or two related pandemics: coronavirus disease and vitamin D deficiency, British Journal of Nutrition
Khan, Javed, Ahsan, Khan, Ahmad et al., The Unspoken Wounds: Understanding the Psychological Impact on Healthcare Professionals Fighting COVID-19 in Pakistan, Transboundary and Emerging Diseases
Kuba, Imai, Rao, Gao, Guo et al., A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury, Nature medicine
Kumar, Rathi, Haq, Wimalawansa, Sharma, Putative roles of vitamin D in modulating immune response and immunopathology associated with COVID-19, Virus research
Lamberg-Allardt, Vitamin D in foods and as supplements, Progress in biophysics and molecular biology
Lee, Channappanavar, Kanneganti, Coronaviruses: innate immunity, inflammasome activation, inflammatory cell death, and cytokines, Trends in immunology
Lemire, Archer, Beck, Spiegelberg, Immunosuppressive actions of 1, 25dihydroxyvitamin D3: preferential inhibition of Th1 functions, The Journal of nutrition
Mahdavi, A brief review of interplay between vitamin D and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: Implications for a potential treatment for COVID-19, Reviews in medical virology
Mckinney, Patel, Benns, Nash, Miller, Vitamin D status and supplementation in the critically ill, Current gastroenterology reports
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of vitamin D status and other clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results, JAMA network open
Menger, Lee, Notz, Wallqvist, Hasan et al., Administration of vitamin D and its metabolites in critically ill adult patients: an updated systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Critical Care
Mercola, Grant, Wagner, Evidence regarding vitamin D and risk of COVID-19 and its severity, Nutrients
Mohan, Cherian, Sharma, Exploring links between vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19, PLoS pathogens
Niet, Trémège, Coffiner, Rousseau, Calmes et al., Positive effects of vitamin D supplementation in patients hospitalized for COVID-19: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, Nutrients
Oristrell, Oliva, Casado, Subirana, Domínguez et al., Vitamin D supplementation and COVID-19 risk: A population-based, cohort study, Journal of endocrinological investigation
Pahar, Madonna, Das, Albanesi, Girolomoni, Immunomodulatory role of the antimicrobial LL-37 peptide in autoimmune diseases and viral infections, Vaccines
Peng, Liu, Zheng, Lu, Hou et al., Immunological aspects of SARS-CoV-2 infection and the putative beneficial role of vitamin-D, International journal of molecular sciences
Radujkovic, Hippchen, Tiwari-Heckler, Dreher, Boxberger, Vitamin D deficiency and outcome of COVID-19 patients, Nutrients
Raharusun, Priambada, Budiarti, Agung, Budi, Patterns of COVID-19 mortality and vitamin D: an Indonesian study, SSRN Electron J
Raju, Luthra, Shahbaz, Almatooq, Foucambert et al., Role of Vitamin D Deficiency in Increased Susceptibility to Respiratory Infections Among Children: A Systematic Review, Cureus
Rastogi, Bhansali, Khare, Suri, Yaddanapudi et al., Short term, high-dose vitamin D supplementation for COVID-19 disease: a randomised, placebo-controlled, study (SHADE study), Postgraduate medical journal
Sanyaolu, Okorie, Marinkovic, Patidar, Younis et al., Comorbidity and its impact on patients with COVID-19, SN comprehensive clinical medicine
Shen, Mei, Zhang, Xu, The effect of vitamin D supplementation on clinical outcomes for critically ill patients: a systemic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials, Frontiers in Nutrition
Shoaib, Noureen, Faisal, Zaheer, Imran et al., Factors associated with cycle threshold values (Ct-values) of SARS-CoV2-rRT-PCR, Molecular Biology Reports
Simões E Silva, Silveira, Ferreira, Teixeira, ACE2, angiotensin-(1-7) and M as receptor axis in inflammation and fibrosis, British journal of pharmacology
Singh, Sarkar, Gupta, Rout, Vitamin D Supplementation in Critically Ill Patients: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, Cureus
Speeckaert, Delanghe, Association of Vitamin D Status and COVID-19-Related Hospitalization and Mortality, Journal of General Internal Medicine
Speeckaert, Delanghe, Contribution of Vitamin D-Binding Protein Polymorphism to Susceptibility and Outcome of COVID-19 Patients, The Journal of Nutrition
Speeckaert, Delanghe, Some COVID hospitalizations are due to poor Vitamin D genes (Binding Protein in this commentary
Szodoray, Nakken, Gaal, Jonsson, Szegedi et al., The complex role of vitamin D in autoimmune diseases, Scandinavian journal of immunology
Tikellis, Thomas, Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is a key modulator of the renin angiotensin system in health and disease, International journal of peptides
Tsai, Lai, Lin, Luo, Lin et al., Clinical manifestation and disease progression in COVID-19 infection, Journal of the Chinese Medical Association
Valle, Yaktine, Taylor, Ross, Dietary reference intakes for calcium and vitamin D
Vanherwegen, Gysemans, Mathieu, Vitamin D endocrinology on the cross-road between immunity and metabolism, Molecular and cellular endocrinology
Villasis-Keever, López-Alarcón, Miranda-Novales, Zurita-Cruz, Barrada-Vázquez et al., Efficacy and safety of vitamin D supplementation to prevent COVID-19 in frontline healthcare workers. A randomized clinical trial, Archives of medical research
Weir, Thenappan, Bhargava, Chen, Does vitamin D deficiency increase the severity of COVID-19?, Clinical Medicine
Wimalawansa, Global epidemic of coronavirus-Covid-19: what can we do to minimize risks, Eur J Biomed
Xu, Baylink, Chen, Reeves, Xiao et al., The importance of vitamin d metabolism as a potential prophylactic, immunoregulatory and neuroprotective treatment for COVID-19, Journal of translational medicine
Xu, Yang, Chen, Luo, Zhang et al., Vitamin D alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via regulation of the renin-angiotensin system, Molecular medicine reports
Yazdanpanah, Hamblin, Rezaei, The immune system and COVID-19: Friend or foe?, Life sciences
Yuan, Pan, Kong, Zheng, Szeto et al., 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 suppresses renin gene transcription by blocking the activity of the cyclic AMP response element in the renin gene promoter, Journal of biological chemistry
Yuki, Fujiogi, Koutsogiannaki, COVID-19 pathophysiology: A review, Clinical immunology
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nutos.2024.07.004",
"ISSN": [
"2667-2685"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nutos.2024.07.004",
"alternative-id": [
"S2667268524000627"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Therapeutic Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19 Patients"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Clinical Nutrition Open Science"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nutos.2024.07.004"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd on behalf of European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0005-6402-1622",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Imran",
"given": "Muhammad",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zia",
"given": "Ramna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ali",
"given": "Maryam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sadaf",
"given": "Saima",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iqbal",
"given": "Kiran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ali",
"given": "Asad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iqbal",
"given": "Usama",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Din",
"given": "Sana Muhammad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shahid",
"given": "Jawaria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahsan",
"given": "Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kalim",
"given": "Zahra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shabbir",
"given": "Chaudhry Ahmed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ullah",
"given": "Sajjad",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical Nutrition Open Science",
"container-title-short": "Clinical Nutrition Open Science",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalnutritionopenscience.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-16T22:32:33Z",
"timestamp": 1721169153000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-16T22:32:33Z",
"timestamp": 1721169153000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-17T00:28:12Z",
"timestamp": 1721176092737
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1719792000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/legal/tdmrep-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1719792000000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 4,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-05T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1720137600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2667268524000627?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2667268524000627?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2667268524000627"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Therapeutic Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19 Patients",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}
