Involvement of the secosteroid vitamin D in autoimmune rheumatic diseases and COVID-19
et al., Nature Reviews Rheumatology, doi:10.1038/s41584-023-00944-2, Mar 2023
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
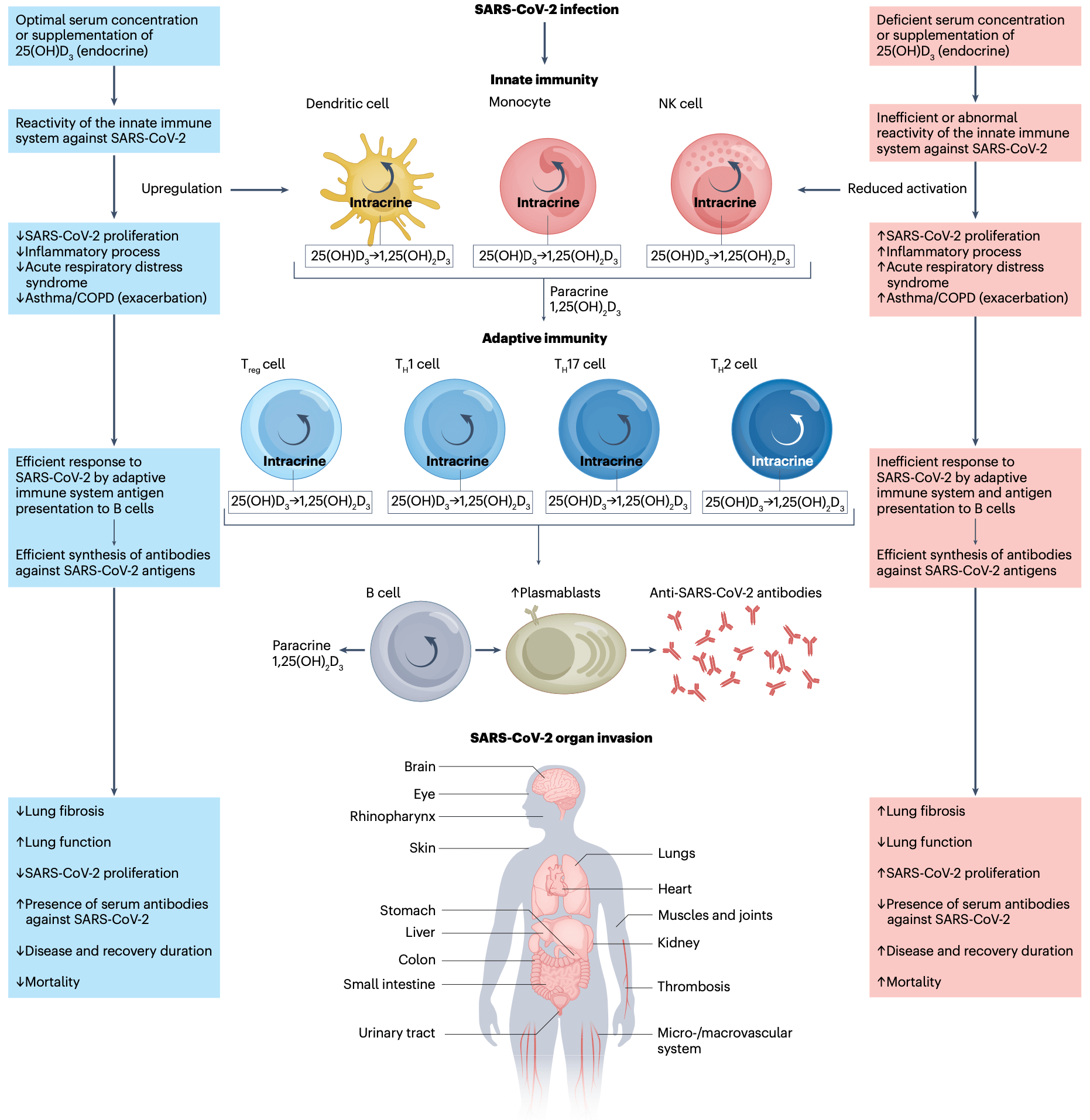
Review of the role of vitamin D in autoimmune rheumatic diseases and COVID-19. For COVID-19, vitamin D deficiency is associated with increased risk of infection and severe outcomes. Authors discuss the immunomodulatory effects of vitamin D, including enhancing innate antiviral response, downregulating inflammatory cytokines, and shifting T cell responses. Several randomized controlled trials suggest vitamin D supplementation may reduce COVID-19 severity and mortality. Authors find that monitoring vitamin D levels and appropriate supplementation is recommended for ARDs and COVID-19.
1.
Jaurrieta-Largo et al., A Machine Learning Approach to Understanding the Genetic Role in COVID-19 Prognosis: The Influence of Gene Polymorphisms Related to Inflammation, Vitamin D, and ACE2, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms26167975.
2.
Al-Khrasani et al., Do vitamins halt the COVID-19-evoked pro-inflammatory cytokines involved in the development of neuropathic pain?, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2025.118346.
3.
Kow et al., Vitamin D and COVID‐19: How much more evidence do we need?, Nutrition in Clinical Practice, doi:10.1002/ncp.11349.
4.
Bigman et al., A Comprehensive Scoping Review on Diet and Nutrition in Relation to Long COVID-19 Symptoms and Recovery, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17111802.
5.
Hewison, M., COVID-19 and our understanding of vitamin D and immune function, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2025.106710.
6.
Wimalawansa, S., Vitamin D Deficiency Meets Hill’s Criteria for Causation in SARS-CoV-2 Susceptibility, Complications, and Mortality: A Systematic Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17030599.
7.
Sanduzzi Zamparelli et al., Immune-Boosting and Antiviral Effects of Antioxidants in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Therapeutic Perspective, Life, doi:10.3390/life15010113.
8.
Fazli et al., Possible Link between Gut Microbiota, Diet, and COVID-19 Infection, Journal of Medical Bacteriology, 12:4, jmb.tums.ac.ir/index.php/jmb/article/view/525.
9.
Wojciulik et al., The impact of genetic polymorphism on course and severity of the SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease, Przeglad Epidemiologiczny, doi:10.32394/pe/194862.
10.
Wimalawansa (B), S., Unveiling the Interplay—Vitamin D and ACE-2 Molecular Interactions in Mitigating Complications and Deaths from SARS-CoV-2, Biology, doi:10.3390/biology13100831.
11.
Santa et al., Comparative analysis of COVID-19 responses in Japan and Africa: diet, phytochemicals, vitamin D, and gut microbiota in reducing mortality—A systematic review and meta-analysis, Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1465324.
12.
Kaushal, A., Nutraceuticals and pharmacological to balance the transitional microbiome to extend immunity during COVID-19 and other viral infections, Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12967-024-05587-9.
13.
Mu et al., Anti-inflammatory and Nutritional Interventions Against SARS-CoV-2: A Comprehensive Review, Journal of Agriculture and Food Research, doi:10.1016/j.jafr.2024.101422.
14.
Wimalawansa (C), S., Unlocking Insights: Navigating COVID-19 Challenges and Emulating Future Pandemic Resilience Strategies with Strengthening Natural Immunity, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34691.
15.
Imran et al., Therapeutic Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19 Patients, Clinical Nutrition Open Science, doi:10.1016/j.nutos.2024.07.004.
16.
Grant, W., Vitamin D and viral infections: Infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases, and cancers, Advances in Food and Nutrition Research, doi:10.1016/bs.afnr.2023.12.007.
17.
Polonowita et al., Molecular Quantum and Logic Process of Consciousness—Vitamin D Big-Data in COVID-19—A Case for Incorporating Machine Learning In Medicine, European Journal of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical sciences, doi:10.5281/zenodo.10435649.
18.
Gomaa et al., Pharmacological evaluation of vitamin D in COVID-19 and long COVID-19: recent studies confirm clinical validation and highlight metformin to improve VDR sensitivity and efficacy, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01383-x.
19.
Gotelli et al., Understanding the immune-endocrine effects of vitamin D in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a role in protecting against neurodamage?, Neuroimmunomodulation, doi:10.1159/000533286.
20.
Cutolo et al., Involvement of the secosteroid vitamin D in autoimmune rheumatic diseases and COVID-19, Nature Reviews Rheumatology, doi:10.1038/s41584-023-00944-2.
21.
Schloss et al., Nutritional deficiencies that may predispose to long COVID, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01183-3.
22.
Arora et al., Global Dietary and Herbal Supplement Use during COVID-19—A Scoping Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15030771.
23.
Nicoll et al., COVID-19 Prevention: Vitamin D Is Still a Valid Remedy, Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm11226818.
24.
Foshati et al., Antioxidants and clinical outcomes of patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A systematic review of observational and interventional studies, Food Science & Nutrition, doi:10.1002/fsn3.3034.
25.
Quesada-Gomez et al., Vitamin D Endocrine System and COVID-19: Treatment with Calcifediol, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14132716.
26.
DiGuilio et al., Micronutrient Improvement of Epithelial Barrier Function in Various Disease States: A Case for Adjuvant Therapy, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms23062995.
27.
Grant (B) et al., A Narrative Review of the Evidence for Variations in Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentration Thresholds for Optimal Health, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14030639.
28.
Shah Alam et al., The role of vitamin D in reducing SARS-CoV-2 infection: An update, International Immunopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107686.
29.
Griffin et al., Perspective: Vitamin D supplementation prevents rickets and acute respiratory infections when given as daily maintenance but not as intermittent bolus: implications for COVID-19, Clinical Medicine, doi:10.7861/clinmed.2021-0035.
30.
Kohlmeier et al., When Mendelian randomisation fails, BMJ Nutrition, Prevention & Health, doi:10.1136/bmjnph-2021-000265.
31.
Brenner, H., Vitamin D Supplementation to Prevent COVID-19 Infections and Deaths—Accumulating Evidence from Epidemiological and Intervention Studies Calls for Immediate Action, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13020411.
32.
Mercola et al., Evidence Regarding Vitamin D and Risk of COVID-19 and Its Severity, Nutrients 2020, 12:11, 3361, doi:10.3390/nu12113361.
33.
Basha et al., Is the shielding effect of cholecalciferol in SARS CoV-2 infection dependable? An evidence based unraveling, Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health, doi:10.1016/j.cegh.2020.10.005.
34.
Xu et al., The importance of vitamin d metabolism as a potential prophylactic, immunoregulatory and neuroprotective treatment for COVID-19, Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12967-020-02488-5.
35.
Alexander et al., Early Nutritional Interventions with Zinc, Selenium and Vitamin D for Raising Anti-Viral Resistance Against Progressive COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12082358.
36.
Andrade et al., Vitamin A and D deficiencies in the prognosis of respiratory tract infections: A systematic review with perspectives for COVID-19 and a critical analysis on supplementation, SciELO preprints, doi:10.1590/SciELOPreprints.839.
37.
Grant (C) et al., Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients, 12:4, 988, doi:10.3390/nu12040988.
38.
McCullough et al., Daily oral dosing of vitamin D3 using 5000 TO 50,000 international units a day in long-term hospitalized patients: Insights from a seven year experience, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.12.010.
39.
EFSA, Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to vitamin D and normal function of the immune system and inflammatory response (ID 154, 159), maintenance of normal muscle function (ID 155) and maintenance of normal cardiovascular function (ID 159) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (E, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1468.
40.
EFSA (B), Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of a health claim related to vitamin D and contribution to the normal function of the immune system pursuant to Article 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2015.4096.
Cutolo et al., 28 Mar 2023, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
Contact: mcutolo@unige.it.
Involvement of the secosteroid vitamin D in autoimmune rheumatic diseases and COVID-19
Nature Reviews Rheumatology, doi:10.1038/s41584-023-00944-2
Evidence supporting the extra-skeletal role of vitamin D in modulating immune responses is centred on the effects of its final m et ab ol ite, 1 ,2 5-di hy dr ox yvitamin D 3 (1,25(OH) 2 D 3 , also known as calcitriol), which is regarded as a t r u e s t e r o id h o r m o ne. 1,25(OH) 2 D 3 , the active form of vitamin D, can modulate the innate immune system in response to invading pathogens, downregulate inflammatory responses and support the adaptive arm of the immune system. Serum concentrations of its inactive precursor 25-hydroxyvitamin D 3 (25(OH)D 3 , also known as calcidiol) fluctuate seasonally (being lowest in winter) and correlate negatively with the activation of the immune system as well as with the incidence and severity of autoimmune rheumatic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus and systemic sclerosis. Thus, a low serum concentration of 25(OH)D 3 is considered to be a risk factor for autoimmune rheumatic diseases and vitamin D 3 supplementation seems to improve the prognosis; moreover, long-term vitamin D 3 supplementation seems to reduce their incidence (i.e. rheumatoid arthritis). In the setting of COVID-19, 1,25(OH) 2 D 3 seems to downregulate the early viral phase (SARS-CoV-2 infection), by enhancing innate antiviral effector mechanisms, as well as the later cytokine-mediated hyperinflammatory phase. This Review provides an update of the latest scientific and clinical evidence concerning vitamin D and immune response in autoimmune rheumatic diseases and COVID-19, which justify the need for monitoring of serum 25(OH)D 3 concentrations and for appropriate supplementation following clinical trial-based approaches.
Sections Key points • Vitamin D 3 (cholecalciferol) is a prototypical secosteroid, a type of steroid with a 'broken' ring, which originates from cholesterol, as do all steroid hormones (including glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids and sex hormones). • The activation of vitamin D 3 is accomplished by sequential hydroxylations that produce 25(OH)D 3 (calcidiol) in the liver and then the active metabolite 1,25(OH) 2 D 3 (calcitriol) in the kidney and at extra-renal sites (including immune cells). • 1,25(OH) 2 D 3 modulates the innate immune response against pathogens and invading microorganisms, downregulates the inflammatory response and supports the adaptive arm of the immune system. • Reduced serum concentrations of 25(OH)D 3 are detected in autoimmune rheumatic diseases such as rheumatoid, systemic lupus erythematosus and systemic sclerosis; vitamin D supplementation seems to improve at least the prognosis. • Serum concentrations of vitamin D fluctuate seasonally (being lowest in winter) and correlate negatively with the activation of the immune system and with the incidence and severity of autoimmune rheumatic diseases. • 1,25(OH) 2 D 3 downregulates both the early viral phase of COVID-19, through the enhancement of innate antiviral effector mechanisms, and the later..
Author contributions M.C. and E.G. researched data for the article. V.S. and S.P. made a substantial contribution to discussion of the content. M.C. and E.G. wrote the manuscript. All authors reviewed and/or edited the manuscript before submission.
Competing interests M.C. declares that his university laboratory has received funds for research from Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim and Pfizer. V.S. declares that she has received funds for research from Boehringer-Ingelheim and Janssen-Cilag. S.P. and E.G. declare no competing interests.
References
Adami, An exploratory study on the role of vitamin D supplementation in improving pain and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis, Mod. Rheumatol
An, Sun, Chen, Li, Vitamin D levels in systemic sclerosis patients: a meta-analysis, Drug Des. Dev. Ther
Andersson, Carlsen, Petersen, Skakkebaek, Variation in levels of serum inhibin B, testosterone, estradiol, luteinizing (83) hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, and sex hormone-binding globulin in monthly samples from healthy men during a 17-month period: possible effects of seasons, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab
Andreoli, A 24-month prospective study on the efficacy and safety of two different monthly regimens of vitamin D supplementation in pre-menopausal women with systemic lupus erythematosus, Lupus
Arkema, Exposure to ultraviolet-B and risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis among women in the Nurses' Health Study, Ann. Rheum. Dis
Arnson, Serum 25-OH vitamin D concentrations are linked with various clinical aspects in patients with systemic sclerosis: a retrospective cohort study and review of the literature, Autoimmun. Rev
Aslam, John, Bhatti, Jahangir, Kamboh, Vitamin D as a principal factor in mediating rheumatoid arthritis-derived immune response, Biomed. Res. Int
Atteritano, Skin involvement and pulmonary hypertension are associated with vitamin D insufficiency in scleroderma, Int. J. Mol. Sci
Baeke, Takiishi, Korf, Gysemans, Mathieu, Vitamin D: modulator of the immune system, Curr. Opin. Pharmacol
Bagheri-Hosseinabadi, Vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene polymorphism and risk of rheumatoid arthritis (RA): systematic review and meta-analysis, Clin. Rheumatol
Barbhaiya, Costenbader, Ultraviolet radiation and systemic lupus erythematosus, Lupus
Barbáchano, The endocrine vitamin D system in the gut, Mol. Cell Endocrinol
Barrat, In vitro generation of interleukin 10-producing regulatory CD4 + T cells is induced by immunosuppressive drugs and inhibited by T helper type 1 (Th1)-and Th2-inducing cytokines, J. Exp. Med
Bellan, Pathophysiological role and therapeutic implications of vitamin D in autoimmunity: focus on chronic diseases, Nutrients
Ben-Zvi, The impact of vitamin D on dendritic cell function in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, PLoS One
Bikle, 25 Hydroxyvitamin D 1 α-hydroxylase is required for optimal epidermal differentiation and permeability barrier homeostasis, J. Invest. Dermatol
Bikle, Gee, Halloran, Haddad, Free 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D levels in serum from normal subjects, pregnant subjects, and subjects with liver disease, J. Clin. Invest
Bikle, Vitamin D regulation of and by long non coding RNAs, Mol. Cell Endocrinol
Bikle, Vitamin D regulation of immune function during COVID-19, Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord
Bikle, Vitamin D: production, metabolism and mechanisms of action
Bills, Mcdonald, Antiricketic substances: II. The action of n-Butyl nitrite on activated cholesterol and the antiricketic vitamin, J. Biol. Chem
Birmingham, Evidence that abnormally large seasonal declines in vitamin D status may trigger SLE flare in non-African Americans, Lupus
Bishop, Ismailova, Dimeloe, Hewison, White, Vitamin D and immune regulation: antibacterial, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, JBMR Plus
Borba, Shoenfeld, Vitamin D and immune system function in patients with COVID-19, Isr. Med. Assoc. J
Borsche, Glauner, Von Mendel, COVID-19 mortality risk correlates inversely with vitamin D 3 status, and a mortality rate close to zero could theoretically be achieved at 50 ng/mL 25(OH)D 3 : results of a systematic review and meta-analysis, Nutrients
Bouillon, Comparative analysis of nutritional guidelines for vitamin D, Nat. Rev. Endocrinol
Bronson, Are humans seasonally photoperiodic?, J. Biol. Rhythm
Buchanan, The effect of endogenous estrogen fluctuation on metabolism of 25-hydroxyvitamin D, Calcif. Tissue Int
Buckland, Rheumatoid arthritis: control of T H 17 cell activity in RA by a combination of vitamin D receptor signaling and TNF-blockade, Nat. Rev. Rheumatol
Buondonno, Vitamin D and immunomodulation in early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study, PLoS One
Caimmi, Vitamin D serum levels and the risk of digital ulcers in systemic sclerosis: a longitudinal study, Int. J. Rheum. Dis
Cantorna, Snyder, Lin, Yang, Vitamin D and 1,25(OH)2D regulation of T cells, Nutrients
Cantorna, Yu, Bruce, The paradoxical effects of vitamin D on type 1 mediated immunity, Mol. Asp. Med
Caramaschi, Very low levels of vitamin D in systemic sclerosis patients, Clin. Rheumatol
Carlberg, Endocrine functions of vitamin D, Mol. Cell Endocrinol
Carlberg, Genome-wide (over)view on the actions of vitamin D, Front. Physiol
Charoenngam, Holick, Immunologic effects of vitamin D on human health and disease, Nutrients
Chauss, Autocrine vitamin D signaling switches off pro-inflammatory programs of T H 1 cells, Nat. Immunol
Chen, Modulatory effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 on human B cell differentiation, J. Immunol
Chillon, Relationship between vitamin D status and antibody response to COVID-19 mRNA vaccination in healthy adults, Biomedicines
Corallo, Sarcopenia in systemic sclerosis: the impact of nutritional, clinical, and laboratory features, Rheumatol. Int
Corrado, Relationship between body mass composition, bone mineral density, skin fibrosis and 25(OH) Vitamin D serum levels in systemic sclerosis, PLoS One
Costenbader, Chang, Laden, Puett, Karlson, Geographic variation in rheumatoid arthritis incidence among women in the United States, Arch. Intern. Med
Cutolo, Campitiello, Gotelli, Soldano, The role of M1/M2 macrophage polarization in rheumatoid arthritis synovitis, Front. Immunol
Cutolo, Further emergent evidence for the vitamin D endocrine system involvement in autoimmune rheumatic disease risk and prognosis, Ann. Rheum. Dis
Cutolo, Otsa, Uprus, Paolino, Seriolo, Vitamin D in rheumatoid arthritis, Autoimmun. Rev
Cutolo, Paolino, Smith, Evidences for a protective role of vitamin D in COVID-19, RMD Open
Cutolo, Pizzorni, Sulli, Vitamin D endocrine system involvement in autoimmune rheumatic diseases, Autoimmun. Rev
Cutolo, Plebani, Shoenfeld, Adorini, Tincani, Vitamin D endocrine system and the immune response in rheumatic diseases, Vitam. Horm
Cutolo, Rheumatoid arthritis: circadian and circannual rhythms in RA, Nat. Rev. Rheumatol
Cutolo, Smith, Detection of microvascular changes in systemic sclerosis and other rheumatic diseases, Nat. Rev. Rheumatol
Cutolo, Smith, Paolino, Understanding immune effects of oestrogens to explain the reduced morbidity and mortality in female versus male COVID-19 patients. Comparisons with autoimmunity and vaccination, Clin. Exp. Rheumatol
Cutolo, Soldano, Sulli, Smith, Gotelli, Influence of seasonal vitamin D changes on clinical manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic sclerosis, Front. Immunol
Cutolo, Straub, Sex steroids and autoimmune rheumatic diseases: state of the art, Nat. Rev. Rheumatol
Cutolo, Vitamin D and autoimmune rheumatic diseases, Rheumatology
Cutolo, Vitamin D involvement in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythaematosus, Ann. Rheum. Dis
Cutolo, Vitamin D or hormone D deficiency in autoimmune rheumatic diseases, including undifferentiated connective tissue disease, Arthritis Res. Ther
Cutolo, Vitamin D, steroid hormones, and autoimmunity, Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci
D'ambrosio, Inhibition of IL-12 production by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 . Involvement of NF-κB downregulation in transcriptional repression of the p40 gene, J. Clin. Invest
D'ecclesiis, Vitamin D and SARS-CoV2 infection, severity and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis, PLoS One
Daiger, Schanfield, Cavalli-Sforza, Group-specific component (Gc) proteins bind vitamin D and 25-hydroxyvitamin D, Proc. Natl Acad. Sci
Dall'ara, Cutolo, Andreoli, Tincani, Paolino, Vitamin D and systemic lupus erythematous: a review of immunological and clinical aspects, Clin. Exp. Rheumatol
Dall'ara, Winter lupus flares are associated with low vitamin D levels in a retrospective longitudinal study of Italian adult patients, Clin. Exp. Rheumatol
Daniel, Sartory, Zahn, Radeke, Stein, Immune modulatory treatment of trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid colitis with calcitriol is associated with a change of a T helper (Th) 1/Th17 to a Th2 and regulatory T cell profile, J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther
Davies, Jenkins, Allen, Taylor, Tissue-resident macrophages, Nat. Immunol
De Vries, Immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory properties of interleukin 10, Ann. Med
De, Seasonal changes in gene expression represent cell-type composition in whole blood, Hum. Mol. Genet
Dehghan, Rahimpour, Soleymani-Salehabadi, Owlia, Role of vitamin D in flare ups of rheumatoid arthritis, Z. Rheumatol
Dhawan, Christakos, Novel regulation of 25-hydroxyvitamin D 3 24-hydroxylase (24(OH)ase) transcription by glucocorticoids: cooperative effects of the glucocorticoid receptor, C/EBPβ, and the Vitamin D receptor in 24(OH)ase transcription, J. Cell Biochem
Diaconu, Role of Vitamin D in systemic sclerosis: a systematic literature review, J. Immunol. Res
Dionne, Duchatelier, Seidman, The influence of vitamin D on M1 and M2 macrophages in patients with Crohn's disease, Innate Immun
Dissanayake, Prognostic and therapeutic role of vitamin D in COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab
Donati, Rapid nontranscriptional effects of calcifediol and calcitriol, Nutrients
Dopico, Widespread seasonal gene expression reveals annual differences in human immunity and physiology, Nat. Commun
Drozdenko, Heine, Worm, Oral vitamin D increases the frequencies of CD38 + human B cells and ameliorates IL-17-producing T cells, Exp. Dermatol
Drozdenko, Scheel, Heine, Baumgrass, Worm, Impaired T cell activation and cytokine production by calcitriol-primed human B cells, Clin. Exp. Immunol
Dupuis, Pagano, Pierdominici, Ortona, The role of vitamin D in autoimmune diseases: could sex make the difference?, Biol. Sex. Differ
Dutta, Kakati, Barman, Bora, Vitamin D status and its relationship with systemic lupus erythematosus as a determinant and outcome of disease activity, Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig, doi:10.1515/hmbci-2018-0064
Enjuanes, Functional analysis of the I.3, I.6, pII and I.4 promoters of CYP19 (aromatase) gene in human osteoblasts and their role in vitamin D and dexamethasone stimulation, Eur. J. Endocrinol
Escaleira, Sonohara, Brentani, Sex steroids induced up-regulation of 1,25-(OH)2 vitamin D 3 receptors in T 47D breast cancer cells, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol
Eyles, Smith, Kinobe, Hewison, Mcgrath, Distribution of the vitamin D receptor and 1 α-hydroxylase in human brain, J. Chem. Neuroanat
Feldthusen, Grimby-Ekman, Forsblad-D'elia, Jacobsson, Mannerkorpi, Seasonal variations in fatigue in persons with rheumatoid arthritis: a longitudinal study, BMC Musculoskelet. Disord
Finch, Higher concentrations of vitamin D in Canadian children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis compared to healthy controls are associated with more frequent use of vitamin D supplements and season of birth, Nutr. Res
Finsen, Om, Bekaempelse af Lupus vulgaris med en Redegørelse for de i Danmark opnaaede Resultater
Foocharoen, Effect of season on clinical outcomes of Thai systemic sclerosis: analysis of the Thai National Healthcare Database, Mod. Rheumatol
Franco, Freitas, Bernardo, Pereira, Vitamin D supplementation and disease activity in patients with immune-mediated rheumatic diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Medicine
Fritsche, Mondal, Ehrnsperger, Andreesen, Kreutz, Regulation of 25-hydroxyvitamin D 3 -1α-hydroxylase and production of 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 by human dendritic cells, Blood
Gambichler, Chrobok, Höxtermann, Kreuter, Significantly decreased serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in a large German systemic sclerosis cohort, J. Rheumatol
Glossmann, Origin of 7-dehydrocholesterol (provitamin D) in the skin, J. Invest. Dermatol
Gopinath, Danda, Supplementation of 1,25 dihydroxy vitamin D 3 in patients with treatment naive early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomised controlled trial, Int. J. Rheum. Dis
Gray, Omdahl, Ghazarian, Deluca, 25-Hydroxycholecalciferol-1hydroxylase. Subcellular location and properties, J. Biol. Chem
Gregori, Regulatory T cells induced by 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 and mycophenolate mofetil treatment mediate transplantation tolerance, J. Immunol
Groseanu, Low vitamin D status in systemic sclerosis and the impact on disease phenotype, Eur. J. Rheumatol
Guan, Association between circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D and systemic lupus erythematosus: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Int. J. Rheum. Dis
Guan, Hao, Guan, Bu, Wang, The effect of vitamin D supplementation on rheumatoid arthritis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Front. Med
Hahn, Vitamin D and marine omega 3 fatty acid supplementation and incident autoimmune disease: VITAL randomized controlled trial, BMJ
Hajjaj-Hassouni, Evaluation of vitamin D status in rheumatoid arthritis and its association with disease activity across 15 countries: "The COMORA Study, Int. J. Rheumatol
Han, Zhuang, Shumyak, Yang, Reeves, Mechanisms of autoantibody production in systemic lupus erythematosus, Front. Immunol
Hansdottir, Monick, Vitamin D effects on lung immunity and respiratory diseases, Vitam. Horm
Herly, Impact of season on the association between vitamin D levels at diagnosis and one-year remission in early rheumatoid arthritis, Sci. Rep
Hewison, Adams, Extrarenal 1α-hydroxylase
Hewison, Differential regulation of vitamin D receptor and its ligand in human monocyte-derived dendritic cells, J. Immunol
Hidalgo, Deeb, Pike, Johnson, Trump, Dexamethasone enhances 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 effects by increasing vitamin D receptor transcription, J. Biol. Chem
Holick, Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab
Hollis, The determination of circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D: no easy task, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab
Holt, Strickland, Wikström, Jahnsen, Regulation of immunological homeostasis in the respiratory tract, Nat. Rev. Immunol
Horiuchi, Genome-wide analysis reveals unique regulation of transcription of Th2-specific genes by GATA3, J. Immunol
Hosseini, El Abd, Ducharme, Effects of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19 related outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Nutrients
Huff, Boyd, Jialal, Physiology, None, Cholesterol
Humbert, Treatment of scleroderma with oral 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 : evaluation of skin involvement using non-invasive techniques. Results of an open prospective trial, Acta Derm. Venereol
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality, Aging Clin. Exp. Res
Islam, Khandker, Alam, Kotyla, Hassan, Vitamin D status in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): a systematic review and metaanalysis, Autoimmun. Rev
James, Weaver, Cantorna, Control of circulating IgE by the vitamin D receptor in vivo involves B cell intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms, J. Immunol
Jaun, High-dose vitamin D substitution in patients with COVID-19: study protocol for a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-center study-VitCov Trial, Trials
Jenkinson, High throughput LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous analysis of multiple vitamin D analytes in serum, J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci
Jenkinson, The vitamin D metabolome: an update on analysis and function, Cell Biochem. Funct
Jiang, Dysregulation of vitamin D metabolism in the brain and myocardium of rats following prolonged exposure to dexamethasone, Psychopharmacology
Jiang, Yang, Xue, Li, Zhang, 1α, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 attenuates TGF-β-induced pro-fibrotic effects in human lung epithelial cells through inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition, Nutrients
Karimzadeh, Shirzadi, Karimifar, The effect of Vitamin D supplementation in disease activity of systemic lupus erythematosus patients with Vitamin D deficiency: a randomized clinical trial, J. Res. Med. Sci
Karlsson, Carlsson, Larne, Andersson, Pütsep, Vitamin D 3 induces pro-LL-37 expression myeloid precursors from patients with severe congenital neutropenia, J. Leukoc. Biol
Ketha, Comparison of the effect of daily versus bolus dose maternal vitamin D 3 supplementation on the 24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 to 25-hydroxyvitamin D 3 ratio, Bone
Khoo, Regulation of cytokine responses by seasonality of vitamin D status in healthy individuals, Clin. Exp. Immunol
Khoo, Seasonal variation in vitamin D 3 levels is paralleled by changes in the peripheral blood human T cell compartment, Rheumatol
Kosmaczewska, Swierkot, Ciszak, Wiland, The role of Th1, Th17, and Treg cells in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis including anti-inflammatory action of Th1 cytokines, Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw
Kurahashi, Matsunuma, Kawane, Abe, Horiuchi, Dexamethasone enhances vitamin D-24-hydroxylase expression in osteoblastic (UMR-106) and renal (LLC-PK1) cells treated with 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3, Endocrine
Latini, VDR polymorphisms in autoimmune connective tissue diseases: focus on Italian population, J. Immunol. Res
Legacy, Dietary supplements to reduce symptom severity and duration in people with SARS-CoV-2: study protocol for a randomised, double-blind, placebo controlled clinical trial, BMJ Open
Lerman, Burnham, Behrens, 1,25 Dihydroxyvitamin D 3 limits monocyte maturation in lupus sera, Lupus
Li, Efficacy and safety of 22-oxa-calcitriol in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a phase II trial, Med. Sci. Monit
Liang, Cai, Li, Yang, 1,25 Dihydroxy vitamin D 3 induces macrophage polarization to M2 by upregulating T cell Ig mucin 3 expression, Mol. Med. Rep
Liel, Kraus, Levy, Shany, Evidence that estrogens modulate activity and increase the number of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D receptors in osteoblast-like cells (ROS 17/2.8), Endocrinology
Liel, Shany, Smirnoff, Schwartz, Estrogen increases 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D receptors expression and bioresponse in the rat duodenal mucosa, Endocrinology
Lima, Vitamin D supplementation in adolescents and young adults with juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus for improvement in disease activity and fatigue scores: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, Arthritis Care Res
Liu, Toll-like receptor triggering of a vitamin D-mediated human antimicrobial response, Science
Lou, Murtola, Tuohimaa, Regulation of aromatase and 5α-reductase by 25-hydroxyvitamin D(3), 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3), dexamethasone and progesterone in prostate cancer cells, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol
Maghbooli, Treatment with 25-Hydroxyvitamin D 3 (calcifediol) is associated with a reduction in the blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio marker of disease severity in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a pilot multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded clinical trial, Endocr. Pract
Mak, The impact of Vitamin D on the immunopathophysiology, disease activity, and extra-musculoskeletal manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus, Int. J. Mol. Sci
Martineau, Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and metaanalysis of individual participant data, BMJ
Mateen, Moin, Shahzad, Khan, Level of inflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis patients: correlation with 25-hydroxy vitamin D and reactive oxygen species, PLoS One
Matsumoto, Relationships between serum 25-hydroxycalciferol, vitamin D intake and disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-TOMORROW study, Mod. Rheumatol
Merlino, Iowa Women's Health Study. Vitamin D intake is inversely associated with rheumatoid arthritis: results from the Iowa Women's Health Study, Arthritis Rheum
Merriman, Powell, Santos, Nelson, Intramammary 25-hydroxyvitamin D 3 treatment modulates innate immune responses to endotoxin-induced mastitis, J. Dairy. Sci
Mohammad, Mishra, Ashraf, Emerging role of vitamin D and its associated molecules in pathways related to pathogenesis of thrombosis, Biomolecules
Mok, Bro, Ho, Singh, Jannetto, Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D 3 levels and flares of systemic lupus erythematosus: a longitudinal cohort analysis, Clin. Rheumatol
Monticielo, Vitamin D and polymorphisms of VDR gene in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, Clin. Rheumatol
Moore, De Waal Malefyt, Coffman, O'garra, Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor, Annu. Rev. Immunol
Moore, Piazza, Nolan, Lynch, Treatment with dexamethasone and vitamin D 3 attenuates neuroinflammatory age-related changes in rat hippocampus, Synapse
Morgan, Sliney, Morgan, Maizel, Differential regulation of gene transcription in subpopulations of human B lymphocytes by vitamin D 3, Endocrinology
Mori, Influence of seasonal changes on disease activity and distribution of affected joints in rheumatoid arthritis, BMC Musculoskelet. Disord
Morris, Anderson, Autocrine and paracrine actions of vitamin D, Clin. Biochem. Rev
Mouterde, Association between vitamin D deficiency and disease activity, disability, and radiographic progression in early rheumatoid arthritis: the ESPOIR Cohort, J. Rheumatol
Mouterde, Predictors of radiographic progression in the ESPOIR Cohort: the season of first symptoms may influence the short-term outcome in early arthritis, Ann. Rheum. Dis
Muhammad Yusoff, Wong, Mohd Redzwan, Th1, Th2, and Th17 cytokines in systemic lupus erythematosus, Autoimmunity
Mukherjee, Lahiry, Thakur, Chakraborty, Effect of 1,25 dihydroxy vitamin D 3 supplementation on pain relief in early rheumatoid arthritis, J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care
Munshi, Vitamin D insufficiency as a potential culprit in critical COVID-19 patients, J. Med. Virol
Nashold, Spach, Spanier, Hayes, Estrogen controls vitamin D 3 -mediated resistance to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by controlling vitamin D 3 metabolism and receptor expression, J. Immunol
Nguyen, Bryant, O'neill, Vitamin D in SLE: a role in pathogenesis and fatigue? A review of the literature, Lupus
Nguyen, Efficacy of oral vitamin supplementation in inflammatory rheumatic disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Nutrients
Oristrell, Association of calcitriol supplementation with reduced COVID-19 mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease: a population-based study, Biomedicines
Ota, 1,25-Dihydroxy-vitamin D 3 regulates NK-cell cytotoxicity, cytokine secretion, and degranulation in women with recurrent pregnancy losses, Eur. J. Immunol
Overbergh, Identification and immune regulation of 25-hydroxyvitamin D-1-α-hydroxylase in murine macrophages, Clin. Exp. Immunol
Panagiotou, Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 are associated with greater disease severity, Clin. Endocrinol
Paradowska-Gorycka, Th17/Treg-Related transcriptional factor expression and cytokine profile in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, Front. Immunol
Penna, Adorini, 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 inhibits differentiation, maturation, activation, and survival of dendritic cells leading to impaired alloreactive T cell activation, J. Immunol
Petri, Bello, Fang, Magder, Vitamin D in systemic lupus erythematosus: modest association with disease activity and the urine protein-to-creatinine ratio, Arthritis Rheum
Piantoni, Phenotype modifications of T-cells and their shift toward a Th2 response in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus supplemented with different monthly regimens of vitamin D, Lupus
Piedra-Quintero, Wilson, Nava, Guerau-De-Arellano, CD38: an immunomodulatory molecule in inflammation and autoimmunity, Front. Immunol
Piemonti, Vitamin D3 affects differentiation, maturation, and function of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells, J. Immunol
Pike, Genome-wide principles of gene regulation by the vitamin D receptor and its activating ligand, Mol. Cell Endocrinol
Postal, Th1/Th2 cytokine profile in childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus, Cytokine
Prabhu, Luu, Sharpe, Brown, Cholesterol-mediated degradation of 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase switches the balance from cholesterol to vitamin D synthesis, J. Biol. Chem
Prosser, Jones, Enzymes involved in the activation and inactivation of vitamin D, Trends Biochem. Sci
Quesada-Gomez, Bouillon, Is calcifediol better than cholecalciferol for vitamin D supplementation?, Osteoporos. Int
Rao Muvva, Parasa, Lerm, Svensson, Brighenti, Polarization of human monocyte-derived cells with vitamin D promotes control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, Front. Immunol
Rolf, Damoiseaux, Hupperts, Huitinga, Smolders, Network of nuclear receptor ligands in multiple sclerosis: common pathways and interactions of sexsteroids, corticosteroids and vitamin D 3 -derived molecules, Autoimmun. Rev
Rozmus, Vitamin D Binding Protein (VDBP) and its gene polymorphisms-the risk of malignant tumors and other diseases, Int. J. Mol. Sci
Ruiz-Irastorza, Gordo, Olivares, Egurbide, Aguirre, Changes in vitamin D levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Effects on fatigue, disease activity, and damage, Arthritis Care Res
Saadoun, SARS-CoV-2 outbreak in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases: the Euro-COVIMID multicentre cross-sectional study, Lancet Rheumatol
Sabio, Vargas-Hitos, Martínez-Bordonado, Mediavilla-García, Association between non-dipper hypertension and vitamin D deficiency in women with systemic lupus erythematosus, Clin. Exp. Rheumatol
Sahebari, Nabavi, Salehi, Correlation between serum 25(OH)D values and lupus disease activity: an original article and a systematic review with meta-analysis focusing on serum Vit D confounders, Lupus
Sakaguchi, Yamaguchi, Nomura, Ono, Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance, Cell
Salesi, Farajzadegan, Efficacy of vitamin D in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis receiving methotrexate therapy, Rheumatol. Int
Sampaio-Barros, Takayama, Sampaio-Barros, Bonfá, Pereira, Low vitamin D serum levels in diffuse systemic sclerosis: a correlation with worst quality of life and severe capillaroscopic findings, Rev. Bras. Reumatol. Engl. Ed
Scabbia, Does climate help modeling COVID-19 risk and to what extent?, PLoS One
Schwartz, Smirnoff, Shany, Liel, Estrogen controls expression and bioresponse of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D receptors in the rat colon, Mol. Cell Biochem
Selye, On the stimulation of new bone-formation with parathyroid extract and irradiated ergosterol, Endocrinology
Seriolo, Molfetta, Cutolo, Seasonal variations in serum levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in patients with systemic sclerosis, Clin. Rheumatol
Sharif, Vitamin D, autoimmunity and recurrent pregnancy loss: more than an association, Am. J. Reprod. Immunol
Sharun, Tiwari, Dha, COVID-19 and sunlight: Impact on SARS-CoV-2 transmissibility, morbidity, and mortality, Ann. Med. Surg, doi:10.1016/j.amsu.2021.102419
Shinjo, Bonfá, De Falco Caparbo, Pereira, Low bone mass in juvenile onset sclerosis systemic: the possible role for 25-hydroxyvitamin D insufficiency, Rheumatol. Int
Sloka, Silva, Wang, Yong, Predominance of Th2 polarization by vitamin D through a STAT6-dependent mechanism, J. Neuroinflammation
Staples, Ponsonby, Lim, Mcmichael, Ecologic analysis of some immune-related disorders, including type 1 diabetes, in Australia: latitude, regional ultraviolet radiation, and disease prevalence, Env. Health Perspect
Stoffels, Immune regulation of 25-hydroxyvitamin-D 3 -1α-hydroxylase in human monocytes, J. Bone Min. Res
Sulli, Vitamin D and lung outcomes in elderly COVID-19 patients, Nutrients
Sumethkul, The predictive factors of low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and vitamin D deficiency in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, Rheumatol. Int
Sun, Zhang, Liu, Gui, Zhang et al., Vitamin D 3 and its synthetic analogs inhibit the spontaneous in vitro immunoglobulin production by SLE-derived PBMC, Clin. Immunol
Suárez-Fueyo, Bradley, Tsokos, T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus, Curr. Opin. Immunol
Széles, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 is an autonomous regulator of the transcriptional changes leading to a tolerogenic dendritic cell phenotype, J. Immunol
Takahashi, Human neutrophils express messenger RNA of vitamin D receptor and respond to 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3, Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol
Talarico, The impact of COVID-19 on rare and complex connective tissue diseases: the experience of ERN ReCONNET, Nat. Rev. Rheumatol
Terrier, Restoration of regulatory and effector T cell balance and B cell homeostasis in systemic lupus erythematosus patients through vitamin D supplementation, Arthritis Res. Ther
Thangamani, Cutting edge: Progesterone directly upregulates vitamin D receptor gene expression for efficient regulation of T cells by calcitriol, J. Immunol
Torres, Changes in the immune response against SARS-CoV-2 in individuals with severe COVID-19 treated with high dose of vitamin D, Biomed. Pharmacother
Tripkovic, Comparison of vitamin D2 and vitamin D 3 supplementation in raising serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D status: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Am. J. Clin. Nutr
Trombetta, Vitamin D deficiency and clinical correlations in systemic sclerosis patients: a retrospective analysis for possible future developments, PLoS One
Van Der Lugt, Rottier, Finsen therapy and vitamin D, Acta Derm
Van Etten, Mathieu, Immunoregulation by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 : basic concepts, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol
Vearing, Vitamin D status of the British African-Caribbean residents: analysis of the UK Biobank Cohort, Nutrients
Verma, Kim, 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D 3 facilitates M2 polarization and upregulates TLR10 expression on human microglial cells, Neuroimmunomodulation
Verway, Vitamin D induces interleukin-1β expression: paracrine macrophage epithelial signaling controls M. tuberculosis infection, PLoS Pathog
Vieira, Association between residences in U.S. northern latitudes and rheumatoid arthritis: a spatial analysis of the Nurses' Health Study, Environ. Health Perspect
Villaggio, Soldano, Cutolo, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 downregulates aromatase expression and inflammatory cytokines in human macrophages, Clin. Exp. Rheumatol
Villasis-Keever, Efficacy and safety of Vitamin D supplementation to prevent COVID-19 in frontline healthcare workers. A randomized clinical trial, Arch. Med. Res
Vojinovic, European multicentre pilot survey to assess vitamin D status in rheumatoid arthritis patients and early development of a new patient reported outcome questionnaire (D-PRO), Autoimmun. Rev
Waldron, Vitamin D: a negative acute phase reactant, J. Clin. Pathol
Wang, Association of vitamin D deficiency with COVID-19 infection severity: systematic review and meta-analysis, Clin. Endocrinol
Wang, Cutting edge: 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 is a direct inducer of antimicrobial peptide gene expression, J. Immunol
Wang, Direct and indirect induction by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 of the NOD2/ CARD15-defensin β2 innate immune pathway defective in Crohn disease, J. Biol. Chem
Wang, Vitamin D inhibits COX-2 expression and inflammatory response by targeting thioesterase superfamily member 4, J. Biol. Chem
Weir, Thenappan, Bhargava, Chen, Does vitamin D deficiency increase the severity of COVID-19?, Clin. Med
Williams, Cod-liver oil in phthisis, Lond. J. Med
Williams, am America: a review of research on systemic lupus erythematosus in African-Americans, Lupus Sci. Med
Windaus, Schenk, Werder, Antirachitically active irradiation product of 7-dehydrocholesterol, Hoppe-Seylers Z. Physiol. Chem
Wu, The role of vitamin D in combination treatment for patients with rheumatoid arthritis, Front. Med
Xu, Vitamin D alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via regulation of the renin-angiotensin system, Mol. Med. Rep
Xystrakis, Reversing the defective induction of IL-10-secreting regulatory T cells in glucocorticoid-resistant asthma patients, J. Clin. Invest
Yague, Garcia-Segura, Azcoitia, Selective transcriptional regulation of aromatase gene by vitamin D, dexamethasone, and mifepristone in human glioma cells, Endocrine
Yang, Liu, Zhang, Li, Wang, Effect of vitamin D on the recurrence rate of rheumatoid arthritis, Exp. Ther. Med
Yim, Dhawan, Ragunath, Christakos, Diamond, Induction of cathelicidin in normal and CF bronchial epithelial cells by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3, J. Cyst. Fibros
Yu, Vitamin D protects podocytes from autoantibodies induced injury in lupus nephritis by reducing aberrant autophagy, Arthritis Res. Ther
Yuk, Vitamin D 3 induces autophagy in human monocytes/macrophages via cathelicidin, Cell Host Microbe
Zhang, Association between the serum level of vitamin D and systemic sclerosis in a Chinese population: a case control study, Int. J. Rheum. Dis
Zhu, 1,25 Dihydroxyvitamin D regulates macrophage polarization and ameliorates experimental inflammatory bowel disease by suppressing miR-125b, Int. Immunopharmacol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41584-023-00944-2",
"ISSN": [
"1759-4790",
"1759-4804"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41584-023-00944-2",
"alternative-id": [
"944"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "1 March 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 2,
"value": "28 March 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1,
"value": "M.C. declares that his university laboratory has received funds for research from Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim and Pfizer. V.S. declares that she has received funds for research from Boehringer-Ingelheim and Janssen-Cilag. S.P. and E.G. declare no competing interests."
},
{
"label": "Free to read",
"name": "free",
"value": "This content has been made available to all."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5396-0932",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Cutolo",
"given": "Maurizio",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6271-7945",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Vanessa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9269-5089",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Paolino",
"given": "Sabrina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4732-0306",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Gotelli",
"given": "Emanuele",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nature Reviews Rheumatology",
"container-title-short": "Nat Rev Rheumatol",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-28T11:03:34Z",
"timestamp": 1680001414000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-09T19:51:22Z",
"timestamp": 1702151482000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-27T15:08:41Z",
"timestamp": 1711552121513
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 12,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
28
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springernature.com/gp/researchers/text-and-data-mining",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-28T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1679961600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springernature.com/gp/researchers/text-and-data-mining",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-28T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1679961600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41584-023-00944-2.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41584-023-00944-2",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41584-023-00944-2.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"page": "265-287",
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
28
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
28
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mce.2017.06.025",
"author": "C Carlberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell Endocrinol.",
"key": "944_CR1",
"unstructured": "Carlberg, C. Endocrine functions of vitamin D. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 453, 1–2 (2017).",
"volume": "453",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"author": "HA Morris",
"first-page": "129",
"journal-title": "Clin. Biochem. Rev.",
"key": "944_CR2",
"unstructured": "Morris, H. A. & Anderson, P. H. Autocrine and paracrine actions of vitamin D. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 31, 129–138 (2010).",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2011-0385",
"author": "MF Holick",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1911",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "944_CR3",
"unstructured": "Holick, M. F. et al. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 96, 1911–1930 (2011).",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cbf.3421",
"author": "C Jenkinson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "408",
"journal-title": "Cell Biochem. Funct.",
"key": "944_CR4",
"unstructured": "Jenkinson, C. The vitamin D metabolome: an update on analysis and function. Cell Biochem. Funct. 37, 408–423 (2019).",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0021-9258(18)84762-7",
"author": "CE Bills",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "451",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "944_CR5",
"unstructured": "Bills, C. E. & McDonald, F. G. Antiricketic substances: II. The action of n-Butyl nitrite on activated cholesterol and the antiricketic vitamin. J. Biol. Chem. 66, 451–457 (1925).",
"volume": "66",
"year": "1925"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/endo-16-5-547",
"author": "H Selye",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "547",
"journal-title": "Endocrinology",
"key": "944_CR6",
"unstructured": "Selye, H. On the stimulation of new bone-formation with parathyroid extract and irradiated ergosterol. Endocrinology 16, 547–588 (1932).",
"volume": "16",
"year": "1932"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/bchm2.1936.241.1-3.100",
"author": "A Windaus",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100",
"journal-title": "Hoppe-Seylers Z. Physiol. Chem.",
"key": "944_CR7",
"unstructured": "Windaus, A., Schenk, F. & Werder, F. V. Antirachitically active irradiation product of 7-dehydrocholesterol. Hoppe-Seylers Z. Physiol. Chem. 241, 100–103 (1936).",
"volume": "241",
"year": "1936"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mce.2016.11.028",
"author": "A Barbáchano",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "79",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell Endocrinol.",
"key": "944_CR8",
"unstructured": "Barbáchano, A. et al. The endocrine vitamin D system in the gut. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 453, 79–87 (2017).",
"volume": "453",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/jid.2010.118",
"author": "HH Glossmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2139",
"journal-title": "J. Invest. Dermatol.",
"key": "944_CR9",
"unstructured": "Glossmann, H. H. Origin of 7-dehydrocholesterol (provitamin D) in the skin. J. Invest. Dermatol. 130, 2139–2141 (2010).",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"key": "944_CR10",
"unstructured": "Huff, T., Boyd B., Jialal, I. Physiology, Cholesterol. 2022 Mar 9. In: StatPearls [Internet] (StatPearls, 2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M115.699546",
"author": "AV Prabhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "8363",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "944_CR11",
"unstructured": "Prabhu, A. V., Luu, W., Sharpe, L. J. & Brown, A. J. Cholesterol-mediated degradation of 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase switches the balance from cholesterol to vitamin D synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 291, 8363–8373 (2016).",
"volume": "291",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.0022-202X.2004.22424.x",
"author": "DD Bikle",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "984",
"journal-title": "J. Invest. Dermatol.",
"key": "944_CR12",
"unstructured": "Bikle, D. D. et al. 25 Hydroxyvitamin D 1 α-hydroxylase is required for optimal epidermal differentiation and permeability barrier homeostasis. J. Invest. Dermatol. 122, 984–992 (2004).",
"volume": "122",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1123933",
"author": "PT Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1770",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "944_CR13",
"unstructured": "Liu, P. T. et al. Toll-like receptor triggering of a vitamin D-mediated human antimicrobial response. Science 311, 1770–1773 (2006).",
"volume": "311",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0021-9258(19)44557-2",
"author": "RW Gray",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "7528",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "944_CR14",
"unstructured": "Gray, R. W., Omdahl, J. L., Ghazarian, J. G. & DeLuca, H. F. 25-Hydroxycholecalciferol-1-hydroxylase. Subcellular location and properties. J. Biol. Chem. 247, 7528–7532 (1972).",
"volume": "247",
"year": "1972"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tibs.2004.10.005",
"author": "DE Prosser",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "664",
"journal-title": "Trends Biochem. Sci.",
"key": "944_CR15",
"unstructured": "Prosser, D. E. & Jones, G. Enzymes involved in the activation and inactivation of vitamin D. Trends Biochem. Sci. 29, 664–673 (2004).",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"key": "944_CR16",
"unstructured": "Bikle, D. D. in Vitamin D: production, metabolism and mechanisms of action (eds Feingold, K. R. et al.) (Endotext, 2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/B978-0-12-381978-9.10045-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "944_CR17",
"unstructured": "Hewison, M. & Adams, J. S. Extrarenal 1α-hydroxylase. In: Vitamin D, 3rd edn. (eds Feldman, D., Pike, J. W. & Adams, J. S.) 777–806 (Academic Press, 2011)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.72.6.2076",
"author": "SP Daiger",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2076",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "944_CR18",
"unstructured": "Daiger, S. P., Schanfield, M. S. & Cavalli-Sforza, L. L. Group-specific component (Gc) proteins bind vitamin D and 25-hydroxyvitamin D. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 72, 2076–2080 (1975).",
"volume": "72",
"year": "1975"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mce.2011.05.012",
"author": "JW Pike",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell Endocrinol.",
"key": "944_CR19",
"unstructured": "Pike, J. W. Genome-wide principles of gene regulation by the vitamin D receptor and its activating ligand. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 347, 3–10 (2011).",
"volume": "347",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphys.2014.00167",
"author": "C Carlberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "167",
"journal-title": "Front. Physiol.",
"key": "944_CR20",
"unstructured": "Carlberg, C. Genome-wide (over)view on the actions of vitamin D. Front. Physiol. 5, 167 (2014).",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14061291",
"author": "S Donati",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1291",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "944_CR21",
"unstructured": "Donati, S. et al. Rapid nontranscriptional effects of calcifediol and calcitriol. Nutrients 14, 1291 (2022).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2021/5812136",
"author": "A Latini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5812136",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol. Res.",
"key": "944_CR22",
"unstructured": "Latini, A. et al. VDR polymorphisms in autoimmune connective tissue diseases: focus on Italian population. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 5812136 (2021).",
"volume": "2021",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mce.2021.111317",
"author": "DD Bikle",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "111317",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell Endocrinol.",
"key": "944_CR23",
"unstructured": "Bikle, D. D. Vitamin D regulation of and by long non coding RNAs. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 532, 111317 (2021).",
"volume": "532",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "CJB Williams",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Lond. J. Med.",
"key": "944_CR24",
"unstructured": "Williams, C. J. B. Cod-liver oil in phthisis. Lond. J. Med. 1, 1–18 (1849).",
"volume": "1",
"year": "1849"
},
{
"key": "944_CR25",
"unstructured": "Finsen, N. R. Om Bekæmpelse af Lupus vulgaris med en Redegørelse for de i Danmark opnaaede Resultater. (Gyldendalske Boghandels Forlag, 1902)."
},
{
"author": "L Van Der Lugt",
"first-page": "264",
"journal-title": "Acta Derm. Venereol.",
"key": "944_CR26",
"unstructured": "Van Der Lugt, L. & Rottier, P. B. Finsen therapy and vitamin D. Acta Derm. Venereol. 38, 264–273 (1958).",
"volume": "38",
"year": "1958"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01204.x",
"author": "L Overbergh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "139",
"journal-title": "Clin. Exp. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR27",
"unstructured": "Overbergh, L. et al. Identification and immune regulation of 25-hydroxyvitamin D-1-α-hydroxylase in murine macrophages. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 120, 139–146 (2000).",
"volume": "120",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1359/JBMR.050908",
"author": "K Stoffels",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "37",
"journal-title": "J. Bone Min. Res.",
"key": "944_CR28",
"unstructured": "Stoffels, K. et al. Immune regulation of 25-hydroxyvitamin-D3-1α-hydroxylase in human monocytes. J. Bone Min. Res. 21, 37–47 (2006).",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3168/jds.2017-14143",
"author": "KE Merriman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "7593",
"journal-title": "J. Dairy. Sci.",
"key": "944_CR29",
"unstructured": "Merriman, K. E., Powell, J. L., Santos, J. E. P. & Nelson, C. D. Intramammary 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 treatment modulates innate immune responses to endotoxin-induced mastitis. J. Dairy. Sci. 101, 7593–7607 (2018).",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1081/IPH-120014721",
"author": "K Takahashi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "335",
"journal-title": "Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol.",
"key": "944_CR30",
"unstructured": "Takahashi, K. et al. Human neutrophils express messenger RNA of vitamin D receptor and respond to 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 24, 335–347 (2002).",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"author": "EL Bishop",
"journal-title": "JBMR Plus",
"key": "944_CR31",
"unstructured": "Bishop, E. L., Ismailova, A., Dimeloe, S., Hewison, M. & White, J. H. Vitamin D and immune regulation: antibacterial, antiviral, anti-inflammatory. JBMR Plus 5, e10405 (2020).",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1189/jlb.0607437",
"author": "J Karlsson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1279",
"journal-title": "J. Leukoc. Biol.",
"key": "944_CR32",
"unstructured": "Karlsson, J., Carlsson, G., Larne, O., Andersson, M. & Pütsep, K. Vitamin D3 induces pro-LL-37 expression in myeloid precursors from patients with severe congenital neutropenia. J. Leukoc. Biol. 84, 1279–1286 (2008).",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcf.2007.03.003",
"author": "S Yim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "403",
"journal-title": "J. Cyst. Fibros.",
"key": "944_CR33",
"unstructured": "Yim, S., Dhawan, P., Ragunath, C., Christakos, S. & Diamond, G. Induction of cathelicidin in normal and CF bronchial epithelial cells by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. J. Cyst. Fibros. 6, 403–410 (2007).",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.173.5.2909",
"author": "TT Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2909",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR34",
"unstructured": "Wang, T. T. et al. Cutting edge: 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is a direct inducer of antimicrobial peptide gene expression. J. Immunol. 173, 2909–2912 (2004).",
"volume": "173",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.C109.071225",
"author": "TT Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2227",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "944_CR35",
"unstructured": "Wang, T. T. et al. Direct and indirect induction by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 of the NOD2/CARD15-defensin β2 innate immune pathway defective in Crohn disease. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 2227–2231 (2010).",
"volume": "285",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/eji.201545541",
"author": "K Ota",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3188",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR36",
"unstructured": "Ota, K. et al. 1,25-Dihydroxy-vitamin D3 regulates NK-cell cytotoxicity, cytokine secretion, and degranulation in women with recurrent pregnancy losses. Eur. J. Immunol. 45, 3188–3199 (2015).",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1003407",
"author": "M Verway",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog.",
"key": "944_CR37",
"unstructured": "Verway, M. et al. Vitamin D induces interleukin-1β expression: paracrine macrophage epithelial signaling controls M. tuberculosis infection. PLoS Pathog. 9, e1003407 (2013).",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41590-021-01080-3",
"author": "D Chauss",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "62",
"journal-title": "Nat. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR38",
"unstructured": "Chauss, D. et al. Autocrine vitamin D signaling switches off pro-inflammatory programs of TH1 cells. Nat. Immunol. 23, 62–74 (2022).",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M113.517581",
"author": "Q Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "11681",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "944_CR39",
"unstructured": "Wang, Q. et al. Vitamin D inhibits COX-2 expression and inflammatory response by targeting thioesterase superfamily member 4. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 11681–11694 (2014).",
"volume": "289",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.164.9.4443",
"author": "L Piemonti",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4443",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR40",
"unstructured": "Piemonti, L. et al. Vitamin D3 affects differentiation, maturation, and function of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 164, 4443–4451 (2000).",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.0803345",
"author": "L Széles",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2074",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR41",
"unstructured": "Széles, L. et al. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is an autonomous regulator of the transcriptional changes leading to a tolerogenic dendritic cell phenotype. J. Immunol. 182, 2074–2083 (2009).",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI1050",
"author": "D D’Ambrosio",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "252",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Invest.",
"key": "944_CR42",
"unstructured": "D’Ambrosio, D. et al. Inhibition of IL-12 production by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Involvement of NF-κB downregulation in transcriptional repression of the p40 gene. J. Clin. Invest. 101, 252–262 (1998).",
"volume": "101",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ni.2705",
"author": "LC Davies",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "986",
"journal-title": "Nat. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR43",
"unstructured": "Davies, L. C., Jenkins, S. J., Allen, J. E. & Taylor, P. R. Tissue-resident macrophages. Nat. Immunol. 14, 986–995 (2013).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2018.12.015",
"author": "X Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "106",
"journal-title": "Int. Immunopharmacol.",
"key": "944_CR44",
"unstructured": "Zhu, X. et al. 1,25 Dihydroxyvitamin D regulates macrophage polarization and ameliorates experimental inflammatory bowel disease by suppressing miR-125b. Int. Immunopharmacol. 67, 106–118 (2019).",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.867260",
"author": "M Cutolo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "867260",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR45",
"unstructured": "Cutolo, M., Campitiello, R., Gotelli, E. & Soldano, S. The role of M1/M2 macrophage polarization in rheumatoid arthritis synovitis. Front. Immunol. 13, 867260 (2022).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000444300",
"author": "R Verma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "75",
"journal-title": "Neuroimmunomodulation",
"key": "944_CR46",
"unstructured": "Verma, R. & Kim, J. Y. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 facilitates M2 polarization and upregulates TLR10 expression on human microglial cells. Neuroimmunomodulation 23, 75–80 (2016).",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1753425917721965",
"author": "S Dionne",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "557",
"journal-title": "Innate Immun.",
"key": "944_CR47",
"unstructured": "Dionne, S., Duchatelier, C. F. & Seidman, E. G. The influence of vitamin D on M1 and M2 macrophages in patients with Crohn’s disease. Innate Immun. 23, 557–565 (2017).",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2019.03157",
"author": "J Rao Muvva",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3157",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR48",
"unstructured": "Rao Muvva, J., Parasa, V. R., Lerm, M., Svensson, M. & Brighenti, S. Polarization of human monocyte-derived cells with vitamin D promotes control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Front. Immunol. 10, 3157 (2020).",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "S Liang",
"first-page": "3707",
"journal-title": "Mol. Med. Rep.",
"key": "944_CR49",
"unstructured": "Liang, S., Cai, J., Li, Y. & Yang, R. 1,25 Dihydroxy vitamin D3 induces macrophage polarization to M2 by upregulating T cell Ig mucin 3 expression. Mol. Med. Rep. 19, 3707–3713 (2019).",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mam.2008.04.004",
"author": "MT Cantorna",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "369",
"journal-title": "Mol. Asp. Med.",
"key": "944_CR50",
"unstructured": "Cantorna, M. T., Yu, S. & Bruce, D. The paradoxical effects of vitamin D on type 1 mediated immunity. Mol. Asp. Med. 29, 369–375 (2008).",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.coph.2010.04.001",
"author": "F Baeke",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "482",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Pharmacol.",
"key": "944_CR51",
"unstructured": "Baeke, F., Takiishi, T., Korf, H., Gysemans, C. & Mathieu, C. Vitamin D: modulator of the immune system. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 10, 482–496 (2010).",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11154-021-09707-4",
"author": "DD Bikle",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "279",
"journal-title": "Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord.",
"key": "944_CR52",
"unstructured": "Bikle, D. D. Vitamin D regulation of immune function during COVID-19. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 23, 279–285 (2022).",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nri2236",
"author": "PG Holt",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "142",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR53",
"unstructured": "Holt, P. G., Strickland, D. H., Wikström, M. E. & Jahnsen, F. L. Regulation of immunological homeostasis in the respiratory tract. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 8, 142–152 (2008).",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.170.11.5382",
"author": "M Hewison",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5382",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR54",
"unstructured": "Hewison, M. et al. Differential regulation of vitamin D receptor and its ligand in human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 170, 5382–5390 (2003).",
"volume": "170",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood-2002-11-3521",
"author": "J Fritsche",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3314",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "944_CR55",
"unstructured": "Fritsche, J., Mondal, K., Ehrnsperger, A., Andreesen, R. & Kreutz, M. Regulation of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3-1α-hydroxylase and production of 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 by human dendritic cells. Blood 102, 3314–3316 (2003).",
"volume": "102",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2005.06.002",
"author": "E van Etten",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "93",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "944_CR56",
"unstructured": "van Etten, E. & Mathieu, C. Immunoregulation by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3: basic concepts. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 97, 93–101 (2005).",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1124/jpet.107.127209",
"author": "C Daniel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "23",
"journal-title": "J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.",
"key": "944_CR57",
"unstructured": "Daniel, C., Sartory, N. A., Zahn, N., Radeke, H. H. & Stein, J. M. Immune modulatory treatment of trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid colitis with calcitriol is associated with a change of a T helper (Th) 1/Th17 to a Th2 and regulatory T cell profile. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 324, 23–33 (2008).",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.167.4.1945",
"author": "S Gregori",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1945",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR58",
"unstructured": "Gregori, S. et al. Regulatory T cells induced by 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and mycophenolate mofetil treatment mediate transplantation tolerance. J. Immunol. 167, 1945–1953 (2001).",
"volume": "167",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1742-2094-8-56",
"author": "S Sloka",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J. Neuroinflammation",
"key": "944_CR59",
"unstructured": "Sloka, S., Silva, C., Wang, J. & Yong, V. W. Predominance of Th2 polarization by vitamin D through a STAT6-dependent mechanism. J. Neuroinflammation 8, 56 (2011).",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1100179",
"author": "S Horiuchi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6378",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR60",
"unstructured": "Horiuchi, S. et al. Genome-wide analysis reveals unique regulation of transcription of Th2-specific genes by GATA3. J. Immunol. 186, 6378–6389 (2011).",
"volume": "186",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/aji.12991",
"author": "K Sharif",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Reprod. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR61",
"unstructured": "Sharif, K. et al. Vitamin D, autoimmunity and recurrent pregnancy loss: more than an association. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 80, e12991 (2018).",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2008.05.009",
"author": "S Sakaguchi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "775",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "944_CR62",
"unstructured": "Sakaguchi, S., Yamaguchi, T., Nomura, T. & Ono, M. Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell 133, 775–787 (2008).",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.20011629",
"author": "FJ Barrat",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "603",
"journal-title": "J. Exp. Med.",
"key": "944_CR63",
"unstructured": "Barrat, F. J. et al. In vitro generation of interleukin 10-producing regulatory CD4+ T cells is induced by immunosuppressive drugs and inhibited by T helper type 1 (Th1)- and Th2-inducing cytokines. J. Exp. Med. 195, 603–616 (2002).",
"volume": "195",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.164.5.2405",
"author": "G Penna",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2405",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR64",
"unstructured": "Penna, G. & Adorini, L. 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 inhibits differentiation, maturation, activation, and survival of dendritic cells leading to impaired alloreactive T cell activation. J. Immunol. 164, 2405–2411 (2000).",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cei.12406",
"author": "G Drozdenko",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "364",
"journal-title": "Clin. Exp. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR65",
"unstructured": "Drozdenko, G., Scheel, T., Heine, G., Baumgrass, R. & Worm, M. Impaired T cell activation and cytokine production by calcitriol-primed human B cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 178, 364–372 (2014).",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/endo.140.1.6395",
"author": "JW Morgan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "381",
"journal-title": "Endocrinology",
"key": "944_CR66",
"unstructured": "Morgan, J. W., Sliney, D. J., Morgan, D. M. & Maizel, A. L. Differential regulation of gene transcription in subpopulations of human B lymphocytes by vitamin D3. Endocrinology 140, 381–391 (1999).",
"volume": "140",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.179.3.1634",
"author": "S Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1634",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR67",
"unstructured": "Chen, S. et al. Modulatory effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on human B cell differentiation. J. Immunol. 179, 1634–1647 (2007).",
"volume": "179",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/exd.12300",
"author": "G Drozdenko",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "107",
"journal-title": "Exp. Dermatol.",
"key": "944_CR68",
"unstructured": "Drozdenko, G., Heine, G. & Worm, M. Oral vitamin D increases the frequencies of CD38+ human B cells and ameliorates IL-17-producing T cells. Exp. Dermatol. 23, 107–112 (2014).",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.597959",
"author": "ZL Piedra-Quintero",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "597959",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR69",
"unstructured": "Piedra-Quintero, Z. L., Wilson, Z., Nava, P. & Guerau-de-Arellano, M. CD38: an immunomodulatory molecule in inflammation and autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 11, 597959 (2020).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1601213",
"author": "J James",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1164",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR70",
"unstructured": "James, J., Weaver, V. & Cantorna, M. T. Control of circulating IgE by the vitamin D receptor in vivo involves B cell intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms. J. Immunol. 198, 1164–1171 (2017).",
"volume": "198",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/07853899509002465",
"author": "JE de Vries",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "537",
"journal-title": "Ann. Med.",
"key": "944_CR71",
"unstructured": "de Vries, J. E. Immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory properties of interleukin 10. Ann. Med. 27, 537–541 (1995).",
"volume": "27",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.683",
"author": "KW Moore",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "683",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR72",
"unstructured": "Moore, K. W., de Waal Malefyt, R., Coffman, R. L. & O’Garra, A. Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 19, 683–765 (2001).",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12072097",
"author": "N Charoenngam",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2097",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "944_CR73",
"unstructured": "Charoenngam, N. & Holick, M. F. Immunologic effects of vitamin D on human health and disease. Nutrients 12, 2097 (2020).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/B978-0-12-386960-9.00014-9",
"author": "M Cutolo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "327",
"journal-title": "Vitam. Horm.",
"key": "944_CR74",
"unstructured": "Cutolo, M., Plebani, M., Shoenfeld, Y., Adorini, L. & Tincani, A. Vitamin D endocrine system and the immune response in rheumatic diseases. Vitam. Horm. 86, 327–351 (2011).",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/nyas.12432",
"author": "M Cutolo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "39",
"journal-title": "Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci.",
"key": "944_CR75",
"unstructured": "Cutolo, M. et al. Vitamin D, steroid hormones, and autoimmunity. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1317, 39–46 (2014).",
"volume": "1317",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M111.244061",
"author": "AA Hidalgo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "36228",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "944_CR76",
"unstructured": "Hidalgo, A. A., Deeb, K. K., Pike, J. W., Johnson, C. S. & Trump, D. L. Dexamethasone enhances 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 effects by increasing vitamin D receptor transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 36228–36237 (2011).",
"volume": "286",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcb.22645",
"author": "P Dhawan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1314",
"journal-title": "J. Cell Biochem.",
"key": "944_CR77",
"unstructured": "Dhawan, P. & Christakos, S. Novel regulation of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 24-hydroxylase (24(OH)ase) transcription by glucocorticoids: cooperative effects of the glucocorticoid receptor, C/EBPβ, and the Vitamin D receptor in 24(OH)ase transcription. J. Cell Biochem. 110, 1314–1323 (2010).",
"volume": "110",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1385/ENDO:17:2:109",
"author": "I Kurahashi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "109",
"journal-title": "Endocrine",
"key": "944_CR78",
"unstructured": "Kurahashi, I., Matsunuma, A., Kawane, T., Abe, M. & Horiuchi, N. Dexamethasone enhances vitamin D-24-hydroxylase expression in osteoblastic (UMR-106) and renal (LLC-PK1) cells treated with 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Endocrine 17, 109–118 (2002).",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00213-014-3440-6",
"author": "P Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3445",
"journal-title": "Psychopharmacology",
"key": "944_CR79",
"unstructured": "Jiang, P. et al. Dysregulation of vitamin D metabolism in the brain and myocardium of rats following prolonged exposure to dexamethasone. Psychopharmacology 231, 3445–3451 (2014).",
"volume": "231",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jchemneu.2004.08.006",
"author": "DW Eyles",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "21",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Neuroanat.",
"key": "944_CR80",
"unstructured": "Eyles, D. W., Smith, S., Kinobe, R., Hewison, M. & McGrath, J. J. Distribution of the vitamin D receptor and 1 α-hydroxylase in human brain. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 29, 21–30 (2005).",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/syn.20433",
"author": "M Moore",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "851",
"journal-title": "Synapse",
"key": "944_CR81",
"unstructured": "Moore, M., Piazza, A., Nolan, Y. & Lynch, M. A. Treatment with dexamethasone and vitamin D3 attenuates neuroinflammatory age-related changes in rat hippocampus. Synapse 61, 851–861 (2007).",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI21759",
"author": "E Xystrakis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "146",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Invest.",
"key": "944_CR82",
"unstructured": "Xystrakis, E. et al. Reversing the defective induction of IL-10-secreting regulatory T cells in glucocorticoid-resistant asthma patients. J. Clin. Invest. 116, 146–155 (2006).",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2016.07.002",
"author": "L Rolf",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "900",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun. Rev.",
"key": "944_CR83",
"unstructured": "Rolf, L., Damoiseaux, J., Hupperts, R., Huitinga, I. & Smolders, J. Network of nuclear receptor ligands in multiple sclerosis: common pathways and interactions of sex-steroids, corticosteroids and vitamin D3-derived molecules. Autoimmun. Rev. 185, 900–910 (2016).",
"volume": "185",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2002-020838",
"author": "AM Andersson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "932",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "944_CR84",
"unstructured": "Andersson, A. M., Carlsen, E., Petersen, J. H. & Skakkebaek, N. E. Variation in levels of serum inhibin B, testosterone, estradiol, luteinizing (83) hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, and sex hormone-binding globulin in monthly samples from healthy men during a 17-month period: possible effects of seasons. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 88, 932–937 (2003).",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12020-008-9134-2",
"author": "JG Yague",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "252",
"journal-title": "Endocrine",
"key": "944_CR85",
"unstructured": "Yague, J. G., Garcia-Segura, L. M. & Azcoitia, I. Selective transcriptional regulation of aromatase gene by vitamin D, dexamethasone, and mifepristone in human glioma cells. Endocrine 35, 252–261 (2009).",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/eje.1.02032",
"author": "A Enjuanes",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "981",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Endocrinol.",
"key": "944_CR86",
"unstructured": "Enjuanes, A. et al. Functional analysis of the I.3, I.6, pII and I.4 promoters of CYP19 (aromatase) gene in human osteoblasts and their role in vitamin D and dexamethasone stimulation. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 153, 981–988 (2005).",
"volume": "153",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2005.01.024",
"author": "YR Lou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "151",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "944_CR87",
"unstructured": "Lou, Y. R., Murtola, T. & Tuohimaa, P. Regulation of aromatase and 5α-reductase by 25-hydroxyvitamin D(3), 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3), dexamethasone and progesterone in prostate cancer cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 94, 151–157 (2005).",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"author": "B Villaggio",
"first-page": "934",
"journal-title": "Clin. Exp. Rheumatol.",
"key": "944_CR88",
"unstructured": "Villaggio, B., Soldano, S. & Cutolo, M. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 downregulates aromatase expression and inflammatory cytokines in human macrophages. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 30, 934–938 (2012).",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.0901351",
"author": "FE Nashold",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3672",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR89",
"unstructured": "Nashold, F. E., Spach, K. M., Spanier, J. A. & Hayes, C. E. Estrogen controls vitamin D3-mediated resistance to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by controlling vitamin D3 metabolism and receptor expression. J. Immunol. 183, 3672–3681 (2009).",
"volume": "183",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/endo.130.5.1315250",
"author": "Y Liel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2597",
"journal-title": "Endocrinology",
"key": "944_CR90",
"unstructured": "Liel, Y., Kraus, S., Levy, J. & Shany, S. Evidence that estrogens modulate activity and increase the number of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D receptors in osteoblast-like cells (ROS 17/2.8). Endocrinology 130, 2597–2601 (1992).",
"volume": "130",
"year": "1992"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0960-0760(93)90340-3",
"author": "MT Escaleira",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "257",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "944_CR91",
"unstructured": "Escaleira, M. T., Sonohara, S. & Brentani, M. M. Sex steroids induced up-regulation of 1,25-(OH)2 vitamin D3 receptors in T 47D breast cancer cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 45, 257–263 (1993).",
"volume": "45",
"year": "1993"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1023/A:1007015027268",
"author": "B Schwartz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "87",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell Biochem.",
"key": "944_CR92",
"unstructured": "Schwartz, B., Smirnoff, P., Shany, S. & Liel, Y. Estrogen controls expression and bioresponse of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D receptors in the rat colon. Mol. Cell Biochem. 203, 87–93 (2000).",
"volume": "203",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/endo.140.1.6408",
"author": "Y Liel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "280",
"journal-title": "Endocrinology",
"key": "944_CR93",
"unstructured": "Liel, Y., Shany, S., Smirnoff, P. & Schwartz, B. Estrogen increases 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D receptors expression and bioresponse in the rat duodenal mucosa. Endocrinology 140, 280–285 (1999).",
"volume": "140",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI111617",
"author": "DD Bikle",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1966",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Invest.",
"key": "944_CR94",
"unstructured": "Bikle, D. D., Gee, E., Halloran, B. & Haddad, J. G. Free 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D levels in serum from normal subjects, pregnant subjects, and subjects with liver disease. J. Clin. Invest. 74, 1966–1971 (1984).",
"volume": "74",
"year": "1984"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF02555109",
"author": "JR Buchanan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "139",
"journal-title": "Calcif. Tissue Int.",
"key": "944_CR95",
"unstructured": "Buchanan, J. R. et al. The effect of endogenous estrogen fluctuation on metabolism of 25-hydroxyvitamin D. Calcif. Tissue Int. 39, 139–144 (1986).",
"volume": "39",
"year": "1986"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13293-021-00358-3",
"author": "ML Dupuis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "12",
"journal-title": "Biol. Sex. Differ.",
"key": "944_CR96",
"unstructured": "Dupuis, M. L., Pagano, M. T., Pierdominici, M. & Ortona, E. The role of vitamin D in autoimmune diseases: could sex make the difference? Biol. Sex. Differ. 12, 12 (2021).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1401923",
"author": "S Thangamani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "883",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR97",
"unstructured": "Thangamani, S. et al. Cutting edge: Progesterone directly upregulates vitamin D receptor gene expression for efficient regulation of T cells by calcitriol. J. Immunol. 194, 883–886 (2015).",
"volume": "194",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/ar2552",
"author": "M Cutolo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "123",
"journal-title": "Arthritis Res. Ther.",
"key": "944_CR98",
"unstructured": "Cutolo, M. Vitamin D or hormone D deficiency in autoimmune rheumatic diseases, including undifferentiated connective tissue disease. Arthritis Res. Ther. 10, 123 (2008).",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/rheumatology/ken394",
"author": "M Cutolo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "210",
"journal-title": "Rheumatology",
"key": "944_CR99",
"unstructured": "Cutolo, M. Vitamin D and autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Rheumatology 48, 210–212 (2009).",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2011.08.003",
"author": "M Cutolo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "84",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun. Rev.",
"key": "944_CR100",
"unstructured": "Cutolo, M., Pizzorni, C. & Sulli, A. Vitamin D endocrine system involvement in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 11, 84–87 (2011).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202538",
"author": "M Cutolo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "473",
"journal-title": "Ann. Rheum. Dis.",
"key": "944_CR101",
"unstructured": "Cutolo, M. Further emergent evidence for the vitamin D endocrine system involvement in autoimmune rheumatic disease risk and prognosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 72, 473–475 (2013).",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/ard.2008.093476",
"author": "M Cutolo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "446",
"journal-title": "Ann. Rheum. Dis.",
"key": "944_CR102",
"unstructured": "Cutolo, M. et al. Vitamin D involvement in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythaematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 68, 446–447 (2009).",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1289/ehp.5941",
"author": "JA Staples",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "518",
"journal-title": "Env. Health Perspect.",
"key": "944_CR103",
"unstructured": "Staples, J. A., Ponsonby, A. L., Lim, L. L. & McMichael, A. J. Ecologic analysis of some immune-related disorders, including type 1 diabetes, in Australia: latitude, regional ultraviolet radiation, and disease prevalence. Env. Health Perspect. 111, 518–523 (2003).",
"volume": "111",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1289/ehp.0901861",
"author": "VM Vieira",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "957",
"journal-title": "Environ. Health Perspect.",
"key": "944_CR104",
"unstructured": "Vieira, V. M. et al. Association between residences in U.S. northern latitudes and rheumatoid arthritis: a spatial analysis of the Nurses’ Health Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 118, 957–961 (2010).",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrendo.2017.31",
"author": "R Bouillon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "466",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Endocrinol.",
"key": "944_CR105",
"unstructured": "Bouillon, R. Comparative analysis of nutritional guidelines for vitamin D. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 13, 466–479 (2017).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2019/3494937",
"author": "MM Aslam",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3494937",
"journal-title": "Biomed. Res. Int.",
"key": "944_CR106",
"unstructured": "Aslam, M. M., John, P., Bhatti, A., Jahangir, S. & Kamboh, M. I. Vitamin D as a principal factor in mediating rheumatoid arthritis-derived immune response. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 3494937 (2019).",
"volume": "2019",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.572858",
"author": "A Paradowska-Gorycka",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3189",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR107",
"unstructured": "Paradowska-Gorycka, A. et al. Th17/Treg-Related transcriptional factor expression and cytokine profile in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Front. Immunol. 11, 3189 (2020).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5604/17322693.948971",
"author": "A Kosmaczewska",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "397",
"journal-title": "Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw.",
"key": "944_CR108",
"unstructured": "Kosmaczewska, A., Swierkot, J., Ciszak, L. & Wiland, P. The role of Th1, Th17, and Treg cells in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis including anti-inflammatory action of Th1 cytokines. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. 65, 397–403 (2011).",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrrheum.2012.3",
"author": "J Buckland",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "124",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Rheumatol.",
"key": "944_CR109",
"unstructured": "Buckland, J. Rheumatoid arthritis: control of TH17 cell activity in RA by a combination of vitamin D receptor signaling and TNF-blockade. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 8, 124 (2012).",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0178879",
"author": "S Mateen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "944_CR110",
"unstructured": "Mateen, S., Moin, S., Shahzad, S. & Khan, A. Q. Level of inflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis patients: correlation with 25-hydroxy vitamin D and reactive oxygen species. PLoS One 12, e0178879 (2017).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10067-020-05143-y",
"author": "Z Bagheri-Hosseinabadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3555",
"journal-title": "Clin. Rheumatol.",
"key": "944_CR111",
"unstructured": "Bagheri-Hosseinabadi, Z. et al. Vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene polymorphism and risk of rheumatoid arthritis (RA): systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 39, 3555–3569 (2020).",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21217822",
"author": "D Rozmus",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "7822",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "944_CR112",
"unstructured": "Rozmus, D. et al. Vitamin D Binding Protein (VDBP) and its gene polymorphisms-the risk of malignant tumors and other diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 7822 (2020).",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202302",
"author": "EV Arkema",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "506",
"journal-title": "Ann. Rheum. Dis.",
"key": "944_CR113",
"unstructured": "Arkema, E. V. et al. Exposure to ultraviolet-B and risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis among women in the Nurses’ Health Study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 72, 506–511 (2013).",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/archinte.168.15.1664",
"author": "KH Costenbader",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1664",
"journal-title": "Arch. Intern. Med.",
"key": "944_CR114",
"unstructured": "Costenbader, K. H., Chang, S. C., Laden, F., Puett, R. & Karlson, E. W. Geographic variation in rheumatoid arthritis incidence among women in the United States. Arch. Intern. Med. 168, 1664–1670 (2008).",
"volume": "168",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2017/5491676",
"author": "N Hajjaj-Hassouni",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5491676",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Rheumatol.",
"key": "944_CR115",
"unstructured": "Hajjaj-Hassouni, N. et al. Evaluation of vitamin D status in rheumatoid arthritis and its association with disease activity across 15 countries: “The COMORA Study”. Int. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 5491676 (2017).",
"volume": "2017",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3899/jrheum.190795",
"author": "G Mouterde",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1624",
"journal-title": "J. Rheumatol.",
"key": "944_CR116",
"unstructured": "Mouterde, G. et al. Association between vitamin D deficiency and disease activity, disability, and radiographic progression in early rheumatoid arthritis: the ESPOIR Cohort. J. Rheumatol. 47, 1624–1628 (2020).",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/art.11434",
"author": "LA Merlino",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "72",
"journal-title": "Arthritis Rheum.",
"key": "944_CR117",
"unstructured": "Merlino, L. A. et al. Iowa Women’s Health Study. Vitamin D intake is inversely associated with rheumatoid arthritis: results from the Iowa Women’s Health Study. Arthritis Rheum. 50, 72–77 (2004).",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2020.596007",
"author": "Y Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "596007",
"journal-title": "Front. Med.",
"key": "944_CR118",
"unstructured": "Guan, Y., Hao, Y., Guan, Y., Bu, H. & Wang, H. The effect of vitamin D supplementation on rheumatoid arthritis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Med. 7, 596007 (2020).",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13010107",
"author": "Y Nguyen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "107",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "944_CR119",
"unstructured": "Nguyen, Y. et al. Efficacy of oral vitamin supplementation in inflammatory rheumatic disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutrients 13, 107 (2020).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/etm.2015.2747",
"author": "J Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1812",
"journal-title": "Exp. Ther. Med.",
"key": "944_CR120",
"unstructured": "Yang, J., Liu, L., Zhang, Q., Li, M. & Wang, J. Effect of vitamin D on the recurrence rate of rheumatoid arthritis. Exp. Ther. Med. 10, 1812–1816 (2015).",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1756-185X.2011.01684.x",
"author": "K Gopinath",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "332",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Rheum. Dis.",
"key": "944_CR121",
"unstructured": "Gopinath, K. & Danda, D. Supplementation of 1,25 dihydroxy vitamin D3 in patients with treatment naive early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomised controlled trial. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 14, 332–339 (2011).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12659/MSM.911628",
"author": "C Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9127",
"journal-title": "Med. Sci. Monit.",
"key": "944_CR122",
"unstructured": "Li, C. et al. Efficacy and safety of 22-oxa-calcitriol in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a phase II trial. Med. Sci. Monit. 24, 9127–9135 (2018).",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_446_18",
"author": "D Mukherjee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "517",
"journal-title": "J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care",
"key": "944_CR123",
"unstructured": "Mukherjee, D., Lahiry, S., Thakur, S. & Chakraborty, D. S. Effect of 1,25 dihydroxy vitamin D3 supplementation on pain relief in early rheumatoid arthritis. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 8, 517–522 (2019).",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0178463",
"author": "I Buondonno",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "944_CR124",
"unstructured": "Buondonno, I. et al. Vitamin D and immunomodulation in early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. PLoS One 12, e0178463 (2017).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14397595.2018.1532622",
"author": "G Adami",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1059",
"journal-title": "Mod. Rheumatol.",
"key": "944_CR125",
"unstructured": "Adami, G. et al. An exploratory study on the role of vitamin D supplementation in improving pain and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Mod. Rheumatol. 29, 1059–1062 (2019).",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00296-011-1944-5",
"author": "M Salesi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2129",
"journal-title": "Rheumatol. Int.",
"key": "944_CR126",
"unstructured": "Salesi, M. & Farajzadegan, Z. Efficacy of vitamin D in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis receiving methotrexate therapy. Rheumatol. Int. 32, 2129–2133 (2012).",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00393-013-1297-4",
"author": "A Dehghan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "461",
"journal-title": "Z. Rheumatol.",
"key": "944_CR127",
"unstructured": "Dehghan, A., Rahimpour, S., Soleymani-Salehabadi, H. & Owlia, M. B. Role of vitamin D in flare ups of rheumatoid arthritis. Z. Rheumatol. 73, 461–464 (2014).",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/14397595.2014.952487",
"author": "Y Matsumoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "246",
"journal-title": "Mod. Rheumatol.",
"key": "944_CR128",
"unstructured": "Matsumoto, Y. et al. Relationships between serum 25-hydroxycalciferol, vitamin D intake and disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis–TOMORROW study. Mod. Rheumatol. 25, 246–250 (2015).",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000007024",
"author": "AS Franco",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Medicine",
"key": "944_CR129",
"unstructured": "Franco, A. S., Freitas, T. Q., Bernardo, W. M. & Pereira, R. M. R. Vitamin D supplementation and disease activity in patients with immune-mediated rheumatic diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 96, e7024 (2017).",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2020.00312",
"author": "J Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "312",
"journal-title": "Front. Med.",
"key": "944_CR130",
"unstructured": "Wu, J. et al. The role of vitamin D in combination treatment for patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Front. Med. 7, 312 (2020).",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj-2021-066452",
"author": "J Hahn",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "944_CR131",
"unstructured": "Hahn, J. et al. Vitamin D and marine omega 3 fatty acid supplementation and incident autoimmune disease: VITAL randomized controlled trial. BMJ 376, e066452 (2022).",
"volume": "376",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.coi.2016.09.001",
"author": "A Suárez-Fueyo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "32",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR132",
"unstructured": "Suárez-Fueyo, A., Bradley, S. J. & Tsokos, G. C. T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 43, 32–38 (2016).",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2015.00228",
"author": "S Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "228",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR133",
"unstructured": "Han, S., Zhuang, H., Shumyak, S., Yang, L. & Reeves, W. H. Mechanisms of autoantibody production in systemic lupus erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 6, 228 (2015).",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cyto.2012.11.023",
"author": "M Postal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "785",
"journal-title": "Cytokine",
"key": "944_CR134",
"unstructured": "Postal, M. et al. Th1/Th2 cytokine profile in childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Cytokine 61, 785–791 (2013).",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/08916934.2019.1693545",
"author": "F Muhammad Yusoff",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "8",
"journal-title": "Autoimmunity",
"key": "944_CR135",
"unstructured": "Muhammad Yusoff, F., Wong, K. K. & Mohd Redzwan, N. Th1, Th2, and Th17 cytokines in systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmunity 53, 8–20 (2020).",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0961203314540966",
"author": "M Sahebari",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1164",
"journal-title": "Lupus",
"key": "944_CR136",
"unstructured": "Sahebari, M., Nabavi, N. & Salehi, M. Correlation between serum 25(OH)D values and lupus disease activity: an original article and a systematic review with meta-analysis focusing on serum Vit D confounders. Lupus 23, 1164–1177 (2014).",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2019.102392",
"author": "MA Islam",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102392",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun. Rev.",
"key": "944_CR137",
"unstructured": "Islam, M. A., Khandker, S. S., Alam, S. S., Kotyla, P. & Hassan, R. Vitamin D status in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Autoimmun. Rev. 18, 102392 (2019).",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10067-012-2021-5",
"author": "OA Monticielo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1411",
"journal-title": "Clin. Rheumatol.",
"key": "944_CR138",
"unstructured": "Monticielo, O. A. et al. Vitamin D and polymorphisms of VDR gene in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Rheumatol. 31, 1411–1421 (2012).",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0961203319826704",
"author": "J Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "290",
"journal-title": "Lupus",
"key": "944_CR139",
"unstructured": "Sun, J., Zhang, S., Liu, J. S., Gui, M. & Zhang, H. Expression of vitamin D receptor in renal tissue of lupus nephritis and its association with renal injury activity. Lupus 28, 290–294 (2019).",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/clim.2000.4998",
"author": "M Linker-Israeli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "82",
"journal-title": "Clin. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR140",
"unstructured": "Linker-Israeli, M., Elstner, E., Klinenberg, J. R., Wallace, D. J. & Koeffler, H. P. Vitamin D3 and its synthetic analogs inhibit the spontaneous in vitro immunoglobulin production by SLE-derived PBMC. Clin. Immunol. 99, 82–93 (2001).",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/ar4060",
"author": "B Terrier",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "R221",
"journal-title": "Arthritis Res. Ther.",
"key": "944_CR141",
"unstructured": "Terrier, B. et al. Restoration of regulatory and effector T cell balance and B cell homeostasis in systemic lupus erythematosus patients through vitamin D supplementation. Arthritis Res. Ther. 14, R221 (2012).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0961203310394542",
"author": "M Lerman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "749",
"journal-title": "Lupus",
"key": "944_CR142",
"unstructured": "Lerman, M., Burnham, J. & Behrens, E. 1,25 Dihydroxyvitamin D3 limits monocyte maturation in lupus sera. Lupus 20, 749–753 (2011).",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0009193",
"author": "I Ben-Zvi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "944_CR143",
"unstructured": "Ben-Zvi, I. et al. The impact of vitamin D on dendritic cell function in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS One 5, e9193 (2010).",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0961203314530488",
"author": "M Barbhaiya",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "588",
"journal-title": "Lupus",
"key": "944_CR144",
"unstructured": "Barbhaiya, M. & Costenbader, K. H. Ultraviolet radiation and systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 23, 588–595 (2014).",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13114104",
"author": "RM Vearing",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4104",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "944_CR145",
"unstructured": "Vearing, R. M. et al. Vitamin D status of the British African-Caribbean residents: analysis of the UK Biobank Cohort. Nutrients 13, 4104 (2021).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/lupus-2015-000144",
"author": "EM Williams",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lupus Sci. Med.",
"key": "944_CR146",
"unstructured": "Williams, E. M. et al. I too, am America: a review of research on systemic lupus erythematosus in African-Americans. Lupus Sci. Med. 3, e000144 (2016).",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/art.37953",
"author": "M Petri",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1865",
"journal-title": "Arthritis Rheum.",
"key": "944_CR147",
"unstructured": "Petri, M., Bello, K. J., Fang, H. & Magder, L. S. Vitamin D in systemic lupus erythematosus: modest association with disease activity and the urine protein-to-creatinine ratio. Arthritis Rheum. 65, 1865–1871 (2013).",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0961203314559089",
"author": "L Andreoli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "499",
"journal-title": "Lupus",
"key": "944_CR148",
"unstructured": "Andreoli, L. et al. A 24-month prospective study on the efficacy and safety of two different monthly regimens of vitamin D supplementation in pre-menopausal women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 24, 499–506 (2015).",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"author": "H Karimzadeh",
"first-page": "22",
"journal-title": "J. Res. Med. Sci.",
"key": "944_CR149",
"unstructured": "Karimzadeh, H., Shirzadi, M. & Karimifar, M. The effect of Vitamin D supplementation in disease activity of systemic lupus erythematosus patients with Vitamin D deficiency: a randomized clinical trial. J. Res. Med. Sci. 27, 22–24 (2017).",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/acr.22621",
"author": "GL Lima",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "91",
"journal-title": "Arthritis Care Res.",
"key": "944_CR150",
"unstructured": "Lima, G. L. et al. Vitamin D supplementation in adolescents and young adults with juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus for improvement in disease activity and fatigue scores: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Care Res. 68, 91–98 (2016).",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00296-012-2537-7",
"author": "K Sumethkul",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1461",
"journal-title": "Rheumatol. Int.",
"key": "944_CR151",
"unstructured": "Sumethkul, K. et al. The predictive factors of low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and vitamin D deficiency in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol. Int. 33, 1461–1467 (2013).",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13075-018-1803-9",
"author": "Q Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "19",
"journal-title": "Arthritis Res. Ther.",
"key": "944_CR152",
"unstructured": "Yu, Q. et al. Vitamin D protects podocytes from autoantibodies induced injury in lupus nephritis by reducing aberrant autophagy. Arthritis Res. Ther. 21, 19 (2019).",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12030789",
"author": "M Bellan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "789",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "944_CR153",
"unstructured": "Bellan, M. et al. Pathophysiological role and therapeutic implications of vitamin D in autoimmunity: focus on chronic autoimmune diseases. Nutrients 12, 789 (2020).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0961203314559090",
"author": "S Piantoni",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "490",
"journal-title": "Lupus",
"key": "944_CR154",
"unstructured": "Piantoni, S. et al. Phenotype modifications of T-cells and their shift toward a Th2 response in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus supplemented with different monthly regimens of vitamin D. Lupus 24, 490–498 (2015).",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/acr.20186",
"author": "G Ruiz-Irastorza",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1160",
"journal-title": "Arthritis Care Res.",
"key": "944_CR155",
"unstructured": "Ruiz-Irastorza, G., Gordo, S., Olivares, N., Egurbide, M. V. & Aguirre, C. Changes in vitamin D levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Effects on fatigue, disease activity, and damage. Arthritis Care Res. 62, 1160–1165 (2010).",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms19082355",
"author": "A Mak",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2355",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "944_CR156",
"unstructured": "Mak, A. The impact of Vitamin D on the immunopathophysiology, disease activity, and extra-musculoskeletal manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 2355 (2018).",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"author": "JM Sabio",
"first-page": "286",
"journal-title": "Clin. Exp. Rheumatol.",
"key": "944_CR157",
"unstructured": "Sabio, J. M., Vargas-Hitos, J. A., Martínez-Bordonado, J. & Mediavilla-García, J. D. Association between non-dipper hypertension and vitamin D deficiency in women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 37, 286–292 (2019).",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0961203318796293",
"author": "MH Nguyen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2003",
"journal-title": "Lupus",
"key": "944_CR158",
"unstructured": "Nguyen, M. H., Bryant, K. & O’Neill, S. G. Vitamin D in SLE: a role in pathogenesis and fatigue? A review of the literature. Lupus 27, 2003–2011 (2018).",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10067-018-4204-1",
"author": "CC Mok",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2685",
"journal-title": "Clin. Rheumatol.",
"key": "944_CR159",
"unstructured": "Mok, C. C., Bro, E. T., Ho, L. Y., Singh, R. J. & Jannetto, P. J. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 levels and flares of systemic lupus erythematosus: a longitudinal cohort analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 37, 2685–2692 (2018).",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"author": "F Dall’Ara",
"first-page": "153",
"journal-title": "Clin. Exp. Rheumatol.",
"key": "944_CR160",
"unstructured": "Dall’Ara, F., Cutolo, M., Andreoli, L., Tincani, A. & Paolino, S. Vitamin D and systemic lupus erythematous: a review of immunological and clinical aspects. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 36, 153–162 (2018).",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/hmbci-2018-0064",
"author": "C Dutta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig.",
"key": "944_CR161",
"unstructured": "Dutta, C., Kakati, S., Barman, B. & Bora, K. Vitamin D status and its relationship with systemic lupus erythematosus as a determinant and outcome of disease activity. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. https://doi.org/10.1515/hmbci-2018-0064 (2019).",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1756-185X.13676",
"author": "SY Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1803",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Rheum. Dis.",
"key": "944_CR162",
"unstructured": "Guan, S. Y. et al. Association between circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D and systemic lupus erythematosus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 22, 1803–1813 (2019).",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/DDDT.S144860",
"author": "L An",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3119",
"journal-title": "Drug Des. Dev. Ther.",
"key": "944_CR163",
"unstructured": "An, L., Sun, M. H., Chen, F. & Li, J. R. Vitamin D levels in systemic sclerosis patients: a meta-analysis. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 11, 3119–3125 (2017).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0137912",
"author": "A Corrado",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "944_CR164",
"unstructured": "Corrado, A. et al. Relationship between body mass composition, bone mineral density, skin fibrosis and 25(OH) Vitamin D serum levels in systemic sclerosis. PLoS One 10, e0137912 (2015).",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5152/eurjrheum.2015.0065",
"author": "L Groseanu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "50",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Rheumatol.",
"key": "944_CR165",
"unstructured": "Groseanu, L. et al. Low vitamin D status in systemic sclerosis and the impact on disease phenotype. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 3, 50–55 (2016).",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2021/9782994",
"author": "AD Diaconu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9782994",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol. Res.",
"key": "944_CR166",
"unstructured": "Diaconu, A. D. et al. Role of Vitamin D in systemic sclerosis: a systematic literature review. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 9782994 (2021).",
"volume": "2021",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1756-185X.13554",
"author": "C Caimmi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1041",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Rheum. Dis.",
"key": "944_CR167",
"unstructured": "Caimmi, C. et al. Vitamin D serum levels and the risk of digital ulcers in systemic sclerosis: a longitudinal study. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 22, 1041–1045 (2019).",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2011.02.002",
"author": "Y Arnson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "490",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun. Rev.",
"key": "944_CR168",
"unstructured": "Arnson, Y. et al. Serum 25-OH vitamin D concentrations are linked with various clinical aspects in patients with systemic sclerosis: a retrospective cohort study and review of the literature. Autoimmun. Rev. 10, 490–494 (2011).",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms17122103",
"author": "M Atteritano",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2103",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "944_CR169",
"unstructured": "Atteritano, M. et al. Skin involvement and pulmonary hypertension are associated with vitamin D insufficiency in scleroderma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17, 2103 (2016).",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2340/0001555573449451",
"author": "P Humbert",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "449",
"journal-title": "Acta Derm. Venereol.",
"key": "944_CR170",
"unstructured": "Humbert, P. et al. Treatment of scleroderma with oral 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3: evaluation of skin involvement using non-invasive techniques. Results of an open prospective trial. Acta Derm. Venereol. 73, 449–451 (1993).",
"volume": "73",
"year": "1993"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3899/jrheum.110695",
"author": "T Gambichler",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2492",
"journal-title": "J. Rheumatol.",
"key": "944_CR171",
"unstructured": "Gambichler, T., Chrobok, I., Höxtermann, S. & Kreuter, A. Significantly decreased serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in a large German systemic sclerosis cohort. J. Rheumatol. 38, 2492–2493 (2011).",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1756-185X.12794",
"author": "L Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1002",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Rheum. Dis.",
"key": "944_CR172",
"unstructured": "Zhang, L. et al. Association between the serum level of vitamin D and systemic sclerosis in a Chinese population: a case control study. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 20, 1002–1008 (2017).",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41584-021-00685-0",
"author": "M Cutolo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "665",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Rheumatol.",
"key": "944_CR173",
"unstructured": "Cutolo, M. & Smith, V. Detection of microvascular changes in systemic sclerosis and other rheumatic diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 17, 665–677 (2021).",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.rbr.2016.03.004",
"author": "MM Sampaio-Barros",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "337",
"journal-title": "Rev. Bras. Reumatol. Engl. Ed.",
"key": "944_CR174",
"unstructured": "Sampaio-Barros, M. M., Takayama, L., Sampaio-Barros, P. D., Bonfá, E. & Pereira, R. M. Low vitamin D serum levels in diffuse systemic sclerosis: a correlation with worst quality of life and severe capillaroscopic findings. Rev. Bras. Reumatol. Engl. Ed. 56, 337–344 (2016).",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10067-010-1478-3",
"author": "P Caramaschi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1419",
"journal-title": "Clin. Rheumatol.",
"key": "944_CR175",
"unstructured": "Caramaschi, P. et al. Very low levels of vitamin D in systemic sclerosis patients. Clin. Rheumatol. 29, 1419–1425 (2010).",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00296-019-04401-w",
"author": "C Corallo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1767",
"journal-title": "Rheumatol. Int.",
"key": "944_CR176",
"unstructured": "Corallo, C. et al. Sarcopenia in systemic sclerosis: the impact of nutritional, clinical, and laboratory features. Rheumatol. Int. 39, 1767–1775 (2019).",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0179062",
"author": "AC Trombetta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "944_CR177",
"unstructured": "Trombetta, A. C. et al. Vitamin D deficiency and clinical correlations in systemic sclerosis patients: a retrospective analysis for possible future developments. PLoS One 12, e0179062 (2017).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00296-010-1421-6",
"author": "SK Shinjo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1075",
"journal-title": "Rheumatol. Int.",
"key": "944_CR178",
"unstructured": "Shinjo, S. K., Bonfá, E., de Falco Caparbo, V. & Pereira, R. M. Low bone mass in juvenile onset sclerosis systemic: the possible role for 25-hydroxyvitamin D insufficiency. Rheumatol. Int. 31, 1075–1080 (2011).",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.683665",
"author": "M Cutolo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "683665",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR179",
"unstructured": "Cutolo, M., Soldano, S., Sulli, A., Smith, V. & Gotelli, E. Influence of seasonal vitamin D changes on clinical manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 12, 683665 (2021).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2007.07.001",
"author": "M Cutolo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "59",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun. Rev.",
"key": "944_CR180",
"unstructured": "Cutolo, M., Otsa, K., Uprus, M., Paolino, S. & Seriolo, B. Vitamin D in rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 7, 59–64 (2007).",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jchromb.2016.01.049",
"author": "C Jenkinson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "56",
"journal-title": "J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci.",
"key": "944_CR181",
"unstructured": "Jenkinson, C. et al. High throughput LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous analysis of multiple vitamin D analytes in serum. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 1014, 56–63 (2016).",
"volume": "1014",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0748730404264658",
"author": "S De Jong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "180",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Rhythm.",
"key": "944_CR182",
"unstructured": "De Jong, S. et al. Seasonal changes in gene expression represent cell-type composition in whole blood. Hum. Mol. Genet. 23, 2721–2728 (2014). Bronson, F. H. Are humans seasonally photoperiodic? J. Biol. Rhythm. 19, 180–192 (2004).",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ncomms8000",
"author": "XC Dopico",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "944_CR183",
"unstructured": "Dopico, X. C. et al. Widespread seasonal gene expression reveals annual differences in human immunity and physiology. Nat. Commun. 12, 7000 (2015).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04315.x",
"author": "AL Khoo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "72",
"journal-title": "Clin. Exp. Immunol.",
"key": "944_CR184",
"unstructured": "Khoo, A. L. et al. Regulation of cytokine responses by seasonality of vitamin D status in healthy individuals. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 164, 72–79 (2011).",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0029250",
"author": "AL Khoo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "944_CR185",
"unstructured": "Khoo, A. L. et al. Seasonal variation in vitamin D3 levels is paralleled by changes in the peripheral blood human T cell compartment. PLoS One 7, e29250 (2012).",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/rheumatology/kel414",
"author": "N Iikuni",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "846",
"journal-title": "Rheumatol",
"key": "944_CR186",
"unstructured": "Iikuni, N. et al. What’s in season for rheumatoid arthritis patients? Seasonal fluctuations in disease activity. Rheumatol 46, 846–848 (2007).",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12891-019-2418-2",
"author": "H Mori",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMC Musculoskelet. Disord.",
"key": "944_CR187",
"unstructured": "Mori, H. et al. Influence of seasonal changes on disease activity and distribution of affected joints in rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 20, 30 (2019).",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12891-016-0911-4",
"author": "C Feldthusen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMC Musculoskelet. Disord.",
"key": "944_CR188",
"unstructured": "Feldthusen, C., Grimby-Ekman, A., Forsblad-d’Elia, H., Jacobsson, L. & Mannerkorpi, K. Seasonal variations in fatigue in persons with rheumatoid arthritis: a longitudinal study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 17, 59 (2016).",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/ard.2010.144402",
"author": "G Mouterde",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1251",
"journal-title": "Ann. Rheum. Dis.",
"key": "944_CR189",
"unstructured": "Mouterde, G. et al. Predictors of radiographic progression in the ESPOIR Cohort: the season of first symptoms may influence the short-term outcome in early arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 70, 1251–1256 (2011).",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-64284-x",
"author": "M Herly",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "944_CR190",
"unstructured": "Herly, M. et al. Impact of season on the association between vitamin D levels at diagnosis and one-year remission in early rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Rep. 10, 7371 (2020).",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2017.03.002",
"author": "J Vojinovic",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "548",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun. Rev.",
"key": "944_CR191",
"unstructured": "Vojinovic, J. et al. European multicentre pilot survey to assess vitamin D status in rheumatoid arthritis patients and early development of a new patient reported outcome questionnaire (D-PRO). Autoimmun. Rev. 16, 548–554 (2017).",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrrheum.2011.115",
"author": "M Cutolo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "500",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Rheumatol.",
"key": "944_CR192",
"unstructured": "Cutolo, M. Rheumatoid arthritis: circadian and circannual rhythms in RA. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 7, 500–502 (2011).",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nutres.2021.05.007",
"author": "SL Finch",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "139",
"journal-title": "Nutr. Res.",
"key": "944_CR193",
"unstructured": "Finch, S. L. et al. Higher concentrations of vitamin D in Canadian children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis compared to healthy controls are associated with more frequent use of vitamin D supplements and season of birth. Nutr. Res. 92, 139–149 (2021).",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0961203312439640",
"author": "DJ Birmingham",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "855",
"journal-title": "Lupus",
"key": "944_CR194",
"unstructured": "Birmingham, D. J. et al. Evidence that abnormally large seasonal declines in vitamin D status may trigger SLE flare in non-African Americans. Lupus 21, 855–864 (2012).",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"author": "F Dall’Ara",
"first-page": "153",
"journal-title": "Clin. Exp. Rheumatol.",
"key": "944_CR195",
"unstructured": "Dall’Ara, F. et al. Winter lupus flares are associated with low vitamin D levels in a retrospective longitudinal study of Italian adult patients. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 33, 153–158 (2015).",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10067-011-1684-7",
"author": "B Seriolo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "445",
"journal-title": "Clin. Rheumatol.",
"key": "944_CR196",
"unstructured": "Seriolo, B., Molfetta, L. & Cutolo, M. Seasonal variations in serum levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin. Rheumatol. 30, 445–446 (2011).",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14397595.2019.1702238",
"author": "C Foocharoen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1025",
"journal-title": "Mod. Rheumatol.",
"key": "944_CR197",
"unstructured": "Foocharoen, C. et al. Effect of season on clinical outcomes of Thai systemic sclerosis: analysis of the Thai National Healthcare Database. Mod. Rheumatol. 30, 1025–1032 (2020).",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41584-020-00565-z",
"author": "R Talarico",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "177",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Rheumatol.",
"key": "944_CR198",
"unstructured": "Talarico, R. et al. The impact of COVID-19 on rare and complex connective tissue diseases: the experience of ERN ReCONNET. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 17, 177–184 (2021).",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(21)00112-0",
"author": "D Saadoun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e481",
"journal-title": "Lancet Rheumatol.",
"key": "944_CR199",
"unstructured": "Saadoun, D. et al. SARS-CoV-2 outbreak in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases: the Euro-COVIMID multicentre cross-sectional study. Lancet Rheumatol. 3, e481–e488 (2021).",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001454",
"author": "M Cutolo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "RMD Open",
"key": "944_CR200",
"unstructured": "Cutolo, M., Paolino, S. & Smith, V. Evidences for a protective role of vitamin D in COVID-19. RMD Open 6, e001454 (2020).",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26360",
"author": "R Munshi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "733",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "944_CR201",
"unstructured": "Munshi, R. et al. Vitamin D insufficiency as a potential culprit in critical COVID-19 patients. J. Med. Virol. 93, 733–740 (2021).",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cen.14276",
"author": "G Panagiotou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "508",
"journal-title": "Clin. Endocrinol.",
"key": "944_CR202",
"unstructured": "Panagiotou, G. et al. Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 are associated with greater disease severity. Clin. Endocrinol. 93, 508–511 (2020).",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8",
"author": "PC Ilie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1195",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin. Exp. Res.",
"key": "944_CR203",
"unstructured": "Ilie, P. C., Stefanescu, S. & Smith, L. The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 32, 1195–1198 (2020).",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cen.14540",
"author": "Z Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "281",
"journal-title": "Clin. Endocrinol.",
"key": "944_CR204",
"unstructured": "Wang, Z. et al. Association of vitamin D deficiency with COVID-19 infection severity: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Endocrinol. 96, 281–287 (2022).",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0268396",
"author": "O D’Ecclesiis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "944_CR205",
"unstructured": "D’Ecclesiis, O. et al. Vitamin D and SARS-CoV2 infection, severity and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 17, e0268396 (2022).",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14102134",
"author": "B Hosseini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2134",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "944_CR206",
"unstructured": "Hosseini, B., El Abd, A. & Ducharme, F. M. Effects of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19 related outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 14, 2134 (2022).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "V Borba",
"first-page": "439",
"journal-title": "Isr. Med. Assoc. J.",
"key": "944_CR207",
"unstructured": "Borba, V. & Shoenfeld, Y. Vitamin D and immune system function in patients with COVID-19. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 24, 439–440 (2022).",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "AR Martineau",
"first-page": "356:i6583",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "944_CR208",
"unstructured": "Martineau, A. R. et al. Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and metaanalysis of individual participant data. BMJ 15, 356:i6583 (2017).",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgab892",
"author": "HA Dissanayake",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1484",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "944_CR209",
"unstructured": "Dissanayake, H. A. et al. Prognostic and therapeutic role of vitamin D in COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 107, 1484–1502 (2022).",
"volume": "107",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "M Cutolo",
"first-page": "383",
"journal-title": "Clin. Exp. Rheumatol.",
"key": "944_CR210",
"unstructured": "Cutolo, M., Smith, V. & Paolino, S. Understanding immune effects of oestrogens to explain the reduced morbidity and mortality in female versus male COVID-19 patients. Comparisons with autoimmunity and vaccination. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 38, 383–386 (2020).",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41584-020-0503-4",
"author": "M Cutolo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "628",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Rheumatol.",
"key": "944_CR211",
"unstructured": "Cutolo, M. & Straub, R. H. Sex steroids and autoimmune rheumatic diseases: state of the art. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 16, 628–644 (2020).",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/B978-0-12-386960-9.00009-5",
"author": "S Hansdottir",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "217",
"journal-title": "Vitam. Horm.",
"key": "944_CR212",
"unstructured": "Hansdottir, S. & Monick, M. M. Vitamin D effects on lung immunity and respiratory diseases. Vitam. Horm. 86, 217–237 (2011).",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7861/clinmed.2020-0301",
"author": "EK Weir",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e107",
"journal-title": "Clin. Med.",
"key": "944_CR213",
"unstructured": "Weir, E. K., Thenappan, T., Bhargava, M. & Chen, Y. Does vitamin D deficiency increase the severity of COVID-19? Clin. Med. 20, e107–e108 (2020).",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/jclinpath-2012-201301",
"author": "JL Waldron",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "620",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Pathol.",
"key": "944_CR214",
"unstructured": "Waldron, J. L. et al. Vitamin D: a negative acute phase reactant. J. Clin. Pathol. 66, 620–622 (2013).",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2009.08.004",
"author": "JM Yuk",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "231",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "944_CR215",
"unstructured": "Yuk, J. M. et al. Vitamin D3 induces autophagy in human monocytes/macrophages via cathelicidin. Cell Host Microbe 6, 231–243 (2009).",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu7043011",
"author": "MT Cantorna",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3011",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "944_CR216",
"unstructured": "Cantorna, M. T., Snyder, L., Lin, Y. D. & Yang, L. Vitamin D and 1,25(OH)2D regulation of T cells. Nutrients 7, 3011–3021 (2015).",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/mmr.2017.7546",
"author": "J Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "7432",
"journal-title": "Mol. Med. Rep.",
"key": "944_CR217",
"unstructured": "Xu, J. et al. Vitamin D alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via regulation of the renin-angiotensin system. Mol. Med. Rep. 16, 7432–7438 (2017).",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biom9110649",
"author": "S Mohammad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "649",
"journal-title": "Biomolecules",
"key": "944_CR218",
"unstructured": "Mohammad, S., Mishra, A. & Ashraf, M. Z. Emerging role of vitamin D and its associated molecules in pathways related to pathogenesis of thrombosis. Biomolecules 9, 649 (2019).",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu9090980",
"author": "F Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "944_CR219",
"unstructured": "Jiang, F., Yang, Y., Xue, L., Li, B. & Zhang, Z. 1α, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 attenuates TGF-β-induced pro-fibrotic effects in human lung epithelial cells through inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nutrients 9, 1–13 (2017).",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965",
"author": "M Torres",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "112965",
"journal-title": "Biomed. Pharmacother.",
"key": "944_CR220",
"unstructured": "Torres, M. et al. Changes in the immune response against SARS-CoV-2 in individuals with severe COVID-19 treated with high dose of vitamin D. Biomed. Pharmacother. 150, 112965 (2022).",
"volume": "150",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00198-018-4520-y",
"author": "JM Quesada-Gomez",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1697",
"journal-title": "Osteoporos. Int.",
"key": "944_CR221",
"unstructured": "Quesada-Gomez, J. M. & Bouillon, R. Is calcifediol better than cholecalciferol for vitamin D supplementation? Osteoporos. Int. 29, 1697–1711 (2018).",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines9050509",
"author": "J Oristrell",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "509",
"journal-title": "Biomedicines",
"key": "944_CR222",
"unstructured": "Oristrell, J. et al. Association of calcitriol supplementation with reduced COVID-19 mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease: a population-based study. Biomedicines 9, 509 (2021).",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003",
"author": "MA Villasis-Keever",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "423",
"journal-title": "Arch. Med. Res.",
"key": "944_CR223",
"unstructured": "Villasis-Keever, M. A. et al. Efficacy and safety of Vitamin D supplementation to prevent COVID-19 in frontline healthcare workers. A randomized clinical trial. Arch. Med. Res. 53, 423–430 (2022).",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016",
"author": "Z Maghbooli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1242",
"journal-title": "Endocr. Pract.",
"key": "944_CR224",
"unstructured": "Maghbooli, Z. et al. Treatment with 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 (calcifediol) is associated with a reduction in the blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio marker of disease severity in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a pilot multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded clinical trial. Endocr. Pract. 27, 1242–1251 (2021).",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-022-06016-2",
"author": "F Jaun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "944_CR225",
"unstructured": "Jaun, F. et al. High-dose vitamin D substitution in patients with COVID-19: study protocol for a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-center study-VitCov Trial. Trials 23, 114 (2022).",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2021-057024",
"author": "M Legacy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "944_CR226",
"unstructured": "Legacy, M. et al. Dietary supplements to reduce symptom severity and duration in people with SARS-CoV-2: study protocol for a randomised, double-blind, placebo controlled clinical trial. BMJ Open 12, e057024 (2022).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines9111714",
"author": "TS Chillon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1714",
"journal-title": "Biomedicines",
"key": "944_CR227",
"unstructured": "Chillon, T. S. et al. Relationship between vitamin D status and antibody response to COVID-19 mRNA vaccination in healthy adults. Biomedicines 9, 1714 (2021).",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13030717",
"author": "A Sulli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "717",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "944_CR228",
"unstructured": "Sulli, A. et al. Vitamin D and lung outcomes in elderly COVID-19 patients. Nutrients 213, 717–723 (2021).",
"volume": "213",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13103596",
"author": "L Borsche",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3596",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "944_CR229",
"unstructured": "Borsche, L., Glauner, B. & von Mendel, J. COVID-19 mortality risk correlates inversely with vitamin D3 status, and a mortality rate close to zero could theoretically be achieved at 50 ng/mL 25(OH)D3: results of a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 13, 3596 (2021).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0273078",
"author": "G Scabbia",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "944_CR230",
"unstructured": "Scabbia, G. et al. Does climate help modeling COVID-19 risk and to what extent? PLoS One 17, e0273078 (2022).",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amsu.2021.102419",
"author": "K Sharun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Ann. Med. Surg.",
"key": "944_CR231",
"unstructured": "Sharun, K., Tiwari, R. & Dha, K. COVID-19 and sunlight: Impact on SARS-CoV-2 transmissibility, morbidity, and mortality. Ann. Med. Surg. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amsu.2021.102419 (2021).",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2004-0682",
"author": "BW Hollis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3149",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "944_CR232",
"unstructured": "Hollis, B. W. Editorial: The determination of circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D: no easy task. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89, 3149–3151 (2004).",
"volume": "89",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.111.031070",
"author": "L Tripkovic",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1357",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "944_CR233",
"unstructured": "Tripkovic, L. et al. Comparison of vitamin D2 and vitamin D3 supplementation in raising serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D status: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 95, 1357–1364 (2012).",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bone.2018.02.024",
"author": "H Ketha",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "321",
"journal-title": "Bone",
"key": "944_CR234",
"unstructured": "Ketha, H. et al. Comparison of the effect of daily versus bolus dose maternal vitamin D3 supplementation on the 24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 to 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 ratio. Bone 110, 321–325 (2018).",
"volume": "110",
"year": "2018"
}
],
"reference-count": 234,
"references-count": 234,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41584-023-00944-2"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Rheumatology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Involvement of the secosteroid vitamin D in autoimmune rheumatic diseases and COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "19"
}
