A Narrative Review of the Evidence for Variations in Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentration Thresholds for Optimal Health
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14030639, Feb 2022
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
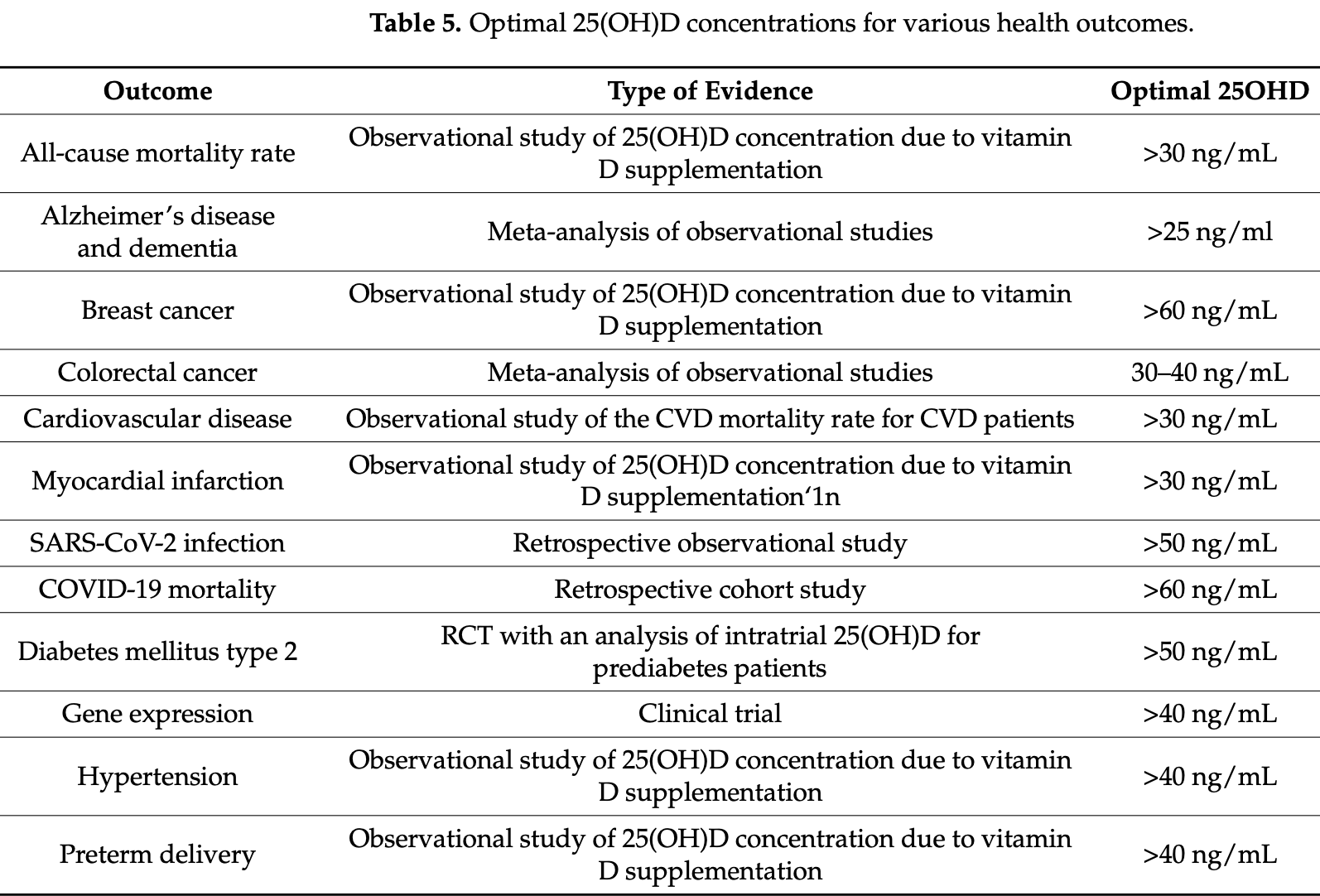
Review of the benefits of vitamin D for cardiovascular disease, hypertension, cancer, type 2 diabetes, and COVID-19. Authors conclude that optimal levels are above 30ng/mL for cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality, whereas the thresholds for other outcomes may range up to 40 or 50 ng/mL.
1.
Jaurrieta-Largo et al., A Machine Learning Approach to Understanding the Genetic Role in COVID-19 Prognosis: The Influence of Gene Polymorphisms Related to Inflammation, Vitamin D, and ACE2, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms26167975.
2.
Al-Khrasani et al., Do vitamins halt the COVID-19-evoked pro-inflammatory cytokines involved in the development of neuropathic pain?, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2025.118346.
3.
Kow et al., Vitamin D and COVID‐19: How much more evidence do we need?, Nutrition in Clinical Practice, doi:10.1002/ncp.11349.
4.
Bigman et al., A Comprehensive Scoping Review on Diet and Nutrition in Relation to Long COVID-19 Symptoms and Recovery, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17111802.
5.
Hewison, M., COVID-19 and our understanding of vitamin D and immune function, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2025.106710.
6.
Wimalawansa, S., Vitamin D Deficiency Meets Hill’s Criteria for Causation in SARS-CoV-2 Susceptibility, Complications, and Mortality: A Systematic Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17030599.
7.
Sanduzzi Zamparelli et al., Immune-Boosting and Antiviral Effects of Antioxidants in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Therapeutic Perspective, Life, doi:10.3390/life15010113.
8.
Fazli et al., Possible Link between Gut Microbiota, Diet, and COVID-19 Infection, Journal of Medical Bacteriology, 12:4, jmb.tums.ac.ir/index.php/jmb/article/view/525.
9.
Wojciulik et al., The impact of genetic polymorphism on course and severity of the SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease, Przeglad Epidemiologiczny, doi:10.32394/pe/194862.
10.
Wimalawansa (B), S., Unveiling the Interplay—Vitamin D and ACE-2 Molecular Interactions in Mitigating Complications and Deaths from SARS-CoV-2, Biology, doi:10.3390/biology13100831.
11.
Santa et al., Comparative analysis of COVID-19 responses in Japan and Africa: diet, phytochemicals, vitamin D, and gut microbiota in reducing mortality—A systematic review and meta-analysis, Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1465324.
12.
Kaushal, A., Nutraceuticals and pharmacological to balance the transitional microbiome to extend immunity during COVID-19 and other viral infections, Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12967-024-05587-9.
13.
Mu et al., Anti-inflammatory and Nutritional Interventions Against SARS-CoV-2: A Comprehensive Review, Journal of Agriculture and Food Research, doi:10.1016/j.jafr.2024.101422.
14.
Wimalawansa (C), S., Unlocking Insights: Navigating COVID-19 Challenges and Emulating Future Pandemic Resilience Strategies with Strengthening Natural Immunity, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34691.
15.
Imran et al., Therapeutic Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19 Patients, Clinical Nutrition Open Science, doi:10.1016/j.nutos.2024.07.004.
16.
Grant, W., Vitamin D and viral infections: Infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases, and cancers, Advances in Food and Nutrition Research, doi:10.1016/bs.afnr.2023.12.007.
17.
Polonowita et al., Molecular Quantum and Logic Process of Consciousness—Vitamin D Big-Data in COVID-19—A Case for Incorporating Machine Learning In Medicine, European Journal of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical sciences, doi:10.5281/zenodo.10435649.
18.
Gomaa et al., Pharmacological evaluation of vitamin D in COVID-19 and long COVID-19: recent studies confirm clinical validation and highlight metformin to improve VDR sensitivity and efficacy, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01383-x.
19.
Gotelli et al., Understanding the immune-endocrine effects of vitamin D in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a role in protecting against neurodamage?, Neuroimmunomodulation, doi:10.1159/000533286.
20.
Cutolo et al., Involvement of the secosteroid vitamin D in autoimmune rheumatic diseases and COVID-19, Nature Reviews Rheumatology, doi:10.1038/s41584-023-00944-2.
21.
Schloss et al., Nutritional deficiencies that may predispose to long COVID, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01183-3.
22.
Arora et al., Global Dietary and Herbal Supplement Use during COVID-19—A Scoping Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15030771.
23.
Nicoll et al., COVID-19 Prevention: Vitamin D Is Still a Valid Remedy, Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm11226818.
24.
Foshati et al., Antioxidants and clinical outcomes of patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A systematic review of observational and interventional studies, Food Science & Nutrition, doi:10.1002/fsn3.3034.
25.
Quesada-Gomez et al., Vitamin D Endocrine System and COVID-19: Treatment with Calcifediol, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14132716.
26.
DiGuilio et al., Micronutrient Improvement of Epithelial Barrier Function in Various Disease States: A Case for Adjuvant Therapy, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms23062995.
27.
Grant (B) et al., A Narrative Review of the Evidence for Variations in Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentration Thresholds for Optimal Health, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14030639.
28.
Shah Alam et al., The role of vitamin D in reducing SARS-CoV-2 infection: An update, International Immunopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107686.
29.
Griffin et al., Perspective: Vitamin D supplementation prevents rickets and acute respiratory infections when given as daily maintenance but not as intermittent bolus: implications for COVID-19, Clinical Medicine, doi:10.7861/clinmed.2021-0035.
30.
Kohlmeier et al., When Mendelian randomisation fails, BMJ Nutrition, Prevention & Health, doi:10.1136/bmjnph-2021-000265.
31.
Brenner, H., Vitamin D Supplementation to Prevent COVID-19 Infections and Deaths—Accumulating Evidence from Epidemiological and Intervention Studies Calls for Immediate Action, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13020411.
32.
Mercola et al., Evidence Regarding Vitamin D and Risk of COVID-19 and Its Severity, Nutrients 2020, 12:11, 3361, doi:10.3390/nu12113361.
33.
Basha et al., Is the shielding effect of cholecalciferol in SARS CoV-2 infection dependable? An evidence based unraveling, Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health, doi:10.1016/j.cegh.2020.10.005.
34.
Xu et al., The importance of vitamin d metabolism as a potential prophylactic, immunoregulatory and neuroprotective treatment for COVID-19, Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12967-020-02488-5.
35.
Alexander et al., Early Nutritional Interventions with Zinc, Selenium and Vitamin D for Raising Anti-Viral Resistance Against Progressive COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12082358.
36.
Andrade et al., Vitamin A and D deficiencies in the prognosis of respiratory tract infections: A systematic review with perspectives for COVID-19 and a critical analysis on supplementation, SciELO preprints, doi:10.1590/SciELOPreprints.839.
37.
Grant (C) et al., Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients, 12:4, 988, doi:10.3390/nu12040988.
38.
McCullough et al., Daily oral dosing of vitamin D3 using 5000 TO 50,000 international units a day in long-term hospitalized patients: Insights from a seven year experience, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.12.010.
39.
EFSA, Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to vitamin D and normal function of the immune system and inflammatory response (ID 154, 159), maintenance of normal muscle function (ID 155) and maintenance of normal cardiovascular function (ID 159) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (E, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1468.
40.
EFSA (B), Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of a health claim related to vitamin D and contribution to the normal function of the immune system pursuant to Article 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2015.4096.
Grant et al., 2 Feb 2022, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
A Narrative Review of the Evidence for Variations in Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentration Thresholds for Optimal Health
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14030639
Vitamin D 3 has many important health benefits. Unfortunately, these benefits are not widely known among health care personnel and the general public. As a result, most of the world's population has serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) concentrations far below optimal values. This narrative review examines the evidence for the major causes of death including cardiovascular disease, hypertension, cancer, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and COVID-19 with regard to sub-optimal 25(OH)D concentrations. Evidence for the beneficial effects comes from a variety of approaches including ecological and observational studies, studies of mechanisms, and Mendelian randomization studies. Although randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are generally considered the strongest form of evidence for pharmaceutical drugs, the study designs and the conduct of RCTs performed for vitamin D have mostly been flawed for the following reasons: they have been based on vitamin D dose rather than on baseline and achieved 25(OH)D concentrations; they have involved participants with 25(OH)D concentrations above the population mean; they have given low vitamin D doses; and they have permitted other sources of vitamin D. Thus, the strongest evidence generally comes from the other types of studies. The general finding is that optimal 25(OH)D concentrations to support health and wellbeing are above 30 ng/mL (75 nmol/L) for cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality rate, whereas the thresholds for several other outcomes appear to range up to 40 or 50 ng/mL. The most efficient way to achieve these concentrations is through vitamin D supplementation. Although additional studies are warranted, raising serum 25(OH)D concentrations to optimal concentrations will result in a significant reduction in preventable illness and death.
References
Acharya, Dalia, Ranka, Sethi, Oni et al., The Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation and 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Levels on the Risk of Myocardial Infarction and Mortality, J. Endocr. Soc, doi:10.1210/jendso/bvab124
Afzal, Bojesen, Nordestgaard, Low 25-hydroxyvitamin D and risk of type 2 diabetes: A prospective cohort study and metaanalysis, Clin. Chem, doi:10.1373/clinchem.2012.193003
Alcala-Diaz, Limia-Perez, Gomez-Huelgas, Martin-Escalante, Cortez-Rodriguez et al., Calcifediol Treatment and Hospital Mortality Due to COVID-19: A Cohort Study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13061760
Andrukhova, Slavic, Zeitz, Riesen, Heppelmann et al., Vitamin D is a regulator of endothelial nitric oxide synthase and arterial stiffness in mice, Mol. Endocrinol
Autier, Mullie, Macacu, Dragomir, Boniol et al., Effect of vitamin D supplementation on non-skeletal disorders: A systematic review of meta-analyses and randomised trials, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30357-1
Borissova, Tankova, Kirilov, Dakovska, Kovacheva, The effect of vitamin D3 on insulin secretion and peripheral insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic patients, Int J. Clin. Pract
Boscoe, Schymura, Solar ultraviolet-B exposure and cancer incidence and mortality in the United States, 1993-2002, BMC Cancer, doi:10.1186/1471-2407-6-264
Boucher, Amin, No evidence that vitamin D is able to prevent or affect the severity of COVID-19 in individuals with European ancestry: A Mendelian randomisation study of open data, BMJ Nutr. Prev. Health, doi:10.1136/bmjnph-2021-000263
Boucher, Can Vitamin D Supplementation Reduce Insulin Resistance and Hence the Risks of Type 2 Diabetes?, J. Diabetes Clin. Res
Brouwer-Brolsma, Bischoff-Ferrari, Bouillon, Feskens, Gallagher et al., Do we get enough? A discussion between vitamin D experts in order to make a step towards the harmonisation of dietary reference intakes for vitamin D across Europe, Osteoporos Int
Butler-Laporte, Nakanishi, Mooser, Morrison, Abdullah et al., Vitamin D and COVID-19 susceptibility and severity in the COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative: A Mendelian randomization study, PLoS Med, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1003605
Cannell, Vieth, Umhau, Holick, Grant et al., Epidemic influenza and vitamin D, Epidemiol. Infect, doi:10.1017/S0950268806007175
Carlberg, Haq, The concept of the personal vitamin D response index, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol
Chai, Gao, Wu, Dong, Gu et al., Vitamin D deficiency as a risk factor for dementia and Alzheimer's disease: An updated meta-analysis, BMC Neurol, doi:10.1186/s12883-019-1500-6
Chen, Clements, Rahman, Zhang, Qiao et al., Relationship between cancer mortality/incidence and ambient ultraviolet B irradiance in China, Cancer Causes Control, doi:10.1007/s10552-010-9599-1
Cheng, So, Zhang, Cheng, Boucher et al., Calcitriol Reduces Hepatic Triglyceride Accumulation and Glucose Output Through Ca2+/CaMKKβ/AMPK Activation Under Insulin-Resistant Conditions in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Curr Mol. Med, doi:10.2174/1566524016666160920111407
Cherrie, Clemens, Colandrea, Feng, Webb et al., Ultraviolet A radiation and COVID-19 deaths in the USA with replication studies in England and Italy, Br. J. Dermatol, doi:10.1111/bjd.20093
Crowe, Steur, Allen, Appleby, Travis et al., Plasma concentrations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in meat eaters, fish eaters, vegetarians and vegans: Results from the EPIC-Oxford study, Public Health Nutr, doi:10.1017/S1368980010002454
Dai, Liu, Chen, Association of Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations with All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality Among Adult Patients with Existing Cardiovascular Disease, Front. Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.740855
Dawson-Hughes, Staten, Knowler, Nelson, Vickery et al., Intratrial Exposure to Vitamin D and New-Onset Diabetes Among Adults with Prediabetes: A Secondary Analysis From the Vitamin D and Type 2 Diabetes (D2d) Study, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-1765
De Pergola, Martino, Zupo, Caccavo, Pecorella et al., Hydroxyvitamin D Levels are Negatively and Independently Associated with Fat Mass in a Cohort of Healthy Overweight and Obese Subjects, Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets, doi:10.2174/1871530319666190122094039
De Sousa Almeida-Filho, De Luca, Vespoli, Pessoa, Machado et al., Vitamin D deficiency is associated with poor breast cancer prognostic features in postmenopausal women, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol
Dissanayake, Prognostic and therapeutic role of vitamin D in COVID-19: Systematic review and meta-analysis, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab892
Dursun, Gezen-Ak, Vitamin D basis of Alzheimer's disease: From genetics to biomarkers, Hormones
Entrenas-Castillo, Entrenas Costa, Vaquero Barrios, Alcala Diaz, Lopez Miranda et al., Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751
Evans, Lippman, Shining Light on the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Vitamin D Receptor Checkpoint in Defense of Unregulated Wound Healing, Cell Metab, doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.09.007
Fasching, Hein, Burghaus, Beckmann, Lambrechts et al., Association of vitamin D levels and risk of ovarian cancer: A Mendelian randomization study, Int. J. Epidemiol, doi:10.1093/ije/dyw207
Feart, Helmer, Merle, Herrmann, Annweiler et al., Associations of lower vitamin D concentrations with cognitive decline and long-term risk of dementia and Alzheimer's disease in older adults, Alzheimers Dement, doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2017.03.003
Ferrer-Mayorga, Larriba, Crespo, Munoz, Mechanisms of action of vitamin D in colon cancer, J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.07.002
Fioletov, Mcarthur, Mathews, Marrett, Estimated ultraviolet exposure levels for a sufficient vitamin D status in North America, J. Photochem. Photobiol. B, doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2010.05.002
Fleet, Desmet, Johnson, Li, Vitamin D and cancer: A review of molecular mechanisms, Biochem. J, doi:10.1042/BJ20110744
Forouhi, Luan, Cooper, Boucher, Wareham, Baseline serum 25-hydroxy vitamin d is predictive of future glycemic status and insulin resistance: The Medical Research Council Ely Prospective Study 1990-2000, Diabetes, doi:10.2337/db08-0593
Forouhi, Ye, Rickard, Khaw, Luben et al., Circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration and the risk of type 2 diabetes: Results from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer (EPIC)-Norfolk cohort and updated meta-analysis of prospective studies, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-012-2544-y
Gaksch, Jorde, Grimnes, Joakimsen, Schirmer et al., Vitamin D and mortality: Individual participant data meta-analysis of standardized 25-hydroxyvitamin D in 26916 individuals from a European consortium, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0170791
Garland, Garland, Do sunlight and vitamin D reduce the likelihood of colon cancer?, Int. J. Epidemiol, doi:10.1093/ije/9.3.227
Garland, Kim, Mohr, Gorham, Grant et al., Meta-analysis of all-cause mortality according to serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D, Am. J. Public Health, doi:10.2105/AJPH.2014.302034
Gezen-Ak, Atasoy, Candas, Alaylioglu, Yilmazer et al., Vitamin D Receptor Regulates Amyloid Beta 1-42 Production with Protein Disulfide Isomerase A3, ACS Chem. Neurosci, doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.7b00245
Gezen-Ak, Dursun, Molecular basis of vitamin D action in neurodegeneration: The story of a team perspective, Hormones, doi:10.1007/s42000-018-0087-4
Gianella, Hsia, Sakhaee, The role of vitamin D in sarcoidosis, Fac. Rev, doi:10.12703/b/9-14
Gonen, Alaylioglu, Durcan, Ozdemir, Sahin et al., Rapid and Effective Vitamin D Supplementation May Present Better Clinical Outcomes in COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) Patients by Altering Serum INOS1, IL1B, IFNg, Cathelicidin-LL37, and ICAM1, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13114047
Grant, 25-hydroxyvitamin D and breast cancer, colorectal cancer, and colorectal adenomas: Case-control versus nested case-control studies, Anticancer Res
Grant, An estimate of premature cancer mortality in the U.S. due to inadequate doses of solar ultraviolet-B radiation, Cancer, doi:10.1002/cncr.10427
Grant, Boucher, Bhattoa, Lahore, Why vitamin D clinical trials should be based on 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.08.009
Grant, Effect of follow-up time on the relation between prediagnostic serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and all-cause mortality rate, Dermatoendocrinology, doi:10.4161/derm.20514
Grant, Garland, The association of solar ultraviolet B (UVB) with reducing risk of cancer: Multifactorial ecologic analysis of geographic variation in age-adjusted cancer mortality rates, Anticancer Res
Grant, Giovannucci, The possible roles of solar ultraviolet-B radiation and vitamin D in reducing case-fatality rates from the 1918-1919 influenza pandemic in the United States, Dermatoendocrinology, doi:10.4161/derm.1.4.9063
Grant, Karras, Bischoff-Ferrari, Annweiler, Boucher et al., Do studies reporting 'U'-shaped serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D-health outcome relationships reflect adverse effects?, Dermatoendocrinology, doi:10.1080/19381980.2016.1187349
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, Franch et al., Evidence That Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12040988
Grant, Vitamin D Levels Affect Breast Cancer Survival Rates, Ann. Surg. Oncol, doi:10.1245/s10434-017-6159-x
Han, Guo, Yu, Liu, Cui et al., 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and Total Cancer Incidence and Mortality: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu11102295
Haq, Svobodova, Imran, Stanford, Razzaque, Vitamin D deficiency: A single centre analysis of patients from 136 countries, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.02.007
Hariyanto, Intan, Hananto, Harapan, Kaurniawan, Vitamin D supplementation and Covid-19 outcomes: A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression, Rev. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2269
Haykal, Samji, Zayed, Gakhal, Dhillon et al., The role of vitamin D supplementation for primary prevention of cancer: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, J. Community Hosp. Intern. Med. Perspect, doi:10.1080/20009666.2019.1701839
Heaney, Guidelines for optimizing design and analysis of clinical studies of nutrient effects, Nutr. Rev
Hernandez-Alonso, Boughanem, Canudas, Becerra-Tomas, Fernandez De La Puente et al., Circulating vitamin D levels and colorectal cancer risk: A meta-analysis and systematic review of case-control and prospective cohort studies, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr, doi:10.1080/10408398.2021.1939649
Hiller, O'sullivan, Brenner, Peters, King, Solar Ultraviolet Radiation and Breast Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Environ. Health Perspect, doi:10.1289/EHP4861
Holick, Binkley, Bischoff-Ferrari, Gordon, Hanley et al., Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: An Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1210/jc.2011-0385
Holick, Environmental factors that influence the cutaneous production of vitamin D, Am. J. Clin. Nutr
Jaaskelainen, Itkonen, Lundqvist, Erkkola, Koskela et al., The positive impact of general vitamin D food fortification policy on vitamin D status in a representative adult Finnish population: Evidence from an 11-y follow-up based on standardized 25-hydroxyvitamin D data, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.3945/ajcn.116.151415
Jayedi, Rashidy-Pour, Shab-Bidar, Vitamin D status and risk of dementia and Alzheimer's disease: A meta-analysis of dose-response (dagger), Nutr. Neurosci, doi:10.1080/1028415X.2018.1436639
Karonova, Stepanova, Bystrova, Jude, High-Dose Vitamin D Supplementation Improves Microcirculation and Reduces Inflammation in Diabetic Neuropathy Patients, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092518
Kaufman, Niles, Kroll, Bi, Holick, SARS-CoV-2 positivity rates associated with circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0239252
Kerner, Bruckel, German Diabetes, Definition, classification and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus, Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes, doi:10.1055/s-0034-1366278
Kimball, Mirhosseini, Holick, Evaluation of vitamin D3 intakes up to 15,000 international units/day and serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations up to 300 nmol/L on calcium metabolism in a community setting, Dermatoendocrinology, doi:10.1080/19381980.2017.1300213
Krishnan, Feldman, Mechanisms of the anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory actions of vitamin D, Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol, doi:10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010510-100611
Kunutsor, Apekey, Steur, Vitamin D and risk of future hypertension: Meta-analysis of 283,537 participants, Eur. J. Epidemiol, doi:10.1007/s10654-013-9790-2
Lappe, Travers-Gustafson, Davies, Recker, Heaney, Vitamin D and calcium supplementation reduces cancer risk: Results of a randomized trial, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/85.6.1586
Lappe, Watson, Travers-Gustafson, Recker, Garland et al., Effect of Vitamin D and Calcium Supplementation on Cancer Incidence in Older Women: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2017.2115
Leung, The Potential Protective Action of Vitamin D in Hepatic Insulin Resistance and Pancreatic Islet Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu8030147
Lewallen, Courtright, Epidemiology in practice: Case-control studies, Community Eye Health
Li, Tong, Rowland, Radcliff, Bare et al., Association of changes in lipid levels with changes in vitamin D levels in a real-world setting, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-01064-1
Li, Wu, Zhang, Huang, Thabane et al., Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Risk of Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, Front. Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.655727
Lips, De Jongh, Van Schoor, Trends in Vitamin D Status Around the World, JBMR Plus, doi:10.1002/jbm4.10585
Liu, Zhang, Xu, Li, Hu et al., The Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Vitamin D in Tumorigenesis, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms19092736
Lo, Nguyen, Drew, Warner, Joshi et al., Race, ethnicity, community-level socioeconomic factors, and risk of COVID-19 in the United States and the United Kingdom, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101029
Lucas, Rodney Harris, On the Nature of Evidence and 'Proving' Causality: Smoking and Lung Cancer vs. Sun Exposure, Vitamin D and Multiple Sclerosis, Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph15081726
Madden, Murphy, Zgaga, Bennett, De novo vitamin D supplement use post-diagnosis is associated with breast cancer survival, Breast Cancer Res. Treat, doi:10.1007/s10549-018-4896-6
Manson, Cook, Lee, Christen, Bassuk et al., Vitamin D Supplements and Prevention of Cancer and Cardiovascular Disease, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1809944
Marti-Soler, Gubelmann, Aeschbacher, Alves, Bobak et al., Seasonality of cardiovascular risk factors: An analysis including over 230,000 participants in 15 countries, Heart, doi:10.1136/heartjnl-2014-305623
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: Systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.i6583
Mccullough, Lehrer, Amend, Daily oral dosing of vitamin D3 using 5000 TO 50,000 international units a day in long-term hospitalized patients: Insights from a seven year experience, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.12.010
Mccullough, Zoltick, Weinstein, Fedirko, Wang et al., Circulating Vitamin D and Colorectal Cancer Risk: An International Pooling Project of 17 Cohorts, J. Natl. Cancer Inst, doi:10.1093/jnci/djy087
Mcdonnell, Baggerly, Baggerly, Aliano, French et al., Maternal 25(OH)D concentrations >/=40 ng/mL associated with 60% lower preterm birth risk among general obstetrical patients at an urban medical center, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0180483
Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French, Baggerly, Garland et al., Breast cancer risk markedly lower with serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations >/=60 vs. <20 ng/mL (150 vs. 50 nmol/L): Pooled analysis of two randomized trials and a prospective cohort, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0199265
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of Vitamin D Levels, Race/Ethnicity, and Clinical Characteristics With COVID-19 Test Results, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.4117
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of Vitamin D Status and Other Clinical Characteristics With COVID-19 Test Results, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722
Merzon, Tworowski, Gorohovski, Vinker, Golan Cohen et al., Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: An Israeli population-based study, FEBS J, doi:10.1111/febs.15495
Mirhosseini, Rainsbury, Kimball, Vitamin, Supplementation, Serum 25(OH)D Concentrations and Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Front. Cardiovasc. Med, doi:10.3389/fcvm.2018.00087
Mirhosseini, Vatanparast, Kimball, The Association between Serum 25(OH)D Status and Blood Pressure in Participants of a Community-Based Program Taking Vitamin D Supplements, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu9111244
Mokry, Ross, Ahmad, Forgetta, Smith et al., Vitamin D and Risk of Multiple Sclerosis: A Mendelian Randomization Study, PLoS Med
Montenegro, Cruzat, Carlessi, Newsholme, Mechanisms of vitamin D action in skeletal muscle, Nutr Res. Rev, doi:10.1017/S0954422419000064
Moukayed, Grant, Molecular link between vitamin D and cancer prevention, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu5103993
Moukayed, Grant, The roles of UVB and vitamin D in reducing risk of cancer incidence and mortality: A review of the epidemiology, clinical trials, and mechanisms, Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord, doi:10.1007/s11154-017-9415-2
Norman, Frankel, Heldt, Grodsky, Vitamin D deficiency inhibits pancreatic secretion of insulin, Science, doi:10.1126/science.6250216
Numerous, Vitamin, Biochemistry, Physiology and Diagnostics
Oh, Ansell, Nawaz, Yang, Wood et al., Global breast cancer seasonality, Breast Cancer Res. Treat, doi:10.1007/s10549-009-0676-7
Ong, Cuellar-Partida, Lu, Australian Ovarian Cancer Study
Ong, Dixon-Suen, Han, An, Cancer et al., A comprehensive re-assessment of the association between vitamin D and cancer susceptibility using Mendelian randomization, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-20368-w
Oristrell, Oliva, Casado, Subirana, Dominguez et al., Vitamin D supplementation and COVID-19 risk: A population-based, cohort study, J. Endocrinol. Invest, doi:10.1007/s40618-021-01639-9
Palomer, Gonzalez-Clemente, Blanco-Vaca, Mauricio, Role of vitamin D in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus, Diabetes Obes. Metab, doi:10.1111/j.1463-1326.2007.00710.x
Pilz, Marz, Cashman, Kiely, Whiting et al., Rationale and Plan for Vitamin D Food Fortification: A Review and Guidance Paper, Front. Endocrinol, doi:10.3389/fendo.2018.00373
Pittas, Dawson-Hughes, Sheehan, Ware, Knowler et al., Vitamin D Supplementation and Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1900906
Pludowski, Holick, Grant, Konstantynowicz, Mascarenhas et al., Vitamin D supplementation guidelines, Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.01.021
Priemel, Von Domarus, Klatte, Kessler, Schlie et al., Bone mineralization defects and vitamin D deficiency: Histomorphometric analysis of iliac crest bone biopsies and circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D in 675 patients, J. Bone Miner. Res, doi:10.1359/jbmr.090728
Radujkovic, Hippchen, Tiwari-Heckler, Dreher, Boxberger et al., Vitamin D Deficiency and Outcome of COVID-19 Patients, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092757
Rejnmark, Bislev, Cashman, Eiriksdottir, Gaksch et al., Non-skeletal health effects of vitamin D supplementation: A systematic review on findings from meta-analyses summarizing trial data, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0180512
Ross, Manson, Abrams, Aloia, Brannon et al., The 2011 report on dietary reference intakes for calcium and vitamin D from the Institute of Medicine: What clinicians need to know, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1210/jc.2010-2704
Scragg, Limitations of vitamin D supplementation trials: Why observational studies will continue to help determine the role of vitamin D in health, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.06.006
Scragg, Seasonality of cardiovascular disease mortality and the possible protective effect of ultra-violet radiation, Int. J. Epidemiol, doi:10.1093/ije/10.4.337
Seal, Bertenthal, Carey, Grunfeld, Bikle et al., Association of Vitamin D Status and COVID-19-Related Hospitalization and Mortality, J. Gen. Intern. Med, doi:10.1007/s11606-021-07170-0
Sergeev, Rhoten, 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 evokes oscillations of intracellular calcium in a pancreatic beta-cell line, Endocrinology, doi:10.1210/endo.136.7.7789310
Shirvani, Kalajian, Song, Allen, Charoenngam et al., Variable Genomic and Metabolomic Responses to Varying Doses of Vitamin D Supplementation, Anticancer. Res, doi:10.21873/anticanres.13982
Shirvani, Kalajian, Song, Holick, Disassociation of Vitamin D's Calcemic Activity and Non-calcemic Genomic Activity and Individual Responsiveness: A Randomized Controlled Double-Blind Clinical Trial, Sci. Rep
Shoelson, Herrero, Naaz, Obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.059
Smolders, Van Den Ouweland, Geven, Pickkers, Kox, Letter to the Editor: Vitamin D deficiency in COVID-19: Mixing up cause and consequence, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154434
Song, Deng, Liu, Zhou, Li et al., Vitamin D intake, blood vitamin D levels, and the risk of breast cancer: A dose-response meta-analysis of observational studies, Aging
Staley, Burgess, Semiparametric methods for estimation of a nonlinear exposure-outcome relationship using instrumental variables with application to Mendelian randomization, Genet. Epidemiol, doi:10.1002/gepi.22041
Szymczak-Pajor, Sliwinska, Analysis of Association between Vitamin D Deficiency and Insulin Resistance, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu11040794
Timms, Mannan, Hitman, Noonan, Mills et al., Circulating MMP9, vitamin D and variation in the TIMP-1 response with VDR genotype: Mechanisms for inflammatory damage in chronic disorders?, QJM, doi:10.1093/qjmed/95.12.787
Vasheghani, Jannati, Baghaei, Rezaei, Aliyari et al., The relationship between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and the severity of COVID-19 disease and its mortality, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-97017-9
Vimaleswaran, Cavadino, Berry, Jorde, Dieffenbach et al., Association of vitamin D status with arterial blood pressure and hypertension risk: A mendelian randomisation study, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(14)70113-5
Wang, Pencina, Booth, Jacques, Ingelsson et al., Vitamin D deficiency and risk of cardiovascular disease, Circulation, doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.706127
Wang, Qiao, Zhang, Zhang, Hua et al., Circulating Vitamin D Levels and Alzheimer's Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Study in the IGAP and UK Biobank, J. Alzheimers Dis, doi:10.3233/JAD-190713
Wang, Wang, Li, Chen, Han et al., Human Cathelicidin Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Killing Two Birds with One Stone, ACS Infect. Dis, doi:10.1021/acsinfecdis.1c00096
Weller, Wang, He, Maddux, Usvyat et al., Does Incident Solar Ultraviolet Radiation Lower Blood Pressure?, J. Am. Heart Assoc, doi:10.1161/JAHA.119.013837
Wise, Camara, Sempos, Lukas, Le Goff et al., Vitamin D Standardization Program (VDSP) intralaboratory study for the assessment of 25-hydroxyvitamin D assay variability and bias, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105917
Xia, Man, Li, Song, Jia et al., Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms modify the association of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with handgrip strength in the elderly in Northern China, Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2018.05.025
Yetley, Pfeiffer, Schleicher, Phinney, Lacher et al., NHANES monitoring of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D: A roundtable summary, J. Nutr
Zhang, Fang, Tang, Jia, Feng et al., Association between vitamin D supplementation and mortality: Systematic review and meta-analysis, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.l4673
Zhao, Chen, Pan, Gao, He et al., Comparative efficacy of vitamin D status in reducing the risk of bladder cancer: A systematic review and network meta-analysis, Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2015.10.023
Zhou, Chen, Sheng, Turner, The effect of vitamin D supplementation on the risk of breast cancer: A trial sequential meta-analysis, Breast Cancer Res. Treat, doi:10.1007/s10549-020-05669-4
Zhou, Selvanayagam, Hypponen, Non-linear Mendelian randomization analyses support a role for vitamin D deficiency in cardiovascular disease risk, Eur. Heart J, doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehab809
Zhou, Selvanayagam, Hyppönen, Non-linear Mendelian randomization analyses support a role for vitamin D deficiency in cardiovascular disease risk, Eur. Heart J, doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehab809
Zittermann, Iodice, Pilz, Grant, Bagnardi et al., Vitamin D deficiency and mortality risk in the general population: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.3945/ajcn.111.014779
Zittermann, Schleithoff, Koerfer, Putting cardiovascular disease and vitamin D insufficiency into perspective, Br. J. Nutr, doi:10.1079/BJN20051544
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14030639",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu14030639",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Vitamin D3 has many important health benefits. Unfortunately, these benefits are not widely known among health care personnel and the general public. As a result, most of the world’s population has serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) concentrations far below optimal values. This narrative review examines the evidence for the major causes of death including cardiovascular disease, hypertension, cancer, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and COVID-19 with regard to sub-optimal 25(OH)D concentrations. Evidence for the beneficial effects comes from a variety of approaches including ecological and observational studies, studies of mechanisms, and Mendelian randomization studies. Although randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are generally considered the strongest form of evidence for pharmaceutical drugs, the study designs and the conduct of RCTs performed for vitamin D have mostly been flawed for the following reasons: they have been based on vitamin D dose rather than on baseline and achieved 25(OH)D concentrations; they have involved participants with 25(OH)D concentrations above the population mean; they have given low vitamin D doses; and they have permitted other sources of vitamin D. Thus, the strongest evidence generally comes from the other types of studies. The general finding is that optimal 25(OH)D concentrations to support health and wellbeing are above 30 ng/mL (75 nmol/L) for cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality rate, whereas the thresholds for several other outcomes appear to range up to 40 or 50 ng/mL. The most efficient way to achieve these concentrations is through vitamin D supplementation. Although additional studies are warranted, raising serum 25(OH)D concentrations to optimal concentrations will result in a significant reduction in preventable illness and death.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu14030639"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1439-3285",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Grant",
"given": "William B.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1993-6656",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Al Anouti",
"given": "Fatme",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1206-7555",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Boucher",
"given": "Barbara J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3701-6674",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Dursun",
"given": "Erdinç",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7611-2111",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Gezen-Ak",
"given": "Duygu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3186-4122",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Jude",
"given": "Edward B.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1547-0123",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Karonova",
"given": "Tatiana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8475-7112",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Pludowski",
"given": "Pawel",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Nutrients"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-03T10:42:33Z",
"timestamp": 1643884953000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-03T11:26:24Z",
"timestamp": 1643887584000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-21T02:29:31Z",
"timestamp": 1647829771848
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 3,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "2072-6643"
}
],
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
2
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-02T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1643760000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/14/3/639/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "639",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
2
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jbm4.10585",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jendso/bvab124",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ije/10.4.337",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/heartjnl-2014-305623",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.706127",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1079/BJN20051544",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/qjmed/95.12.787",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-01064-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2021.740855",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00263-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4161/derm.20514",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/eurheartj/ehab809",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/gepi.22041",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10654-013-9790-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(14)70113-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu9111244",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ije/9.3.227",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2407-6-264",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"article-title": "The association of solar ultraviolet B (UVB) with reducing risk of cancer: Multifactorial ecologic analysis of geographic variation in age-adjusted cancer mortality rates",
"author": "Grant",
"first-page": "2687",
"journal-title": "Anticancer Res.",
"key": "ref19",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu5103993",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10552-010-9599-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2010.05.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1289/EHP4861",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2021.655727",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1003605",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref25"
},
{
"article-title": "25-hydroxyvitamin D and breast cancer, colorectal cancer, and colorectal adenomas: Case-control versus nested case-control studies",
"author": "Grant",
"first-page": "1153",
"journal-title": "Anticancer Res.",
"key": "ref26",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154434",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2015.10.023",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.102597",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2021.1939649",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/85.6.1586",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2017.2115",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0199265",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jnci/djy087",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/19381980.2016.1187349",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cncr.10427",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa1809944",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/20009666.2019.1701839",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11102295",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref39"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010510-100611",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref40"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BJ20110744",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref41"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11154-017-9415-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref42"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms19092736",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref43"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.07.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref44"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-019-53864-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref45"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21873/anticanres.13982",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref46"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/nure.12090",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref47"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.08.009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref48"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.12.011",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref49"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10549-020-05669-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref50"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-0034-1366278",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref51"
},
{
"DOI": "10.33696/diabetes.1.011",
"article-title": "Can Vitamin D Supplementation Reduce Insulin Resistance and Hence the Risks of Type 2 Diabetes?",
"author": "Boucher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Diabetes Clin. Res.",
"key": "ref52",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/endo.136.7.7789310",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref53"
},
{
"article-title": "The effect of vitamin D3 on insulin secretion and peripheral insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic patients",
"author": "Borissova",
"first-page": "258",
"journal-title": "Int J. Clin. Pract",
"key": "ref54",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.6250216",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref55"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1463-1326.2007.00710.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref56"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1566524016666160920111407",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref57"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu8030147",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref58"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0954422419000064",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref59"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11040794",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref60"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1871530319666190122094039",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref61"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.059",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref62"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1373/clinchem.2012.193003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref63"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/db08-0593",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref64"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-012-2544-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref65"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsinfecdis.1c00096",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref66"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcvm.2018.00087",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref67"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092518",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref68"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa1900906",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref69"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-1765",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref70"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref71"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.09.007",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref72"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4161/derm.1.4.9063",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref73"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref74"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0239252",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref75"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101029",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref76"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.15495",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref77"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref78"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.4117",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref79"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092757",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref80"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgab892",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref81"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11606-021-07170-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref82"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13114047",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref83"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref84"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13061760",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref85"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-97017-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref86"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2269",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref87"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40618-021-01639-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref88"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s42000-018-0086-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref89"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acschemneuro.7b00245",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref90"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s42000-018-0087-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref91"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jalz.2017.03.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref92"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/1028415X.2018.1436639",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref93"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12883-019-1500-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref94"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3233/JAD-190713",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref95"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.111.014779",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref96"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2105/AJPH.2014.302034",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref97"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0170791",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref98"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.l4673",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref99"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00198-012-2231-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref100"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105917",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref101"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2010-2704",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref102"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2011-0385",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref103"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1359/jbmr.090728",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref104"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.01.021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref105"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0180483",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref106"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/61.3.638S",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref107"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/19381980.2017.1300213",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref108"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.12.010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref109"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12703/b/9-14",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref110"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.116.151415",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref111"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2018.00373",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref112"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10549-018-4896-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref113"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph15081726",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref114"
},
{
"first-page": "1141",
"key": "ref115",
"series-title": "Vitamin D. Biochemistry, Physiology and Diagnostics",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0950268806007175",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref116"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/me.2013-1252",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref117"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/JAHA.119.013837",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref118"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bjd.20093",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref119"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1245/s10434-017-6159-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref120"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.10.009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref121"
},
{
"article-title": "Epidemiology in practice: Case-control studies",
"author": "Lewallen",
"first-page": "57",
"journal-title": "Community Eye Health",
"key": "ref122",
"volume": "11",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10549-009-0676-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref123"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.06.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref124"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/jn.110.121483",
"article-title": "NHANES monitoring of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D: A roundtable summary",
"author": "Yetley",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2030S",
"journal-title": "J. Nutr.",
"key": "ref125",
"volume": "140",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.02.007",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref126"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S1368980010002454",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref127"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30357-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref128"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0180512",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref129"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2018.05.025",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref130"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1001866",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref131"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ije/dyw207",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref132"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-20368-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref133"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjnph-2021-000263",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref134"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/eurheartj/ehab809",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref135"
}
],
"reference-count": 135,
"references-count": 135,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Nutrients"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Food Science",
"Nutrition and Dietetics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"A Narrative Review of the Evidence for Variations in Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentration Thresholds for Optimal Health"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "14"
}
