Rapid and Effective Vitamin D Supplementation May Present Better Clinical Outcomes in COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) Patients by Altering Serum INOS1, IL1B, IFNg, Cathelicidin-LL37, and ICAM1
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13114047, Nov 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 867 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Turkey, showing worse outcomes with vitamin D deficiency (without statistical significance); followed by a prospective study of 210 patients with vitamin D supplementation for those that were deficient, showing significantly lower mortality compared to the retrospective study without treatment.
This is the 103rd of 228 COVID-19 sufficiency studies for vitamin D, which collectively show higher levels reduce risk with p<0.0000000001.
|
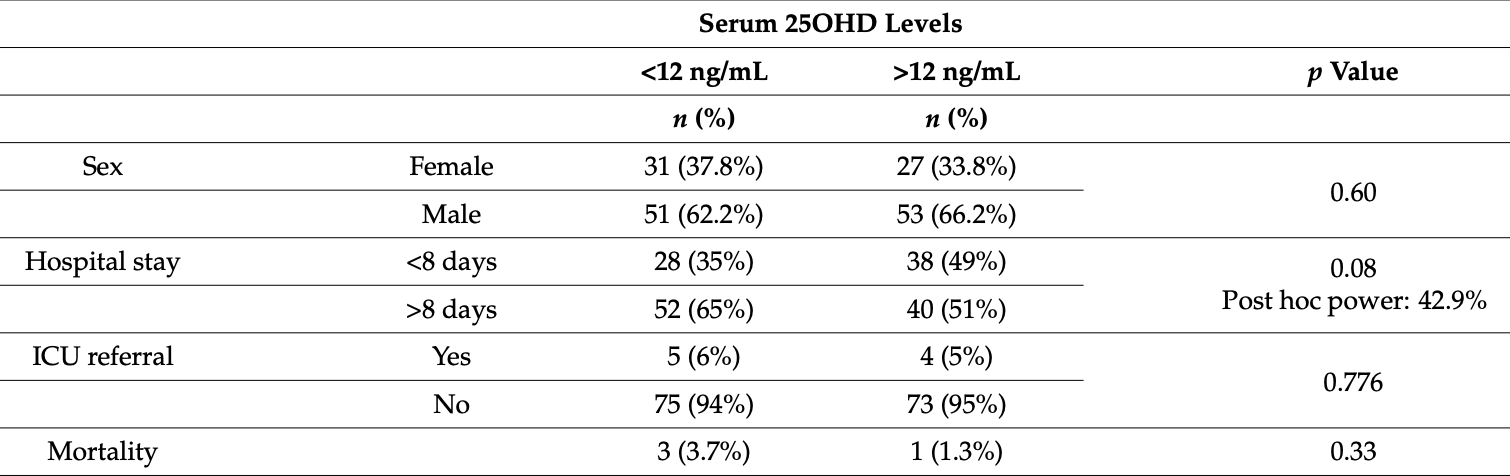
risk of death, 65.8% lower, RR 0.34, p = 0.62, high D levels (≥12ng/mL) 1 of 80 (1.2%), low D levels (<12ng/mL) 3 of 82 (3.7%), NNT 42, retrospective study.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 16.9% lower, RR 0.83, p = 1.00, high D levels (≥12ng/mL) 4 of 77 (5.2%), low D levels (<12ng/mL) 5 of 80 (6.2%), NNT 95, retrospective study.
|
|
hospital stay >8 days, 21.1% lower, RR 0.79, p = 0.11, high D levels (≥12ng/mL) 40 of 78 (51.3%), low D levels (<12ng/mL) 52 of 80 (65.0%), NNT 7.3, retrospective study.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Gönen et al., 12 Nov 2021, retrospective, Turkey, peer-reviewed, 20 authors, dosage varies.
Contact: karraspiros@yahoo.gr, duygugezenak@iuc.edu.tr, duygugezenak@gmail.com, erdinc.dursun@iuc.edu.tr, erdincdu@gmail.com.
Rapid and Effective Vitamin D Supplementation May Present Better Clinical Outcomes in COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) Patients by Altering Serum INOS1, IL1B, IFNg, Cathelicidin-LL37, and ICAM1
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13114047
Background: We aimed to establish an acute treatment protocol to increase serum vitamin D, evaluate the effectiveness of vitamin D3 supplementation, and reveal the potential mechanisms in COVID-19. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the data of 867 COVID-19 cases. Then, a prospective study was conducted, including 23 healthy individuals and 210 cases. A total of 163 cases had vitamin D supplementation, and 95 were followed for 14 days. Clinical outcomes, routine blood biomarkers, serum levels of vitamin D metabolism, and action mechanism-related parameters were evaluated. Results: Our treatment protocol increased the serum 25OHD levels significantly to above
Institutional Review Board Statement: The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by, and the study was approved by the Ethics Committee of ISTANBUL UNIVERSITY-CERRAHPASA, and the REPUBLIC OF TURKEY MINISTRY OF HEALTH (Approval Number: Mustafa Sait Gönen-2020-05-06T19_51_05). Informed Consent Statement: Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Conflicts of Interest: All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
Aceti, Margarucci, Scaramucci, Orsini, Salerno et al., Serum S100B protein as a marker of severity in COVID-19 patients, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-75618-0
Alipio, Vitamin D Supplementation Could Possibly Improve Clinical Outcomes of Patients Infected with Coronavirus
Alsafar, Grant, Hijazi, Uddin, Alkaabi et al., COVID-19 disease severity and death in relation to vitamin d status among SARS-CoV-2-positive uae residents, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13051714
Amrein, Schnedl, Holl, Riedl, Christopher et al., Effect of high-dose vitamin d3 on hospi-tal length of stay in critically ill patients with vitamin d deficiency: The vitdal-icu randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2014.13204
Andrukhova, Slavic, Zeitz, Riesen, Heppelmann et al., Vitamin d is a regulator of endothelial nitric oxide syn-thase and arterial stiffness in mice, Mol. Endocrinol, doi:10.1210/me.2013-1252
Annweiler, Dursun, Feron, Gezen-Ak, Kalueff et al., Vitamin d and cognition in older adults: Internation-al consensus guidelines, Geriatr. Psychol. Neuropsychiatr. Vieil, doi:10.1684/pnv.2016.0613
Aranow, Vitamin D and the Immune System, J. Investig. Med, doi:10.2310/JIM.0b013e31821b8755
Azevedo, Zanchettin, Vaz De Paula, Motta Junior, Malaquias et al., Lung neutro-philic recruitment and il-8/il-17a tissue expression in COVID-19, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.656350
Azizi-Soleiman, Vafa, Abiri, Safavi, Effects of iron on Vitamin D metabolism: A systematic review, Int. J. Prev. Med, doi:10.4103/2008-7802.195212
Bauer, Ulke, Galtung, Strasser-Marsik, Neuwinger et al., Role of Cell Adhesion Molecules for Prognosis of Disease Development of Patients with and Without COVID-19 in the Emergency Department, J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab042
Blanco-Rojo, Pérez-Granados, Toxqui, Zazo, De La Piedra et al., Relationship between vitamin D deficiency, bone remodelling and iron status in iron-deficient young women consuming an iron-fortified food, Eur. J. Nutr, doi:10.1007/s00394-012-0375-8
Bodnar, Krohn, Simhan, Maternal Vitamin D Deficiency Is Associated with Bacterial Vaginosis in the First Trimester of Pregnancy, J. Nutr, doi:10.3945/jn.108.103168
Cannell, Vieth, Umhau, Holick, Grant et al., Epidemic influenza and vitamin D, Epidemiol. Infect, doi:10.1017/S0950268806007175
Cao, Li, COVID-19: Towards understanding of pathogenesis, Cell Res, doi:10.1038/s41422-020-0327-4
Chen, Feng, Zhang, Wang, Identification of COVID-19 subtypes based on immunogenomic profiling, Int. Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107615
Corwin, Gettinger, Pearl, Fink, Levy et al., The CRIT Study: Anemia and blood transfusion in the critically ill-Current clinical practice in the United States *, Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1097/01.CCM.0000104112.34142.79
Durlak, How to Select, Calculate, and Interpret Effect Sizes, J. Pediatric Psychol, doi:10.1093/jpepsy/jsp004
Dursun, Alaylioglu, Bilgic, Hanagasi, Lohmann et al., Vitamin d deficiency might pose a greater risk for apo-evarepsilon4 non-carrier alzheimer's disease patients, Neurol. Sci, doi:10.1007/s10072-016-2647-1
Dursun, Gezen-Ak, Vitamin D basis of Alzheimer's disease: From genetics to biomarkers, Hormones, doi:10.1007/s42000-018-0086-5
Dursun, Gezen-Ak, Yilmazer, A new mechanism for amyloid-beta induction of inos: Vitamin d-vdr pathway disruption, J. Alzheimer's Dis, doi:10.3233/JAD-130416
Dursun, Gezen-Ak, Yilmazer, The influence of vitamin d treatment on the inducible nitric oxide synthase (inos) expression in primary hippocampal neurons, Noro. Psikiyatr. Ars, doi:10.4274/npa.y7089
Elham, Azam, Azam, Mostafa, Nasrin et al., Serum vitamin D, calcium, and zinc levels in patients with COVID-19, Clin. Nutr. ESPEN, doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040
Fernandes De Abreu, Eyles, Féron, Vitamin d, a neuro-immunomodulator: Implications for neurodegenerative and autoimmune diseases, Psychoneuroendocrinology, doi:10.1016/j.psyneuen.2009.05.023
Gezen-Ak, Alaylıo Glu, Genç, Şengül, Keskin et al., Altered Transcriptional Profile of Mitochondrial DNA-Encoded OXPHOS Subunits, Mitochondria Quality Control Genes, and Intracellular ATP Levels in Blood Samples of Patients with Parkinson's Disease, J. Alzheimer's Dis, doi:10.3233/JAD-191164
Gezen-Ak, Dursun, Molecular basis of vitamin D action in neurodegeneration: The story of a team perspective, Hormones, doi:10.1007/s42000-018-0087-4
Gezen-Ak, Yilmazer, Dursun, Why vitamin d in alzheimer's disease? The hypothesis, J. Alzheimers Dis
Golpour, Bereswill, Heimesaat, Antimicrobial and immune-modulatory effects of vitamin D provide promising antibiotics-independent approaches to tackle bacterial infections-lessons learnt from a literature survey, Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol, doi:10.1556/1886.2019.00014
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12040988
Hayden, Albert, Watkins, Swenson, Anemia in critical illness: Insights into etiology, consequences, and management, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1164/rccm.201110-1915CI
Heldenberg, Tenenbaum, Weisman, Effect of iron on serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and 24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D concentrations, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/56.3.533
Holick, Cancer, sunlight and vitamin D, J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/j.jcte.2014.10.001
Holick, Vitamin D: A D-lightful solution for good health, J. Med. Biochem, doi:10.2478/v10011-012-0031-z
Holick, Vitamin D: A millenium perspective, J. Cell. Biochem, doi:10.1002/jcb.10338
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in wuhan, china, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Joshi, Pantalena, Liu, Gaffen, Liu et al., 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin d(3) ameliorates th17 autoimmunity via transcriptional modulation of interleukin-17a, Mol. Cell Biol, doi:10.1128/MCB.05020-11
Kazemi, Mohammadi, Aghababaee, Golzarand, Clark et al., Association of vitamin d status with SARS-CoV-2 infection or COVID-19 severity: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Adv. Nutr, doi:10.1093/advances/nmab012
Kessel, Vollenberg, Masjosthusmann, Hinze, Wittkowski et al., Discrimination of COVID-19 from inflam-mation-induced cytokine storm syndromes by disease-related blood biomarkers, Arthritis Rheumatol, doi:10.1002/art.41763
Kumar, Rathi, Haq, Wimalawansa, Sharma, Putative roles of vitamin D in modulating immune response and immunopathology associated with COVID-19, Virus Res, doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198235
Lakkireddy, Gadiga, Malathi, Karra, Raju et al., Impact of daily high dose oral vitamin d therapy on the inflammatory markers in patients with COVID 19 disease, Sci. Rep
Li, Duan, Li, Li, Gao et al., Differentially expressed immune response genes in COVID-19 patients based on disease severity, Aging, doi:10.18632/aging.202877
Li, Huang, Shen, Wang, Wang et al., Serum Levels of Soluble Platelet Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule 1 in COVID-19 Patients Are Associated with Disease Severity, J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaa642
Lorente, Gómez-Bernal, Martín, Navarro-Gonzálvez, Argueso et al., High serum nitrates levels in non-survivor COVID-19 patients, Med. Intensiva, doi:10.1016/j.medin.2020.10.003
Mazziotti, Lavezzi, Brunetti, Mirani, Favacchio et al., Vitamin d deficiency, secondary hyperpara-thyroidism and respiratory insufficiency in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, J. Endocrinol. Investig, doi:10.1007/s40618-021-01535-2
Osman, Al Fahdi, Al Salmi, Al Khalili, Gokhale et al., Serum Calcium and Vitamin D levels: Correlation with severity of COVID-19 in hospitalized patients in Royal Hospital, Oman, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.04.050
Parekh, Patel, Scott, Lax, Dancer et al., Vitamin D Deficiency in Human and Murine Sepsis, Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000002095
Perrin, Collongues, Baloglu, Bedo, Bassand et al., Cytokine release syndrome-associated encephalo-pathy in patients with COVID-19, Eur. J. Neurol, doi:10.1111/ene.14491
Pizzini, Aichner, Sahanic, Bohm, Egger et al., Impact of vitamin d deficiency on COVID-19-a pro-spective analysis from the covild registry, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092775
Radujkovic, Hippchen, Tiwari-Heckler, Dreher, Boxberger et al., Vitamin D Deficiency and Outcome of COVID-19 Patients, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092757
Rodríguez, Daniels, Gunawardene, Robbins, High Frequency of Vitamin D Deficiency in Ambulatory HIV-Positive Patients, AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir, doi:10.1089/aid.2008.0183
Sanchez-Zuno, Gonzalez-Estevez, Matuz-Flores, Macedo-Ojeda, Hernandez-Bello et al., Vitamin d levels in COVID-19 outpatients from western mexico: Clinical correlation and effect of its supplementation, J. Clin. Med, doi:10.3390/jcm10112378
Santos, Natural history of COVID-19 and current knowledge on treatment therapeutic options, Biomed. Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110493
Smith, Jones, Han, Alvarez, Sloan et al., High-dose vitamin d3 administration is associated with increases in hemoglobin concentrations in mechanically ventilated critically ill adults: A pilot double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial, J. Parenter Enter. Nutr, doi:10.1177/0148607116678197
Spadaro, Fogagnolo, Campo, Zucchetti, Verri et al., Markers of endothelial and epithelial pulmonary injury in mechanically ventilated COVID-19 ICU patients, Crit. Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-021-03499-4
Villamor, A potential role for vitamin d on hiv infection?, Nutr. Rev, doi:10.1111/j.1753-4887.2006.tb00205.x
Vincent, Baron, Reinhart, Gattinoni, Thijs et al., For the ABC Investigators Anemia and Blood Transfusion in Critically Ill Patients, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.288.12.1499
Visweswaran, Lekha, Extraskeletal effects and manifestations of Vitamin D deficiency, Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.4103/2230-8210.113750
Wan, Yi, Fan, Lv, Zhang et al., Relationships among lymphocyte subsets, cytokines, and the pulmonary inflammation index in coronavirus (COVID-19) infected patients, Br. J. Haematol, doi:10.1111/bjh.16659
Wright, Blanco-Rojo, Fernández, Toxqui, Moreno et al., Bone remodelling is reduced by recovery from iron-deficiency anaemia in premenopausal women, J. Physiol. Biochem, doi:10.1007/s13105-013-0266-3
Yamasaki, Blood nitrate and nitrite modulating nitric oxide bioavailability: Potential therapeutic functions in COVID-19, Nitric Oxide, doi:10.1016/j.niox.2020.07.005
Yang, Liu, Wan, Zhonghua, Zhong et al., Role and mechanism of vitamin D in sepsis, Jiu Yi Xue
Yardan, Erenler, Baydin, Aydin, Cokluk, Usefulness of S100B protein in neurological disorders, J. Pak. Med. Assoc
Zawawi, Naser, Alwafi, Minshawi, Profile of Circulatory Cytokines and Chemokines in Human Coronaviruses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.666223
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13114047",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu13114047",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: We aimed to establish an acute treatment protocol to increase serum vitamin D, evaluate the effectiveness of vitamin D3 supplementation, and reveal the potential mechanisms in COVID-19. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the data of 867 COVID-19 cases. Then, a prospective study was conducted, including 23 healthy individuals and 210 cases. A total of 163 cases had vitamin D supplementation, and 95 were followed for 14 days. Clinical outcomes, routine blood biomarkers, serum levels of vitamin D metabolism, and action mechanism-related parameters were evaluated. Results: Our treatment protocol increased the serum 25OHD levels significantly to above 30 ng/mL within two weeks. COVID-19 cases (no comorbidities, no vitamin D treatment, 25OHD <30 ng/mL) had 1.9-fold increased risk of having hospitalization longer than 8 days compared with the cases with comorbidities and vitamin D treatment. Having vitamin D treatment decreased the mortality rate by 2.14 times. The correlation analysis of specific serum biomarkers with 25OHD indicated that the vitamin D action in COVID-19 might involve regulation of INOS1, IL1B, IFNg, cathelicidin-LL37, and ICAM1. Conclusions: Vitamin D treatment shortened hospital stay and decreased mortality in COVID-19 cases, even in the existence of comorbidities. Vitamin D supplementation is effective on various target parameters; therefore, it is essential for COVID-19 treatment.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu13114047"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1089-623X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Gönen",
"given": "Mustafa Sait",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alaylıoğlu",
"given": "Merve",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Durcan",
"given": "Emre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Özdemir",
"given": "Yusuf",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Şahin",
"given": "Serdar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Konukoğlu",
"given": "Dildar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8111-8072",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Nohut",
"given": "Okan Kadir",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ürkmez",
"given": "Seval",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Küçükece",
"given": "Berna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Balkan",
"given": "İlker İnanç",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7702-9731",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kara",
"given": "H. Volkan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0089-1312",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Börekçi",
"given": "Şermin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Özkaya",
"given": "Hande",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kutlubay",
"given": "Zekayi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dikmen",
"given": "Yalım",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Keskindemirci",
"given": "Yılmaz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4225-2746",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Karras",
"given": "Spyridon N.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7199-8109",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Annweiler",
"given": "Cedric",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gezen-Ak",
"given": "Duygu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3701-6674",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Dursun",
"given": "Erdinç",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-15T01:51:53Z",
"timestamp": 1636941113000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-15T02:09:10Z",
"timestamp": 1636942150000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"TSG-2020-34998"
],
"name": "Istanbul University Cerrahpaşa"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-26T23:09:23Z",
"timestamp": 1711494563507
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 45,
"issue": "11",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
12
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "11",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-12T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1636675200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/11/4047/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "4047",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
12
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bjh.16659",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-0327-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110493",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10072-016-2647-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcb.10338",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2478/v10011-012-0031-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcte.2014.10.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/2230-8210.113750",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s42000-018-0087-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3233/JAD-131970",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1684/pnv.2016.0613",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s42000-018-0086-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2310/JIM.0b013e31821b8755",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0950268806007175",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/jn.108.103168",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1753-4887.2006.tb00205.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/aid.2008.0183",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/MCB.05020-11",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.psyneuen.2009.05.023",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1556/1886.2019.00014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198235",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/2008-7802.195212",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00394-012-0375-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/56.3.533",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13105-013-0266-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.201110-1915CI",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref27"
},
{
"article-title": "Role and mechanism of vitamin D in sepsis",
"author": "Yang",
"first-page": "1170",
"journal-title": "Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue",
"key": "ref28",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0000000000002095",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref29"
},
{
"author": "Alipio",
"key": "ref30",
"series-title": "Vitamin D Supplementation Could Possibly Improve Clinical Outcomes of Patients Infected with Coronavirus-2019 (COVID-2019)",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092757",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13051714",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/advances/nmab012",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm10112378",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jpepsy/jsp004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3233/JAD-191164",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/01.CCM.0000104112.34142.79",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.288.12.1499",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2014.13204",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref39"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0148607116678197",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref40"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092775",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref41"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40618-021-01535-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref42"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref43"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.04.050",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref44"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref45"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.656350",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref46"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.202877",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref47"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.666223",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref48"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-90189-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref49"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/art.41763",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref50"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107615",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref51"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.07.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref52"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3233/JAD-130416",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref53"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4274/npa.y7089",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref54"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/me.2013-1252",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref55"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medin.2020.10.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref56"
},
{
"article-title": "Usefulness of S100B protein in neurological disorders",
"author": "Yardan",
"first-page": "276",
"journal-title": "J. Pak. Med. Assoc.",
"key": "ref57",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ene.14491",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref58"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-75618-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref59"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiab042",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref60"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiaa642",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref61"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-021-03499-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref62"
}
],
"reference-count": 62,
"references-count": 62,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/11/4047"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Food Science",
"Nutrition and Dietetics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Rapid and Effective Vitamin D Supplementation May Present Better Clinical Outcomes in COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) Patients by Altering Serum INOS1, IL1B, IFNg, Cathelicidin-LL37, and ICAM1",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "13"
}
