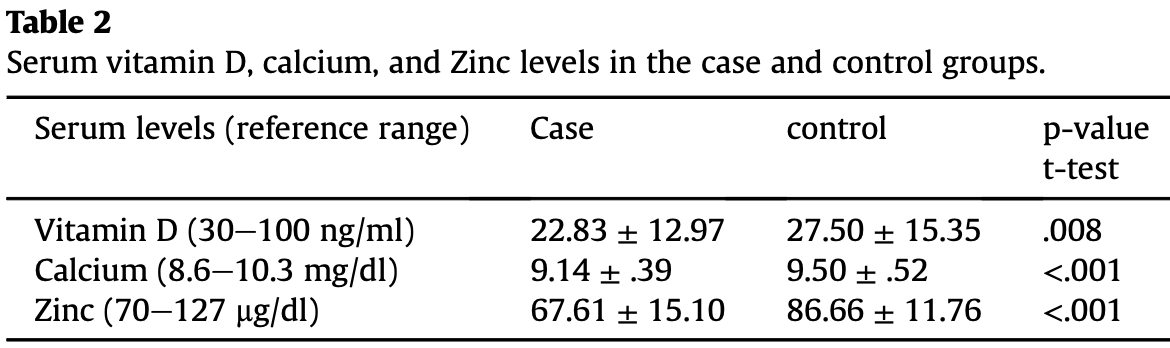
Serum vitamin D, calcium, and zinc levels in patients with COVID-19
et al., Clinical Nutrition ESPEN, doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040, Apr 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Case control study with 93 hospitalized patients in Iran and 186 control patients, showing significantly lower vitamin D, zinc, and calcium levels in cases. IR.SHOUSHTAR.REC.1399.017.
Study covers vitamin D and zinc.
Elham et al., 18 Apr 2021, retrospective, case control, Iran, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
Serum vitamin D, calcium, and zinc levels in patients with COVID-19
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN, doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040
Background and aim: COVID-19 is a global public health concern. As no standard treatment has been found for it yet, several minerals and vitamins with antioxidants, immunomodulators, and antimicrobials roles can be sufficient for the immune response against the disease. The present study evaluates the serum vitamin D, calcium, and Zinc levels in patients with COVID-19. Materials & methods: This research is a caseecontrol study performed in May 2020 on 93 patients with COVID-19 hospitalized in a Shoushtar city hospital and on 186 healthy subjects with no symptoms of COVID-19. The serum vitamin D, calcium, and zinc levels were collected and analyzed using correlation coefficient and independent t-test via SPSS 18. Results: Vitamin D levels had a significant difference between the case and control groups (p ¼ 0.008). Serum calcium and serum zinc levels also had statistically significant differences between the two groups (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: The research results showed that serum zinc, calcium, and vitamin D levels in COVID-19 patients are lower than in the control group. The supplementation with such nutrients is a safe and low-cost measure that can help cope with the increased demand for these nutrients in risk of acquiring the COVID-19 virus.
References
Bailey, Gahche, Lentino, Dwyer, Engel et al., Dietary supplement use in the United States, 2003e2006, J Nutr
Banajeh, Nutritional rickets and vitamin D deficiencydassociation with the outcomes of childhood very severe pneumonia: a prospective cohort study, Pediatr Pulmonol
Bhutta, Black, Brown, Gardner, Gore et al., Prevention of diarrhea and pneumonia by zinc supplementation in children in developing countries: pooled analysis of randomized controlled trials, J Pediatr
Bikle, What is new in vitamin D: 2006e2007, Curr Opin Rheumatol
Cakman, Kirchner, Rink, Zinc supplementation reconstitutes the production of interferon-a by leukocytes from elderly persons, J Interferon Cytokine Res
Camargo, Ganmaa, Frazier, Kirchberg, Stuart et al., Randomized trial of vitamin D supplementation and risk of acute respiratory infection in Mongolia, Pediatrics
Chausmer, Zinc, insulin and diabetes, J Am Coll Nutr
Christianto, Smarandache, Umniyati, A review of major role of vitamin D3 in human immune system and its possible use for novel corona virus treatment, Jurnal Penelitian Fisika dan Aplikasinya
Constantin, Dose-response effects of viral exposure in COVID-19
El-Kurdi, Khatua, Rood, Snozek, Cartin-Ceba et al., Mortality from COVID-19 increases with unsaturated fat, and may be reduced by early calcium and albumin supplementation, Gastroenterology
Foster, Samman, Zinc and regulation of inflammatory cytokines: implications for cardiometabolic disease, Nutrients
Foster, Samman, Zinc and regulation of inflammatory cytokines: implications for cardiometabolic disease, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu4070676PMID:22852057
Gombart, Pierre, Maggini, A review of micronutrients and the immune SystemeWorking in harmony to reduce the risk of infection, Nutrients
Gralinski, Menachery, Return of the coronavirus: 2019-nCoV, Viruses
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients
Gray, Lowe, Lester, Vitamin D and pregnancy: the maternal-fetal metabolism of vitamin D, Endocr Rev
Griffin, Xing, Kumar, Vitamin D and its analogs as regulators of immune activation and antigen presentation, Annu Rev Nutr
Habibian, Khoshdel, Kheiri, Torabi, The effect of zinc sulphate syrup on children's respiratory tract infections, J Babol Univ Med Sci
Hosseininejad, Kalbasi, Afshar, Vitamin D and childhood pneumonia, Razi J Med Sci
Jovic, Ali, Ibrahim, Jessop, Tarassoli et al., Could vitamins help in the fight against COVID-19?, Nutrients
Khemka, Suri, Singh, Bansal, Role of vitamin D supplementation in prevention and treatment of COVID-19, Indian J Clin Biochem
Lai, Shih, Ko, Tang, Hsueh, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and corona virus disease-2019 (COVID-19): the epidemic and the challenges, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Mahmoudian, Poya, Effects of zinc and, Tehran Univ Med J
Mocchegiani, Muzzioli, Therapeutic application of zinc in human immunodeficiency virus against opportunistic infections, J Nutr
Moukayed, Grant, Molecular link between vitamin D and cancer prevention, Nutrients
Note, PLATELET(PLT), LYMPHO-CYTE(Lym), neutrophils(Neut), Arterial Blood Gas Test(PH,PO2,PCO2, HCO3), Erythrocyte sedimentation rate(ESR)
Prasad, Fitzgerald, Bao, Beck, Chandrasekar, Duration of symptoms and plasma cytokine levels in patients with the common cold treated with zinc acetate: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, Ann Intern Med
Razzaque, COVID-19 pandemic: can maintaining optimal zinc balance enhance host resistance?, Tohoku J Exp Med
Saeedi, Rezvanfar, Hadidi, Mahani, Ahmadlou, The effect of active VitaminD on treatment of proteinuria in patients with diabetic nephropathy without vitamin D deficiency, J Arak Univ Med Sci
Sahni, Gupta, Rana, Prasad, Bhalla, Intake of antioxidants and their status in chronic kidney disease patients, J Ren Nutr
Salek, Rafati, Hashemipour, Memar, Nezhadnik et al., Is vitamin D deficiency prevalent in healthy 6-yearold children in Isfahan City
Shakoor, Feehan, Dhaheri, Ali, Platat et al., Immuneboosting role of vitamins D, C, E, zinc, selenium and omega-3 fatty acids: could they help against COVID-19?, Maturitas
Somi, Rezaeifar, Rahimi, Moshrefi, Effects of low dose zinc supplementation on biochemical markers in non-alcoholic cirrhosis: a randomized clinical trial, Arch Iran Med
Souza, Vasconcelos, Prado, Pereira, Zinc, vitamin D and vitamin C: perspectives for COVID-19 with a focus on physical tissue barrier integrity, Front Nutr
Sun, Zhang, Zou, Liu, Li et al., Serum calcium as a biomarker of clinical severity and prognosis in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: a retrospective cross-sectional study, Jun
Tavakoli, Vahdat, Keshavarz, Novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): an emerging infectious disease in the 21st century, ISMJ
Van Etten, Mathieu, Immunoregulation by 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3: basic concepts, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol
Wang, Chen, Wang, Fan, Pan et al., Synthesis of novel nanomaterials and their application in efficient removal of radionuclides, Sci China Chem
Weir, Thenappan, Bhargava, Chen, Does vitamin D deficiency increase the severity of COVID-19?, Clin Med
Wessels, Rolles, Rink, The potential impact of Zinc supplementation on COVID-19 pathogenesis, Front Immunol
Zisi, Challa, Makis, The association between vitamin D status and infectious diseases of the respiratory system in infancy and childhood, Hormones
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040",
"ISSN": [
"2405-4577"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040",
"alternative-id": [
"S2405457721001431"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Serum vitamin D, calcium, and zinc levels in patients with COVID-19"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Clinical Nutrition ESPEN"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2021 European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elham",
"given": "Abdolahi Shahvali",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Azam",
"given": "Khalighi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Azam",
"given": "Jahangirimehr",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mostafa",
"given": "Labibzadeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nasrin",
"given": "Bahmanyari",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marzieh",
"given": "Najafi",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical Nutrition ESPEN",
"container-title-short": "Clinical Nutrition ESPEN",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com",
"clinicalnutritionespen.com",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.fr",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-19T13:30:11Z",
"timestamp": 1618839011000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-20T19:47:23Z",
"timestamp": 1621540043000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-14T12:29:30Z",
"timestamp": 1678796970348
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 31,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1622505600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2405457721001431?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2405457721001431?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "276-282",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Immune-boosting role of vitamins D, C, E, zinc, selenium and omega-3 fatty acids: could they help against COVID-19?",
"author": "Shakoor",
"journal-title": "Maturitas",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v12020135",
"article-title": "Return of the coronavirus: 2019-nCoV",
"author": "Gralinski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "135",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib2",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105924",
"article-title": "Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and corona virus disease-2019 (COVID-19): the epidemic and the challenges",
"author": "Lai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105924",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): an emerging infectious disease in the 21st century",
"author": "Tavakoli",
"first-page": "432",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "ISMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib4",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Constantin",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib5",
"series-title": "Dose-response effects of viral exposure in COVID-19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11426-019-9492-4",
"article-title": "Synthesis of novel nanomaterials and their application in efficient removal of radionuclides",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "933",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Sci China Chem",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib6",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12010236",
"article-title": "A review of micronutrients and the immune System–Working in harmony to reduce the risk of infection",
"author": "Gombart",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "236",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib7",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092550",
"article-title": "Could vitamins help in the fight against COVID-19?",
"author": "Jovic",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2550",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib8",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Zinc, vitamin D and vitamin C: perspectives for COVID-19 with a focus on physical tissue barrier integrity",
"author": "Souza",
"first-page": "295",
"journal-title": "Front Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib9",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/BOR.0b013e32818e9d58",
"article-title": "What is new in vitamin D: 2006–2007",
"author": "Bikle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "383",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Rheumatol",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib10",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/edrv-2-3-264",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and pregnancy: the maternal-fetal metabolism of vitamin D",
"author": "Gray",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "264",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Endocr Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib11",
"volume": "2",
"year": "1981"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s42000-019-00155-z",
"article-title": "The association between vitamin D status and infectious diseases of the respiratory system in infancy and childhood",
"author": "Zisi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "353",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Hormones",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib12",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2005.06.002",
"article-title": "Immunoregulation by 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3: basic concepts",
"author": "van Etten",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "93",
"issue": "1–2",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib13",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev.nutr.23.011702.073114",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and its analogs as regulators of immune activation and antigen presentation",
"author": "Griffin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "117",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Annu Rev Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib14",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu5103993",
"article-title": "Molecular link between vitamin D and cancer prevention",
"author": "Moukayed",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3993",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib15",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "A review of major role of vitamin D3 in human immune system and its possible use for novel corona virus treatment",
"author": "Christianto",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Jurnal Penelitian Fisika dan Aplikasinya (JPFA)",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib16",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"article-title": "Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths",
"author": "Grant",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "988",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib17",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Dietary supplement use in the United States, 2003–2006",
"author": "Bailey",
"first-page": "261",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib18",
"volume": "141",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"article-title": "Serum calcium as a biomarker of clinical severity and prognosis in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: a retrospective cross-sectional study",
"author": "Sun",
"first-page": "11287",
"issue": "12",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib19",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu4070676",
"article-title": "Zinc and regulation of inflammatory cytokines: implications for cardiometabolic disease",
"author": "Foster",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "676",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib20",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"article-title": "The effect of zinc sulphate syrup on children's respiratory tract infections",
"author": "Habibian",
"first-page": "22",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Babol Univ Med Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib21",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0022-3476(99)70086-7",
"article-title": "Prevention of diarrhea and pneumonia by zinc supplementation in children in developing countries: pooled analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Bhutta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "689",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Pediatr",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib22",
"volume": "135",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-133-4-200008150-00006",
"article-title": "Duration of symptoms and plasma cytokine levels in patients with the common cold treated with zinc acetate: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Prasad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "245",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib23",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/jir.1997.17.469",
"article-title": "Zinc supplementation reconstitutes the production of interferon-α by leukocytes from elderly persons",
"author": "Cakman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "469",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "J Interferon Cytokine Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib24",
"volume": "17",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"article-title": "Therapeutic application of zinc in human immunodeficiency virus against opportunistic infections",
"author": "Mocchegiani",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib25",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"article-title": "The potential impact of Zinc supplementation on COVID-19 pathogenesis",
"author": "Wessels",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Effects of zinc and",
"author": "Mahmoudian",
"first-page": "29",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Tehran Univ Med J",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib27",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1542/peds.2011-3029",
"article-title": "Randomized trial of vitamin D supplementation and risk of acute respiratory infection in Mongolia",
"author": "Camargo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e561",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Pediatrics",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib28",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"article-title": "Role of vitamin D supplementation in prevention and treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Khemka",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Indian J Clin Biochem",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib29",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7861/clinmed.2020-0301",
"article-title": "Does vitamin D deficiency increase the severity of COVID-19?",
"author": "Weir",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e107",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Clin Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib30",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.057",
"article-title": "Mortality from COVID-19 increases with unsaturated fat, and may be reduced by early calcium and albumin supplementation",
"author": "El-Kurdi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1015",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib31",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1620/tjem.251.175",
"article-title": "COVID-19 pandemic: can maintaining optimal zinc balance enhance host resistance?",
"author": "Razzaque",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "175",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Tohoku J Exp Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib32",
"volume": "251",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu4070676",
"article-title": "Zinc and regulation of inflammatory cytokines: implications for cardiometabolic disease",
"author": "Foster",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "676",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib33",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D and childhood pneumonia",
"author": "Hosseininejad",
"first-page": "109",
"issue": "140",
"journal-title": "Razi J Med Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib34",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "Is vitamin D deficiency prevalent in healthy 6-yearold children in Isfahan City?",
"author": "Salek",
"first-page": "95",
"issue": "85",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib35",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ppul.21121",
"article-title": "Nutritional rickets and vitamin D deficiency—association with the outcomes of childhood very severe pneumonia: a prospective cohort study",
"author": "Banajeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1207",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Pediatr Pulmonol",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib36",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07315724.1998.10718735",
"article-title": "Zinc, insulin and diabetes",
"author": "Chausmer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "109",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Am Coll Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib37",
"volume": "17",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"article-title": "The effect of active VitaminD on treatment of proteinuria in patients with diabetic nephropathy without vitamin D deficiency",
"author": "Saeedi",
"first-page": "57",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Arak Univ Med Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib38",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "Effects of low dose zinc supplementation on biochemical markers in non-alcoholic cirrhosis: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Somi",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Arch Iran Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib39",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"article-title": "Intake of antioxidants and their status in chronic kidney disease patients",
"author": "Sahni",
"first-page": "389",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Ren Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040_bib40",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2012"
}
],
"reference-count": 40,
"references-count": 40,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2405457721001431"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Nutrition and Dietetics",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Serum vitamin D, calcium, and zinc levels in patients with COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "43"
}
