Treatment with 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (calcifediol) is associated with a reduction in the blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio marker of disease severity in patients hospitalized with COVID-19: a pilot, multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled double blind clinical trial
et al., Endocrine Practice, doi:10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016, Oct 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
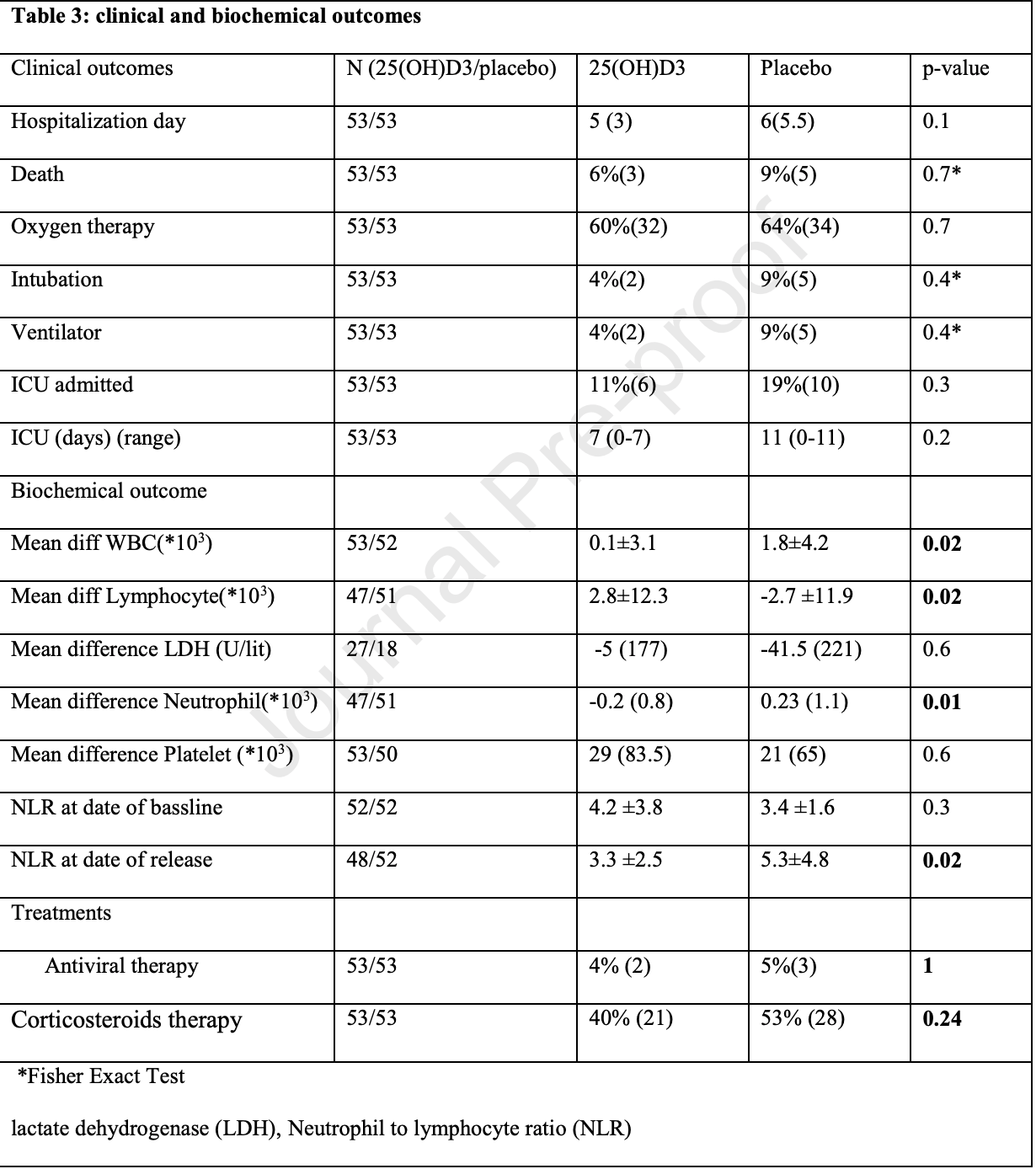
RCT 106 hospitalized patients with vitamin D levels <30ng/ml in Iran, 53 treated with calcifediol, showing that treatment was able to correct vitamin D deficiency/insufficiency, resulting in improved immune system function. Hospitalization, ICU duration, ventilation, and mortality was lower with treatment, without reaching statistical significance with the small sample size. The dosage used in this trial was much lower than other trials.
Although the 40% lower mortality is not statistically significant, it is consistent with the significant 39% lower mortality [32‑45%] from meta-analysis of the 79 mortality results to date.
Meta-analysis shows that late stage treatment with calcitriol / calcifediol (or
paricalcitol, alfacalcidol, etc.) is more effective than cholecalciferol: 66% [47‑78%] lower risk vs. 45% [34‑54%] lower risk.
Cholecalciferol requires two hydroxylation steps to become activated - first
in the liver to calcifediol, then in the kidney to calcitriol. Calcitriol,
paricalcitol, and alfacalcidol are active vitamin D analogs that do not
require conversion. This allows them to have more rapid onset of action
compared to cholecalciferol. The time delay for cholecalciferol to increase
serum calcifediol levels can be 2-3 days, and the delay for converting
calcifediol to active calcitriol can be up to 7 days.
This is the 8th of 40 COVID-19 RCTs for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0000001.
This is the 56th of 135 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p<0.0000000001.
|
risk of death, 40.0% lower, RR 0.60, p = 0.72, treatment 3 of 53 (5.7%), control 5 of 53 (9.4%), NNT 26.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 60.0% lower, RR 0.40, p = 0.44, treatment 2 of 53 (3.8%), control 5 of 53 (9.4%), NNT 18.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 40.0% lower, RR 0.60, p = 0.42, treatment 6 of 53 (11.3%), control 10 of 53 (18.9%), NNT 13.
|
|
ICU time, 36.4% lower, relative time 0.64, p = 0.20, treatment 53, control 53.
|
|
hospitalization time, 16.7% lower, relative time 0.83, p = 0.10, treatment 53, control 53.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Maghbooli et al., 13 Oct 2021, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, Iran, peer-reviewed, 12 authors, dosage calcifediol 25μg daily, mean daily dose.
Treatment With 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 (Calcifediol) Is Associated With a Reduction in the Blood Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Marker of Disease Severity in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: A Pilot Multicenter, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blinded Clinical Trial
Endocrine Practice, doi:10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016
Since January 2020 Elsevier has created a COVID-19 resource centre with free information in English and Mandarin on the novel coronavirus COVID-19. The COVID-19 resource centre is hosted on Elsevier Connect, the company's public news and information website. Elsevier hereby grants permission to make all its COVID-19-related research that is available on the COVID-19 resource centre -including this research content -immediately available in PubMed Central and other publicly funded repositories, such as the WHO COVID database with rights for unrestricted research re-use and analyses in any form or by any means with acknowledgement of the original source. These permissions are granted for free by Elsevier for as long as the COVID-19 resource centre remains active. Treatment with 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (calcifediol) is associated with a reduction in the blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio marker of disease severity in patients hospitalized with COVID-19: a pilot, multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled double blind clinical trial
J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f
J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f
Declaration of interests ☐ The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. ☒The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: The authors declare the following personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Michael F. Holick was a consultant for Quest Diagnostics Inc. is a consultant for Ontometrics Inc and Biogena Inc., received a grant from Carbogen Amcis BV and was on the speaker's Bureau for Abbott Inc. The remaining authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
Alcala-Diaz, Limia-Perez, Gomez-Huelgas, Calcifediol Treatment and Hospital Mortality Due to COVID-19: A Cohort Study, Nutrients
Annweiler, Hanotte, De L'eprevier, Sabatier, Lafaie et al., None
Barger-Lux, Heaney, Dowell, Chen, Holick, Vitamin D and its Major Metabolites: Serum Levels after Graded Oral Dosing in Healthy Men, Osteoporosis International
Biancuzzo, Clarke, Reitz, Travison, Holick, Serum concentrations of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D2 and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in response to vitamin D2 and vitamin D3 supplementation, The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism
Bischoff-Ferrari, Hughes, Stöcklin, Oral supplementation with 25(OH)D3 versus vitamin D3: effects on 25(OH)D levels, lower extremity function, blood pressure, and markers of innate immunity. Journal of bone and mineral research : the official journal of the American, Society for Bone and Mineral Research
Borges, Pithon-Curi, Curi, Hatanaka, COVID-19 and neutrophils: The relationship between hyperinflammation and neutrophil extracellular traps, Mediators of Inflammation
Bouillon, Marcocci, Carmeliet, Skeletal and Extraskeletal Actions of Vitamin D: Current Evidence and Outstanding Questions, Endocrine reviews
Castillo, Costa, Barrios, Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study, The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology
Cesareo, Falchetti, Attanasio, Tabacco, Naciu et al., Hypovitaminosis D: Is It Time to Consider the Use of Calcifediol?, Nutrients
Cesareo, Falchetti, Attanasio, Tabacco, Naciu et al., None
Charoenngam, Holick, Immunologic Effects of Vitamin D on Human Health and Disease, Nutrients
Charoenngam, Kalajian, Shirvani, A pilot-randomized, double-blind crossover trial to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of orally administered 25
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, The lancet
Denman, Lymphocyte function and virus infections, Journal of clinical pathology Supplement (Royal College of Pathologists)
Fa, Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and lymphocyte-to-Creactive protein ratio in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a metaanalysis, Journal of medical virology
Goncalves-Mendes, Talvas, Dualé, Impact of Vitamin D Supplementation on Influenza Vaccine Response and Immune Functions in Deficient Elderly Persons: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial, Frontiers in immunology
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients
Guan, Liang, Zhao, Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with COVID-19 in China: a nationwide analysis, The European respiratory journal
Hewison, Vitamin D and the immune system: new perspectives on an old theme. Endocrinology and metabolism clinics of North America
Holick, Binkley, Bischoff-Ferrari, Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline, The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism
Hossein-Nezhad, Holick, Vitamin D for health: a global perspective, Mayo Clinic proceedings
Huang, Berube, Mcnamara, Lymphocyte Subset Counts in COVID-19
Hypovitaminosis, Is It Time to Consider the Use of Calcifediol?, Nutrients
Kaufman, Niles, Kroll, Bi, Holick, SARS-CoV-2 positivity rates associated with circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels, PloS one
Lippi, Plebani, Procalcitonin in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A meta-analysis, Clinica chimica acta; international journal of clinical chemistry
Maghbooli, Omidifar, Varzandi, Salehnezhad, Sahraian, Reduction in circulating vitamin D binding protein in patients with multiple sclerosis, BMC neurology
Maghbooli, Sahraian, Ebrahimi, Vitamin D sufficiency, a serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D at least 30 ng/mL reduced risk for adverse clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infection, PloS one
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ (Clinical research ed
Mccullough, Lehrer, Amend, expressed as the mean ± SD for parametric tests or median (IRQ) for non-parametric tests and categorical variables were presented as percentages. N=available data for each variable Albumin (Alb), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), Body mass index (BMI), calcium (Ca), creatinine (Cr), creatine phosphokinase (CPK), C-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), bicarbonate (HCO3), potassium (K), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
Misra, Agarwal, Gasparyan, Zimba, Rheumatologists' perspective on coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) and potential therapeutic targets, Clinical rheumatology
Murai, Fernandes, Sales, Effect of a Single High Dose of Vitamin D3 on Hospital Length of Stay in Patients With Moderate to Severe COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, Jama
Navarro-Valverde, Sosa-Henríquez, Alhambra-Expósito, Quesada-Gómez, None
Nogues, Ovejero, Pineda-Moncusí, Calcifediol treatment and COVID-19-related outcomes, The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism
Pereira, Damascena, Azevedo, De Almeida Oliveira, Da et al., Vitamin D deficiency aggravates COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis, Critical reviews in food science and nutrition
Quesada-Gomez, Bouillon, Is calcifediol better than cholecalciferol for vitamin D supplementation? Osteoporosis international : a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA
Sosa Henríquez, De, Romero, Cholecalciferol or Calcifediol in the Management of Vitamin D Deficiency, Nutrients
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Jama
Xu, Shi, Wang, Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome, The Lancet respiratory medicine
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016",
"ISSN": [
"1530-891X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016",
"alternative-id": [
"S1530891X21012593"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Treatment With 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 (Calcifediol) Is Associated With a Reduction in the Blood Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Marker of Disease Severity in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: A Pilot Multicenter, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blinded Clinical Trial"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Endocrine Practice"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to the associated document",
"name": "associatedlink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eprac.2021.10.001"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2021 AACE. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maghbooli",
"given": "Zhila",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sahraian",
"given": "Mohammad Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jamalimoghadamsiahkali",
"given": "Saeidreza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Asadi",
"given": "Asma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zarei",
"given": "Azadeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zendehdel",
"given": "Abolfazl",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Varzandi",
"given": "Tarlan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mohammadnabi",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alijani",
"given": "Neda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karimi",
"given": "Mehrdad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shirvani",
"given": "Arash",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holick",
"given": "Michael F.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Endocrine Practice",
"container-title-short": "Endocrine Practice",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"aacejournalendocrinepractice.org",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-14T07:26:06Z",
"timestamp": 1634196366000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-08T18:47:15Z",
"timestamp": 1638989235000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004484",
"award": [
"47095-235-1-99"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Tehran University of Medical Sciences"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-02T15:00:07Z",
"timestamp": 1712070007160
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 53,
"issue": "12",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "12",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1638316800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1530891X21012593?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1530891X21012593?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1242-1251",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cca.2020.03.004",
"article-title": "Procalcitonin in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis",
"author": "Lippi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "190",
"journal-title": "Clin Chim Acta",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib2",
"volume": "505",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.00547-2020",
"article-title": "Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with COVID-19 in China: a nationwide analysis",
"author": "Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2000547",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib3",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data",
"author": "Martineau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "i6583",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib4",
"volume": "356",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0239799",
"article-title": "Vitamin D sufficiency, a serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D at least 30 ng/mL reduced risk for adverse clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infection",
"author": "Maghbooli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "PloS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib5",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0239252",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 positivity rates associated with circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels",
"author": "Kaufman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "PloS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib6",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency aggravates COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Pereira",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.26848",
"article-title": "Effect of a single high dose of vitamin D3 on hospital length of stay in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Murai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1053",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib8",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751",
"article-title": "Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: a pilot randomized clinical study",
"author": "Entrenas Castillo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105751",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib9",
"volume": "203",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"article-title": "Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths",
"author": "Grant",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "988",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib10",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2019.00065",
"article-title": "Impact of vitamin D supplementation on influenza vaccine response and immune functions in deficient elderly persons: a randomized placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Goncalves-Mendes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "65",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib11",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10067-020-05073-9",
"article-title": "Rheumatologists’ perspective on coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) and potential therapeutic targets",
"author": "Misra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2055",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Clin Rheumatol",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib12",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2011-0385",
"article-title": "Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline",
"author": "Holick",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1911",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib13",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00198-018-4520-y",
"article-title": "Is calcifediol better than cholecalciferol for vitamin D supplementation?",
"author": "Quesada-Gomez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1697",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Osteoporos Int",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib14",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2012-2114",
"article-title": "Serum concentrations of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D2 and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in response to vitamin D2 and vitamin D3 supplementation",
"author": "Biancuzzo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "973",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib15",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jbmr.551",
"article-title": "Oral supplementation with 25(OH)D3 versus vitamin D3: effects on 25(OH)D levels, lower extremity function, blood pressure, and markers of innate immunity",
"author": "Bischoff-Ferrari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "160",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Bone Miner Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib16",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11051016",
"article-title": "Hypovitaminosis D: is it time to consider the use of calcifediol?",
"author": "Cesareo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1016",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib17",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/er.2018-00126",
"article-title": "Skeletal and extraskeletal actions of vitamin D: current evidence and outstanding questions",
"author": "Bouillon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1109",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Endocr Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib18",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2013.05.011",
"article-title": "Vitamin D for health: a global perspective",
"author": "Hossein-Nezhad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "720",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Mayo Clin Proc",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib19",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12883-021-02200-0",
"article-title": "Reduction in circulating vitamin D binding protein in patients with multiple sclerosis",
"author": "Maghbooli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "168",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Neurol",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib20",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12072097",
"article-title": "Immunologic effects of vitamin D on human health and disease",
"author": "Charoenngam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2097",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib21",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12061617",
"article-title": "Cholecalciferol or calcifediol in the management of vitamin D deficiency",
"author": "Sosa Henríquez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1617",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib22",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.01.014",
"article-title": "Vitamin D3 and calcidiol are not equipotent",
"author": "Navarro-Valverde",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "205",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib23",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s001980050058",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and its major metabolites: serum levels after graded oral dosing in healthy men",
"author": "Barger-Lux",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "222",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Osteoporos Int",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib24",
"volume": "8",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/nqab123",
"article-title": "A pilot-randomized, double-blind crossover trial to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of orally administered 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 and vitamin D3 in healthy adults with differing BMI and in adults with intestinal malabsorption",
"author": "Charoenngam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1189",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib25",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ecl.2010.02.010",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and the immune system: new perspectives on an old theme",
"author": "Hewison",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "365",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib26",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/jcp.s3-13.1.39",
"article-title": "Lymphocyte function and virus infections",
"author": "Denman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "39",
"journal-title": "J Clin Pathol Suppl (R Coll Pathol)",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib27",
"volume": "13",
"year": "1979"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cyto.a.24172",
"article-title": "Lymphocyte subset counts in COVID-19 patients: a meta-analysis",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "772",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Cytometry A",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib28",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2020/8829674",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and neutrophils: the relationship between hyperinflammation and neutrophil extracellular traps",
"author": "Borges",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8829674",
"journal-title": "Mediators Inflamm",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib29",
"volume": "2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25819",
"article-title": "Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and lymphocyte-to-C-reactive protein ratio in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis",
"author": "Lagunas-Rangel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1733",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib30",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13061760",
"article-title": "Calcifediol treatment and hospital mortality due to COVID-19: a cohort study",
"author": "Alcala-Diaz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1760",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib31",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgab405",
"article-title": "Calcifediol treatment and COVID-19-related outcomes",
"author": "Nogues",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e4017",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib32",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105771",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and survival in COVID-19 patients: a quasi-experimental study",
"author": "Annweiler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105771",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib33",
"volume": "204",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"article-title": "Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "507",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib34",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"article-title": "Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1239",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib35",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-X",
"article-title": "Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "420",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib36",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.12.010",
"article-title": "Daily oral dosing of vitamin D3 using 5000 to 50,000 international units a day in long-term hospitalized patients: insights from a seven year experience",
"author": "McCullough",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "228",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016_bib37",
"volume": "189",
"year": "2019"
}
],
"reference-count": 36,
"references-count": 36,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1530891X21012593"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Endocrinology",
"General Medicine",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Treatment With 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 (Calcifediol) Is Associated With a Reduction in the Blood Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Marker of Disease Severity in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: A Pilot Multicenter, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blinded Clinical Trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "27"
}
