COVID-19 Mortality Risk Correlates Inversely with Vitamin D3 Status, and a Mortality Rate Close to Zero Could Theoretically Be Achieved at 50 ng/mL 25(OH)D3: Results of a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13103596, Sep 2021 (preprint)
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
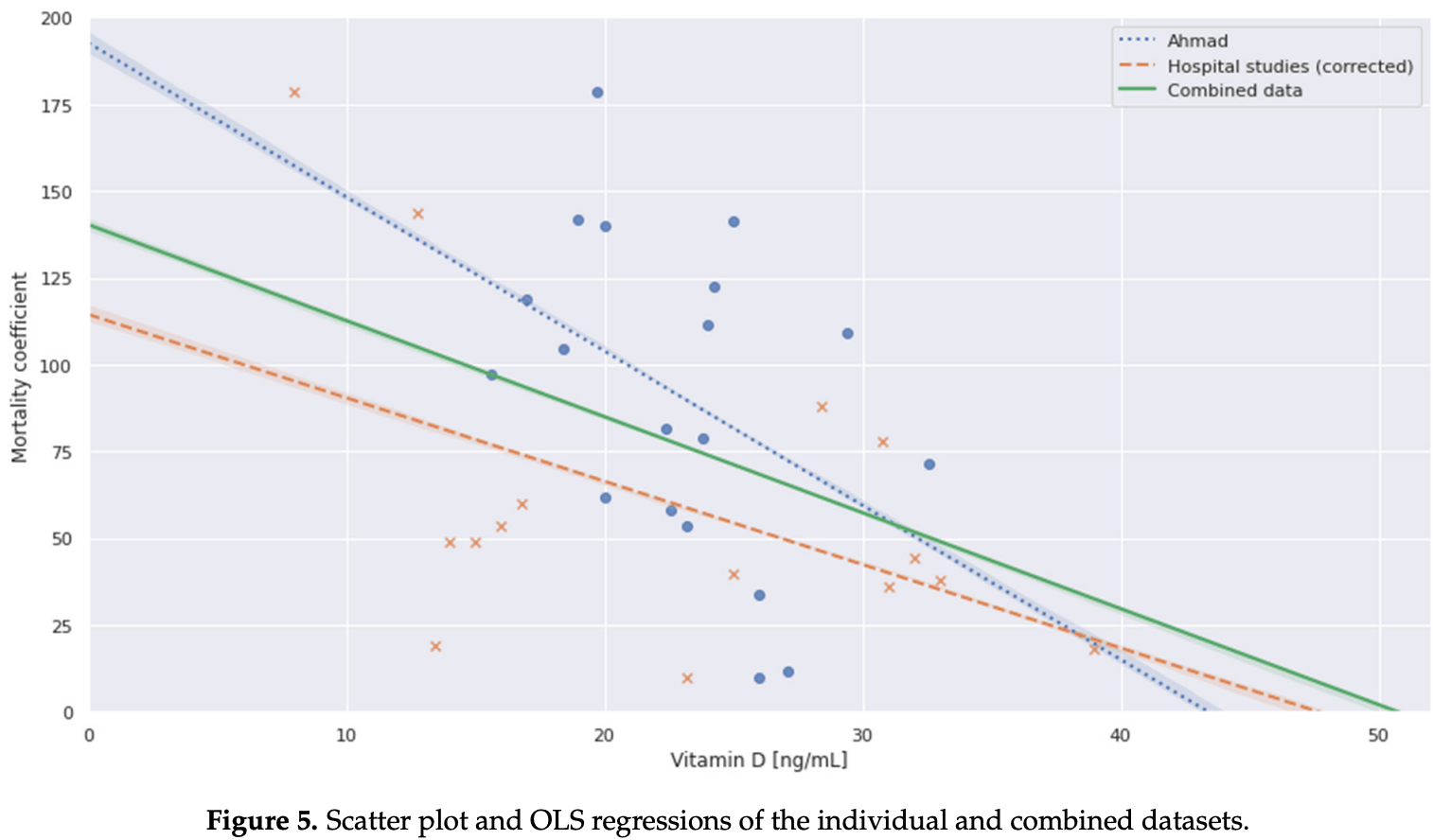
Meta analysis of 8 studies with vitamin D levels measured pre-infection or on the day of hospital admission, showing a correlation between the levels and mortality. Authors recommend combining vaccination with vitamin D supplementation to maintain levels above 50 ng/ml. Authors extrapolate to predict a point of zero mortality, however there is no reason to predict a linear relationship where zero mortality would be reached.
20 meta-analyses show significant improvements with vitamin D treatment for mortality1-14,
mechanical ventilation1,5,6,11,15-17 ,
ICU admission1,3,5,6,9,11,13,15-19 ,
hospitalization11,
severity2,4,5,10,20 , and
cases7,19,20 .
Currently there are 135 vitamin D treatment for COVID-19 studies, showing 39% lower mortality [32‑45%], 17% lower ventilation [-5‑35%], 45% lower ICU admission [28‑57%], 22% lower hospitalization [13‑30%], and 17% fewer cases [9‑25%].
1.
Shah et al., Does vitamin D supplementation reduce COVID-19 severity? - a systematic review, QJM: An International Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcac040.
2.
Nikniaz et al., The impact of vitamin D supplementation on mortality rate and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.34172/PS.2021.13.
3.
Hosseini et al., Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation on COVID-19 Related Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14102134.
4.
D’Ecclesiis et al., Vitamin D and SARS-CoV2 infection, severity and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0268396.
5.
Xie et al., Micronutrient perspective on COVID-19: Umbrella review and reanalysis of meta-analyses, Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, doi:10.1080/10408398.2023.2174948.
6.
Hariyanto et al., Vitamin D supplementation and Covid‐19 outcomes: A systematic review, meta‐analysis and meta‐regression, Reviews in Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/rmv.2269.
7.
Begum et al., The Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19 Survival and Prevention: A Meta-analysis, Sudan Journal of Medical Sciences, doi:10.18502/sjms.v19i1.15776.
8.
Jamilian et al., The role of vitamin D in outcomes of critical care in COVID-19 patients: Evidence from an umbrella meta-analysis of interventional and observational studies, Public Health Nutrition, doi:10.1017/S1368980024000934.
9.
Sobczak et al., Effect of Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Severe COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16101402.
10.
Petrelli et al., Therapeutic and prognostic role of vitamin D for COVID-19 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 43 observational studies, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105883.
11.
Asla et al., Vitamin D on COVID-19 Patients During the Pandemic, 2022. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Current Research in Nutrition and Food Science Journal, doi:10.12944/CRNFSJ.11.1.3.
12.
Kow et al., The impact of vitamin D administration on mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-024-01564-2.
13.
Zhang et al., The impact of supplementing vitamin D through different methods on the prognosis of COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1441847.
14.
Doustmohammadian et al., Impact of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19 mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Nutrition Clinique et Métabolisme, doi:10.1016/j.nupar.2025.12.001.
15.
Meng et al., The role of vitamin D in the prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Clinical Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2023.09.008.
16.
Yang et al., Therapeutic effects of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19 aggravation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1367686.
17.
Szarpak et al., Vitamin D supplementation to treat SARS-CoV-2 positive patients. Evidence from meta-analysis, Cardiology Journal, doi:10.5603/CJ.a2021.0122.
18.
Tentolouris et al., The effect of vitamin D supplementation on mortality and intensive care unit admission of COVID-19 patients. A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression, Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews, doi:10.1002/dmrr.3517.
Borsche et al., 25 Sep 2021, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
COVID-19 Mortality Risk Correlates Inversely with Vitamin D3 Status, and a Mortality Rate Close to Zero Could Theoretically Be Achieved at 50 ng/mL 25(OH)D3: Results of a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13103596
Risk Correlates Inversely with Vitamin D3 Status, and a Mortality Rate Close to Zero Could Theoretically Be Achieved at 50 ng/mL 25(OH)D3: Results of a Systematic Review and
References
Abhimanyu, Coussens, The role of UV radiation and vitamin D in the seasonality and outcomes of infectious disease, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci, doi:10.1039/C6PP00355A
Abrishami, Dalili, Torbati, Asgari, Arab-Ahmadi et al., Possible association of vitamin D status with lung involvement and outcome in patients with COVID-19: A retrospective study, Eur. J. Nutr, doi:10.1007/s00394-020-02411-0
Adams, Hewison, Unexpected actions of vitamin D: New perspectives on the regulation of innate and adaptive immunity, Nat. Clin. Pract. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1038/ncpendmet0716
Adams, Hewison, Update in vitamin D, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1210/jc.2009-1773
Afshar, Ghaffaripour, Sajjadi, Suggested Role of Vitamin D Supplementation in COVID-19 Severity
Agrawal, Yin, Vitamin D and inflammatory diseases, J. Inflamm Res, doi:10.2147/JIR.S63898
Ahmad, Heumann, Ali, Oliver, Mean Vitamin D levels in 19 European Countries & COVID-19 Mortality over 10 months, Cold Spring Harb. Lab, doi:10.1101/2021.03.11.21253361
Amrein, Scherkl, Hoffmann, Neuwersch-Sommeregger, Köstenberger et al., Vitamin D deficiency 2.0: An update on the current status worldwide, Eur. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1038/s41430-020-0558-y
Angelidi, Belanger, Lorinsky, Karamanis, Chamorro-Pareja et al., Vitamin D Status is Associated With In-hospital Mortality and Mechanical Ventilation: A Cohort of COVID-19 Hospitalized Patients, Mayo Clin. Proc, doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001
Annweiler, Cao, Sabatier, Point of view: Should COVID-19 patients be supplemented with vitamin D?, Maturitas, doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2020.06.003
Annweiler, Corvaisier, Gautier, Dubée, Legrand et al., Vitamin D Supplementation Associated to Better Survival in Hospitalized Frail Elderly COVID-19 Patients: The GERIA-COVID Quasi-Experimental Study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113377
Annweiler, Hanotte, De L'eprevier, Sabatier, Lafaie et al., Vitamin D and survival in COVID-19 patients: A quasi-experimental study, J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105771
Antico, Tampoia, Tozzoli, Bizzaro, Can supplementation with vitamin D reduce the risk or modify the course of autoimmune diseases? A systematic review of the literature, Autoimmun. Rev, doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2012.07.007
Antonelli, Kushner, Low Serum Levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D Accompany Severe COVID-19 because it is a Negative Acute Phase Reactant, Am. J. Med. Sci
Autier, Boniol, Pizot, Mullie, Vitamin D status and ill health: A systematic review, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(13)70165-7
Aygun, Vitamin D can prevent COVID-19 infection-induced multiple organ damage, Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol, doi:10.1007/s00210-020-01911-4
Baeke, Takiishi, Korf, Gysemans, Mathieu et al., Modulator of the immune system, Curr. Opin. Pharm, doi:10.1016/j.coph.2010.04.001
Barlow, Findlay, Currie, Davidson, Antiviral potential of cathelicidins, Future Microbiol, doi:10.2217/fmb.13.135
Battault, Whiting, Peltier, Sadrin, Gerber et al., Vitamin D metabolism, functions and needs: From science to health claims, Eur. J. Nutr, doi:10.1007/s00394-012-0430-5
Beard, Bearden, Striker, Vitamin D and the anti-viral state, J. Clin. Virol, doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2010.12.006
Bennouar, Cherif, Kessira, Bennouar, Abdi, Vitamin D Deficiency and Low Serum Calcium as Predictors of Poor Prognosis in Patients with Severe COVID, J. Am. Coll. Nutr, doi:10.1080/07315724.2020.1856013
Benskin, A Basic Review of the Preliminary Evidence That COVID-19 Risk and Severity Is Increased in Vitamin D Deficiency, Front. Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2020.00513
Berridge, Vitamin D deficiency and diabetes, Biochem. J, doi:10.1042/BCJ20170042
Berry, Hesketh, Power, Hyppönen, Vitamin D status has a linear association with seasonal infections and lung function in British adults, Br. J. Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114511001991
Biesalski, Vitamin D deficiency and co-morbidities in COVID-19 patients-A fatal relationship?, NFLs J, doi:10.1016/j.nfs.2020.06.001
Birhane, Bressler, Chang, Clark, Dorough et al., COVID-19 Vaccine Breakthrough Infections Reported to CDC-United States, MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly Rep, doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7021e3
Bishop, Ismailova, Dimeloe, Hewison, White, Vitamin D and Immune Regulation: Antibacterial, Antiviral, Anti-Inflammatory, JBMR Plus, doi:10.1002/jbm4.10405
Boonstra, Barrat, Crain, Heath, Savelkoul et al., 25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 has a direct effect on naive CD4+ T cells to enhance the development of Th2 cells, J. Immunol. Am. Assoc. Immnol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.167.9.4974
Braun, Chang, Mahadevappa, Gibbons, Liu et al., Association of low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and mortality in the critically ill, Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e318206ccdf
Brown, Vostok, Johnson, Burns, Gharpure et al., Outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 Infections, Including COVID-19
Butt, Nafady-Hego, Chemaitelly, Abou-Samra, Khal Aal Coyle, Outcomes Among Patients with Breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 Infection After Vaccination, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.008
Cantorna, Mahon, D-hormone and the immune system, J. Rheumatol. Suppl
Carlberg, Vitamin D Signaling in the Context of Innate Immunity: Focus on Human Monocytes, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.02211
Carpagnano, Lecce Vdi Quaranta, Zito, Buonamico, Capozza, Vitamin D deficiency as a predictor of poor prognosis in patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID, J. Endocrinol. Investig, doi:10.1007/s40618-020-01370-x
Castillo, Costa, Barrios, Díaz, Miranda et al., Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study, J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751
Chambers, Hawrylowicz, The Impact of Vitamin D on Regulatory T Cells, Curr. Allergy Asthma. Rep, doi:10.1007/s11882-010-0161-8
Charoenngam, Holick, Immunologic Effects of Vitamin D on Human Health and Disease, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12072097
Charoenngam, Shirvani, Reddy, Vodopivec, Apovian et al., Association of Vitamin D Status With Hospital Morbidity and Mortality in Adult Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients With COVID, Endocr. Pract
Christakos, Hewison, Gardner, Wagner, Sergeev et al., Beyond bone, Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1111/nyas.12129
Chun, Liu, Modlin, Adams, Hewison, Impact of vitamin D on immune function: Lessons learned from genome-wide analysis, Front. Physiol, doi:10.3389/fphys.2014.00151
Crafa, Cannarella, Condorelli, Mongioì, Barbagallo et al., Influence of 25-hydroxy-cholecalciferol levels on SARS-CoV-2 infection~and COVID-19 severity: A systematic review and meta-analysis, EClinicalMedicine
D'avolio, Avataneo, Manca, Cusato, Nicolò Ade Lucchini, 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations Are Lower in Patients with Positive PCR for SARS-CoV, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12051359
Dancer, Parekh, Lax, D'souza, Zheng et al., Vitamin D deficiency contributes directly to the acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), Thorax BMJ, doi:10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-206680
Daneshkhah, Agrawal, Eshein, Subramanian, Roy et al., Evidence for possible association of vitamin D status with cytokine storm and unregulated inflammation in COVID-19 patients, Aging Clin. Exp. Res
Dawood, Mutated COVID-19 may foretell a great risk for mankind in the future, New Microbes New Infect. Elsevier BV, doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2020.100673
De Borst, Vervloet, Ter Wee, Navis, Cross Talk Between the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System and Vitamin D-FGF-23-klotho in Chronic Kidney Disease: Figure, J. Am. Soc. Nephrol, doi:10.1681/ASN.2010121251
De Haan, Groeneveld, De Geus, Egal, Struijs, Vitamin D deficiency as a risk factor for infection, sepsis and mortality in the critically ill: Systematic review and meta-analysis, Crit. Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-014-0660-4
Deluca, History of the discovery of vitamin D and its active metabolites, Bonekey Rep, doi:10.1038/bonekey.2013.213
Denison, Graham, Donaldson, Eckerle, Baric et al., None, RNA Biol. Inf. UK Ltd
Dong, Du, Gardner, An interactive web-based dashboard to track COVID-19 in real time, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30120-1
Feldman, Krishnan, Swami, Giovannucci, Feldman, The role of vitamin D in reducing cancer risk and progression, Nat. Rev. Cancer, doi:10.1038/nrc3691
Fgunville, Mmourani, Aginde, The role of vitamin D in prevention and treatment of infection, Inflamm. Allergy-Drug Targets, doi:10.2174/18715281113129990046
Forrest, Stuhldreher, Prevalence and correlates of vitamin D deficiency in US adults, Nutr. Res, doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2010.12.001
Gavioli, Miyashita, Hassaneen, Siau, An Evaluation of Serum 25-Hydroxy Vitamin D Levels in Patients with COVID-19 in New York City, J. Am. Coll. Nutr, doi:10.1080/07315724.2020.1869626
Getachew, Tizabi, Vitamin D and COVID-19: Role of ACE2, age, gender, and ethnicity, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27075
Giménez, Inserra, Ferder, García, Manucha, Vitamin D deficiency in African Americans is associated with a high risk of severe disease and mortality by SARS-CoV, J Hum Hypertens. Springer Sci. Bus. Media LLC, doi:10.1038/s41371-020-00398-z
Giménez, Inserra, Tajer, Mariani, Ferder et al., Lungs as target of COVID-19 infection: Protective common molecular mechanisms of vitamin D and melatonin as a new potential synergistic treatment, Life Sci
Gloth, Vitamin D Deficiency in Homebound Elderly Persons, JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc, doi:10.1001/jama.1995.03530210037027
Gombart, Borregaard, Koeffler, Human cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) gene is a direct target of the vitamin D receptor and is strongly up-regulated in myeloid cells by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D, FASEB J, doi:10.1096/fj.04-3284com
Goodall, Granados, Luinstra, Pullenayegum, Coleman et al., Vitamin D3 and gargling for the prevention of upper respiratory tract infections: A randomized controlled trial, BMC Infect. Dis, doi:10.1186/1471-2334-14-273
Grant, Anouti Fal Moukayed, Targeted 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration measurements and vitamin D3 supplementation can have important patient and public health benefits, Eur. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1038/s41430-020-0564-0
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12040988
Greiller, Martineau, Modulation of the Immune Response to Respiratory Viruses by Vitamin D, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu7064240
Gruber Bzura, Vitamin D and Influenza-Prevention or Therapy?, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms19082419
Haddaway, Mcguinness, PRISMA2020: R package and ShinyApp for producing PRISMA 2020 compliant flow diagrams (Version 0.0.1), Zenodo, doi:10.5281/zenodo.4287835
Han, Jones, Tangpricha, Brown, Hao et al., High dose vitamin D administration in ventilated intensive care unit patients: A pilot double blind randomized controlled trial, J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/j.jcte.2016.04.004
Hansdottir, Monick, Hinde, Lovan, Look et al., Respiratory Epithelial Cells Convert Inactive Vitamin D to Its Active Form: Potential Effects on Host Defense, J. Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.181.10.7090
Hariyanto, Intan, Hananto, Harapan, Kurniawan, Vitamin D supplementation and Covid-19 outcomes: A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression, Rev. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2269
Harvey, Carabelli, Jackson, Gupta, Thomson et al., SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-021-00573-0
Hayes, Ntambi, Multiple Sclerosis: Lipids, Lymphocytes, and Vitamin D, Immunometabolism, doi:10.20900/immunometab20200019
Herr, Shaykhiev, Bals, The role of cathelicidin and defensins in pulmonary inflammatory diseases, Expert Opin. Biol, doi:10.1517/14712598.7.9.1449
Hewison, An update on vitamin D and human immunity, Clin. Endocrinol, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2011.04261.x
Hewison, Gacad, Lemire, Adams, Vitamin D as a cytokine and hematopoetic factor, Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord, doi:10.1023/A:1010015013211
Holick, Chen, Vitamin D deficiency: A worldwide problem with health consequences, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/87.4.1080S
Holick, Vitamin, Deficiency, None, N. Engl. J. Med. Mass Med. Soc, doi:10.1056/NEJMra070553
Honardoost, Ghavideldarestani, Khamseh, Role of vitamin D in pathogenesis and severity of COVID-19 infection, Arch. Physiol. Biochem, doi:10.1080/13813455.2020.1792505
Iddir, Brito, Dingeo, Campo, Samouda et al., Strengthening the Immune System and Reducing Inflammation and Oxidative Stress through Diet and Nutrition: Considerations during the COVID-19 Crisis, Nutrients
Idf, IDF Diabetes Atlas
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of Vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality, Aging Clin. Exp. Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8
Imai, Kuba, Penninger, Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in acute respiratory distress syndrome, Cell Mol. Life Sci, doi:10.1007/s00018-007-6228-6
Ingham, Jones, Camargo, Kirman, Dowell et al., Association of vitamin D deficiency with severity of acute respiratory infection: A case-control study in New Zealand children, Eur Respir. J. Eur. Respir. Soc
Jeffery, Burke, Mura, Zheng, Qureshi et al., 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 and IL-2 Combine to Inhibit T Cell Production of Inflammatory Cytokines and Promote Development of Regulatory T Cells Expressing CTLA-4 and FoxP3, J. Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0803217
Jeon, Shin, Exploring vitamin D metabolism and function in cancer, Exp. Mol. Med, doi:10.1038/s12276-018-0038-9
Karim, Vaccines and SARS-CoV-2 variants: The urgent need for a correlate of protection, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00468-2
Kaufman, Niles, Kroll, Bi, Holick, SARS-CoV-2 positivity rates associated with circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0239252
Kazemi, Mohammadi, Aghababaee, Golzarand, Clark et al., Association of Vitamin D Status with SARS-CoV-2 Infection or COVID-19 Severity: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis, Adv. Nutr, doi:10.1093/advances/nmab012
Khoo, Chai, Koenen, Joosten, Netea et al., Translating the role of vitamin D3in infectious diseases, Crit. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.3109/1040841X.2011.622716
Kim, Meza, Clarke, Kim, Hickner, Vitamin D and Endothelial Function, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12020575
Kohlmeier, Avoidance of vitamin D deficiency to slow the COVID-19 pandemic, BMJ Nutr. Prev. Health, doi:10.1136/bmjnph-2020-000096
Kongsbak, Levring, Geisler, Von Essen, The Vitamin D Receptor and T Cell Function, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2013.00148
Laird, Rhodes, Kenny, Vitamin D and inflammation: Potential implications for severity of COVID-19, Ir. Med. J
Lau, Majumder, Torabi, Saeg, Hoffman et al., Vitamin D insufficiency is prevalent in severe COVID-19, Cold Spring Harb. Lab, doi:10.1101/2020.04.24.20075838
Lemire, Archer, Beck, Spiegelberg, Immunosuppressive actions of 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3: Preferential inhibition of Th1 functions, J. Nutr
Levi, Thachil, Iba, Levy, Coagulation abnormalities and thrombosis in patients with COVID, Lancet Haematol, doi:10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30145-9
Li, Qiao, Uskokovic, Xiang, Zheng et al., A negative endocrine regulator of the renin-angiotensin system and blood pressure, J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2004.03.004
Lips, Cashman, Lamberg-Allardt, Bischoff-Ferrari, Obermayer-Pietsch et al., Current vitamin D status in European and Middle East countries and strategies to prevent vitamin D deficiency: A position statement of the European Calcified Tissue Society, Eur. J. Endocrinol, doi:10.1530/EJE-18-0736
Liu, Stenger, Li, Wenzel, Tan et al., Toll-like receptor triggering of a vitamin D-mediated human antimicrobial response, Am. Assoc. Adv. Sci
Lowe, Maiyar, Norman, Vitamin D-Mediated Gene Expression
Luo, Liao, Shen, Li, Cheng, Vitamin D Deficiency Is Associated with COVID-19 Incidence and Disease Severity in Chinese People, J. Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/nxaa332
Luxwolda, Kuipers, Kema, Dijck-Brouwer, Muskiet, Traditionally living populations in East Africa have a mean serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration of 115 nmol/L, Br. J. Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114511007161
Mahdavi, A brief review of interplay between vitamin D and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: Implications for a potential treatment for COVID, Rev. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2119
Malaguarnera, Vitamin D3 as Potential Treatment Adjuncts for COVID, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113512
Mandatori, Pelusi, Schiavone, Pipino, Pietro Ndi Pandolfi, The Dual Role of Vitamin K2 in "Bone-Vascular Crosstalk": Opposite Effects on Bone Loss and Vascular Calcification, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13041222
Manson, Bassuk, Commentary, Eliminating vitamin D deficiency during the COVID-19 pandemic: A call to action, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154322
Maresz, Proper calcium use: Vitamin K2 as a promoter of bone and cardiovascular health, Integr. Med. A Clin. J. InnoVision Media
Martineau, Jolliffe, Greenberg, Aloia, Bergman et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: Individual participant data meta-analysis, Health Technol. Assess, doi:10.3310/hta23020
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: Systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.i6583
Mccartney, O'shea, Faul, Healy, Byrne et al., Vitamin D and SARS-CoV-2 infection-evolution of evidence supporting clinical practice and policy development, Ir. J. Med. Sci, doi:10.1007/s11845-020-02427-9
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of Vitamin D Status and Other Clinical Characteristics with COVID-19 Test Results, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722
Mercola, Grant, Wagner, Evidence Regarding Vitamin D and Risk of COVID-19 and Its Severity, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113361
Merzon, Tworowski, Gorohovski, Vinker, Cohen et al., Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: An Israeli population-based study, FEBS J, doi:10.1111/febs.15495
Michigami, Rickets, Osteomalacia, Consensus on Vitamin D Deficiency and Insufficiency in Children, Clin. Calcium
Mohammad, Mishra, Ashraf, Emerging role of vitamin D and its associated molecules in pathways related to pathogenesis of thrombosis, Biomolecules, doi:10.3390/biom9110649
Munshi, Hussein, Toraih, Elshazli, Jardak et al., Vitamin D insufficiency as a potential culprit in critical COVID-19 patients, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26360
Murdaca, Tonacci, Negrini, Greco, Borro et al., Emerging role of vitamin D in autoimmune diseases: An update on evidence and therapeutic implications, Autoimmun. Rev, doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2019.102350
Nikniaz, Akbarzadeh, Hosseinifard, Hosseini, The impact of vitamin D supplementation on mortality rate and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Cold Spring Harb. Lab, doi:10.1101/2021.01.04.21249219
Ohaegbulam, Swalih, Patel, Smith, Perrin, Vitamin D supplementation in COVID-19 patients: A clinical case series, Am. J. Ther, doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001222
Page, Mckenzie, Bossuyt, Boutron, Hoffmann et al., The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews, BMJ
Pal, Banerjee, Bhadada, Shetty, Singh et al., Vitamin D supplementation and clinical outcomes in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, J. Endocrinol. Investig, doi:10.1007/s40618-021-01614-4
Palacios, Gonzalez, Is vitamin D deficiency a major global public health problem?, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2013.11.003
Palmer, Lee, Maynard, Oliver, Bikle et al., Lineage-specific effects of 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on the development of effector CD4 T cells, J. Biol Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.163790
Panagiotou, Tee, Ihsan, Athar, Marchitelli et al., Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 are associated with greater disease severity, Clin. Endocrinol, doi:10.1111/cen.14276
Papadimitriou, The Big Vitamin D Mistake, J. Prev. Med. Public Health, doi:10.3961/jpmph.16.111
Pizzini, Aichner, Sahanic, Böhm, Egger et al., Impact of Vitamin D Deficiency on COVID-19-A Prospective Analysis from the CovILD Registry, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092775
Porcher, Response2covid19, a dataset of governments' responses to COVID-19 all around the world, Sci. Data, doi:10.1038/s41597-020-00757-y
Pouya, Rasmi, Nemati, Asl, Vitamin D Double-edged Sword Against COVID, Int. J. Infect, doi:10.5812/iji.109043
Prietl, Treiber, Pieber, Amrein, Vitamin D and immune function, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu5072502
Quesada-Gomez, Entrenas-Castillo, Bouillon, Vitamin D receptor stimulation to reduce acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in patients with coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 infections, J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105719
Radujkovic, Hippchen, Tiwari-Heckler, Dreher, Boxberger et al., Vitamin D Deficiency and Outcome of COVID-19 Patients, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092757
Rajakumar, Vitamin D Cod-liver oil, sunlight, and rickets: A historical perspective, Pediatrics Am. Acad. Pediatrics, doi:10.1542/peds.112.2.e132
Rastogi, Bhansali, Khare, Suri, Yaddanapudi et al., Short term, high-dose vitamin D supplementation for COVID-19 disease: A randomised, placebo-controlled, study (SHADE study), Postgrad. Med. J, doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-139065
Reis, Fernandes, Sales, Santos, Dos~santos et al., Influence of vitamin D status on hospital length of stay and prognosis in hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: A multicenter prospective cohort study, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqab151
Rella, Kulikova, Dermitzakis, Kondrashov, Rates of SARS-CoV-2 transmission and vaccination impact the fate of vaccine-resistant strains, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-95025-3
Rella, Kulikova, Dermitzakis, Kondrashov, SARS-CoV-2 transmission, vaccination rate and the fate of resistant strains, Cold Spring Harb. Lab, doi:10.1101/2021.02.08.21251383
Rhodes, Subramanian, Laird, Kenny, Editorial: Low population mortality from COVID-19 in countries south of latitude 35 degrees North supports vitamin D as a factor determining severity, Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther, doi:10.1111/apt.15777
Ricci, Pagliuca, D'ascanio, Innammorato, De Vitis et al., Circulating Vitamin D levels status and clinical prognostic indices in COVID-19 patients, Respir. Res, doi:10.1186/s12931-021-01666-3
Ross, Manson, Abrams, Aloia, Brannon et al., Report on Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D from the Institute of Medicine: What Clinicians need to know, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab
Sabetta, Depetrillo, Cipriani, Smardin, Burns et al., Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin d and the incidence of acute viral respiratory tract infections in healthy adults, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0011088
Sassi, Tamone, D'amelio, Vitamin, Nutrient, Hormone, and Immunomodulator, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu10111656
Schleithoff, Zittermann, Tenderich, Berthold, Stehle et al., Vitamin D supplementation improves cytokine profiles in patients with congestive heart failure: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/83.4.754
Sekine, Perez-Potti, Rivera-Ballesteros, Strålin, Gorin et al., Robust T Cell Immunity in Convalescent Individuals with Asymptomatic or Mild COVID-19, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.017
Sengupta, Majumder, Majumder, Role of vitamin D in treating COVID-19-associated coagulopathy: Problems and perspectives, Mol. Cell Biochem, doi:10.1007/s11010-021-04093-6
Shahmiri, Enciso, Adda, Smith, Perugini et al., Membrane core-specific antimicrobial action of cathelicidin LL-37 peptide switches between pore and nanofibre formation, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/srep38184
Silva, Furlanetto, Does serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D decrease during acute-phase response? A systematic review, Nutr. Res, doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2014.12.008
Simko, Hrenak, Adamcova, Paulis, Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System: Friend or Foe-The Matter of Balance. Insight on History, Therapeutic Implications and {COVID}-19 Interactions, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms22063217
Smet, Smet, Herroelen, Gryspeerdt, Martens, Serum 25(OH)D Level on Hospital Admission Associated With COVID-19 Stage and Mortality, Am. J. Clin. Pathol, doi:10.1093/ajcp/aqaa252
Stanhope, Sugar consumption, metabolic disease and obesity: The state of the controversy, Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci, doi:10.3109/10408363.2015.1084990
Starr, Greaney, Addetia, Hannon, Choudhary et al., Prospective mapping of viral mutations that escape antibodies used to treat COVID-Science (80-), Am. Assoc. Adv. Sci, doi:10.1126/science.abf9302
Susianti, Wahono, Rahman, Pratama, Wulanda et al., Low Levels of Vitamin D were Associated with Coagulopathy Among Hospitalized Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19) Patients: A Single-Centered Study in Indonesia, J. Med. Biochem
Szeto, Zucker, Lasota, Rubin, Walker et al., Vitamin D Status and COVID-19 Clinical Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients, Endocr. Res, doi:10.1080/07435800.2020.1867162
Taha, Abureesh, Alghamdi, Hassan, Cheikh et al., The Relationship Between Vitamin D and Infections Including COVID-19: Any Hopes?, Int. J. Gen. Med, doi:10.2147/IJGM.S317421
Tangpricha, Pearce, Chen, Holick, Vitamin D insufficiency among free-living healthy young adults, Am. J. Med, doi:10.1016/S0002-9343(02)01091-4
Teshome, Adane, Girma, Mekonnen, The Impact of Vitamin D Level on {COVID}-19 Infection: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Front. Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2021.624559
Thickett, Moromizato, Litonjua, Amrein, Quraishi et al., Association between prehospital vitamin D status and incident acute respiratory failure in critically ill patients: A retrospective cohort study, BMJ Open Respir. Res, doi:10.1136/bmjresp-2014-000074
Van Ballegooijen, Pilz, Tomaschitz, Grübler, Verheyen, The Synergistic Interplay between Vitamins D and K for Bone and Cardiovascular Health: A Narrative Review, Int. J. Endocrinol, doi:10.1155/2017/7454376
Vanegas-Cedillo, Bello-Chavolla, Ramirez-Pedraza, Encinas, Carrión et al., Serum Vitamin D levels are associated with increased COVID-19 severity and mortality independent of visceral adiposity, Cold Spring Harb. Lab, doi:10.1101/2021.03.12.21253490
Vanherwegen, Gysemans, Mathieu, Regulation of Immune Function by Vitamin D and Its Use in Diseases of Immunity, Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am, doi:10.1016/j.ecl.2017.07.010
Vassiliou, Jahaj, Pratikaki, Keskinidou, Detsika et al., Vitamin D deficiency correlates with a reduced number of natural killer cells in intensive care unit (ICU) and non-ICU patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, Hell. J. Cardiol
Veugelers, Ekwaru, A Statistical Error in the Estimation of the Recommended Dietary Allowance for Vitamin D, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu6104472
Von Mendel, Borsche, COVID-19 mortality risk correlates inversely with vitamin D3 status, mortality close to zero could theoretically be achieved at 50 ng/ml 25(OH)D3: Results of a systematic review and meta-analysis, Harv. Dataverse
Vukić, Neme, Seuter, Saksa, De Mello et al., Relevance of vitamin D receptor target genes for monitoring the vitamin D responsiveness of primary human cells, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0124339
Williams, Burgers, SARS-CoV-2 evolution and vaccines: Cause for concern?, Lancet Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00075-8
Worldometer, Worldometer, None
Xue, Coexisting with the Coronavirus
Yang, Leung, Adamopoulos, Gershwin, The Implication of Vitamin D and Autoimmunity: A Comprehensive Review, Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol, doi:10.1007/s12016-013-8361-3
Zdrenghea, Makrinioti, Bagacean, Bush, Johnston et al., Vitamin D modulation of innate immune responses to respiratory viral infections, Rev. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.1909
Zemb, Bergman, Camargo, Cavalier, Cormier et al., Vitamin D deficiency and the COVID-19 pandemic, J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist, doi:10.1016/j.jgar.2020.05.006
Zhang, Leung, Richers, Liu, Remigio et al., Vitamin D inhibits monocyte/macrophage proinflammatory cytokine production by targeting MAPK phosphatase, J. Immunol. Am. Assoc. Immnol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1102412
Zhang, Mccullough, Tecson, Vitamin D deficiency in association with endothelial dysfunction: Implications for patients with COVID, Rev. Cardiovasc. Med, doi:10.31083/j.rcm.2020.03.131
Zhang, Shen, Petryk, Tang, Chen et al., English Disease: Historical Notes on Rickets, the Bone Lung Link and Child Neglect Issues, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu8110722
Zheng, Peng, Xu, Zhao, Liu et al., Risk factors of critical & mortal COVID-19 cases: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis, J. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.021
Zhou, Luo, Qin, The association between vitamin D deficiency and community-acquired pneumonia, Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000017252
Zwart, Smith, Vitamin D and COVID-19: Lessons from Spaceflight Analogs, J. Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/nxaa233
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13103596",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu13103596",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: Much research shows that blood calcidiol (25(OH)D3) levels correlate strongly with SARS-CoV-2 infection severity. There is open discussion regarding whether low D3 is caused by the infection or if deficiency negatively affects immune defense. The aim of this study was to collect further evidence on this topic. Methods: Systematic literature search was performed to identify retrospective cohort as well as clinical studies on COVID-19 mortality rates versus D3 blood levels. Mortality rates from clinical studies were corrected for age, sex, and diabetes. Data were analyzed using correlation and linear regression. Results: One population study and seven clinical studies were identified, which reported D3 blood levels preinfection or on the day of hospital admission. The two independent datasets showed a negative Pearson correlation of D3 levels and mortality risk (r(17) = −0.4154, p = 0.0770/r(13) = −0.4886, p = 0.0646). For the combined data, median (IQR) D3 levels were 23.2 ng/mL (17.4–26.8), and a significant Pearson correlation was observed (r(32) = −0.3989, p = 0.0194). Regression suggested a theoretical point of zero mortality at approximately 50 ng/mL D3. Conclusions: The datasets provide strong evidence that low D3 is a predictor rather than just a side effect of the infection. Despite ongoing vaccinations, we recommend raising serum 25(OH)D levels to above 50 ng/mL to prevent or mitigate new outbreaks due to escape mutations or decreasing antibody activity.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu13103596"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Borsche",
"given": "Lorenz",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Glauner",
"given": "Bernd",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5189-3708",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "von Mendel",
"given": "Julian",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-15T02:42:18Z",
"timestamp": 1634265738000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-18T10:21:12Z",
"timestamp": 1634552472000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-25T04:38:51Z",
"timestamp": 1711341531672
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 47,
"issue": "10",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
14
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "10",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-14T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1634169600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/10/3596/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "3596",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
14
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
14
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "Coexisting with the Coronavirus. New Yorkerhttps://www.newyorker.com/science/annals-of-medicine/coexisting-with-the-coronavirus"
},
{
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4161/rna.8.2.15013",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nmni.2020.100673",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-021-00573-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00075-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00468-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abf9302",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7031e2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-95025-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.02.08.21251383",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12061562",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/87.4.1080S",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154322",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2013.11.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nutres.2010.12.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0002-9343(02)01091-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/13813455.2020.1792505",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/EJE-18-0736",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41430-020-0558-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nfs.2020.06.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.1995.03530210037027",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41371-020-00398-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114511001991",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjnph-2020-000096",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apt.15777",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/C6PP00355A",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu8110722",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1542/peds.112.2.e132",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2010-2704",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/bonekey.2013.213",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu5072502",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2013.00148",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2265.2011.04261.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMra070553",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00394-012-0430-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/nyas.12129",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12072097",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2019.02211",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref39"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41430-020-0564-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref40"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrc3691",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref41"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s12276-018-0038-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref42"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BCJ20170042",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref43"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3310/hta23020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref44"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/JIR.S63898",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref45"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20900/immunometab20200019",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref46"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1023/A:1010015013211",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref47"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2009-1773",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref48"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10111656",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref49"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.coph.2010.04.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref50"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphys.2014.00151",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref51"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.181.10.7090",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref52"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ncpendmet0716",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref53"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11882-010-0161-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref54"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jbm4.10405",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref55"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms19082419",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref56"
},
{
"key": "ref57"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-014-0660-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref58"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0b013e318206ccdf",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref59"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(13)70165-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref60"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000017252",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref61"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2334-14-273",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref62"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ecl.2017.07.010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref63"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu7064240",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref64"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.1909",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref65"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0011088",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref66"
},
{
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D deficiency with severity of acute respiratory infection: A case-control study in New Zealand children Eur Respir",
"author": "Ingham",
"first-page": "124",
"journal-title": "J. Eur. Respir. Soc.",
"key": "ref67",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/18715281113129990046",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref68"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/1040841X.2011.622716",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref69"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IJGM.S317421",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref70"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref71"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-206680",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref72"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjresp-2014-000074",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref73"
},
{
"article-title": "D-hormone and the immune system",
"author": "Cantorna",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "J. Rheumatol. Suppl.",
"key": "ref74",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2012.07.007",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref75"
},
{
"article-title": "Rickets/Osteomalacia. Consensus on Vitamin D Deficiency and Insufficiency in Children",
"author": "Michigami",
"first-page": "1307",
"journal-title": "Clin. Calcium",
"key": "ref76",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref77"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu6104472",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref78"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3961/jpmph.16.111",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref79"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2017/7454376",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref80"
},
{
"article-title": "Proper calcium use: Vitamin K2 as a promoter of bone and cardiovascular health",
"author": "Maresz",
"first-page": "34",
"journal-title": "Integr. Med. A Clin. J. InnoVision Media",
"key": "ref81",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13041222",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref82"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105719",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref83"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113361",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref84"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117808",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref85"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00018-007-6228-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref86"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms22063217",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref87"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/nxaa233",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref88"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5812/iji.109043",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref89"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2004.03.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref90"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2119",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref91"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27075",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref92"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1681/ASN.2010121251",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref93"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00210-020-01911-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref94"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113512",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref95"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/83.4.754",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref96"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M110.163790",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref97"
},
{
"article-title": "Immunosuppressive actions of 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3: Preferential inhibition of Th1 functions",
"author": "Lemire",
"first-page": "1704S",
"journal-title": "J. Nutr.",
"key": "ref98",
"volume": "125",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.167.9.4974",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref99"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.0803217",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref100"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01677-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref101"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1517/14712598.7.9.1449",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref102"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep38184",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref103"
},
{
"article-title": "Toll-like receptor triggering of a vitamin D-mediated human antimicrobial response. Science (80-)",
"author": "Liu",
"first-page": "1770",
"journal-title": "Am. Assoc. Adv. Sci.",
"key": "ref104",
"volume": "311",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.04-3284com",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref105"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2010.12.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref106"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/fmb.13.135",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref107"
},
{
"DOI": "10.31083/j.rcm.2020.03.131",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref108"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12020575",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref109"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11010-021-04093-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref110"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biom9110649",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref111"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30145-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref112"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00394-020-02411-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref113"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcp/aqaa252",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref114"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.03.12.21253490",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref115"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40618-020-01370-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref116"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092775",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref117"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.24.20075838",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref118"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/nxaa332",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref119"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency correlates with a reduced number of natural killer cells in intensive care unit (ICU) and non-ICU patients with COVID-19 pneumonia",
"author": "Vassiliou",
"first-page": "241",
"journal-title": "Hell. J. Cardiol.",
"key": "ref120",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref121"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0239252",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref122"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.15495",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref123"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12051359",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref124"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092757",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref125"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07315724.2020.1869626",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref126"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07435800.2020.1867162",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref127"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MJT.0000000000001222",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref128"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-139065",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref129"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113377",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref130"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcte.2016.04.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref131"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cen.14276",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref132"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref133"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105771",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref134"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jgar.2020.05.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref135"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D and inflammation: Potential implications for severity of COVID-19",
"author": "Laird",
"first-page": "81",
"journal-title": "Ir. Med. J.",
"key": "ref136",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11845-020-02427-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref137"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2020.00513",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref138"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nutres.2014.12.008",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref139"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.maturitas.2020.06.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref140"
},
{
"article-title": "Low Serum Levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D Accompany Severe COVID-19 because it is a Negative Acute Phase Reactant",
"author": "Antonelli",
"first-page": "2546",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Med. Sci.",
"key": "ref141",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.03.11.21253361",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref142"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30120-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref143"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41597-020-00757-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref144"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref145"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40618-021-01614-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref146"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.01.04.21249219",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref147"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2269",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref148"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/advances/nmab012",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref149"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26360",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref150"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100967",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref151"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2021.624559",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref152"
},
{
"key": "ref153",
"unstructured": "CADTH COVID-19 Search Stringshttps://covid.cadth.ca/literature-searching-tools/cadth-covid-19-search-strings/"
},
{
"key": "ref154",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 Risk Estimatorhttps://github.com/TheEconomist/covid-19-risk-estimator"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12931-021-01666-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref155"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07315724.2020.1856013",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref156"
},
{
"article-title": "The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews",
"author": "Page",
"first-page": "372",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref157",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5281/zenodo.4287835",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref158"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref159"
},
{
"article-title": "Association of Vitamin D Status With Hospital Morbidity and Mortality in Adult Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients With COVID",
"author": "Charoenngam",
"first-page": "145",
"journal-title": "Endocr. Pract.",
"key": "ref160",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Low Levels of Vitamin D were Associated with Coagulopathy Among Hospitalized Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19) Patients: A Single-Centered Study in Indonesia",
"author": "Susianti",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Biochem.",
"key": "ref161",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "ref162",
"unstructured": "IDF Diabetes Atlas, 9th Edition 2019https://www.diabetesatlas.org/en/"
},
{
"key": "ref163",
"unstructured": "Population Interpolated by Single Age and Single Yearhttps://population.un.org/wpp/Download/Standard/CSV/"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.008",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref164"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7021e3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref165"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref166"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2019.102350",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref167"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12016-013-8361-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref168"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/10408363.2015.1084990",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref169"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref170"
},
{
"key": "ref171",
"unstructured": "Worldometerhttps://www.worldometers.info/faq/"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/nqab151",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref172"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1102412",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref173"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114511007161",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref174"
},
{
"key": "ref175",
"unstructured": "Suggested Role of Vitamin D Supplementation in COVID-19 Severityhttp://www.jocms.org/index.php/jcms/article/view/822"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0124339",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref176"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7910/DVN/7FSWNL",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref177"
}
],
"reference-count": 177,
"references-count": 177,
"relation": {
"has-preprint": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.1101/2021.09.22.21263977",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/10/3596"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "COVID-19 Mortality Risk Correlates Inversely with Vitamin D3 Status, and a Mortality Rate Close to Zero Could Theoretically Be Achieved at 50 ng/mL 25(OH)D3: Results of a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "13"
}
