Serum Vitamin D Levels Are Associated With Increased COVID-19 Severity and Mortality Independent of Whole-Body and Visceral Adiposity
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.03.12.21253490, Mar 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
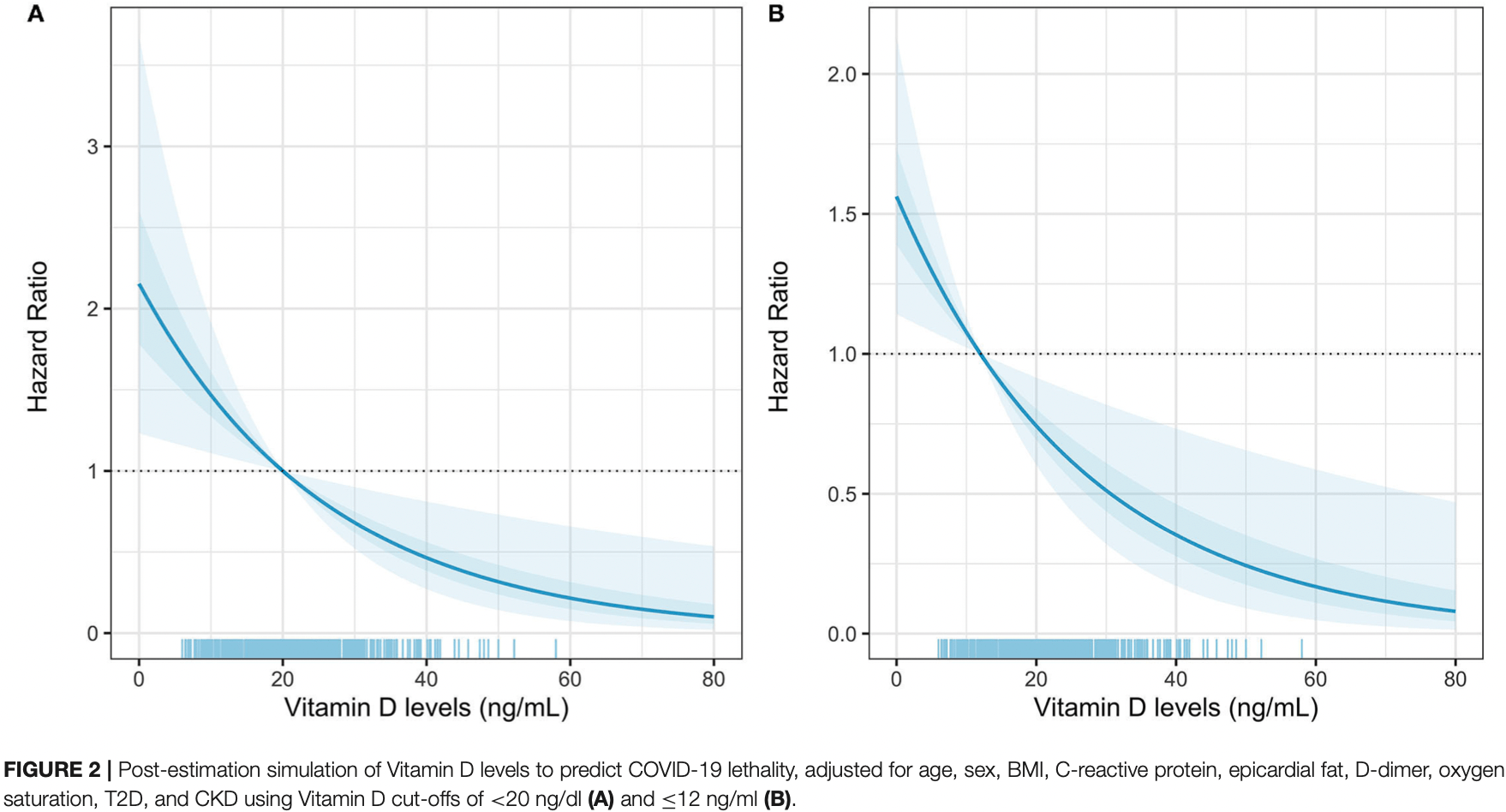
Retrospective 551 moderate to severe COVID-19 patients in Mexico showing vitamin D ≤12ng/mL independently associated with COVID-19 mortality. No association was found between vitamin D levels and the need for intubation. Vitamin D deficiency was more prevalent in women and patients with type 2 diabetes.
This is the 55th of 228 COVID-19 sufficiency studies for vitamin D, which collectively show higher levels reduce risk with p<0.0000000001.
|
risk of death, 52.6% lower, RR 0.47, p = 0.006, high D levels (≥12ng/mL) 95 of 494 (19.2%), low D levels (<12ng/mL) 21 of 57 (36.8%), NNT 5.7, adjusted per study, inverted to make RR<1 favor high D levels (≥12ng/mL).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Vanegas-Cedillo et al., 14 Mar 2021, retrospective, Mexico, peer-reviewed, 15 authors.
Serum Vitamin D Levels Are Associated With Increased COVID-19 Severity and Mortality Independent of Whole-Body and Visceral Adiposity
Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.813485
Conclusion: Vitamin D deficiency (≤12 ng/ml or <30 nmol/L), is independently associated with COVID-19 mortality after adjustment for visceral fat (epicardial fat thickness). Low vitamin D may contribute to a pro-inflammatory and pro-thrombotic state, increasing the risk for adverse COVID-19 outcomes.
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found at: https://github.com/ oyaxbell/covid_metabolism.
ETHICS STATEMENT The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Research and Ethics Committee of the INCMNZ (Ref 3383). Written informed consent for participation was not required for this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS RM, OB-C, and CA-S: research idea and study design. RM, PV-C, NR-P, MJ-Á, CP, BR, JV-G, and CA-S: data acquisition. OB-C, RM, CA-S, NA-V, and AV-V: data analysis/interpretation. OB-C and NA-V: statistical analysis. RM, OB-C, NA-V, AV-V, and CA-S: manuscript drafting. RM, CA-S, AP, and JS-O: supervision or mentorship. All authors contributed important intellectual content during manuscript drafting or revision and accepts accountability for the overall work by ensuring that questions pertaining to the accuracy or integrity of any portion of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. Publisher's Note: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated..
References
Abbas, Physiological functions of Vitamin D in adipose tissue, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.08.004
Acosta, Garg, Pham, Whitaker, Anglin et al., Racial and ethnic disparities in rates of covid-19-associated hospitalization, intensive care unit admission, and in-hospital death in the United States from march 2020 to february 2021, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.30479
Baeke, Takiishi, Korf, Gysemans, Mathieu, Vitamin D: modulator of the immune system, Curr Opin Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.coph.2010.04.001
Bello-Chavolla, Bahena-López, Ne, Vargas-Vázquez, González-Díaz et al., Predicting Mortality Due to SARS-CoV-2: A Mechanistic Score Relating Obesity and Diabetes to COVID-19 Outcomes in Mexico, J Clin Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgaa346
Bello-Chavolla, González-Díaz, Ne, Márquez-Salinas, Vargas-Vázquez, Unequal Impact of Structural Health Determinants and Comorbidity on COVID-19 Severity and Lethality in Older Mexican Adults: Considerations Beyond Chronological Aging, J Gerontol Ser A, doi:10.1093/gerona/glaa163
Bello-Chavolla, Ne, Ortiz-Brizuela, Vargas-Vázquez, González-Lara et al., Validation and repurposing of the MSL-COVID-19 score for prediction of severe COVID-19 using simple clinical predictors in a triage setting: the Nutri-CoV score, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0244051
Bertaso, Bertol, Duncan, Foppa, Epicardial fat: definition, measurements and systematic review of main outcomes, Arq Bras Cardiol, doi:10.5935/abc.20130138
Bilezikian, Bikle, Hewison, Lazaretti-Castro, Formenti et al., Mechanisms in endocrinology: vitamin D and COVID-19, Eur J Endocrinol, doi:10.1530/EJE-20-0665
Cohen, Hall, John, Rapoport, The early natural history of SARS-CoV-2 Infection: clinical observations from an urban, ambulatory COVID-19 clinic, Mayo Clin Proc, doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.04.010
Evans, Lippman, Shining light on the COVID-19 pandemic: a vitamin D receptor checkpoint in defense of unregulated wound healing, Cell Metab, doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.09.007
Hariyanto, Intan, Hananto, Harapan, Kurniawan, Vitamin D supplementation and Covid-19 outcomes: a systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression, Rev Med Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2269
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet Lond Engl, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Jeffery, Burke, Mura, Zheng, Qureshi et al., 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 and IL-2 combine to inhibit T cell production of inflammatory cytokines and promote development of regulatory T cells expressing CTLA-4 and FoxP3, J Immunol Baltim Md, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0803217
Jolliffe, Camargo, Sluyter, Aglipay, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data from randomised controlled trials, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1136/thorax-2020-BTSabstracts.105
Lu, Ersoy, Whitmore, Lipton, Rybicki, Reformatted Four-Chamber and Short-Axis Views of the Heart Using Thin Section (</=2 mm) MDCT Images, Acad Radiol, doi:10.1016/j.acra.2007.05.019
Lu, Zhao, Li, Niu, Yang et al., Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding, Lancet Lond Engl, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8
Ma, Nguyen, Yue, Ding, Drew et al., Associations between predicted vitamin D status, vitamin D intake, and risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection and coronavirus disease 2019 severity, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqab389
Mahdavi, A brief review of interplay between vitamin D and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: Implications for a potential treatment for COVID-19, Rev Med Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2119
Mehta, Bello-Chavolla, Mancillas-Adame, Rodriguez-Flores, Pedraza et al., Epicardial adipose tissue thickness is associated with increased COVID-19 severity and mortality, Int J Obes (Lond), doi:10.1038/s41366-021-01050-7
Mitchell, Vitamin-D and COVID-19: do deficient risk a poorer outcome?, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30183-2
Murai, Fernandes, Sales, Pinto, Goessler et al., Effect of a single high dose of vitamin D3 on hospital length of stay in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.26848
Muscogiuri, Barrea, Somma, Laudisio, Salzano et al., Sex differences of vitamin D status across BMI classes: an observational prospective cohort study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu11123034~
Márquez-Salinas, Fermín-Martínez, Ne, Vargas-Vázquez, Guerra et al., Adaptive Metabolic and Inflammatory Responses Identified Using Accelerated Aging Metrics Are Linked to Adverse Outcomes in Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection, J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, doi:10.1093/gerona/glab078
Ne, Bello-Chavolla, Vargas-Vázquez, Fermín-Martínez, Márquez-Salinas et al., Assessing the Burden of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Among Healthcare Workers in Mexico City: A Data-Driven Call to Action, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1101/2020.07.02.20145169
Ne, Fernandez-Chirino, Pisanty-Alatorre, Mancilla-Galindo, Kammar-García et al., Comprehensive evaluation of the impact of sociodemographic inequalities on adverse outcomes and excess mortality during the COVID-19 pandemic in Mexico City, Clin Infect Dis Off Publ Infect Dis Soc Am, doi:10.1101/2021.03.11.21253402
Pan, Sze, Minhas, Bangash, Pareek et al., The impact of ethnicity on clinical outcomes in COVID-19: a systematic review, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100404
Parra-Ortega, Alcara-Ramírez, Ronzon-Ronzon, Elías-García, Mata-Chapol et al., 25-Hydroxyvitamin D level is associated with mortality in patients with critical covid-19: a prospective observational study in Mexico City, Nutr Res Pract, doi:10.4162/nrp.2021.15.S1.S32
Pascot, Lemieux, Lemieux, Prud'homme, Tremblay et al., Age-related increase in visceral adipose tissue and body fat and the metabolic risk profile of premenopausal women, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/diacare.22.9.1471
Ramirez-Sandoval, Vj, Paz-Cortés, Santillan-Ceron, Hernandez-Jimenez et al., Very low vitamin D levels are a strong independent predictor of mortality in hospitalized patients with severe covid-19, Arch Med Res, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.09.006
Ramírez-Aldana, Gomez-Verjan, Bello-Chavolla, García-Peña, Spatial epidemiological study of the distribution, clustering, and risk factors associated with early COVID-19 mortality in Mexico, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0254884
Salamanna, Maglio, Sartori, Landini, Fini, Vitamin D and platelets: a menacing duo in COVID-19 and potential relation to bone remodeling, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms221810010
Sarengat, Islam, Ardhi, Correlation of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and clinical outcome of acute thrombotic stroke in patients with COVID-19, Narra J, doi:10.52225/narra.v1i3.50
Stoffers, Weber, Levine, An Update on Vitamin D Deficiency in the twenty-first century: nature and nurture, Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes, doi:10.1097/MED.0000000000000691
Sánchez-Zuno, González-Estevez, Matuz-Flores, Macedo-Ojeda, Hernández-Bello et al., Vitamin D levels in covid-19 outpatients from western Mexico: clinical correlation and effect of its supplementation, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/jcm10112378
Tangpricha, Pearce, Chen, Holick, Vitamin D insufficiency among free-living healthy young adults, Am J Med, doi:10.1016/S0002-9343(02)01091-4
Tao, Lou, Liu, The role of vitamin D in the relationship between gender and deep vein thrombosis among stroke patients, Front Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.755883
Vargas-Vázquez, Bello-Chavolla, Ortiz-Brizuela, Campos-Muñoz, Mehta et al., Impact of undiagnosed type 2 diabetes and pre-diabetes on severity and mortality for SARS-CoV-2 infection, BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care, doi:10.1136/bmjdrc-2020-002026
Wang, Lee, Shih, Huang, Chang et al., Relations of epicardial adipose tissue measured by multidetector computed tomography to components of the metabolic syndrome are regionspecific and independent of anthropometric indexes and intraabdominal visceral fat, J Clin Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1210/jc.2008-0834
Yang, Yu, Xu, Shu, Xia et al., Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5
Zhang, Li, Zhu, Chang, Wang et al., Higher visceral fat area increases the risk of vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency in Chinese adults, Nutr Metab, doi:10.1186/s12986-015-0046-x
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.03.12.21253490",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2021.03.12.21253490",
"abstract": "<jats:title>ABSTRACT</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>INTRODUCTION</jats:title><jats:p>Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is a global pandemic. Vitamin D deficiency has been associated with susceptibility to infectious disease. In this study, the association between COVID-19 outcomes and vitamin D levels in patients attending a COVID-19 reference center in Mexico City are examined.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>METHODS</jats:title><jats:p>Consecutive patients with confirmed COVID-19 were evaluated. All patients underwent clinical evaluation and follow-up, laboratory measurements and a thoracic computerized tomography, including the measurement of epicardial fat thickness. Low vitamin D was defined as levels <20ng/mL (<50nmol/L) and deficient Vitamin D as a level ≤12ng/mL (<30nmol/L)</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>RESULTS</jats:title><jats:p>Of the 551 patients included, low vitamin D levels were present in 45.6% and deficient levels in 10.9%. Deficient Vitamin D levels were associated with mortality (HR 2.11, 95%CI 1.24-3.58, p=0.006) but not with critical COVID-19, adjusted for age, sex, body-mass index and epicardial fat. Using model-based causal mediation analyses the increased risk of COVID-19 mortality conferred by low vitamin D levels was partly mediated by its effect on D-dimer and cardiac ultrasensitive troponins. Notably, increased risk of COVID-19 mortality conferred by low vitamin D levels was independent of BMI and epicardial fat.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>CONCLUSION</jats:title><jats:p>Vitamin D deficiency (≤12ng/mL or <30nmol/L), is independently associated with COVID-19 mortality after adjustment for visceral fat (epicardial fat thickness). Low vitamin D may contribute to a pro-inflammatory and pro-thrombotic state, increasing the risk for adverse COVID-19 outcomes.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
29
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1338-9724",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Vanegas-Cedillo",
"given": "Pablo Esteban",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3093-937X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bello-Chavolla",
"given": "Omar Yaxmehen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8268-4869",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ramírez-Pedraza",
"given": "Natalia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6372-5944",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Encinas",
"given": "Bethsabel Rodríguez",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pérez Carrión",
"given": "Carolina Isabel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jasso-Ávila",
"given": "María Isabel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Valladares-García",
"given": "Jorge Carlos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hernández-Juárez",
"given": "Diana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0051-7689",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Vargas-Vázquez",
"given": "Arsenio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6879-1078",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Antonio-Villa",
"given": "Neftali Eduardo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7178-0073",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Chapa-Ibarguengoitia",
"given": "Monica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2640-2916",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "de Leon",
"given": "Alfredo Ponce",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sifuentes-Osornio",
"given": "José",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8517-0241",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Aguilar-Salinas",
"given": "Carlos A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2509-8054",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mehta",
"given": "Roopa",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2021-03-14T04:20:15Z",
"timestamp": 1615695615000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-25T19:33:07Z",
"timestamp": 1653507187000
},
"group-title": "Endocrinology (including Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic Disease)",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-01T23:48:07Z",
"timestamp": 1709336887048
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "medRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 2,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
13
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2021.03.12.21253490",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
13
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
13
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab577",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/gerona/glaa163",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjdrc-2020-002026",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa1487",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.04.010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgaa346",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0244051",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0254884",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.52225/narra.v1i3.50",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2119",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0002-9343(02)01091-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MED.0000000000000691",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/nqab389",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30183-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2269",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00051-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.26848",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12986-015-0046-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/diacare.22.9.1471",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.acra.2007.05.019",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5935/abc.20130138",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.03.14.21253532",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2008-0834",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.09.007",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/EJE-20-0665",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.coph.2010.04.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.0803217",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/gerona/glab078",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms221810010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2021.755883",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.30479",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4162/nrp.2021.15.S1.S32",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm10112378",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.09.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100404",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.08.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.39"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11123034",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022010304100748000_2021.03.12.21253490v3.40"
}
],
"reference-count": 40,
"references-count": 40,
"relation": {
"is-preprint-of": [
{
"asserted-by": "subject",
"id": "10.3389/fnut.2022.813485",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2021.03.12.21253490"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Serum Vitamin D levels are associated with increased COVID-19 severity and mortality independent of whole-body and visceral adiposity",
"type": "posted-content"
}
