Vitamin D supplementation and Covid‐19 outcomes: A systematic review, meta‐analysis and meta‐regression
et al., Reviews in Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/rmv.2269, Jun 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
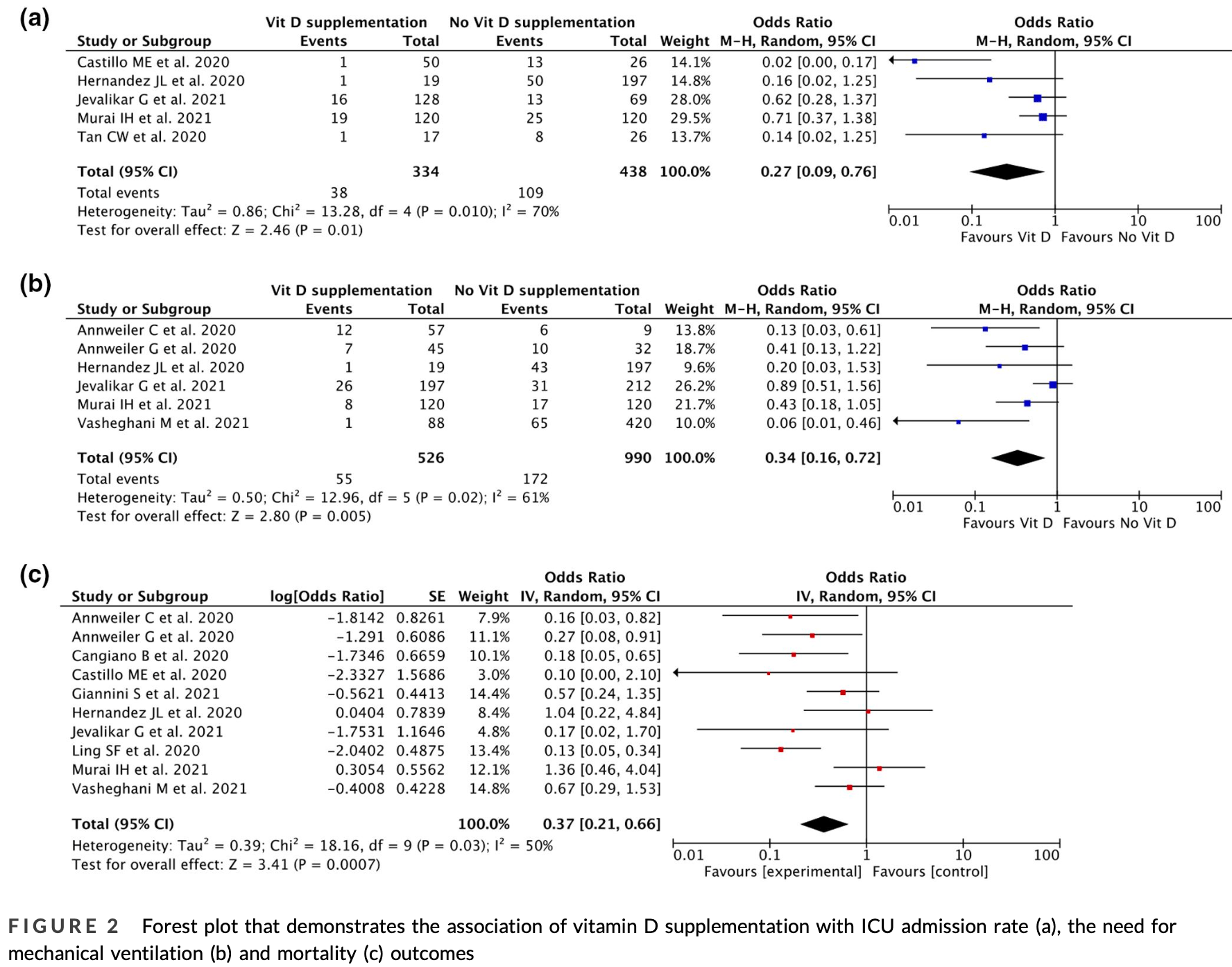
Meta analysis of 11 COVID-19 studies showing lower mortality, mechanical ventilation, and ICU admission with vitamin D. Authors also perform meta-regression showing greater efficacy with increasing age.
20 meta-analyses show significant improvements with vitamin D treatment for mortality1-14,
mechanical ventilation1,5,6,11,15-17 ,
ICU admission1,3,5,6,9,11,13,15-19 ,
hospitalization11,
severity2,4,5,10,20 , and
cases7,19,20 .
Currently there are 135 vitamin D treatment for COVID-19 studies, showing 39% lower mortality [32‑45%], 17% lower ventilation [-5‑35%], 45% lower ICU admission [28‑57%], 22% lower hospitalization [13‑30%], and 17% fewer cases [9‑25%].
|
risk of death, 63.0% lower, OR 0.37, p < 0.001, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 66.0% lower, OR 0.34, p = 0.005, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 73.0% lower, OR 0.27, p = 0.02, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Shah et al., Does vitamin D supplementation reduce COVID-19 severity? - a systematic review, QJM: An International Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcac040.
2.
Nikniaz et al., The impact of vitamin D supplementation on mortality rate and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.34172/PS.2021.13.
3.
Hosseini et al., Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation on COVID-19 Related Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14102134.
4.
D’Ecclesiis et al., Vitamin D and SARS-CoV2 infection, severity and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0268396.
5.
Xie et al., Micronutrient perspective on COVID-19: Umbrella review and reanalysis of meta-analyses, Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, doi:10.1080/10408398.2023.2174948.
6.
Hariyanto et al., Vitamin D supplementation and Covid‐19 outcomes: A systematic review, meta‐analysis and meta‐regression, Reviews in Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/rmv.2269.
7.
Begum et al., The Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19 Survival and Prevention: A Meta-analysis, Sudan Journal of Medical Sciences, doi:10.18502/sjms.v19i1.15776.
8.
Jamilian et al., The role of vitamin D in outcomes of critical care in COVID-19 patients: Evidence from an umbrella meta-analysis of interventional and observational studies, Public Health Nutrition, doi:10.1017/S1368980024000934.
9.
Sobczak et al., Effect of Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Severe COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16101402.
10.
Petrelli et al., Therapeutic and prognostic role of vitamin D for COVID-19 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 43 observational studies, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105883.
11.
Asla et al., Vitamin D on COVID-19 Patients During the Pandemic, 2022. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Current Research in Nutrition and Food Science Journal, doi:10.12944/CRNFSJ.11.1.3.
12.
Kow et al., The impact of vitamin D administration on mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-024-01564-2.
13.
Zhang et al., The impact of supplementing vitamin D through different methods on the prognosis of COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1441847.
14.
Doustmohammadian et al., Impact of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19 mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Nutrition Clinique et Métabolisme, doi:10.1016/j.nupar.2025.12.001.
15.
Meng et al., The role of vitamin D in the prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Clinical Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2023.09.008.
16.
Yang et al., Therapeutic effects of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19 aggravation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1367686.
17.
Szarpak et al., Vitamin D supplementation to treat SARS-CoV-2 positive patients. Evidence from meta-analysis, Cardiology Journal, doi:10.5603/CJ.a2021.0122.
18.
Tentolouris et al., The effect of vitamin D supplementation on mortality and intensive care unit admission of COVID-19 patients. A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression, Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews, doi:10.1002/dmrr.3517.
Hariyanto et al., 27 Jun 2021, peer-reviewed, 5 authors.
Contact: andree.kurniawan@uph.edu.
Vitamin D supplementation and Covid‐19 outcomes: A systematic review, meta‐analysis and meta‐regression
Reviews in Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/rmv.2269
Vitamin D has many protective properties and potential role against acute lung injury. Low serum vitamin D is associated with high risk of pneumonia and development of acute respiratory distress syndrome. This study sought to analyse the efficacy of vitamin D in improving the outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) patients. Using specific keywords, we comprehensively searched the potential articles on PubMed, Europe PMC and ClinicalTrials.gov database until 8th May 2021. All published studies on Covid-19 and vitamin D were retrieved. Statistical analysis was conducted using Review Manager 5.4 software. A total of 11 studies with 22,265 Covid-19 patients were included in the meta-analysis. Our data suggested that vitamin D supplementation was associated with reduction in intensive care unit admission rate (OR 0.27; 95% CI: 0.09-0.76, p = 0.010, I 2 = 70%, random-effect modelling); reduction of the need for mechanical ventilation (OR 0.34; 95% CI: 0.16-0.72, p = 0.005, I 2 = 61%, random-effect modelling) and reduction of mortality from Covid-19 (OR 0.37; 95% CI: 0.21-0.66, p < 0.001, I 2 = 50%, random-effect modelling). Further analysis showed that the associations were influenced by age (p = 0.020). Our study suggests that vitamin D supplementation may offer beneficial effects on Covid-19 outcomes. However, more randomized clinical trials are required to confirm this conclusion. K E Y W O R D S coronavirus disease 2019, Covid-19, vitamin D 1 | INTRODUCTION Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection continues to spread globally causing a pandemic and has become a major medical focus for the last couple of years. The pandemic has involved over 164 million confirmed cases, with more than 3.4 million deaths as of 23 May 2021. 1 While some SARS-CoV-2 infections appear as mild upper respiratory symptoms and may be self-limiting, notable numbers of patients require hospitalizations and intensive treatment following progression into a more severe cases,
CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization
References
Alappat, Valerio, Awad, Effect of vitamin D and β-sitosterol on immune function of macrophages, Int Immunopharm, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2010.08.003
Annweiler, Corvaisier, Gautier, Vitamin D supplementation associated to better survival in hospitalized frail elderly COVID-19 patients: the GERIA-COVID quasi-experimental study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113377
Annweiler, Hanotte, De L'eprevier, Sabatier, Lafaie et al., Vitamin D and survival in COVID-19 patients: a quasiexperimental study, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105771
Begg, Mazumdar, Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias, Biometrics
Buonaguro, Ascierto, Morse, Covid-19: time for a paradigm change, Rev Med Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2134
Cangiano, Fatti, Danesi, Mortality in an Italian nursing home during COVID-19 pandemic: correlation with gender, age, ADL, vitamin D supplementation, and limitations of the diagnostic tests, Aging (Albany NY), doi:10.18632/aging.202307
Castillo, Costa, Barrios, Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: a pilot randomized clinical study, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751
Dancer, Parekh, Lax, Vitamin D deficiency contributes directly to the acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), Thorax, doi:10.1136/thoraxjnl%2D2014-206680
Daneshkhah, Agrawal, Eshein, Subramanian, Roy et al., Evidence for possible association of vitamin D status with cytokine storm and unregulated inflammation in COVID-19 patients, Aging Clin Exp Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01677%2Dy
Gauzzi, Fantuzzi, Reply to Jakovac: COVID-19, vitamin D, and type I interferon, Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00315.2020
Giannini, Passeri, Tripepi, Effectiveness of in-hospital cholecalciferol use on clinical outcomes in comorbid COVID-19 patients: a hypothesis-generating study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13010219
Gold, Sehayek, Gabrielli, Zhang, Mccusker et al., COVID-19 and comorbidities: a systematic review and metaanalysis, Postgrad Med, doi:10.1080/00325481.2020.1786964
Gong, Dong, Xia, Correlation analysis between disease severity and inflammation-related parameters in patients with COVID-19: a retrospective study, BMC Infect Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-020-05681-5
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza
Hariyanto, Christian, Kurniawan, Human immunodeficiency virus and mortality from coronavirus disease 2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis, South Afr J HIV Med, doi:10.4102/sajhivmed.v22i1.1220
Hariyanto, Halim, Gunawan, Kurniawan, Ivermectin and outcomes from Covid-19 pneumonia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trial studies, Rev Med Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2265
Hariyanto, Halim, Jodhinata, Yanto, Kurniawan, Colchicine treatment can improve outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a systematic review and meta-analysis, Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol, doi:10.1111/1440-1681.13488
Hariyanto, Hardyson, Kurniawan, Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab for coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Drug Res (Stuttg), doi:10.1055/a%2D1336-2371
Hariyanto, Japar, Damay, Kwenandar, Sieto, Kurniawan A. The use of ACE inhibitor/ARB in SARS-CoV-2 patients: a comprehensive narrative review, Asian J Med Sci, doi:10.3126/ajms.v11i6.29911
Hariyanto, Japar, Kwenandar, Inflammatory and hematologic markers as predictors of severe outcomes in COVID-19 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Am J Emerg Med, doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2020.12.076
Hariyanto, Kurniawan, Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) inhibitor and outcome from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in diabetic patients: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression, J Diabetes Metab Disord, doi:10.1007/s40200-021-00777-4
Hariyanto, Kurniawan, Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and outcomes from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Sleep Med, doi:10.1016/j.sleep.2021.03.029
Hariyanto, Kurniawan, Tocilizumab administration is associated with the reduction in biomarkers of coronavirus disease 2019 infection, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26698
Hariyanto, None
Hariyanto, Putri, Situmeang, Kurniawan, Dementia is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, Am J Med Sci, doi:10.1016/j.amjms.2020.10.026
Hariyanto, Rizki, Kurniawan, Anosmia/Hyposmia is a good predictor of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection: a meta-analysis, Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol, doi:10.1055/s%2D0040-1719120
Hashemi, Thijssen, Hosseini, Tabarraei, Pourkarim et al., Human gene polymorphisms and their possible impact on the clinical outcome of SARS-CoV-2 infection, Arch Virol, doi:10.1007/s00705-021-05070-6
Hernández, Nan, Fernandez-Ayala, Vitamin D status in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, J Clin Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgaa733
Huang, Wang, Chen, Song, Liu et al., Perioperative antibiotics to prevent acute endophthalmitis after ophthalmic surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0166141
Jain, Chaurasia, Sengar, Singh, Mahor et al., Analysis of vitamin D level among asymptomatic and critically ill COVID-19 patients and its correlation with inflammatory markers, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-77093%2Dz
Jakovac, COVID-19 and vitamin D-Is there a link and an opportunity for intervention?, Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00138.2020
Jayawardena, Jeyakumar, Francis, Misra, Impact of the vitamin D deficiency on COVID-19 infection and mortality in Asian countries, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.03.006
Jevalikar, Mithal, Singh, Lack of association of baseline 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with disease severity and mortality in Indian patients hospitalized for COVID-19, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-85809%2Dy
Jolliffe, Greiller, Mein, Vitamin D receptor genotype influences risk of upper respiratory infection, Br J Nutr, doi:10.1017/S000711451800209X
Kralj, Jakovac, Vitamin D and COVID-19 in an immunocompromised patient with multiple comorbidities-A Case Report, Clin Case Rep, doi:10.1002/ccr3.4010
Kwenandar, Japar, Damay, Coronavirus disease 2019 and cardiovascular system: a narrative review, Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc, doi:10.1016/j.ijcha.2020.100557
Laplana, Royo, Fibla, Hariyanto, Intan et al., Vitamin D supplementation and Covid-19 outcomes: a systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression, Rev Med Virol
Ling, Broad, Murphy, High-dose cholecalciferol booster therapy is associated with a reduced risk of mortality in patients with COVID-19: a cross-sectional multi-centre observational study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12123799
Liu, Zhang, Joo, Sun, NF-κB signaling in inflammation, Signal Transduct Target Ther, doi:10.1038/sigtrans.2017.23
Mahdavi, A brief review of interplay between vitamin D and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: implications for a potential treatment for COVID-19, Rev Med Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2119
Malaguarnera, Vitamin D3 as potential treatment adjuncts for COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113512
Mcnally, Sampson, Matheson, Hutton, Little, Vitamin D receptor (VDR) polymorphisms and severe RSV bronchiolitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Pediatr Pulmonol, doi:10.1002/ppul.22877
Mirković, De Borst, Beyond the RAAS: dissecting the antifibrotic effects of vitamin D analogues, Lab Invest, doi:10.1038/labinvest.2012.150
Mokhtari, Hassani, Ghaffari, Ebrahimi, Yarahmadi, Hassanzadeh G. COVID-19 and multiorgan failure: a narrative review on potential mechanisms, J Mol Histol, doi:10.1007/s10735-020-09915-3
Murai, Fernandes, Sales, Effect of a single high dose of vitamin D3 on hospital length of stay in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, J Am Med Assoc, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.26848
Murdaca, Pioggia, Negrini, Vitamin D and Covid-19: an update on evidence and potential therapeutic implications, Clin Mol Allergy, doi:10.1186/s12948-020-00139-0
Pereira, Damascena, Azevedo, De Almeida Oliveira, Da et al., Vitamin D deficiency aggravates COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis, Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, doi:10.1080/10408398.2020.1841090
Pinzon, Pradana, Vitamin D deficiency among patients with COVID-19: case series and recent literature review, Trop Med Health, doi:10.1186/s41182-020-00277%2Dw
Putri, Hariyanto, Hananto, Christian, Situmeang et al., Parkinson's disease may worsen outcomes from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia in hospitalized patients: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression
Qin, Zhou, Hu, Dysregulation of immune response in patients with coronavirus, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa248
Relat, None, doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2021.04.019
Schwalfenberg, A review of the critical role of vitamin D in the functioning of the immune system and the clinical implications of vitamin D deficiency, Mol Nutr Food Res, doi:10.1002/mnfr.201000174
Tan, Ho, Kalimuddin, Cohort study to evaluate the effect of vitamin D, magnesium, and vitamin B12 in combination on progression to severe outcomes in older patients with coronavirus (COVID-19), Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2020.111017
Terrin, Schmid, Lau, Olkin, Adjusting for publication bias in the presence of heterogeneity, Stat Med, doi:10.1002/sim.1461
Thornton, Lee, Publication bias in meta-analysis: its causes and consequences, J Clin Epidemiol, doi:10.1016/s0895-4356%2899%2900161-4
Van Harten, Van Woudenbergh, Van Dijk, Haagsman, Cathelicidins: immunomodulatory antimicrobials. Vaccines (Basel), doi:10.3390/vaccines6030063
Vasheghani, Jannati, Baghaei, Rezaei, Marjani, The association of 25 (OH) vitamin D levels and severity and outcome of COVID-19: a cross-sectional study, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs%2D141034/v1
Weir, Thenappan, Bhargava, Chen, Does vitamin D deficiency increase the severity of COVID-19, Clin Med (Lond), doi:10.7861/clinmed.2020-0301
Xu, Shi, Wang, Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600%2820%2930076%2DX
Zheng, Gao, Wang, Functional exhaustion of antiviral lymphocytes in COVID-19 patients, Cell Mol Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41423-020-0402-2
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2269",
"ISSN": [
"1052-9276",
"1099-1654"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/rmv.2269",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/rmv.2269"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2021-05-31"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2021-06-16"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2021-06-27"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1748-9776",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Medicine Pelita Harapan University Tangerang Indonesia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hariyanto",
"given": "Timotius Ivan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Medicine Pelita Harapan University Tangerang Indonesia"
}
],
"family": "Intan",
"given": "Denny",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Medicine Pelita Harapan University Tangerang Indonesia"
}
],
"family": "Hananto",
"given": "Joshua Edward",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7630-8413",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Research Unit School of Medicine Universitas Syiah Kuala Banda Aceh Indonesia"
},
{
"name": "Tropical Disease Center School of Medicine Universitas Syiah Kuala Banda Aceh Indonesia"
},
{
"name": "Department of Microbiology Universitas Syiah Kuala Banda Aceh Indonesia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Harapan",
"given": "Harapan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5219-9029",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine Faculty of Medicine Pelita Harapan University Tangerang Indonesia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kurniawan",
"given": "Andree",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Reviews in Medical Virology",
"container-title-short": "Reviews in Medical Virology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-27T17:45:42Z",
"timestamp": 1624815942000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-04T10:51:51Z",
"timestamp": 1646391111000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-05T02:23:26Z",
"timestamp": 1685931806854
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 21,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
27
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1624752000000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/tdm_license_1.1",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1624752000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/rmv.2269",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.1002/rmv.2269",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/rmv.2269",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
27
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
27
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"key": "e_1_2_11_2_1",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID‐19): situation report.https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly‐epidemiological‐update‐on‐covid‐19‐‐‐18‐may‐2021. Accessed May 22 2020."
},
{
"article-title": "Anosmia/Hyposmia is a good predictor of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) infection: a meta‐analysis",
"author": "Hariyanto TI",
"first-page": "e170",
"journal-title": "Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol",
"key": "e_1_2_11_3_1",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2020.100557",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.parkreldis.2021.04.019",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4102/sajhivmed.v22i1.1220",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjms.2020.10.026",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/00325481.2020.1786964",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.sleep.2021.03.029",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40200-021-00777-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_10_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab for coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid‐19) patients: a systematic review and meta‐analysis",
"author": "Hariyanto TI",
"first-page": "265",
"journal-title": "Drug Res (Stuttg)",
"key": "e_1_2_11_11_1",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26698",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1440-1681.13488",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_13_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Ivermectin and outcomes from Covid‐19 pneumonia: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized clinical trial studies",
"author": "Hariyanto TI",
"first-page": "e2265",
"journal-title": "Rev Med Virol",
"key": "e_1_2_11_14_1",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12948-020-00139-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpendo.00138.2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-206680",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01677-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7861/clinmed.2020-0301",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_19_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0166141",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_20_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2307/2533446",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113377",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105771",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.202307",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_24_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13010219",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgaa733",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-85809-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12123799",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_29_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.26848",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_30_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_31_1"
},
{
"article-title": "The association of 25 (OH) vitamin D levels and severity and outcome of COVID‐19: a cross‐sectional study",
"author": "Vasheghani M",
"journal-title": "Research Square",
"key": "e_1_2_11_32_1",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0895-4356(99)00161-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_33_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/sim.1461",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_34_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-020-05681-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_35_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajem.2020.12.076",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_36_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41423-020-0402-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_37_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2134",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_38_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-X",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_39_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa248",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_40_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10735-020-09915-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_41_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113512",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_42_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines6030063",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_43_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mnfr.201000174",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_44_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_45_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2010.08.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_46_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.03.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_47_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s41182-020-00277-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_48_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpendo.00315.2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_49_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ccr3.4010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_50_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2020.1841090",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_51_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-77093-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_52_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3126/ajms.v11i6.29911",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_53_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2119",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_54_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/labinvest.2012.150",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_55_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sigtrans.2017.23",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_56_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S000711451800209X",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_57_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ppul.22877",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_58_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Human gene polymorphisms and their possible impact on the clinical outcome of SARS‐CoV‐2 infection",
"author": "Hashemi SMA",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Arch Virol",
"key": "e_1_2_11_59_1",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.gene.2018.08.017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_60_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 59,
"references-count": 59,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/rmv.2269"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Virology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Vitamin D supplementation and Covid‐19 outcomes: A systematic review, meta‐analysis and meta‐regression",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "32"
}
