The impact of vitamin D supplementation on mortality rate and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
et al., Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.34172/PS.2021.13, Mar 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
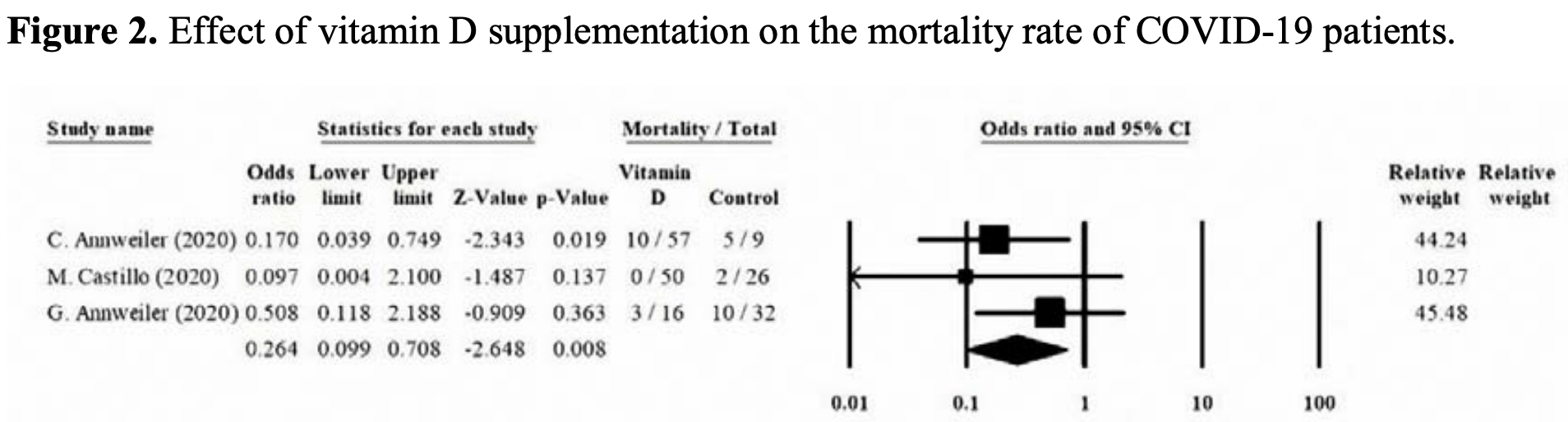
Meta analysis of 4 supplementation studies, finding that vitamin D supplementation "seems to decrease the mortality rate, the severity of the disease, and serum levels of the inflammatory markers". Mortality odds ratio OR 0.264, p = 0.008.
20 meta-analyses show significant improvements with vitamin D treatment for mortality1-14,
mechanical ventilation1,5,6,11,15-17 ,
ICU admission1,3,5,6,9,11,13,15-19 ,
hospitalization11,
severity2,4,5,10,20 , and
cases7,19,20 .
Currently there are 135 vitamin D treatment for COVID-19 studies, showing 39% lower mortality [32‑45%], 17% lower ventilation [-5‑35%], 45% lower ICU admission [28‑57%], 22% lower hospitalization [13‑30%], and 17% fewer cases [9‑25%].
|
risk of death, 73.6% lower, OR 0.26, p = 0.008, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Shah et al., Does vitamin D supplementation reduce COVID-19 severity? - a systematic review, QJM: An International Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcac040.
2.
Nikniaz et al., The impact of vitamin D supplementation on mortality rate and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.34172/PS.2021.13.
3.
Hosseini et al., Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation on COVID-19 Related Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14102134.
4.
D’Ecclesiis et al., Vitamin D and SARS-CoV2 infection, severity and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0268396.
5.
Xie et al., Micronutrient perspective on COVID-19: Umbrella review and reanalysis of meta-analyses, Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, doi:10.1080/10408398.2023.2174948.
6.
Hariyanto et al., Vitamin D supplementation and Covid‐19 outcomes: A systematic review, meta‐analysis and meta‐regression, Reviews in Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/rmv.2269.
7.
Begum et al., The Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19 Survival and Prevention: A Meta-analysis, Sudan Journal of Medical Sciences, doi:10.18502/sjms.v19i1.15776.
8.
Jamilian et al., The role of vitamin D in outcomes of critical care in COVID-19 patients: Evidence from an umbrella meta-analysis of interventional and observational studies, Public Health Nutrition, doi:10.1017/S1368980024000934.
9.
Sobczak et al., Effect of Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Severe COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16101402.
10.
Petrelli et al., Therapeutic and prognostic role of vitamin D for COVID-19 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 43 observational studies, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105883.
11.
Asla et al., Vitamin D on COVID-19 Patients During the Pandemic, 2022. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Current Research in Nutrition and Food Science Journal, doi:10.12944/CRNFSJ.11.1.3.
12.
Kow et al., The impact of vitamin D administration on mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-024-01564-2.
13.
Zhang et al., The impact of supplementing vitamin D through different methods on the prognosis of COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1441847.
14.
Doustmohammadian et al., Impact of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19 mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Nutrition Clinique et Métabolisme, doi:10.1016/j.nupar.2025.12.001.
15.
Meng et al., The role of vitamin D in the prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Clinical Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2023.09.008.
16.
Yang et al., Therapeutic effects of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19 aggravation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1367686.
17.
Szarpak et al., Vitamin D supplementation to treat SARS-CoV-2 positive patients. Evidence from meta-analysis, Cardiology Journal, doi:10.5603/CJ.a2021.0122.
18.
Tentolouris et al., The effect of vitamin D supplementation on mortality and intensive care unit admission of COVID-19 patients. A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression, Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews, doi:10.1002/dmrr.3517.
Nikniaz et al., 9 Mar 2021, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
The impact of vitamin D supplementation on mortality rate and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.34172/ps.2021.13
Background: Several studies have suggested the positive impact of vitamin D on patients infected with SARS-CoV-2. This systematic review aims to evaluate the effects of vitamin D supplementation on clinical outcomes and mortality rate of COVID-19 patients. Methods: A comprehensive search was conducted through the databases of PubMed, Scopus, Web of Knowledge, Embase, Ovid, and The Cochrane Library without time and language limitation, until December 16, 2020. The results were screened, and the outcomes of interest were extracted. Using the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) Critical Appraisal Tools, the remaining results were appraised critically. Statistical analysis was performed using the Comprehensive Meta-Analysis (CMA) software version 2.0. Results: Of the 2311 results, four studies and 259 patients were enrolled, including 139 patients in vitamin D intervention groups. The pooled analysis of three studies, reporting the patients' survival and mortality rate, showed a significantly lower mortality rate among the intervention groups compared with the control groups (OR=0.264, 95% CI=0.099-0.708, p-value=0.008). Two of the studies reported the clinical outcomes based on the World Health Organization's Ordinal Scale for Clinical Improvement (OSCI) score for COVID-19, where both of them showed a significant decrease in OSCI score in the vitamin D intervention groups. One study reported a lower rate of intensive care unit (ICU) admission, and one study reported a significant decrease in serum levels of Fibrinogen. Conclusion: Prescribing vitamin D supplementation to patients with COVID-19 infection seems to decrease the mortality rate, the severity of the disease, and serum levels of the inflammatory markers. Further studies are needed to determine the ideal type, dosage, and duration of supplementation.
Author Contributions MAA and MSH contributed to the conceptualization and study design, LN and MSH defined the search strategy and performed the search through the databases, LN and MAA screened the results, LN and MSH critically assessed the studies, HH and MSH performed the analyses. MAA and MSH contributed to preparing the original draft of the manuscript, and LN and HH critically revised the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest The authors declare no competing interests regarding the submission and publication of this manuscript.
Supplementary Data Supplementary data are available on the journal's web site along with the published article.
References
Akbari, Tabrizi, Lankarani, Aria, Vakili et al., The role of cytokine profile and lymphocyte subsets in the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis, Life Sci, doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118167
Alvarez, Aguilar-Jimenez, Rugeles, The potential protective role of vitamin D supplementation on HIV-1 infection, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.02291
Annweiler, Corvaisier, Gautier, Dubée, Legrand et al., Vitamin D supplementation associated to better survival in hospitalized frail elderly COVID-19 patients: The GERIA-COVID quasiexperimental study, Nutrients
Annweiler, Hanotte, De L'eprevier, Sabatier, Lafaie et al., Vitamin D and survival in COVID-19 patients: A quasi-experimental study, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105771
Aranow, Vitamin D and the immune system, J Investig Med, doi:10.2310/JIM.0b013e31821b8755
Aziz, Fatima, Assaly, Elevated interleukin-6 and severe COVID-19: A meta-analysis, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.25948
Azrielant, Shoenfeld, Vitamin D and the immune system, Isr Med Assoc J
Belderbos, Houben, Wilbrink, Lentjes, Bloemen et al., Cord blood vitamin D deficiency is associated with respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis, Pediatrics, doi:10.1542/peds.2010-3054
Bikle, Vitamin D metabolism, mechanism of action, and clinical applications, Chem Biol, doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2013.12.016
Brenner, Holleczek, Schöttker, Vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency and mortality from respiratory diseases in a cohort of older adults: potential for limiting the death toll during and beyond the COVID-19 pandemic?, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12082488
Brockman-Schneider, Pickles, Gern, Effects of vitamin D on airway epithelial cell morphology and rhinovirus replication, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0086755
Carpagnano, Lecce, Quaranta, Zito, Buonamico et al., Vitamin D deficiency as a predictor of poor prognosis in patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19, J Endocrinol Invest, doi:10.1007/s40618-020-01370-x
Castillo, Costa, Barrios, Díaz, Miranda et al., Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751
Charan, Goyal, Saxena, Yadav, Vitamin D for prevention of respiratory tract infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis, J Pharmacol Pharmacother, doi:10.4103/0976-500X.103685
Chirumbolo, Bjørklund, Sboarina, Vella, The role of vitamin D in the immune system as a prosurvival molecule, Clin Ther, doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.03.021
Daniel, Sartory, Zahn, Radeke, Stein, Immune modulatory treatment of trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid colitis with calcitriol is associated with a change of a T helper (Th) 1/Th17 to a Th2 and regulatory T cell profile, J Pharmacol Exp Ther, doi:10.1124/jpet.107.127209
Deluccia, Clegg, Sukumar, The implications of vitamin D deficiency on COVID-19 for atrisk populations, Nutr Rev, doi:10.1093/nutrit/nuaa092
Fiorino, Gallo, Zippi, Sabbatani, Manfredi et al., Cytokine storm in aged people with CoV-2: possible role of vitamins as therapy or preventive strategy, Aging Clin Exp Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01669-y
Greiller, Martineau, Modulation of the immune response to respiratory viruses by vitamin D, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu7064240
Harris, Carson, Baillie, Horby, Nair, An evidence-based framework for priority clinical research questions for COVID-19, J Glob Health, doi:10.7189/jogh.10-011001
Kearns, Alvarez, Seidel, Tangpricha, Impact of vitamin D on infectious disease, Am J Med Sci, doi:10.1097/MAJ.0000000000000360
Krishnan, Feldman, Mechanisms of the anticancer and anti-inflammatory actions of vitamin D, Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol, doi:10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010510-100611
Laird, Rhodes, Kenny, Vitamin D and inflammation: potential implications for severity of covid-19, Ir Med J
Lancet, Endocrinology, Vitamin D and COVID-19: why the controversy?, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00003-6
Leal, Lima, De Aquino, De Sousa, Gadelha et al., Vitamin D (VD3) antioxidative and anti-inflammatory activities: Peripheral and central effects, Eur J Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173099
Lips, Cashman, Lamberg-Allardt, Bischoff-Ferrari, Obermayer-Pietsch et al., Current vitamin D status in European and S12 | Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2021, 27(Suppl 1), S1-S12 Middle East countries and strategies to prevent vitamin D deficiency: a position statement of the European Calcified Tissue Society, Eur J Endocrinol, doi:10.1530/EJE-18-0736
Liu, Long, Xiong, Chen, Ma et al., Association of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers with risk of COVID-19, inflammation level, severity, and death in patients with COVID-19: a rapid systematic review and meta-analysis, Clin Cardiol, doi:10.1002/clc.23421
Liu, Sun, Wang, Zhang, Zhao et al., Low vitamin D status is associated with coronavirus disease 2019 outcomes: a systematic review and metaanalysis, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.12.077
Loeb, Dang, Thiem, Thanabalan, Wang et al., Effect of Vitamin D supplementation to reduce respiratory infections in children and adolescents in Vietnam: A randomized controlled trial, Influenza Other Respir Viruses, doi:10.1111/irv.12615
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.i6583
Mccartney, Byrne, Optimisation of vitamin D status for enhanced Immuno-protection against covid-19, Ir Med J
Meehan, Penckofer, The role of vitamin D in the aging adult, J Aging Gerontol, doi:10.12974/2309-6128.2014.02.02.1
Moan, Dahlback, Ma, Juzeniene, Influenza, solar radiation and vitamin D, Dermatoendocrinol, doi:10.4161/derm.1.6.11357
Mohamed, Almonaem, Mansour, Algebaly, Khattab et al., Importance of studying the levels of hepcidin and vitamin D in Egyptian children with chronic hepatitis C, J Transl Int Med, doi:10.2478/jtim-2019-0004
Mohan, Cherian, Sharma, Exploring links between vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1008874
Moher, Liberati, Tetzlaff, Altman, Group, Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement, PLoS Med, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Pang, Cardosa, Guzman, Of cascades and perfect storms: the immunopathogenesis of dengue haemorrhagic fever-dengue shock syndrome (DHF/DSS), Immunol Cell Biol, doi:10.1038/sj.icb.7100008
Pereira, Damascena, Azevedo, De Almeida Oliveira, Da et al., Vitamin D deficiency aggravates COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis, Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, doi:10.1080/10408398.2020.1841090
Potempa, Rajab, Hart, Bordon, Fernandez-Botran, Insights into the use of C-reactive protein as a diagnostic index of disease severity in COVID-19 infections, Am J Trop Med Hyg, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.20-0473
Rastogi, Bhansali, Khare, Suri, Yaddanapudi et al., Short term, high-dose vitamin D supplementation for COVID-19 disease: a randomised, placebo-controlled, study (SHADE study), Postgrad Med J, doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-139065
Rhodes, Dunstan, Laird, Subramanian, Kenny, COVID-19 mortality increases with northerly latitude after adjustment for age suggesting a link with ultraviolet and vitamin D, BMJ Nutr Prev Health, doi:10.1136/bmjnph-2020-000110
Rhodes, Subramanian, Laird, Griffin, Kenny, Perspective: Vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 severity-plausibly linked by latitude, ethnicity, impacts on cytokines, ACE2 and thrombosis (R1), J Intern Med, doi:10.1111/joim.13149
Shojaeefar, Malih, Rezaei, The possible doubleedged sword effects of vitamin D on COVID-19: A hypothesis, Cell Biol Int, doi:10.1002/cbin.11469
Spinelli, Pellino, COVID-19 pandemic: perspectives on an unfolding crisis, Br J Surg, doi:10.1002/bjs.11627
Urashima, Segawa, Okazaki, Kurihara, Wada et al., Randomized trial of vitamin D supplementation to prevent seasonal influenza A in schoolchildren, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.3945/ajcn.2009.29094
Vanherwegen, Gysemans, Mathieu, Regulation of immune function by vitamin D and its use in diseases of immunity, Endocrinol Metab Clin, doi:10.1016/j.ecl.2017.07.010
Viard, Souberbielle, Kirk, Reekie, Knysz et al., Vitamin D and clinical disease progression in HIV infection: results from the EuroSIDA study, Aids, doi:10.1097/QAD.0b013e328347f6f7
Vieira, Omdp, Hannas, Kanadani, Tds et al., What do we know about COVID-19? A review article, Rev Assoc Med Bras, doi:10.1590/1806-9282.66.4.534
Wei, Christakos, Mechanisms underlying the regulation of innate and adaptive immunity by vitamin D, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu7105392
Whittemore, COVID-19 fatalities, latitude, sunlight, and vitamin D, Am J Infect Control, doi:10.1016/j.ajic.2020.06.193
Who, World Health Organization Coronavirus disease (COVID
Yanez, Weiss, Romand, Treggiari, COVID-19 mortality risk for older men and women, BMC Public Health, doi:10.1186/s12889-020-09826-8
Zhang, Wang, Fu, Luo, Zhang et al., Potential factors for prediction of disease severity of COVID-19 patients, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.03.20.20039818
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.34172/ps.2021.13",
"ISSN": [
"1735-403X",
"2383-2886"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.34172/ps.2021.13",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: Several studies have suggested the positive impact of vitamin D on patients infected with SARS-CoV-2. This systematic review aims to evaluate the effects of vitamin D supplementation on clinical outcomes and mortality rate of COVID-19 patients. Methods: A comprehensive search was conducted through the databases of PubMed, Scopus, Web of Knowledge, Embase, Ovid, and The Cochrane Library without time and language limitation, until December 16, 2020. The results were screened, and the outcomes of interest were extracted. Using the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) Critical Appraisal Tools, the remaining results were appraised critically. Statistical analysis was performed using the Comprehensive Meta-Analysis (CMA) software version 2.0. Results: Of the 2311 results, four studies and 259 patients were enrolled, including 139 patients in vitamin D intervention groups. The pooled analysis of three studies, reporting the patients’ survival and mortality rate, showed a significantly lower mortality rate among the intervention groups compared with the control groups (OR=0.264, 95% CI=0.099–0.708, p-value=0.008). Two of the studies reported the clinical outcomes based on the World Health Organization’s Ordinal Scale for Clinical Improvement (OSCI) score for COVID-19, where both of them showed a significant decrease in OSCI score in the vitamin D intervention groups. One study reported a lower rate of intensive care unit (ICU) admission, and one study reported a significant decrease in serum levels of Fibrinogen. Conclusion: Prescribing vitamin D supplementation to patients with COVID-19 infection seems to decrease the mortality rate, the severity of the disease, and serum levels of the inflammatory markers. Further studies are needed to determine the ideal type, dosage, and duration of supplementation. </jats:p>",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "Journal Owner",
"name": "journal_owner",
"value": "Tabriz University of Medical Sciences"
},
{
"label": "Journal Publisher",
"name": "journal_publisher",
"value": "Tabriz University of Medical Sciences"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "2021-01-26"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "2021-03-09"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 3,
"value": "2021-03-09"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2951-936X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Nikniaz",
"given": "Leila",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9589-104X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Akbarzadeh",
"given": "Mohammad Amin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1308-1244",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Hosseinifard",
"given": "Hossein",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2765-5018",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Hosseini",
"given": "Mohammad-Salar",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Pharmaceutical Sciences"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"ps.tbzmed.ac.ir"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-30T10:24:48Z",
"timestamp": 1632997488000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-30T10:24:48Z",
"timestamp": 1632997488000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-02T14:15:01Z",
"timestamp": 1648908901940
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 2,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "1735-403X"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "2383-2886"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
9
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://ps.tbzmed.ac.ir/Inpress/ps-34133.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://ps.tbzmed.ac.ir/Inpress/ps-34133.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "20123",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.34172",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
9
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
9
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
9
]
]
},
"publisher": "Maad Rayan Publishing Company",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://ps.tbzmed.ac.ir/Inpress/ps-34133"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Pharm Sci"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Pharmacology, Toxicology and Pharmaceutics",
"Pharmaceutical Science"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"The impact of vitamin D supplementation on mortality rate and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.34172/crossmark_policy"
}
