Does vitamin D supplementation reduce COVID-19 severity? - a systematic review
et al., QJM: An International Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcac040, Feb 2022
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
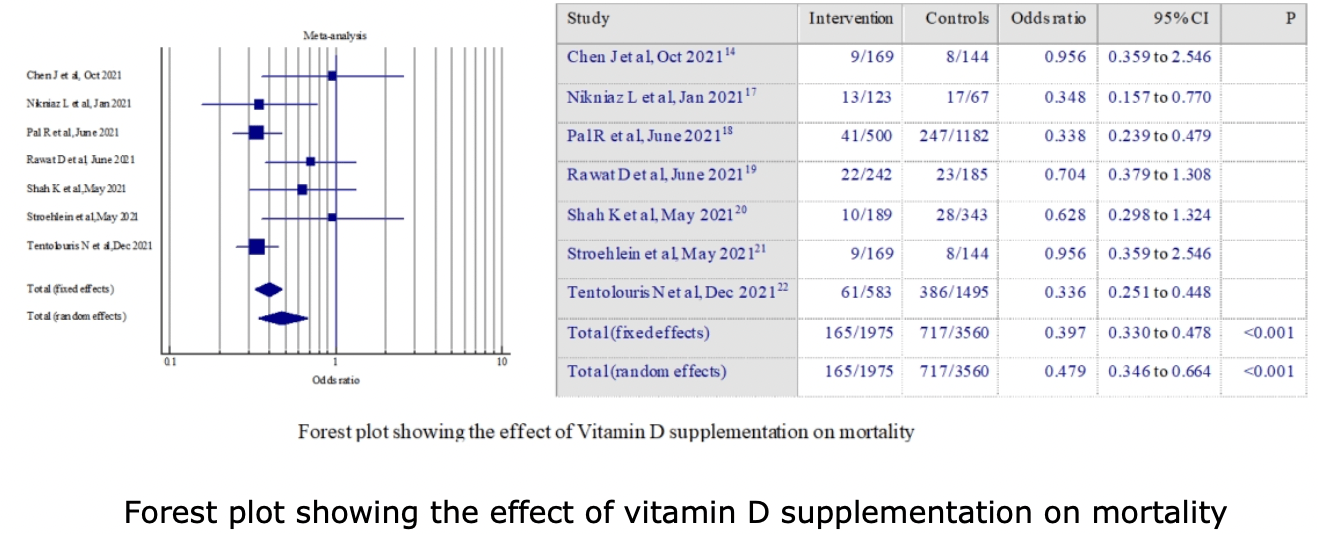
Meta-analysis of seven systematic reviews showing that vitamin D supplementation reduces the risk of COVID-19 mortality, ventilation, and ICU admission. Authors note that oral and IV supplements were well tolerated, safe, and effective.
20 meta-analyses show significant improvements with vitamin D treatment for mortality1-14,
mechanical ventilation1,5,6,11,15-17 ,
ICU admission1,3,5,6,9,11,13,15-19 ,
hospitalization11,
severity2,4,5,10,20 , and
cases7,19,20 .
Currently there are 136 vitamin D treatment for COVID-19 studies, showing 39% lower mortality [31‑45%], 17% lower ventilation [-5‑35%], 45% lower ICU admission [28‑57%], 22% lower hospitalization [13‑30%], and 17% fewer cases [9‑25%].
|
risk of death, 52.1% lower, OR 0.48, p < 0.001, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 46.1% lower, OR 0.54, p < 0.001, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 63.8% lower, OR 0.36, p < 0.001, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Shah et al., Does vitamin D supplementation reduce COVID-19 severity? - a systematic review, QJM: An International Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcac040.
2.
Nikniaz et al., The impact of vitamin D supplementation on mortality rate and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.34172/PS.2021.13.
3.
Hosseini et al., Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation on COVID-19 Related Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14102134.
4.
D’Ecclesiis et al., Vitamin D and SARS-CoV2 infection, severity and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0268396.
5.
Xie et al., Micronutrient perspective on COVID-19: Umbrella review and reanalysis of meta-analyses, Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, doi:10.1080/10408398.2023.2174948.
6.
Hariyanto et al., Vitamin D supplementation and Covid‐19 outcomes: A systematic review, meta‐analysis and meta‐regression, Reviews in Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/rmv.2269.
7.
Begum et al., The Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19 Survival and Prevention: A Meta-analysis, Sudan Journal of Medical Sciences, doi:10.18502/sjms.v19i1.15776.
8.
Jamilian et al., The role of vitamin D in outcomes of critical care in COVID-19 patients: Evidence from an umbrella meta-analysis of interventional and observational studies, Public Health Nutrition, doi:10.1017/S1368980024000934.
9.
Sobczak et al., Effect of Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Severe COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16101402.
10.
Petrelli et al., Therapeutic and prognostic role of vitamin D for COVID-19 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 43 observational studies, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105883.
11.
Asla et al., Vitamin D on COVID-19 Patients During the Pandemic, 2022. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Current Research in Nutrition and Food Science Journal, doi:10.12944/CRNFSJ.11.1.3.
12.
Kow et al., The impact of vitamin D administration on mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-024-01564-2.
13.
Zhang et al., The impact of supplementing vitamin D through different methods on the prognosis of COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1441847.
14.
Doustmohammadian et al., Impact of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19 mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Nutrition Clinique et Métabolisme, doi:10.1016/j.nupar.2025.12.001.
15.
Meng et al., The role of vitamin D in the prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Clinical Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2023.09.008.
16.
Yang et al., Therapeutic effects of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19 aggravation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1367686.
17.
Szarpak et al., Vitamin D supplementation to treat SARS-CoV-2 positive patients. Evidence from meta-analysis, Cardiology Journal, doi:10.5603/CJ.a2021.0122.
18.
Tentolouris et al., The effect of vitamin D supplementation on mortality and intensive care unit admission of COVID-19 patients. A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression, Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews, doi:10.1002/dmrr.3517.
Shah et al., 15 Feb 2022, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
Does vitamin D supplementation reduce COVID-19 severity? -a systematic review
doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcac040/6528876
Background and Aim: The evidence regarding the efficacy of vitamin D supplementation in 10 reducing severity of COVID-19 is still insufficient. This is partially due to the lack of primary 11 robust trial-based data and heterogenous study designs. This evidence summary, aims to study the 12 effect of vitamin D supplementation on morbidity and mortality in hospitalized COVID-19 13 patients.
References
Bouillon, Manousaki, Rosen, Trajanoska, Rivadeneira et al., The 281 health effects of vitamin D supplementation: evidence from human studies, Nat Rev 282 Endocrinol
Chen, Mei, Xie, Yuan, Ma et al., Low vitamin D levels do not aggravate COVID-19 risk or death, and vitamin D supplementation does not improve outcomes in 285 hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis and GRADE assessment of cohort 286 studies and RCTs, BMJ Open, doi:10.1186/s12937-021-00744-y28815
Chung, Silwal, Kim, Modlin, Jo, Vitamin D-cathelicidin axis: At the 330 crossroads between protective immunity and pathological inflammation during infection. 331, Immune Netw
Grønborg, Tetens, Christensen, Andersen, Jakobsen et al., Vitamin 333 D-fortified foods improve wintertime vitamin D status in women of Danish and Pakistani 334 origin living in Denmark: a randomized controlled trial, Eur J Nutr
Han, Jones, Tangpricha, Brown, Hao et al., High dose Vitamin 264 D administration in ventilated intensive care unit patients: A pilot double blind 265 randomized controlled trial, J Clin Transl Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/j.jcte.2016.04.004
Hariyanto, Intan, Hananto, Harapan, Kurniawan, Vitamin D supplementation 293 and Covid-19 outcomes: A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression, Rev 294 Med Virol
Karahan, Katkat, Impact of Serum 25(OH) Vitamin D Level on Mortality in Patients 276 with COVID-19 in Turkey, J Nutr Heal Aging
Kulie, Groff, Redmer, Hounshell, Schrager, Vitamin D: An evidence-based 328 review, J Am Board Fam Med
Mercola, Grant, Wagner, Radujkovic, Hippchen et al., Vitamin D 273 and COVID-19 severity and related mortality: a prospective study in Italy, BMC Infect
Murai, Fernandes, Sales, Pinto, Goessler et al., Effect of a 260 Single High Dose of Vitamin D3on Hospital Length of Stay in Patients with Moderate to 261 Severe COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA -J Am Med Assoc
Nikniaz, Akbarzadeh, Hosseinifard, Hosseini, The impact of vitamin D 296 supplementation on mortality rate and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients: A 297 systematic review and meta-analysis, Pharm Sci
Pal, Banerjee, Bhadada, Shetty, Singh et al., Vitamin D supplementation 299 and clinical outcomes in COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev, doi:10.1007/s40618-021-30101614-4302
Rizzoli, Griffin ; G, Hewison, Hopkin, Kenny, Quinton et al., Vitamin D and 322 COVID-19: Evidence and recommendations for supplementation, R Soc Open Sci, doi:10.1007/s40520-020-32001678-x321
Shah, Saxena, Mavalankar, Vitamin D supplementation, COVID-19 and disease 306 severity: A meta-analysis, Qjm
Shen, Mei, Zhang, Xu, The Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Clinical 278 Outcomes for Critically Ill Patients: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis of 279 Randomized Clinical Trials, Front Nutr
Stroehlein, Wallqvist, Iannizzi, Mikolajewska, Metzendorf et al., Vitamin D supplementation for the treatment of COVID-19: a living systematic review
Vaughan, Trott, Sapkota, Premi, Roberts et al., Changes in 25-315 hydroxyvitamin D levels post-vitamin D supplementation in people of Black and Asian 316 ethnicities and its implications during COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review, Nutr Diet
Wang, Wang, Li, Chen, Han et al., Human Cathelicidin Inhibits 325 SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Killing Two Birds with One Stone, ACS Infect Dis
Webb, Kazantzidis, Kift, Farrar, Wilkinson et al., Colour Counts: 338 Sunlight and Skin Type as Drivers of Vitamin D Deficiency at UK Latitudes, Nutrients
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/qjmed/hcac040",
"ISSN": [
"1460-2725",
"1460-2393"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/qjmed/hcac040",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background and Aim</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The evidence regarding the efficacy of vitamin D supplementation in reducing severity of COVID-19 is still insufficient. This is partially due to the lack of primary robust trial-based data and heterogenous study designs. This evidence summary, aims to study the effect of vitamin D supplementation on morbidity and mortality in hospitalized COVID-19 patients.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>For this study, systematic reviews and meta-analysis published from December 2019 to January 2022 presenting the impact of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19 severity were screened and selected from PubMed and Google scholar. After initial screening, 10 eligible reviews were identified and quality of included reviews were assessed using AMSTAR and GRADE tools and overlapping among the primary studies used were also assessed.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The number of primary studies included in the systematic reviews ranged from 3-13. Meta-analysis of seven systematic reviews showed strong evidence that vitamin D supplementation reduces the risk of mortality (Odds ratio: 0.48, 95% CI: 0.346-0.664; p &lt; 0.001) in COVID patients. It was also observed that supplementation reduces the need for intensive care (Odds ratio: 0.35; 95%CI: 0.28-0.44; p &lt; 0.001) and mechanical ventilation (Odds ratio: 0.54; 95% CI: 0.411-0.708; p &lt; 0.001) requirement. The findings were robust and reliable as level of heterogeneity was considerably low. Qualitative analysis showed that supplements (oral and IV) are well tolerated, safe and effective in COVID patients.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Findings of this study shows that vitamin D supplementation is effective in reducing COVID-19 severity. Hence vitamin D should be recommended as an adjuvant therapy for COVID-19.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Assistant Professor, Indian Institute of Public Health Gandhinagar, Gujarat, 382042, India"
}
],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "Komal",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "MPH Student, Indian Institute of Public Health Gandhinagar, Gujarat, 382042, India"
}
],
"family": "V P",
"given": "Varna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "MPH Student, Indian Institute of Public Health Gandhinagar, Gujarat, 382042, India"
}
],
"family": "Sharma",
"given": "Ujeeta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Director, Indian Institute of Public Health Gandhinagar, Gujarat, 382042, India"
}
],
"family": "Mavalankar",
"given": "Dileep",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"QJM: An International Journal of Medicine"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-09T12:14:07Z",
"timestamp": 1644408847000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-15T14:57:16Z",
"timestamp": 1644937036000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-15T15:15:18Z",
"timestamp": 1644938118891
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "1460-2725"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1460-2393"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
15
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/journals/pages/open_access/funder_policies/chorus/standard_publication_model",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-15T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1644883200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/qjmed/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/qjmed/hcac040/42535932/hcac040.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/qjmed/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/qjmed/hcac040/42535932/hcac040.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
15
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
15
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Does vitamin D supplementation reduce COVID-19 severity? - a systematic review"
],
"type": "journal-article"
}
