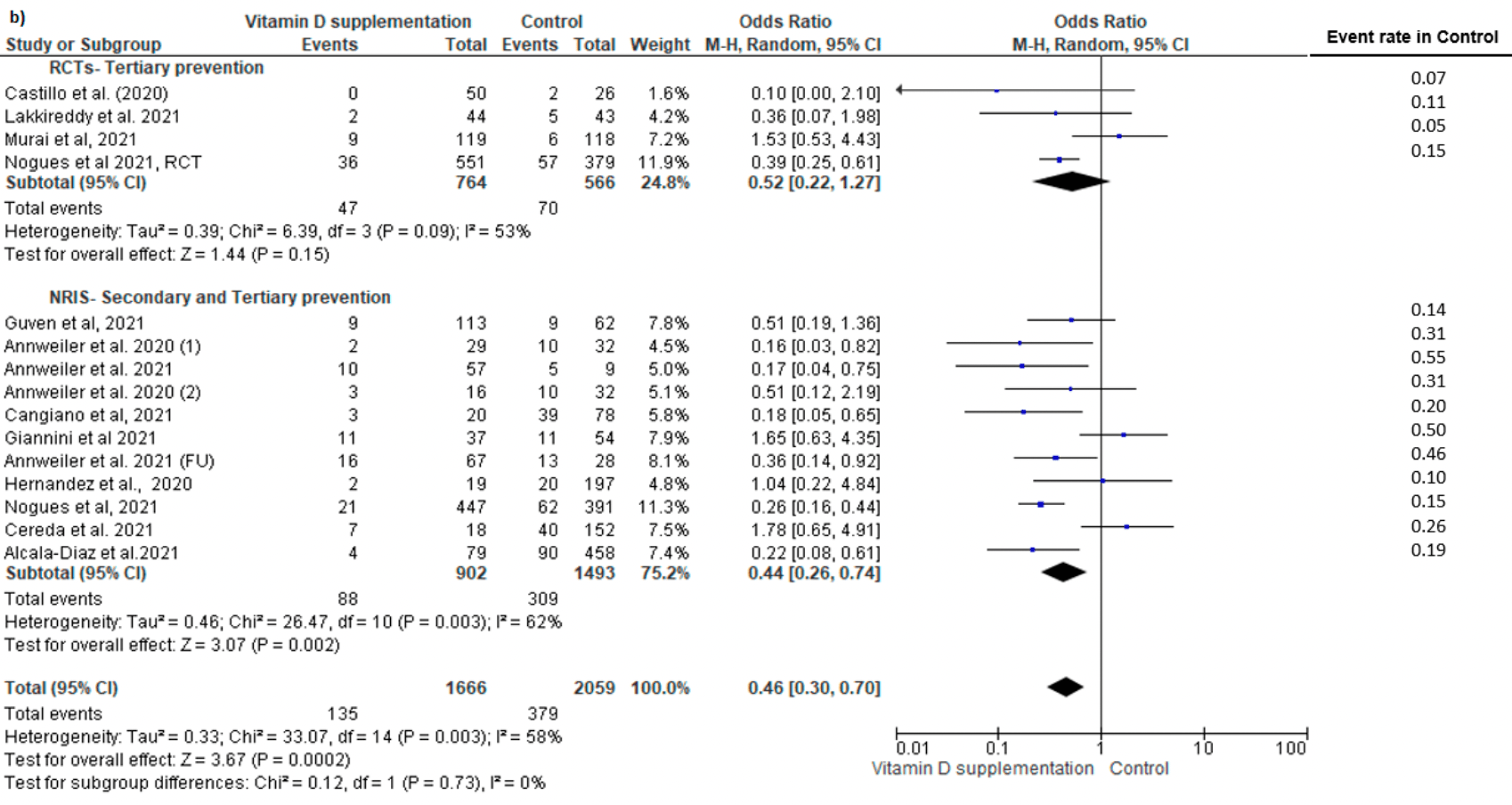
Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation on COVID-19 Related Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14102134, May 2022
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Systematic review and meta analysis showing significantly lower ICU admission and mortality with vitamin D treatment. There was no significant difference for cases.
20 meta-analyses show significant improvements with vitamin D treatment for mortality1-14,
mechanical ventilation1,5,6,11,15-17 ,
ICU admission1,3,5,6,9,11,13,15-19 ,
hospitalization11,
severity2,4,5,10,20 , and
cases7,19,20 .
Currently there are 135 vitamin D treatment for COVID-19 studies, showing 39% lower mortality [32‑45%], 17% lower ventilation [-5‑35%], 45% lower ICU admission [28‑57%], 22% lower hospitalization [13‑30%], and 17% fewer cases [9‑25%].
|
risk of death, 54.0% lower, RR 0.46, p < 0.001.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 65.0% lower, RR 0.35, p < 0.001.
|
|
risk of case, 9.0% lower, RR 0.91, p = 0.11.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Shah et al., Does vitamin D supplementation reduce COVID-19 severity? - a systematic review, QJM: An International Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcac040.
2.
Nikniaz et al., The impact of vitamin D supplementation on mortality rate and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.34172/PS.2021.13.
3.
Hosseini et al., Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation on COVID-19 Related Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14102134.
4.
D’Ecclesiis et al., Vitamin D and SARS-CoV2 infection, severity and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0268396.
5.
Xie et al., Micronutrient perspective on COVID-19: Umbrella review and reanalysis of meta-analyses, Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, doi:10.1080/10408398.2023.2174948.
6.
Hariyanto et al., Vitamin D supplementation and Covid‐19 outcomes: A systematic review, meta‐analysis and meta‐regression, Reviews in Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/rmv.2269.
7.
Begum et al., The Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19 Survival and Prevention: A Meta-analysis, Sudan Journal of Medical Sciences, doi:10.18502/sjms.v19i1.15776.
8.
Jamilian et al., The role of vitamin D in outcomes of critical care in COVID-19 patients: Evidence from an umbrella meta-analysis of interventional and observational studies, Public Health Nutrition, doi:10.1017/S1368980024000934.
9.
Sobczak et al., Effect of Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Severe COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16101402.
10.
Petrelli et al., Therapeutic and prognostic role of vitamin D for COVID-19 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 43 observational studies, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105883.
11.
Asla et al., Vitamin D on COVID-19 Patients During the Pandemic, 2022. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Current Research in Nutrition and Food Science Journal, doi:10.12944/CRNFSJ.11.1.3.
12.
Kow et al., The impact of vitamin D administration on mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-024-01564-2.
13.
Zhang et al., The impact of supplementing vitamin D through different methods on the prognosis of COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1441847.
14.
Doustmohammadian et al., Impact of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19 mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Nutrition Clinique et Métabolisme, doi:10.1016/j.nupar.2025.12.001.
15.
Meng et al., The role of vitamin D in the prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Clinical Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2023.09.008.
16.
Yang et al., Therapeutic effects of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19 aggravation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1367686.
17.
Szarpak et al., Vitamin D supplementation to treat SARS-CoV-2 positive patients. Evidence from meta-analysis, Cardiology Journal, doi:10.5603/CJ.a2021.0122.
18.
Tentolouris et al., The effect of vitamin D supplementation on mortality and intensive care unit admission of COVID-19 patients. A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression, Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews, doi:10.1002/dmrr.3517.
Hosseini et al., 20 May 2022, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
Contact: banafsheh.hosseini@umontreal.ca (corresponding author), asmae.el.abd.hsj@ssss.gouv.qc.ca, francine.m.ducharme@umontreal.ca.
Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation on COVID-19 Related Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14102134
The COVID-19 outbreak has rapidly expanded to a global pandemic; however, our knowledge is limited with regards to the protective factors against this infection. The aim of this systematic literature review and meta-analysis was to evaluate the impact of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19 related outcomes. A systematic search of relevant papers published until January 2022 was conducted to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and non-randomized studies of intervention (NRISs). The primary outcomes included the risk of COVID-19 infection (primary prevention studies on uninfected individuals), hospital admission (secondary prevention studies on mild COVID-19 cases), and ICU admission and mortality rate (tertiary prevention studies on hospitalized COVID-19 patients). We identified five studies (one RCT, four NRISs) on primary prevention, with five (two RCTs, three NRISs) on secondary prevention, and 13 (six RCTs, seven NRISs) on tertiary prevention. Pooled analysis showed no significant effect on the risk of COVID-19 infection. No meta-analysis was possible on hospitalization risk due to paucity of data. Vitamin D supplementation was significantly associated with a reduced risk of ICU admission (RR = 0.35, 95% CI: 0.20, 0.62) and mortality (RR = 0.46, 95% CI: 0.30, 0.70). Vitamin D supplementation had no significant impact on the risk of COVID-19 infection, whereas it showed protective effects against mortality and ICU admission in COVID-19 patients.
Author Contributions: B.H. designed the study, performed the literature search and statistical analysis, and drafted the manuscript. B.H. and A.E.A. performed data extraction and assessed the quality of the included studies. F.M.D. supervised the conduct of this review from inception to analysis and edited the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript. Institutional Review Board Statement: Not Applicable. Informed Consent Statement: Not Applicable.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Abdulateef, Rahman, Salih, Osman, Mahmood et al., COVID-19 severity in relation to sociodemographics and vitamin D use, Open Med, doi:10.1515/med-2021-0273
Alcala-Diaz, Limia-Perez, Gomez-Huelgas, Martin-Escalante, Cortes-Rodriguez et al., Calcifediol Treatment and Hospital Mortality Due to COVID-19: A Cohort Study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13061760
Annweiler, Beaudenon, Simon, Guenet, Otekpo et al., Vitamin D supplementation prior to or during COVID-19 associated with better 3-month survival in geriatric patients: Extension phase of the GERIA-COVID study, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105958
Annweiler, Corvaisier, Gautier, Dubée, Legrand et al., Vitamin D Supplementation Associated to Better Survival in Hospitalized Frail Elderly COVID-19 Patients: The GERIA-COVID Quasi-Experimental Study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113377
Annweiler, Hanotte, De L'eprevier, Sabatier, Lafaie et al., Vitamin D and survival in COVID-19 patients: A quasi-experimental study, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105771
Butler-Laporte, Nakanishi, Mooser, Morrison, Abdullah et al., Vitamin D and COVID-19 susceptibility and severity in the COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative: A Mendelian randomization study, PLoS Med, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1003605
Caballero-García, Pérez-Valdecantos, Guallar, Caballero-Castillo, Roche et al., Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Muscle Status in Old Patients Recovering from COVID-19 Infection, Medicina
Cangiano, Fatti, Danesi, Gazzano, Croci et al., Mortality in an Italian nursing home during COVID-19 pandemic: Correlation with gender, age, ADL, vitamin D supplementation, and limitations of the diagnostic tests, Aging, doi:10.18632/aging.202307
Castillo, Costa, Barrios, Díaz, Miranda et al., Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751
Cereda, Bogliolo, Lobascio, Barichella, Zecchinelli et al., Vitamin D supplementation and outcomes in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients from the outbreak area of Lombardy, Italy, Nutrition
Chen, Wan, Han, Li, Zhang et al., Effect of vitamin D supplementation on the level of circulating high-sensitivity C-reactive protein: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu6062206
Deeks, Altman, Chapter 10: Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses
Giannini, Passeri, Tripepi, Sella, Fusaro et al., Effectiveness of In-Hospital Cholecalciferol Use on Clinical Outcomes in Comorbid COVID-19 Patients: A Hypothesis-Generating Study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13010219
Güven, Gültekin, The effect of high-dose parenteral vitamin D3 on COVID-19-related inhospital mortality in critical COVID-19 patients during intensive care unit admission: An observational cohort study, Eur. J. Clin. Nutr
Handu, Comparison of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics updated Quality Criteria Checklist and Cochrane's ROB 2.0 as risk of bias tools
Hernández, Nan, Fernandez-Ayala, García-Unzueta, Hernández-Hernández et al., Vitamin D Status in Hospitalized Patients with SARS-CoV-2
Higgins, Page, Elbers, Sterne, Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in a randomized trial
Hosseini, Tremblay, Longo, Golchi, White et al., Prevention of COVID-19 with Oral Vitamin D Supplemental Therapy in Essential healthCare Teams (PROTECT): Ancillary Study of a Randomized Controlled Trial
Jolliffe, Camargo, Sluyter, Aglipay, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data from randomised controlled trials, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00051-6
Lakkireddy, Gadiga, Malathi, Karra, Raju et al., Impact of daily high dose oral vitamin D therapy on the inflammatory markers in patients with COVID 19 disease, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-90189-4
Ling, Broad, Murphy, Pappachan, Pardesi-Newton et al., High-Dose Cholecalciferol Booster Therapy is Associated with a Reduced Risk of Mortality in Patients with COVID-19: A Cross-Sectional Multi-Centre Observational Study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12123799
Ma, Zhou, Heianza, Qi, Habitual use of vitamin D supplements and risk of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection: A prospective study in UK Biobank, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqaa381
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of Vitamin D Status and Other Clinical Characteristics With COVID-19 Test Results, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722
Moher, Liberati, Tetzlaff, Altman, The, Group. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement, J. Clin. Epidemiol, doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2009.06.005
Murai, Fernandes, Sales, Pinto, Goessler et al., Effect of a Single High Dose of Vitamin D3 on Hospital Length of Stay in Patients with Moderate to Severe COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.26848
Nikniaz, Akbarzadeh, Hosseinifard, Hosseini, The impact of vitamin D supplementation on mortality rate and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis, MedRxiv, doi:10.34172/PS.2021.13
Nogues, Ovejero, Pineda-Moncusí, Bouillon, Arenas et al., Calcifediol treatment and COVID-19-related outcomes, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab405
Nogués, Diana, Quesada-Gomez, Bouillon, Arenas et al., Calcifediol Treatment and COVID-19-Related Outcomes
Oristrell, Oliva, Subirana, Casado, Domínguez et al., Association of Calcitriol Supplementation with Reduced COVID-19 Mortality in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Population-Based Study, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines9050509
Page, Sterne, Chapter 13: Assessing risk of bias due to missing results in a synthesis
Pal, Banerjee, Bhadada, Shetty, Singh et al., Vitamin D supplementation and clinical outcomes in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, J. Endocrinol. Investig, doi:10.1007/s40618-021-01614-4
Pereira, Dantas Damascena, Galvão Azevedo, De Almeida Oliveira, Da Mota Santana, Vitamin D deficiency aggravates COVID-19: Systematic review and meta-analysis, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr, doi:10.1080/10408398.2020.1841090
Rastogi, Bhansali, Khare, Suri, Yaddanapudi et al., Short term, high-dose vitamin D supplementation for COVID-19 disease: A randomised, placebo-controlled, study (SHADE study), Postgrad. Med. J, doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-139065
Rawat, Roy, Maitra, Shankar, Khanna et al., Vitamin D supplementation and COVID-19 treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102189
Reeves, Deeks, Higgins, Shea, Chapter 24: Including non-randomized studies on intervention effects
Sabico, Enani, Sheshah, Aljohani, Aldisi et al., Effects of a 2-Week 5000 IU versus 1000 IU Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Recovery of Symptoms in Patients with Mild to Moderate Covid-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13072170
Shah, Saxena, Mavalankar, Vitamin D supplementation, COVID-19 and disease severity: A meta-analysis, QJM Int. J. Med, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcab009
Sánchez-Zuno, González-Estevez, Matuz-Flores, Macedo-Ojeda, Hernández-Bello et al., Vitamin D Levels in COVID-19 Outpatients from Western Mexico: Clinical Correlation and Effect of Its Supplementation, J. Clin. Med, doi:10.3390/jcm10112378
Worldometer, None
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14102134",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu14102134",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The COVID-19 outbreak has rapidly expanded to a global pandemic; however, our knowledge is limited with regards to the protective factors against this infection. The aim of this systematic literature review and meta-analysis was to evaluate the impact of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19 related outcomes. A systematic search of relevant papers published until January 2022 was conducted to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and non-randomized studies of intervention (NRISs). The primary outcomes included the risk of COVID-19 infection (primary prevention studies on uninfected individuals), hospital admission (secondary prevention studies on mild COVID-19 cases), and ICU admission and mortality rate (tertiary prevention studies on hospitalized COVID-19 patients). We identified five studies (one RCT, four NRISs) on primary prevention, with five (two RCTs, three NRISs) on secondary prevention, and 13 (six RCTs, seven NRISs) on tertiary prevention. Pooled analysis showed no significant effect on the risk of COVID-19 infection. No meta-analysis was possible on hospitalization risk due to paucity of data. Vitamin D supplementation was significantly associated with a reduced risk of ICU admission (RR = 0.35, 95% CI: 0.20, 0.62) and mortality (RR = 0.46, 95% CI: 0.30, 0.70). Vitamin D supplementation had no significant impact on the risk of COVID-19 infection, whereas it showed protective effects against mortality and ICU admission in COVID-19 patients.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu14102134"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hosseini",
"given": "Banafsheh",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "El Abd",
"given": "Asmae",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5096-0614",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ducharme",
"given": "Francine M.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-20T08:27:22Z",
"timestamp": 1653035242000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-20T08:54:42Z",
"timestamp": 1653036882000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100000024",
"award": [
"172650"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Canadian Institutes of Health Research"
},
{
"award": [
"N/A"
],
"name": "Jamieson Wellness"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-20T09:16:35Z",
"timestamp": 1653038195262
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "10",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
20
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "10",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1653004800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/14/10/2134/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "2134",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
20
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
20
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "Worldometer\nhttps://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00051-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105771",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113377",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13061760",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12123799",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-139065",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13072170",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm10112378",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/med-2021-0273",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.26848",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-90189-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines9050509",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111055",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2020.1841090",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40618-021-01614-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"article-title": "Chapter 24: Including non-randomized studies on intervention effects",
"author": "Reeves",
"key": "ref18",
"series-title": "Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jclinepi.2009.06.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref19"
},
{
"article-title": "Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in a randomized trial",
"author": "Higgins",
"key": "ref20",
"series-title": "Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "ref21",
"unstructured": "Quality Criteria Checklist: Primary Research in Evidence Analysis Manual: Steps in the Academy Evidence Analysis Process\nhttp://andevidencelibrary.com/files/Docs/2012_Jan_EA_Manual.pdf"
},
{
"article-title": "Comparison of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics updated Quality Criteria Checklist and Cochrane’s ROB 2.0 as risk of bias tools",
"author": "Handu",
"key": "ref22",
"series-title": "Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews",
"volume": "Volume 9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Chapter 10: Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses",
"author": "Deeks",
"key": "ref23",
"series-title": "Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Chapter 13: Assessing risk of bias due to missing results in a synthesis",
"author": "Page",
"key": "ref24",
"series-title": "Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "ref25",
"unstructured": "Calcifediol Treatment and COVID-19-Related Outcomes\nhttps://ssrn.com/abstract=3771318"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/medicina57101079",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref26"
},
{
"key": "ref27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105958",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41430-021-00984-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.202307",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/nqaa381",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgab405",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgaa733",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13010219",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1003605",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/qjmed/hcab009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.34172/PS.2021.13",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102189",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref39"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu6062206",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref40"
}
],
"reference-count": 40,
"references-count": 40,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/14/10/2134"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Food Science",
"Nutrition and Dietetics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation on COVID-19 Related Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "14"
}
