Micronutrient perspective on COVID-19: Umbrella review and reanalysis of meta-analyses
et al., Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, doi:10.1080/10408398.2023.2174948, PROSPERO CRD42022353953, Feb 2023
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
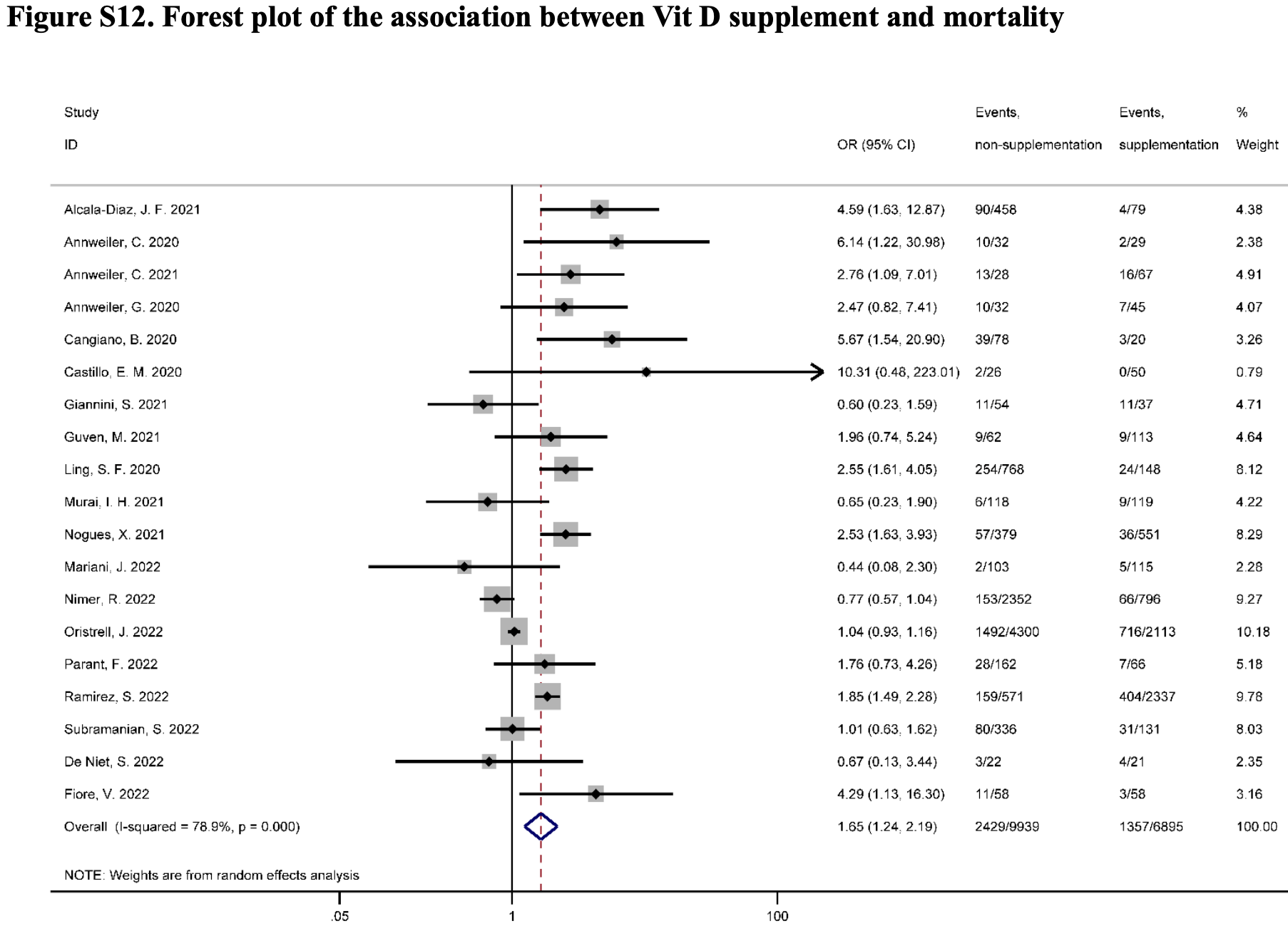
Systematic review and meta analysis of micronutrient supplementation, showing vitamin D supplementation associated with lower mortality, mechanical ventilation, ICU admission, and severity. Note that forest plots have OR>1 favoring supplementation. Vitamin D deficiency was also associated with higher mortality, mechanical ventilation, ICU admission, severity, and cases.
20 meta-analyses show significant improvements with vitamin D treatment for mortality1-14,
mechanical ventilation1,5,6,11,15-17 ,
ICU admission1,3,5,6,9,11,13,15-19 ,
hospitalization11,
severity2,4,5,10,20 , and
cases7,19,20 .
Currently there are 135 vitamin D treatment for COVID-19 studies, showing 39% lower mortality [32‑45%], 17% lower ventilation [-5‑35%], 45% lower ICU admission [28‑57%], 22% lower hospitalization [13‑30%], and 17% fewer cases [9‑25%].
Study covers zinc and vitamin D.
1.
Shah et al., Does vitamin D supplementation reduce COVID-19 severity? - a systematic review, QJM: An International Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcac040.
2.
Nikniaz et al., The impact of vitamin D supplementation on mortality rate and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.34172/PS.2021.13.
3.
Hosseini et al., Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation on COVID-19 Related Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14102134.
4.
D’Ecclesiis et al., Vitamin D and SARS-CoV2 infection, severity and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0268396.
5.
Xie et al., Micronutrient perspective on COVID-19: Umbrella review and reanalysis of meta-analyses, Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, doi:10.1080/10408398.2023.2174948.
6.
Hariyanto et al., Vitamin D supplementation and Covid‐19 outcomes: A systematic review, meta‐analysis and meta‐regression, Reviews in Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/rmv.2269.
7.
Begum et al., The Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19 Survival and Prevention: A Meta-analysis, Sudan Journal of Medical Sciences, doi:10.18502/sjms.v19i1.15776.
8.
Jamilian et al., The role of vitamin D in outcomes of critical care in COVID-19 patients: Evidence from an umbrella meta-analysis of interventional and observational studies, Public Health Nutrition, doi:10.1017/S1368980024000934.
9.
Sobczak et al., Effect of Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Severe COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16101402.
10.
Petrelli et al., Therapeutic and prognostic role of vitamin D for COVID-19 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 43 observational studies, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105883.
11.
Asla et al., Vitamin D on COVID-19 Patients During the Pandemic, 2022. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Current Research in Nutrition and Food Science Journal, doi:10.12944/CRNFSJ.11.1.3.
12.
Kow et al., The impact of vitamin D administration on mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-024-01564-2.
13.
Zhang et al., The impact of supplementing vitamin D through different methods on the prognosis of COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1441847.
14.
Doustmohammadian et al., Impact of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19 mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Nutrition Clinique et Métabolisme, doi:10.1016/j.nupar.2025.12.001.
15.
Meng et al., The role of vitamin D in the prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Clinical Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2023.09.008.
16.
Yang et al., Therapeutic effects of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19 aggravation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1367686.
17.
Szarpak et al., Vitamin D supplementation to treat SARS-CoV-2 positive patients. Evidence from meta-analysis, Cardiology Journal, doi:10.5603/CJ.a2021.0122.
18.
Tentolouris et al., The effect of vitamin D supplementation on mortality and intensive care unit admission of COVID-19 patients. A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression, Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews, doi:10.1002/dmrr.3517.
Xie et al., 15 Feb 2023, peer-reviewed, 16 authors, trial PROSPERO CRD42022353953.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2023.2174948",
"ISSN": [
"1040-8398",
"1549-7852"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2023.2174948",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1080/10408398.2023.2174948"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "Peer Review Statement",
"name": "peerreview_statement",
"order": 1,
"value": "The publishing and review policy for this title is described in its Aims & Scope."
},
{
"URL": "http://www.tandfonline.com/action/journalInformation?show=aimsScope&journalCode=bfsn20",
"label": "Aim & Scope",
"name": "aims_and_scope_url",
"order": 2,
"value": "http://www.tandfonline.com/action/journalInformation?show=aimsScope&journalCode=bfsn20"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 3,
"value": "2023-02-15"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Evidence-Based Medicine Center, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China"
},
{
"name": "The First Clinical Medical College of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China"
},
{
"name": "Key Laboratory of Evidence Based Medicine and Knowledge Translation of Gansu Province, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China"
}
],
"family": "Xie",
"given": "Yafei",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Evidence-Based Medicine Center, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China"
}
],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Jianguo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The First Clinical Medical College of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China"
}
],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Dan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The First Clinical Medical College of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China"
}
],
"family": "Guo",
"given": "Mingyue",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The First Clinical Medical College of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China"
}
],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Mengxiang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Evidence-Based Medicine Center, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Health Research Methods, Evidence, and Impact, McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Gao",
"given": "Ya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Evidence-Based Medicine Center, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Health Research Methods, Evidence, and Impact, McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Ming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Nursing, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China"
}
],
"family": "Shi",
"given": "Jiyuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Public Health and Primary Care, Academic Centre for Nursing and Midwifery, KU Leuven – University of Leuven, Leuven, Belgium"
}
],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Kelu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Evidence-Based Nursing Center, School of Nursing, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China"
}
],
"family": "Zheng",
"given": "Qingyong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Evidence-Based Nursing Center, School of Nursing, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China"
}
],
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Liang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Evidence-Based Medicine Center, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China"
}
],
"family": "Qin",
"given": "Yu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "First Operating Room, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China"
}
],
"family": "Hu",
"given": "Rui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The Second Clinical Medical School of Nanchang University, Jiangxi, China"
}
],
"family": "Wei",
"given": "Jia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Evidence-Based Medicine Center, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin, China"
}
],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Junhua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Evidence-Based Medicine Center, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China"
},
{
"name": "Key Laboratory of Evidence Based Medicine and Knowledge Translation of Gansu Province, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China"
}
],
"family": "Tian",
"given": "Jinhui",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition",
"container-title-short": "Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"www.tandfonline.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-16T09:31:18Z",
"timestamp": 1676539878000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-21T07:37:42Z",
"timestamp": 1676965062000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-22T05:36:01Z",
"timestamp": 1677044161760
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
15
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/10408398.2023.2174948",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "301",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1-19",
"prefix": "10.1080",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
15
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
15
]
]
},
"publisher": "Informa UK Limited",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.755745",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2021.660420",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/ijem.ijem_115_21",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114513001505",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/iid3.528",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12123679",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173099",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1063/5.0021554",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10534-021-00355-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1590/1806-9282.20220165",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ncp.10832",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jtemb.2022.126956",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abd4585",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jtemb.2022.127055",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.12.033",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2012.709550",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2014.11.008",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2134",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu7043011",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu9111211",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thoraxjnl-2012-202125",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2014/426740",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12937-021-00744-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101168",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.archger.2021.104411",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0026"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-206680",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0027"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1381612003401190",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0028"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-021-02997-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0029"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2022.814587",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0030"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ijcp.14675",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0031"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/fmb.09.87",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0032"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12010236",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0033"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0034"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu7064240",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0035"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2018.1522613",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0036"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0037"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11092101",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0038"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2269",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0039"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.11.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0040"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0041"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12123760",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0042"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.08.017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0043"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14102134",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0044"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18433/jpps32590",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0045"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0046"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1468-2389.00156",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0047"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2020-047474",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0048"
},
{
"DOI": "10.24304/kjcp.2021.31.2.136",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0049"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0050"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/s000711451800209x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0051"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biom8030069",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0052"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ccr3.4010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0053"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3126/ajms.v11i6.29911",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0054"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ctim.2021.102797",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0055"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.gene.2018.08.017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0056"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30920-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0057"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1123933",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0058"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.12.077",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0059"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/15287394.2019.1592044",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0060"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10101531",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0061"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-981-13-2835-0_15",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0062"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2213-8587(20)30183-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0063"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.06.21.162396",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "CIT0064",
"unstructured": "Mok, C. K., L. N. Yan, B. A. Ahidjo, et al. 2020. Calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D, is a promising candidate for COVID-19 prophylaxis. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tree.2018.11.007",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0065"
},
{
"DOI": "10.34172/PS.2021.13",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0066"
},
{
"DOI": "10.17305/bjbms.2021.7009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0067"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13643-016-0384-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0068"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nutres.2017.02.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0069"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1002028",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0070"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13091",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0071"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/dmp.2021.177",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0072"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2020.1841090",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0073"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105883",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0074"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jclinepi.2013.11.007",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0075"
},
{
"author": "Pollock M.",
"key": "CIT0076",
"volume-title": "Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109814",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0077"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102324",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0078"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102189",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0079"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/advances/nmz013",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0080"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mnfr.201000174",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0081"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2288-9-10",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0082"
},
{
"author": "Setyarini I. B.",
"first-page": "797",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Journal of International Dental and Medical Research",
"key": "CIT0083",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.j4008",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0084"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26254",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0085"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.l4898",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0086"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD015043",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0087"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20452/pamw.16048",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0088"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5603/CJ.a2021.0072",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0089"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40001-022-00694-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0090"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10654-020-00678-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0091"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0092"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2021.624559",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0093"
},
{
"author": "The Joanna Briggs Institute",
"key": "CIT0094",
"volume-title": "Methodology for JBI umbrella reviews",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-17307-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0095"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114520003827",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0096"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines6030063",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0097"
},
{
"DOI": "10.23970/AHRQEPCMETHGUIDE2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "CIT0098",
"unstructured": "Viswanathan, M., C. D. Patnode, N. D. Berkman, et al. 2017. Assessing the risk of bias in systematic reviews of health care interventions. In Methods guide for effectiveness and comparative effectiveness reviews [Internet], https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519366/"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.058",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0099"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.C109.071225",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0100"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0101"
},
{
"key": "CIT0102",
"unstructured": "Wells, G. A., B. Shea, D. O’Connell, et al. 2000. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. Oxford."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.12839",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0103"
},
{
"author": "World Health Organization",
"key": "CIT0104",
"volume-title": "WHO coronavirus disease (COVID-19) dashboard",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30260-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0105"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0106"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0107"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26515",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0108"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2020.06.082",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0109"
}
],
"reference-count": 109,
"references-count": 109,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/10408398.2023.2174948"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering",
"General Medicine",
"Food Science"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Micronutrient perspective on COVID-19: Umbrella review and reanalysis of meta-analyses",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/tandf_crossmark_01"
}
