Colchicine treatment can improve outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis
et al., Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology, doi:10.1111/1440-1681.13488, Mar 2021
Colchicine for COVID-19
5th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.0000049 from 54 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
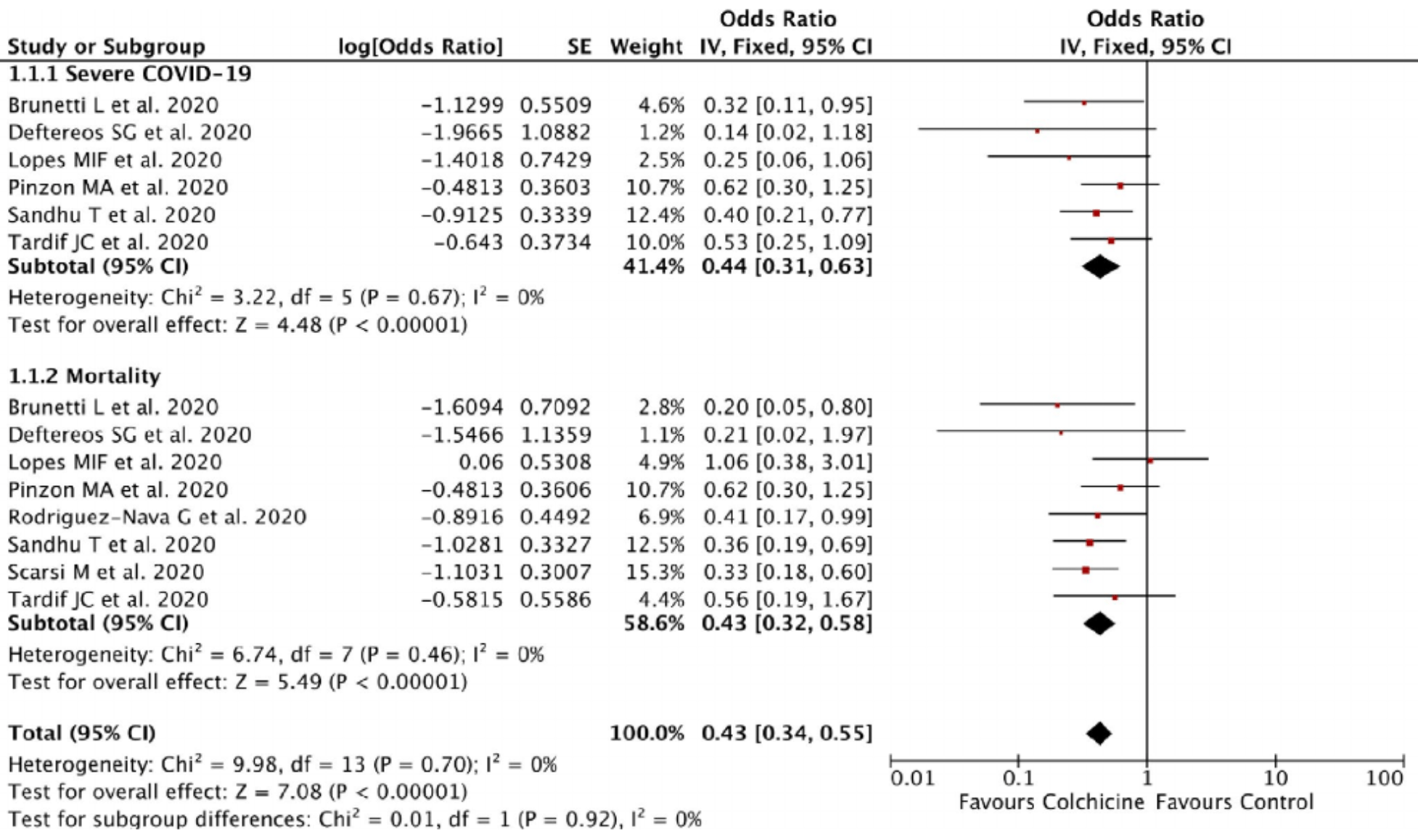
Meta analysis concluding that colchicine can reduce severity and mortality in COVID-19 patients, mortality OR 0.43 [0.32-0.58].
10 meta-analyses show significant improvements with colchicine for mortality1-8,
oxygen therapy8,
hospitalization9, and
severity10.
Currently there are 54 colchicine for COVID-19 studies, showing 22% lower mortality [12‑31%], 29% lower ventilation [-15‑56%], 34% lower ICU admission [8‑52%], 17% lower hospitalization [9‑25%], and 9% more cases [-8‑29%].
1.
Zein et al., Effect of colchicine on mortality in patients with COVID-19 – A systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2022.102395.
2.
Rai et al., The Potential Role of Colchicine in Reducing Mortality and Mechanical Ventilation Rates in COVID-19 Infection: A Meta-analysis, Journal of Advances in Medicine and Medical Research, doi:10.9734/jammr/2022/v34i2031503.
3.
Elshafei et al., Colchicine use might be associated with lower mortality in COVID‐19 patients: A meta‐analysis, European Journal of Clinical Investigation, doi:10.1111/eci.13645.
4.
Lien et al., Repurposing Colchicine in Treating Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Life, doi:10.3390/life11080864.
5.
Danjuma et al., Does Colchicine Reduce Mortality in Patients with Covid-19 Clinical Syndrome? An Umbrella Review of Published Meta-Analyses, Elsevier BV, doi:10.2139/ssrn.4447127.
6.
Salah et al., Meta-analysis of the Effect of Colchicine on Mortality and Mechanical Ventilation in COVID-19, The American Journal of Cardiology, doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2021.02.005.
7.
Golpour et al., The effectiveness of Colchicine as an anti-inflammatory drug in the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019: Meta-analysis, International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology, doi:10.1177/20587384211031763.
8.
Elshiwy et al., The role of colchicine in the management of COVID-19: a meta-analysis, BMC Pulmonary Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12890-024-03001-0.
Hariyanto et al., 14 Mar 2021, peer-reviewed, 5 authors.
Colchicine treatment can improve outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19): A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology, doi:10.1111/1440-1681.13488
Currently, there is no widely acceptable and proven effective treatment for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Colchicine has been shown to offer a benefit in reducing the inflammation in several inflammatory diseases. This study aims to analyze the efficacy of colchicine administration and outcomes of COVID-19. We systematically searched the PubMed and Europe PMC database using specific keywords related to our aims until January 29, 2021. All articles published on COVID-19 and colchicine treatment were retrieved. The quality of the study was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) tool for observational studies and Revised Cochrane risk-of-bias tool for randomized trials (RoB 2) for clinical trial studies. Statistical analysis was done using Review Manager 5.4 software. A total of eight studies with 5778 COVID-19 patients were included in this meta-analysis. This meta-analysis showed that the administration of colchicine was associated with improvement of outcomes of COVID-19 [OR 0.43 (95% CI 0.34-0.55), p < 0.00001, I 2 = 0%, fixed-effect modelling] and its subgroup which comprised of reduction from severe COVID-19 [OR 0.44 (95% CI 0.31-0.63), p < 0.00001, I 2 = 0%, fixed-effect modelling] and reduction of mortality rate from COVID-19 [OR 0.43 (95% CI 0.32-0.58), p < 0.00001, I 2 = 0%, fixed-effect modelling]. Our study suggests the routine use of colchicine for treatment modalities of COVID-19 patients. More randomized clinical trial studies are still needed to confirm the results from this study.
References
Brunetti, Diawara, Tsai, Colchicine to weather the cytokine storm in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, J Clin Med
Deftereos, Giannopoulos, Vrachatis, Effect of colchicine vs standard care on cardiac and inflammatory biomarkers and clinical outcomes in patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019: the GRECCO-19 randomized clinical trial, JAMA Netw Open
Della-Torre, Campochiaro, Cavalli, Interleukin-6 blockade with sarilumab in severe COVID-19 pneumonia with systemic hyperinflammation: an open-label cohort study, Ann Rheum Dis
Della-Torre, Della-Torre, Kusanovic, Treating COVID-19 with colchicine in community healthcare setting, Clin Immunol
Della-Torre, Ramirez, Dagna, Tresoldi, Colchicine treatment in community healthcare setting to prevent severe COVID-19, Ann Rheum Dis, doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218759
Hariyanto, Halim, Jodhinata, Yanto, Kurniawan, Colchicine treatment can improve outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis, Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol
Hariyanto, Hardi, Kurniawan, Efficacy of Lopinavir/Ritonavir compared with standard care for treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a systematic review, Infect Disord Drug Targets, doi:10.2174/1871526520666201029125725
Hariyanto, Japar, Kwenandar, Inflammatory and hematologic markers as predictors of severe outcomes in COVID-19 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Am J Emerg Med
Hariyanto, Kurniawan, Anemia is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, Transfus Apher Sci
Hariyanto, Kurniawan, Statin therapy did not improve the inhospital outcome of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Hariyanto, Kurniawan, Thyroid disease is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Hariyanto, Kurniawan, Tocilizumab administration is associated with the reduction in biomarkers of coronavirus disease 2019 infection, J Med Virol
Hariyanto, Putri, Arisa, Situmeang, Kurniawan, Dementia and outcomes from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Arch Gerontol Geriatr
Hariyanto, Putri, Situmeang, Kurniawan, Dementia is a predictor for mortality outcome from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci, doi:10.1007/s00406-020-01205-z
Hariyanto, Rizki, Kurniawan, Anosmia/Hyposmia is a good predictor of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection: a meta-analysis, Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol
Li, Liu, Mao, Predictive values of neutrophil-tolymphocyte ratio on disease severity and mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Crit Care
Lopes, Bonjorno, Giannini, randomized, double-blinded, placebo controlled clinical trial, doi:10.1101/2020.08.06.20169573
Margulis, Pladevall, Riera-Guardia, Quality assessment of observational studies in a drug-safety systematic review, comparison of two tools: the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale and the RTI item bank, Clin Epidemiol
Piantoni, Colombo, Airò, The rationale for the use of colchicine in COVID-19: comments on the letter by Cumhur Cure M et al, Clin Rheumatol
Pinzon, Arango, Betancur, Clinical outcome of patients with COVID-19 pneumonia treated with corticosteroids and colchicine in Colombia, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-94922/v1
Reyes, Hu, Teperman, Anti-inflammatory therapy for COVID-19 infection: the case for colchicine, Ann Rheum Dis, doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-219174
Rodriguez-Nava, Garcia, Yanez-Bello, Chung, Garcia et al., Atorvastatin associated with decreased hazard for death in COVID-19 patients admitted to an ICU: a retrospective cohort study, Crit Care
Sandhu, Tieng, Chilimuri, Franchin, A case control study to evaluate the impact of colchicine on patients admitted to the hospital with moderate to severe COVID-19 infection, Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol
Scarsi, Piantoni, Colombo, Association between treatment with colchicine and improved survival in a single-centre cohort of adult hospitalised patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome, Ann Rheum Dis
Schlesinger, Firestein, Brunetti, Colchicine in COVID-19: an old drug, new use, Curr Pharmacol Rep
Sterne, Savović, Page, RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials, BMJ
Tardif, Bouabdallaoui, Allier, Efficacy of colchicine in non-hospitalized patients with COVID-19, doi:10.1101/2021.01.26.21250494
Vitiello, Ferrara, Pelliccia, Granata, Porta, Cytokine storm and colchicine potential role in fighting SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia, Ital J Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1440-1681.13488",
"ISSN": [
"0305-1870",
"1440-1681"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1440-1681.13488",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>Currently, there is no widely acceptable and proven effective treatment for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19). Colchicine has been shown to offer a benefit in reducing the inflammation in several inflammatory diseases. This study aims to analyze the efficacy of colchicine administration and outcomes of COVID‐19. We systematically searched the PubMed and Europe PMC database using specific keywords related to our aims until January 29, 2021. All articles published on COVID‐19 and colchicine treatment were retrieved. The quality of the study was assessed using the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) tool for observational studies and Revised Cochrane risk‐of‐bias tool for randomized trials (RoB 2) for clinical trial studies. Statistical analysis was done using Review Manager 5.4 software. A total of eight studies with 5778 COVID‐19 patients were included in this meta‐analysis. This meta‐analysis showed that the administration of colchicine was associated with improvement of outcomes of COVID‐19 [OR 0.43 (95% CI 0.34–0.55), <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> < 0.00001, <jats:italic>I</jats:italic><jats:sup>2</jats:sup> = 0%, fixed‐effect modelling] and its subgroup which comprised of reduction from severe COVID‐19 [OR 0.44 (95% CI 0.31–0.63), <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> < 0.00001, <jats:italic>I</jats:italic><jats:sup>2</jats:sup> = 0%, fixed‐effect modelling] and reduction of mortality rate from COVID‐19 [OR 0.43 (95% CI 0.32–0.58), <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> < 0.00001, <jats:italic>I</jats:italic><jats:sup>2</jats:sup> = 0%, fixed‐effect modelling]. Our study suggests the routine use of colchicine for treatment modalities of COVID‐19 patients. More randomized clinical trial studies are still needed to confirm the results from this study.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1111/1440-1681.13488"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2021-01-13"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2021-02-13"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2021-03-14"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Medicine Pelita Harapan University Karawaci, Tangerang Indonesia"
}
],
"family": "Hariyanto",
"given": "Timotius Ivan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Medicine Pelita Harapan University Karawaci, Tangerang Indonesia"
}
],
"family": "Halim",
"given": "Devina Adella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Medicine Pelita Harapan University Karawaci, Tangerang Indonesia"
}
],
"family": "Jodhinata",
"given": "Claudia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine Faculty of Medicine Pelita Harapan University Karawaci, Tangerang Indonesia"
}
],
"family": "Yanto",
"given": "Theo Audi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5219-9029",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine Faculty of Medicine Pelita Harapan University Karawaci, Tangerang Indonesia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kurniawan",
"given": "Andree",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology",
"container-title-short": "Clin Exp Pharma Physio",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2021-03-15T03:14:32Z",
"timestamp": 1615778072000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-02T01:02:30Z",
"timestamp": 1693616550000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-13T18:31:46Z",
"timestamp": 1715625106161
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 51,
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
14
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2021-03-14T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1615680000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/1440-1681.13488",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.1111/1440-1681.13488",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/1440-1681.13488",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"page": "823-830",
"prefix": "10.1111",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
14
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
14
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"key": "e_1_2_9_2_1",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization.Coronavirus disease (COVID‐19): situation report.https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly‐epidemiological‐update"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-0040-1719120",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_3_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26698",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajem.2020.12.076",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.07.044",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.transci.2020.102926",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.archger.2020.104299",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_8_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Dementia is a predictor for mortality outcome from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) infection",
"author": "Hariyanto TI",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci",
"key": "e_1_2_9_9_1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.08.023",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1871526520666201029125725",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_11_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Cytokine storm and colchicine potential role in fighting SARS‐CoV‐2 pneumonia",
"author": "Vitiello A",
"first-page": "88",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Ital J Med",
"key": "e_1_2_9_12_1",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/CLEP.S66677",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.l4898",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_14_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm9092961",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.13136",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_16_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Beneficial effects of colchicine for moderate to severe COVID‐19: an interim analysis of a randomized, double‐blinded, placebo controlled clinical trial",
"author": "Lopes MIF",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "e_1_2_9_17_1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical outcome of patients with COVID‐19 pneumonia treated with corticosteroids and colchicine in Colombia",
"author": "Pinzon MA",
"journal-title": "Research Square",
"key": "e_1_2_9_18_1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03154-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_19_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2020/8865954",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_20_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217712",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_21_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Efficacy of colchicine in non‐hospitalized patients with COVID‐19",
"author": "Tardif JC",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "e_1_2_9_22_1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clim.2020.108490",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218759",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_24_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40495-020-00225-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03374-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10067-020-05232-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-219174",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218122",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_29_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 28,
"references-count": 28,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/1440-1681.13488"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Colchicine treatment can improve outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19): A systematic review and meta‐analysis",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "48"
}
