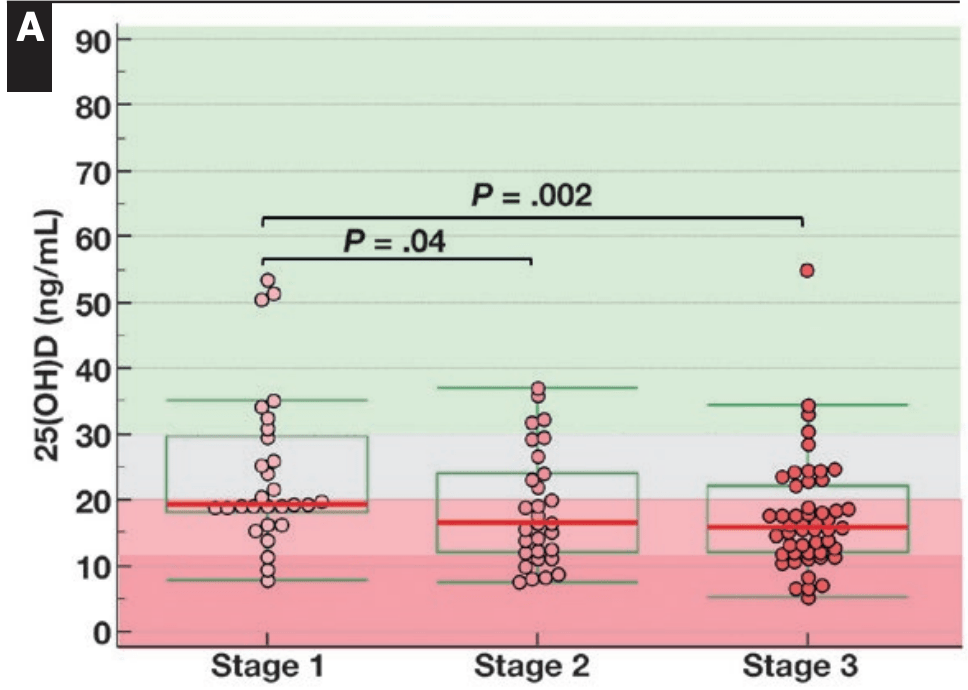
Serum 25(OH)D Level on Hospital Admission Associated With COVID-19 Stage and Mortality
et al., American Journal of Clinical Pathology, doi:10.1093/ajcp/aqaa252, Nov 2020
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 186 hospitalized patients in Belgium showing that 59% of patients were vitamin D deficient, and that non-vitamin D deficient patients had significantly lower mortality risk, RR 0.26, p = 0.015.
This is the 29th of 228 COVID-19 sufficiency studies for vitamin D, which collectively show higher levels reduce risk with p<0.0000000001.
|
risk of death, 70.1% lower, RR 0.30, p = 0.02, high D levels 7 of 77 (9.1%), low D levels 20 of 109 (18.3%), adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, >20ng/mL.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
De Smet et al., 25 Nov 2020, retrospective, Belgium, peer-reviewed, 5 authors.
Serum 25(OH)D Level on Hospital Admission Associated With COVID-19 Stage and Mortality
American Journal of Clinical Pathology, doi:10.1093/ajcp/aqaa252
Objectives: Vitamin D deficiency was previously correlated with incidence and severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). We investigated the association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) level on admission and radiologic stage and outcome of COVID-19 pneumonia.
Methods: A retrospective observational trial was done on 186 severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)-infected individuals hospitalized from March 1, 2020, to April 7, 2020, with combined chest computed tomography (CT) and 25(OH)D measurement on admission. Multivariate regression analysis was performed to study if vitamin D deficiency (25(OH)D <20 ng/mL) correlates with survival independently of confounding comorbidities. Results: Of the patients with COVID-19, 59% were vitamin D deficient on admission: 47% of females and 67% of males. In particular, male patients with COVID-19 showed progressively lower 25(OH)D with advancing radiologic stage, with deficiency rates increasing from 55% in stage 1 to 74% in stage 3. Vitamin D deficiency on admission was not confounded by age, ethnicity, chronic lung disease, coronary artery disease/hypertension, or diabetes and was associated with mortality (odds ratio [
References
Amrein, Papinutti, Mathew, Vitamin D and critical illness: what endocrinology can learn from intensive care and vice versa, Endocr Connect
Amrein, Schnedl, Holl, Effect of high-dose vitamin D3 on hospital length of stay in critically ill patients with vitamin D deficiency: the VITdAL-ICU randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Bello-Chavolla, Bahena-Lopez, Ne, Predicting mortality due to SARS-CoV-2: a mechanistic score relating obesity and diabetes to COVID-19 outcomes in Mexico
Bernheim, Mei, Huang, Chest CT findings in coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19): relationship to duration of infection, Radiology
Bikle, Nonclassic actions of vitamin D, J Clin Endocrinol Metab
Cantorna, Vitamin D and lung infection, Infect Immun
Cantorna, Yu, Bruce, The paradoxical effects of vitamin D on type 1 mediated immunity, Mol Aspects Med
Castillo, Costa, Barrios, Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: a pilot randomized clinical study, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol
Channappanavar, Perlman, Pathogenic human coronavirus infections: causes and consequences of cytokine storm and immunopathology, Semin Immunopathol
Chen, Wu, Guo, Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019, J Clin Invest
Chirumbolo, Bjørklund, Sboarina, The role of vitamin D in the immune system as a pro-survival molecule, Clin Ther
D'avolio, Avataneo, Manca, 25-Hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are lower in patients with positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2, Nutrients
Gouni-Berthold, Berthold, Vitamin D and vascular disease
Greiller, Martineau, Modulation of the immune response to respiratory viruses by vitamin D, Nutrients
Haynes, Pfeiffer, Sternberg, Selected physiologic variables are weakly to moderately associated with 29 biomarkers of diet and nutrition, NHANES 2003-2006, J Nutr
Hiemstra, De Jongh, Vitamin D deficiency in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. a chicken-or-egg story, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Hilger, Friedel, Herr, A systematic review of vitamin D status in populations worldwide, Br J Nutr
Jolliffe, Stefanidis, Wang, Vitamin D metabolism is dysregulated in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Kaufman, Niles, Kroll, SARS-CoV-2 positivity rates associated with circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels, PLoS One
Liu, Stenger, Li, Toll-like receptor triggering of a vitamin D-mediated human antimicrobial response, Science
Macaya, Paeres, Valls, Interaction between age and vitamin D deficiency in severe COVID-19 infection, Nutr Hosp
Maghbooli, Sahraian, Ebrahimi, Vitamin D sufficiency, a serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D at least 30 ng/mL reduced risk for adverse clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infection, PLoS One
Martens, OH)D level on hospital admission is correlated with COVID-19 mortality, doi:10.5061/dryad.37pvmcvh7
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, HLH Across Specialty Collaboration, UK. COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Association of vitamin D status and other clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results, JAMA Netw Open
Merzon, Tworowski, Gorohovski, Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: an Israeli population-based study
Munshi, Hussein, Toraih, Vitamin D insufficiency as a potential culprit in critical COVID-19 patients
Nair, Venkatesh, Center, Vitamin D deficiency and supplementation in critical illness-the known knowns and known unknowns, Crit Care
Panagiotou, Tee, Ihsan, Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 are associated with greater disease severity
Radujkovic, Hippchen, Tiwari-Heckler, Vitamin D deficiency and outcome of COVID-19 patients, Nutrients
Smet, Smet, Ryckaert, Diagnostic performance of chest CT for SARS-CoV-2 infection in individuals with or without COVID-19 symptoms, Radiology
Uddin, Mirbolouk, Kianoush, Role of coronary artery calcium for stratifying cardiovascular risk in adults with hypertension, Hypertension
Van Den Berghe, Van Roosbroeck, Vanhove, Bone turnover in prolonged critical illness: effect of vitamin D, J Clin Endocrinol Metab
Williamson, Walker, Bhaskaran, Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY, Nature
Wu, Chen, Cai, Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan
Ye, Tang, Liao, Does serum vitamin D level affect COVID-19 infection and its severity? A case-control study
Zdrenghea, Makrinioti, Bagacean, Vitamin D modulation of innate immune responses to respiratory viral infections, Rev Med Virol
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcp/aqaa252",
"ISSN": [
"0002-9173",
"1943-7722"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ajcp/aqaa252",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Objectives</jats:title><jats:p>Vitamin D deficiency was previously correlated with incidence and severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). We investigated the association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) level on admission and radiologic stage and outcome of COVID-19 pneumonia.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>A retrospective observational trial was done on 186 severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)–infected individuals hospitalized from March 1, 2020, to April 7, 2020, with combined chest computed tomography (CT) and 25(OH)D measurement on admission. Multivariate regression analysis was performed to study if vitamin D deficiency (25(OH)D &lt;20 ng/mL) correlates with survival independently of confounding comorbidities.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>Of the patients with COVID-19, 59% were vitamin D deficient on admission: 47% of females and 67% of males. In particular, male patients with COVID-19 showed progressively lower 25(OH)D with advancing radiologic stage, with deficiency rates increasing from 55% in stage 1 to 74% in stage 3. Vitamin D deficiency on admission was not confounded by age, ethnicity, chronic lung disease, coronary artery disease/hypertension, or diabetes and was associated with mortality (odds ratio [OR], 3.87; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.30-11.55), independent of age (OR, 1.09; 95% CI, 1.03-1.14), chronic lung disease (OR, 3.61; 95% CI, 1.18-11.09), and extent of lung damage expressed by chest CT severity score (OR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.01-1.25).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>Low 25(OH)D levels on admission are associated with COVID-19 disease stage and mortality.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "AZ Delta Medical Laboratories, Roeselare, Belgium"
}
],
"family": "De Smet",
"given": "Dieter",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Radiology, AZ Delta General Hospital, Roeselare, Belgium"
}
],
"family": "De Smet",
"given": "Kristof",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "AZ Delta Medical Laboratories, Roeselare, Belgium"
}
],
"family": "Herroelen",
"given": "Pauline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Radiology, AZ Delta General Hospital, Roeselare, Belgium"
}
],
"family": "Gryspeerdt",
"given": "Stefaan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1208-6289",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "AZ Delta Medical Laboratories, Roeselare, Belgium"
},
{
"name": "VUB Metabolomics Platform, Brussels Free University, Brussels, Belgium"
},
{
"name": "Department of Biomolecular Medicine, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Martens",
"given": "Geert A",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "American Journal of Clinical Pathology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2020-11-09T20:14:03Z",
"timestamp": 1604952843000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-13T19:30:33Z",
"timestamp": 1618342233000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-27T18:36:09Z",
"timestamp": 1711564569628
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 102,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
25
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
25
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
11
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/journals/pages/open_access/funder_policies/chorus/standard_publication_model",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2020-11-25T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1606262400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/ajcp/article-pdf/155/3/381/36239562/aqaa252.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/ajcp/article-pdf/155/3/381/36239562/aqaa252.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"page": "381-388",
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
25
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
25
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI137244",
"article-title": "Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0001",
"year": "2020;130:2620-2629"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"article-title": "COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression",
"author": "Mehta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1033",
"journal-title": "Lancet.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0002",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.03.021",
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D in the immune system as a pro-survival molecule",
"author": "Chirumbolo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "894",
"journal-title": "Clin Ther.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0003",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mam.2008.04.004",
"article-title": "The paradoxical effects of vitamin D on type 1 mediated immunity",
"author": "Cantorna",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "369",
"journal-title": "Mol Aspects Med.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0004",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2008-1454",
"article-title": "Nonclassic actions of vitamin D",
"author": "Bikle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "26",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0005",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1123933",
"article-title": "Toll-like receptor triggering of a vitamin D-mediated human antimicrobial response",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1770",
"journal-title": "Science.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0006",
"volume": "311",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/IAI.00679-16",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and lung infection",
"author": "Cantorna",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3094",
"journal-title": "Infect Immun.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0007",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.1909",
"article-title": "Vitamin D modulation of innate immune responses to respiratory viral infections",
"author": "Zdrenghea",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Rev Med Virol.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0008",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu7064240",
"article-title": "Modulation of the immune response to respiratory viruses by vitamin D",
"author": "Greiller",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4240",
"journal-title": "Nutrients.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0009",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722",
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D status and other clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results",
"author": "Meltzer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2019722",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0010",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: an Israeli population-based study [published online July 23, 2020]",
"author": "Merzon",
"journal-title": "FEBS J.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0011"
},
{
"article-title": "25-Hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are lower in patients with positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "D’Avolio",
"journal-title": "Nutrients.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0012",
"volume": "12:1359",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0239252",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 positivity rates associated with circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels",
"author": "Kaufman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0239252",
"journal-title": "PLoS One.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0013",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0239799",
"article-title": "Vitamin D sufficiency, a serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D at least 30 ng/mL reduced risk for adverse clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infection",
"author": "Maghbooli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0239799",
"journal-title": "PLoS One.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0014",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency and outcome of COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Radujkovic",
"journal-title": "Nutrients.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0015",
"volume": "12:2757",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Interaction between age and vitamin D deficiency in severe COVID-19 infection",
"author": "Macaya",
"first-page": "1039",
"journal-title": "Nutr Hosp.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0016",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Does serum vitamin D level affect COVID-19 infection and its severity? A case-control study [published online October 13, 2020]",
"author": "Ye",
"journal-title": "J Am Coll Nutr.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0017"
},
{
"article-title": "Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 are associated with greater disease severity [published online July 3, 2020]",
"author": "Panagiotou",
"journal-title": "Clin Endocrinol (Oxf).",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114513001840",
"article-title": "A systematic review of vitamin D status in populations worldwide",
"author": "Hilger",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "23",
"journal-title": "Br J Nutr.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0019",
"volume": "111",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "Serum 25(OH)D level on hospital admission is correlated with COVID-19 mortality",
"author": "Martens",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0020"
},
{
"article-title": "Diagnostic performance of chest CT for SARS-CoV-2 infection in individuals with or without COVID-19 symptoms [published online August 10, 2020]",
"author": "De Smet",
"journal-title": "Radiology.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1148/radiol.2020200463",
"article-title": "Chest CT findings in coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19): relationship to duration of infection",
"author": "Bernheim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "200463",
"journal-title": "Radiology.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0022",
"volume": "295",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.12266",
"article-title": "Role of coronary artery calcium for stratifying cardiovascular risk in adults with hypertension",
"author": "Uddin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "983",
"journal-title": "Hypertension.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0023",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.201909-1867OC",
"article-title": "Vitamin D metabolism is dysregulated in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease",
"author": "Jolliffe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "371",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Crit Care Med.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0024",
"volume": "202",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.202004-1012ED",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. a chicken-or-egg story",
"author": "Hiemstra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "312",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Crit Care Med.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0025",
"volume": "202",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D insufficiency as a potential culprit in critical COVID-19 patients [published online July 27, 2020]",
"author": "Munshi",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0026"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D and vascular disease [published online March 17, 2020]",
"author": "Gouni-Berthold",
"journal-title": "Curr Vasc Pharmacol.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0027"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2521-4",
"article-title": "Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY",
"author": "Williamson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "430",
"journal-title": "Nature.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0028",
"volume": "584",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Predicting mortality due to SARS-CoV-2: a mechanistic score relating obesity and diabetes to COVID-19 outcomes in Mexico [published online May 31, 2020]",
"author": "Bello-Chavolla",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0029"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/jn.112.172882",
"article-title": "Selected physiologic variables are weakly to moderately associated with 29 biomarkers of diet and nutrition, NHANES 2003-2006",
"author": "Haynes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1001S",
"journal-title": "J Nutr.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0030",
"volume": "143",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China [published online March 13, 2020]",
"author": "Wu",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0031"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"journal-title": "Lancet.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0032",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00281-017-0629-x",
"article-title": "Pathogenic human coronavirus infections: causes and consequences of cytokine storm and immunopathology",
"author": "Channappanavar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "529",
"journal-title": "Semin Immunopathol.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0033",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2003-030358",
"article-title": "Bone turnover in prolonged critical illness: effect of vitamin D",
"author": "Van den Berghe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4623",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0034",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/EC-18-0184",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and critical illness: what endocrinology can learn from intensive care and vice versa",
"author": "Amrein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "R304",
"journal-title": "Endocr Connect.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0035",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-018-2185-8",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency and supplementation in critical illness—the known knowns and known unknowns",
"author": "Nair",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "276",
"journal-title": "Crit Care.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0036",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data",
"author": "Martineau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "i6583",
"journal-title": "BMJ.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0037",
"volume": "356",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2014.13204",
"article-title": "Effect of high-dose vitamin D3 on hospital length of stay in critically ill patients with vitamin D deficiency: the VITdAL-ICU randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Amrein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1520",
"journal-title": "JAMA.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0038",
"volume": "312",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751",
"article-title": "Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: a pilot randomized clinical study",
"author": "Entrenas Castillo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105751",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.",
"key": "2021021117060933400_CIT0039",
"volume": "203",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 39,
"references-count": 39,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ajcp/article/155/3/381/6000689"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Serum 25(OH)D Level on Hospital Admission Associated With COVID-19 Stage and Mortality",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "155"
}
