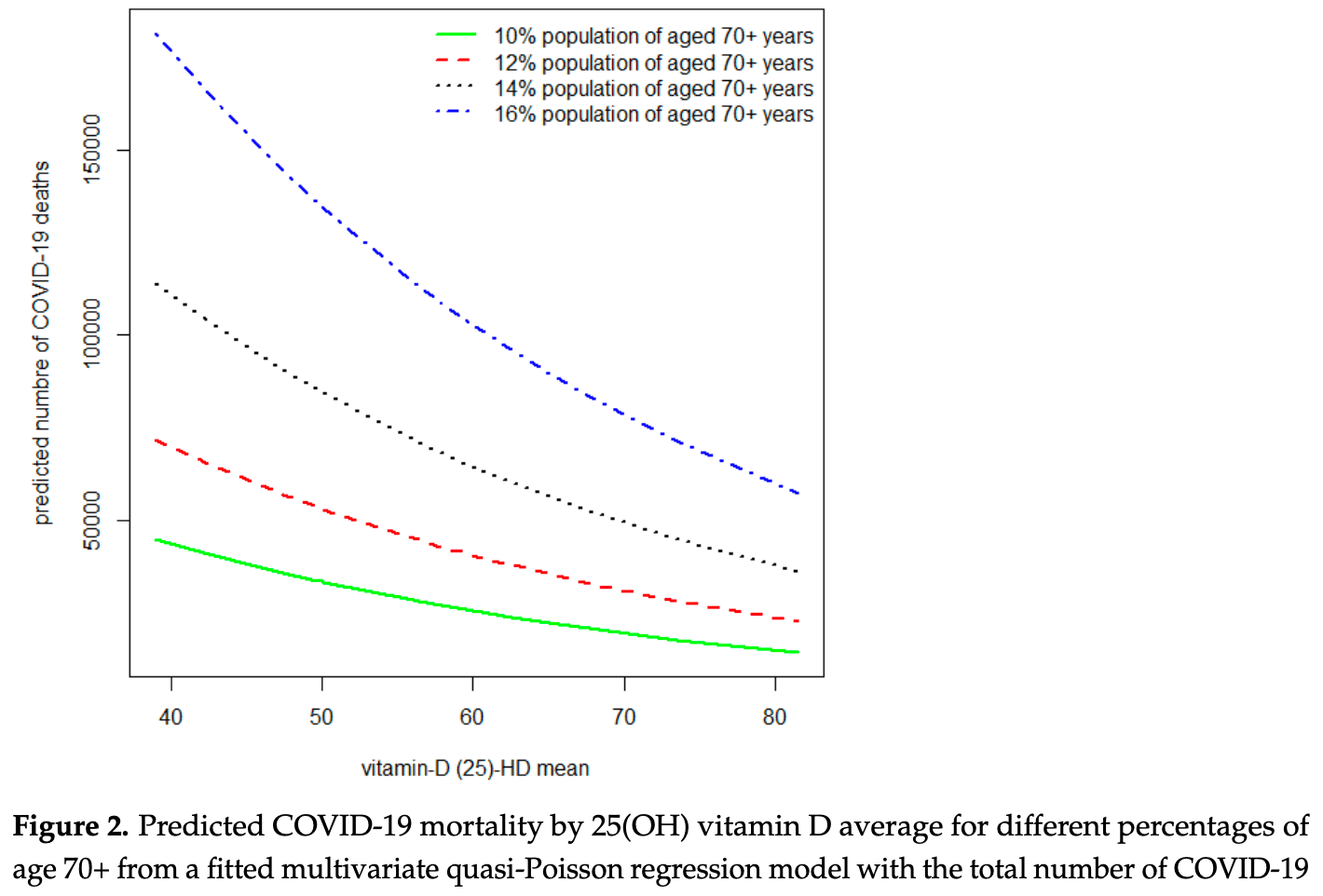
Association between Average Vitamin D Levels and COVID-19 Mortality in 19 European Countries—A Population-Based Study
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15224818, Mar 2021 (preprint)
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Analysis of 19 European countries showing significantly lower mortality with higher vitamin D levels.
|
risk of death, 20.6% lower, RR 0.79, p = 0.01, >50nmol/L.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Ahmad et al., 12 Mar 2021, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, study period 1 March, 2020 - 14 June, 2023.
Contact: amar.ahmad@cancer.org.uk (corresponding author), nirmin.juber@nyu.edu, hman1e20@soton.ac.uk, christian.heumann@stat.uni-muenchen.de, raghib.ali@mrc-epid.cam.ac.uk, r.t.oliver@qmul.ac.uk.
Association between Average Vitamin D Levels and COVID-19 Mortality in 19 European Countries—A Population-Based Study
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15224818
Early epidemic reports have linked low average 25(OH) vitamin D levels with increased COVID-19 mortality. However, there has been limited updated research on 25(OH) vitamin D and its impact on COVID-19 mortality. This study aimed to update the initial report studying the link between vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 mortality by using multi-country data in 19 European countries up to the middle of June 2023. COVID-19 data for 19 European countries included in this study were
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Adams-Prassl, Cloyne, Costa Dias, Parey, Ziliak, The COVID-19 Economic Crisis, Fisc. Stud, doi:10.1111/1475-5890.12248
Annweiler, Corvaisier, Gautier, Dubée, Legrand et al., Vitamin D supplementation associated to better survival in hospitalized frail elderly COVID-19 patients: The GERIA-COVID quasi-experimental study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113377
Axfors, Ioannidis, Infection fatality rate of COVID-19 in community-dwelling elderly populations, Eur. J. Epidemiol, doi:10.1007/s10654-022-00853-w
Bakaloudi, Chourdakis, A critical update on the role of mild and serious vitamin D deficiency prevalence and the COVID-19 epidemic in Europe, Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441
Basi Ńska-Lewandowska, Lewandowski, Horzelski, Lewi Ński, Skowro Ńska-Jóźwiak, Frequency of COVID-19 infection as a function of vitamin D levels, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15071581
Buttriss, Lanham-New, Is a vitamin D fortification strategy needed?, Nutr. Bull, doi:10.1111/nbu.12430
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Qu, Gong et al., Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7
Core, R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing
Demir, Demir, Aygun, Vitamin D deficiency is associated with COVID-19 positivity and severity of the disease, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26832
Dyer, COVID-19: Excess deaths point to hidden toll in South Africa as cases surge, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m3038
Fang, Kasperzyk, Shui, Hendrickson, Hollis et al., Prediagnostic plasma vitamin D metabolites and mortality among patients with prostate cancer, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0018625
Farhadi, Ovchinnikov, The relationship between nutrition and infectious diseases: A review, Biomed. Biotechnol. Res. J
Gerken, Zapata, Kuivinen, Zapata, Comorbidities, sociodemographic factors, and determinants of health on COVID-19 fatalities in the United States, Front. Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2022.993662
Gonçalves, Andrade-Silva, Basso, Câmara, Vitamin D and chronic kidney disease: Insights on lipid metabolism of tubular epithelial cell and macrophages in tubulointerstitial fibrosis, Front. Physiol, doi:10.3389/fphys.2023.1145233
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12040988
Gruber-Bzura, Vitamin D and Influenza-Prevention or Therapy?, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms19082419
Gröber, Kisters, Influence of drugs on vitamin D and calcium metabolism, Derm. Endocrinol, doi:10.4161/derm.20731
Hasell, Mathieu, Beltekian, Macdonald, Giattino et al., A cross-country database of COVID-19 testing, Sci. Data, doi:10.1038/s41597-020-00688-8
Hastie, Mackay, Ho, Celis-Morales, Katikireddi et al., Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank, Diabetes Metab. Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.050
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality, Aging Clin. Exp. Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8
Jayawardena, Jeyakumar, Francis, Misra, Impact of the vitamin D deficiency on COVID-19 infection and mortality in Asian countries, Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.03.006
Jolliffe, Camargo, Sluyter, Aglipay, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: Systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data from randomised controlled trials, medRxiv, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00051-6
Jääskeläinen, Itkonen, Lundqvist, Erkkola, Koskela et al., The positive impact of general vitamin D food fortification policy on vitamin D status in a representative adult Finnish population: Evidence from an 11-y follow-up based on standardized 25-hydroxyvitamin D data, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.3945/ajcn.116.151415
Karahan, Katkat, Impact of Serum 25(OH) Vitamin D Level on Mortality in Patients with COVID-19 in Turkey, J. Nutr. Health Aging, doi:10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0
Katz, Yue, Xue, Increased risk for COVID-19 in patients with vitamin D deficiency, Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2020.111106
Kearns, Alvarez, Seidel, Tangpricha, Impact of vitamin D on infectious disease, Am. J. Med. Sci, doi:10.1097/MAJ.0000000000000360
Kümmel, Krumbein, Fragkou, Hünerbein, Reiter et al., Vitamin D supplementation for the treatment of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.1023903
Li, Guan, Wu, Wang, Zhou et al., Early Transmission Dynamics in Wuhan, China, of Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001316
Lim, Subramaniam, Reddy, Blecher, Kadam et al., Case fatality rates for patients with COVID-19 requiring invasive mechanical ventilation. a meta-analysis, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1164/rccm.202006-2405OC
Lips, Cashman, Lamberg-Allardt, Bischoff-Ferrari, Obermayer-Pietsch et al., Current vitamin D status in European and Middle East countries and strategies to prevent vitamin D deficiency: A position statement of the European Calcified Tissue Society, Eur. J. Endocrinol, doi:10.1530/EJE-18-0736
Maghbooli, Sahraian, Ebrahimi, Pazoki, Kafan et al., Vitamin D sufficiency, a serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D at least 30 ng/mL reduced risk for adverse clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infection, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0239799
Mandal, Baktash, Hosack, Missouris, Vitamin D status and COVID-19 in older adults, Aging Clin. Exp. Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01716-8
Mariani, Antonietti, Tajer, Ferder, Inserra et al., High-dose vitamin D versus placebo to prevent complications in COVID-19 patients: Multicentre randomized controlled clinical trial, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0267918
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: Systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.i6583
Martineau, Vitamin D in the prevention or treatment of COVID-19, Proc. Nutr. Soc, doi:10.1017/S0029665122002798
Massinga Loembe, Tshangela, Salyer, Varma, Ouma et al., COVID-19 in Africa: The spread and response, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0961-x
Mathieu, Ritchie, Rodés-Guirao, Appel, Giattino et al., Coronavirus Pandemic (COVID-19): Our World Data
Mckenna, Lyons, Flynn, Crowley, Twomey et al., COVID-19 pandemic and vitamin D: Rising trends in status and in daily amounts of vitamin D provided by supplements, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2021-059477
Mele, Magazzino, Pollution, economic growth, and COVID-19 deaths in India: A machine learning evidence, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int, doi:10.1007/s11356-020-10689-0
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of vitamin D status and other clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722
Moghaddam, Khorasanchi, Noor, Moghadam, Esfahani et al., High-dose vitamin D supplementation is related to an improvement in serum alkaline phosphatase in COVID-19 patients; a randomized double-blinded clinical trial, J. Health Popul. Nutr, doi:10.1186/s41043-023-00409-y
Nielsen, Junker, Boelt, Cohen, Munger et al., Vitamin D status and severity of COVID-19, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-21513-9
Nikniaz, Akbarzadeh, Hosseinifard, Hosseini, Vitamin D supplementation on mortality rate and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis, medRxiv, doi:10.34172/PS.2021.13
Okonji, Okonji, Mukumbang, Van Wyk, Understanding varying COVID-19 mortality rates reported in Africa compared to Europe, Americas and Asia, Trop. Med. Int. Health, doi:10.1111/tmi.13575
Pal, Banerjee, COVID-19 and the endocrine system: Exploring the unexplored, J. Endocrinol. Investig, doi:10.1007/s40618-020-01276-8
Panagiotou, Tee, Ihsan, Athar, Marchitelli et al., Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 are associated with greater disease severity, Clin. Endocrinol
Pechlivanidou, Vlachakis, Tsarouhas, Panidis, Tsitsimpikou et al., The prognostic role of micronutrient status and supplements in COVID-19 outcomes: A systematic review, Food Chem. Toxicol, doi:10.1016/j.fct.2022.112901
Pereira, Dantas Damascena, Galvao Azevedo, De Almeida Oliveira, Da Mota Santana, Vitamin D deficiency aggravates COVID-19: Systematic review and meta-analysis, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr, doi:10.1080/10408398.2020.1841090
Pham, Analyzing the relationship between the vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 mortality rate and modeling the time-delay interactions between body's immune healthy cells, infected cells, and virus particles with the effect of vitamin D levels, Math. Biosci. Eng, doi:10.3934/mbe.2022417
Pilz, Frisch, Koertke, Kuhn, Dreier et al., Effect of vitamin D supplementation on testosterone levels in men, Horm. Metab. Res, doi:10.1055/s-0030-1269854
Pugach, Pugach, Strong correlation between prevalence of severe vitamin D deficiency and population mortality rate from COVID-19 in Europe, Wien. Klin. Wochenschr, doi:10.1007/s00508-021-01833-y
Radujkovic, Merle, Reply to: Vitamin D Insufficiency May Account for Almost Nine of Ten COVID-19 Deaths: Time to Act
Singh, Kaur, Singh, Revisiting the role of vitamin D levels in the prevention of COVID-19 infection and mortality in European countries post infections peak, Aging Clin. Exp. Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01619-8
Spiro, Buttriss, Vitamin, An overview of vitamin D status and intake in Europe, Nutr. Bull, doi:10.1111/nbu.12108
Strang, Furst, Schultz, Excess deaths from COVID-19 correlate with age and socio-economic status. A database study in the Stockholm region, Upsala J. Med. Sci, doi:10.1080/03009734.2020.1828513
Sulli, Gotelli, Casabella, Paolino, Pizzorni et al., Vitamin D and lung outcomes in elderly COVID-19 patients, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13030717
Sun, Chen, Viboud, Early epidemiological analysis of the coronavirus disease 2019 outbreak based on crowdsourced data: A population-level observational study, Lancet Digit. Health, doi:10.1016/S2589-7500(20)30026-1
Szeto, Zucker, Lasota, Rubin, Walker et al., Vitamin D status and COVID-19 clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients, Endocr. Res, doi:10.1080/07435800.2020.1867162
Söderström, Rosenblad, Adolfsson, Bergkvist, Malnutrition is associated with increased mortality in older adults regardless of the cause of death, Br. J. Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114517000435
Tylavsky, Cheng, Lyytikäinen, Viljakainen, Lamberg-Allardt, Strategies to improve vitamin D status in northern European children: Exploring the merits of vitamin D fortification and supplementation, J. Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/136.4.1130
Varikasuvu, Thangappazham, Vykunta, Duggina, Manne et al., COVID-19 andvitamin D (Co-VIVID study): A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther, doi:10.1080/14787210.2022.2035217
Vickers, Altman, Statistics notes: Missing outcomes in randomised trials, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.f3438
Wacker, Holick, Sunlight and Vitamin D: A global perspective for health, Derm. Endocrinol, doi:10.4161/derm.24494
Wang, Peng, Jackknife Empirical likelihood intervals for Spearman's rho, Am. Actuar. J, doi:10.1080/10920277.2011.10597633
Zittermann, Pilz, Hoffmann, März, Vitamin D and airway infections: A European perspective, Eur. J. Med. Res, doi:10.1186/s40001-016-0208-y
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu15224818",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu15224818",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Early epidemic reports have linked low average 25(OH) vitamin D levels with increased COVID-19 mortality. However, there has been limited updated research on 25(OH) vitamin D and its impact on COVID-19 mortality. This study aimed to update the initial report studying the link between vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 mortality by using multi-country data in 19 European countries up to the middle of June 2023. COVID-19 data for 19 European countries included in this study were downloaded from Our World in Data from 1 March 2020, to 14 June 2023, and were included in the statistical analysis. The 25(OH) vitamin D average data were collected by conducting a literature review. A generalized estimation equation model was used to model the data. Compared to European countries with 25(OH) vitamin D levels of ≤50 nmol/L, European countries with 25(OH) vitamin D average levels greater than >50 nmol/L had lower COVID-19 mortality rates (RR = 0.794, 95% CI: 0.662–0.953). A statistically significant negative Spearman rank correlation was observed between 25(OH) vitamin D average levels and COVID-19 mortality. We also found significantly lower COVID-19 mortality rates in countries with high average 25(OH) vitamin D levels. Randomized trials on vitamin D supplementation are needed. In the meantime, the issue of vitamin D use should be debated in relation to the ongoing discussions of national post-COVID-19 resilience against future pandemics.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu15224818"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Cancer Intelligence, Cancer Research UK, Oxford OX4 9GZ, UK"
}
],
"family": "Ahmad",
"given": "Amar S.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7316-5530",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Public Health Research Center, New York University Abu Dhabi, Abu Dhabi P.O. Box 129188, United Arab Emirates"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Juber",
"given": "Nirmin F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Academic Unit of Medical Education, University of Southampton, Southampton SO17 1BJ, UK"
}
],
"family": "Al-Naseri",
"given": "Heba",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4718-595X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Statistics, Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, 80539 München, Germany"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Heumann",
"given": "Christian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "MRC Epidemiology Unit, University of Cambridge, Cambridge CB2 0SL, UK"
}
],
"family": "Ali",
"given": "Raghib",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Barts Cancer Institute, Queen Mary University of London, London EC1M 6AU, UK"
}
],
"family": "Oliver",
"given": "Tim",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-17T14:23:43Z",
"timestamp": 1700231023000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-17T15:01:35Z",
"timestamp": 1700233295000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-18T00:39:18Z",
"timestamp": 1700267958952
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "22",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
17
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "22",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-17T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1700179200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/15/22/4818/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "4818",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
17
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
17
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"article-title": "Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "507",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2589-7500(20)30026-1",
"article-title": "Early epidemiological analysis of the coronavirus disease 2019 outbreak based on crowdsourced data: A population-level observational study",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e201",
"journal-title": "Lancet Digit. Health",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001316",
"article-title": "Early Transmission Dynamics in Wuhan, China, of Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1199",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10654-022-00853-w",
"article-title": "Infection fatality rate of COVID-19 in community-dwelling elderly populations",
"author": "Axfors",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "235",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Epidemiol.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0961-x",
"article-title": "COVID-19 in Africa: The spread and response",
"author": "Tshangela",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "999",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m3038",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Excess deaths point to hidden toll in South Africa as cases surge",
"author": "Dyer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m3038",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/tmi.13575",
"article-title": "Understanding varying COVID-19 mortality rates reported in Africa compared to Europe, Americas and Asia",
"author": "Okonji",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "716",
"journal-title": "Trop. Med. Int. Health",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/03009734.2020.1828513",
"article-title": "Excess deaths from COVID-19 correlate with age and socio-economic status. A database study in the Stockholm region",
"author": "Strang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "297",
"journal-title": "Upsala J. Med. Sci.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "125",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11356-020-10689-0",
"article-title": "Pollution, economic growth, and COVID-19 deaths in India: A machine learning evidence",
"author": "Mele",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2669",
"journal-title": "Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1475-5890.12234",
"article-title": "The COVID-19 Economic Crisis",
"author": "Cloyne",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "489",
"journal-title": "Fisc. Stud.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441",
"article-title": "A critical update on the role of mild and serious vitamin D deficiency prevalence and the COVID-19 epidemic in Europe",
"author": "Bakaloudi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "111441",
"journal-title": "Nutrition",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114517000435",
"article-title": "Malnutrition is associated with increased mortality in older adults regardless of the cause of death",
"author": "Rosenblad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "532",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/bbrj.bbrj_69_18",
"article-title": "The relationship between nutrition and infectious diseases: A review",
"author": "Farhadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "168",
"journal-title": "Biomed. Biotechnol. Res. J.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MAJ.0000000000000360",
"article-title": "Impact of vitamin D on infectious disease",
"author": "Kearns",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "245",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Med. Sci.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "349",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D and chronic kidney disease: Insights on lipid metabolism of tubular epithelial cell and macrophages in tubulointerstitial fibrosis",
"author": "Basso",
"first-page": "499",
"journal-title": "Front. Physiol.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4161/derm.24494",
"article-title": "Sunlight and Vitamin D: A global perspective for health",
"author": "Wacker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "51",
"journal-title": "Derm. Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms19082419",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_17",
"unstructured": "Gruber-Bzura, B.M. (2018). Vitamin D and Influenza-Prevention or Therapy?. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 19."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: Systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data",
"author": "Martineau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "i6583",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "356",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: Systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data from randomised controlled trials",
"author": "Jolliffe",
"first-page": "276",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.03.006",
"article-title": "Impact of the vitamin D deficiency on COVID-19 infection and mortality in Asian countries",
"author": "Jayawardena",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "757",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26832",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency is associated with COVID-19 positivity and severity of the disease",
"author": "Demir",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2992",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.050",
"article-title": "Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank",
"author": "Hastie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "561",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. Syndr.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu15071581",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_23",
"unstructured": "Basińska-Lewandowska, M., Lewandowski, K., Horzelski, W., Lewiński, A., and Skowrońska-Jóźwiak, E. (2023). Frequency of COVID-19 infection as a function of vitamin D levels. Nutrients, 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.01.04.21249219",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_24",
"unstructured": "Nikniaz, L., Akbarzadeh, M.A., Hosseinifard, H., and Hosseini, M. (2021). Vitamin D supplementation on mortality rate and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. medRxiv."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s41043-023-00409-y",
"article-title": "High-dose vitamin D supplementation is related to an improvement in serum alkaline phosphatase in COVID-19 patients; a randomized double-blinded clinical trial",
"author": "Moghaddam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "71",
"journal-title": "J. Health Popul. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8",
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality",
"author": "Ilie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1195",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin. Exp. Res.",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00508-021-01833-y",
"article-title": "Strong correlation between prevalence of severe vitamin D deficiency and population mortality rate from COVID-19 in Europe",
"author": "Pugach",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "403",
"journal-title": "Wien. Klin. Wochenschr.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3934/mbe.2022417",
"article-title": "Analyzing the relationship between the vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 mortality rate and modeling the time-delay interactions between body’s immune healthy cells, infected cells, and virus particles with the effect of vitamin D levels",
"author": "Pham",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8975",
"journal-title": "Math. Biosci. Eng.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41597-020-00688-8",
"article-title": "A cross-country database of COVID-19 testing",
"author": "Hasell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "345",
"journal-title": "Sci. Data",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref_30",
"unstructured": "Our World in Data (2023, June 15). Explore the Global Situation: COVID-19 Data Explorer 2020–2022. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/coronavirus#explore-the-global-situation."
},
{
"key": "ref_31",
"unstructured": "Mathieu, E., Ritchie, H., Rodés-Guirao, L., Appel, C., Giattino, C., Hasell, J., Herre, B., Macdonald, B., Mathieu, E., and Mersmann, S. (2023, June 15). Coronavirus Pandemic (COVID-19): Our World Data. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/coronavirus."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01619-8",
"article-title": "Revisiting the role of vitamin D levels in the prevention of COVID-19 infection and mortality in European countries post infections peak",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1609",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin. Exp. Res.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/EJE-18-0736",
"article-title": "Current vitamin D status in European and Middle East countries and strategies to prevent vitamin D deficiency: A position statement of the European Calcified Tissue Society",
"author": "Lips",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "23",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-0030-1269854",
"article-title": "Effect of vitamin D supplementation on testosterone levels in men",
"author": "Pilz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "223",
"journal-title": "Horm. Metab. Res.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-21513-9",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status and severity of COVID-19",
"author": "Nielsen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "19823",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111106",
"article-title": "Increased risk for COVID-19 in patients with vitamin D deficiency",
"author": "Katz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "111106",
"journal-title": "Nutrition",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07435800.2020.1867162",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status and COVID-19 clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients",
"author": "Szeto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "66",
"journal-title": "Endocr. Res.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2021-059477",
"article-title": "COVID-19 pandemic and vitamin D: Rising trends in status and in daily amounts of vitamin D provided by supplements",
"author": "McKenna",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e059477",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10920277.2011.10597633",
"article-title": "Jackknife Empirical likelihood intervals for Spearman’s rho",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "475",
"journal-title": "Am. Actuar. J.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.f3438",
"article-title": "Statistics notes: Missing outcomes in randomised trials",
"author": "Vickers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "f3438",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "346",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"key": "ref_41",
"unstructured": "R Core Team (2021). R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.20944/preprints202003.0235.v2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_42",
"unstructured": "Grant, W.B., Lahore, H., McDonnell, S.L., Baggerly, C.A., French, C.B., Aliano, J.L., and Bhattoa, H.P. (2020). Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.1023903",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation for the treatment of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Krumbein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1023903",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0267918",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_44",
"unstructured": "Mariani, J., Antonietti, L., Tajer, C., Ferder, L., Inserra, F., Cunto, M.S., Brosio, D., Ross, F., Zylberman, M., and López, D.E. (2022). High-dose vitamin D versus placebo to prevent complications in COVID-19 patients: Multicentre randomized controlled clinical trial. PLoS ONE, 17."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2020.1841090",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency aggravates COVID-19: Systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Pereira",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1308",
"journal-title": "Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14787210.2022.2035217",
"article-title": "COVID-19 andvitamin D (Co-VIVID study): A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Varikasuvu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "907",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther.",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092757",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_47",
"unstructured": "Radujkovic, A., and Merle, U. (2020). Reply to: Vitamin D Insufficiency May Account for Almost Nine of Ten COVID-19 Deaths: Time to Act. Comment on: Vitamin D Deficiency and Outcome of COVID-19 Patients. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0029665122002798",
"article-title": "Vitamin D in the prevention or treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Martineau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "200",
"journal-title": "Proc. Nutr. Soc.",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40618-020-01276-8",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and the endocrine system: Exploring the unexplored",
"author": "Pal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1027",
"journal-title": "J. Endocrinol. Investig.",
"key": "ref_49",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13030717",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_50",
"unstructured": "Sulli, A., Gotelli, E., Casabella, A., Paolino, S., Pizzorni, C., Alessandri, E., Grosso, M., Ferone, D., Smith, V., and Cutolo, M. (2021). Vitamin D and lung outcomes in elderly COVID-19 patients. Nutrients, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113377",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_51",
"unstructured": "Annweiler, G., Corvaisier, M., Gautier, J., Dubée, V., Legrand, E., Sacco, G., and Annweiler, C. (2020). Vitamin D supplementation associated to better survival in hospitalized frail elderly COVID-19 patients: The GERIA-COVID quasi-experimental study. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01716-8",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status and COVID-19 in older adults",
"author": "Mandal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2425",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin. Exp. Res.",
"key": "ref_52",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.202006-2405OC",
"article-title": "Case fatality rates for patients with COVID-19 requiring invasive mechanical ventilation. a meta-analysis",
"author": "Lim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "54",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "ref_53",
"volume": "203",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40001-016-0208-y",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and airway infections: A European perspective",
"author": "Zittermann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "14",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Med. Res.",
"key": "ref_54",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4161/derm.20731",
"article-title": "Influence of drugs on vitamin D and calcium metabolism",
"author": "Kisters",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "158",
"journal-title": "Derm. Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_55",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/nbu.12430",
"article-title": "Is a vitamin D fortification strategy needed?",
"author": "Buttriss",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "115",
"journal-title": "Nutr. Bull.",
"key": "ref_56",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.116.151415",
"article-title": "The positive impact of general vitamin D food fortification policy on vitamin D status in a representative adult Finnish population: Evidence from an 11-y follow-up based on standardized 25-hydroxyvitamin D data",
"author": "Itkonen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1512",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_57",
"volume": "105",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"key": "ref_58",
"unstructured": "National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) (2023, June 15). COVID-19 Rapid Guideline: Vitamin D 2022. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng187."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/nbu.12108",
"article-title": "Vitamin D: An overview of vitamin D status and intake in Europe",
"author": "Spiro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "322",
"journal-title": "Nutr. Bull.",
"key": "ref_59",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722",
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D status and other clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results",
"author": "Meltzer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2019722",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw. Open.",
"key": "ref_60",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.fct.2022.112901",
"article-title": "The prognostic role of micronutrient status and supplements in COVID-19 outcomes: A systematic review",
"author": "Pechlivanidou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "112901",
"journal-title": "Food Chem. Toxicol.",
"key": "ref_61",
"volume": "162",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2022.993662",
"article-title": "Comorbidities, sociodemographic factors, and determinants of health on COVID-19 fatalities in the United States",
"author": "Gerken",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "993662",
"journal-title": "Front. Public Health",
"key": "ref_62",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0018625",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_63",
"unstructured": "Fang, F., Kasperzyk, J.L., Shui, I., Hendrickson, W., Hollis, B.W., Fall, K., Ma, J., Gaziano, J.M., Stampfer, M.J., and Mucci, L.A. (2011). Prediagnostic plasma vitamin D metabolites and mortality among patients with prostate cancer. PLoS ONE, 6."
},
{
"key": "ref_64",
"unstructured": "National Health Service Laboratory (2023, June 15). Direct Public Vitamin D Testing from our NHS Laboratory in West Bromwich 2022. Available online: https://www.vitamindtest.org.uk/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0",
"article-title": "Impact of Serum 25(OH) Vitamin D Level on Mortality in Patients with COVID-19 in Turkey",
"author": "Karahan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "189",
"journal-title": "J. Nutr. Health Aging",
"key": "ref_65",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0239799",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_66",
"unstructured": "Maghbooli, Z., Sahraian, M.A., Ebrahimi, M., Pazoki, M., Kafan, S., Tabriz, H.M., Hadadi, A., Montazeri, M., Nasiri, M., and Shirvani, A. (2020). Vitamin D sufficiency, a serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D at least 30 ng/mL reduced risk for adverse clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infection. PLoS ONE, 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/136.4.1130",
"article-title": "Strategies to improve vitamin D status in northern European children: Exploring the merits of vitamin D fortification and supplementation",
"author": "Tylavsky",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1130",
"journal-title": "J. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_67",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"key": "ref_68",
"unstructured": "Public Health England (2023, June 15). COVID-19: Understanding the Impact on BAME Communities 2020, Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/covid-19-understanding-the-impact-on-bame-communities."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cen.14276",
"article-title": "Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 are associated with greater disease severity",
"author": "Panagiotou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "508",
"journal-title": "Clin. Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_69",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 69,
"references-count": 69,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/15/22/4818"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Food Science",
"Nutrition and Dietetics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Association between Average Vitamin D Levels and COVID-19 Mortality in 19 European Countries—A Population-Based Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "15"
}
