Impact of Serum 25(OH) Vitamin D Level on Mortality in Patients with COVID-19 in Turkey
et al., J. Nutr. Health Aging, doi:10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0
, Oct 2020
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
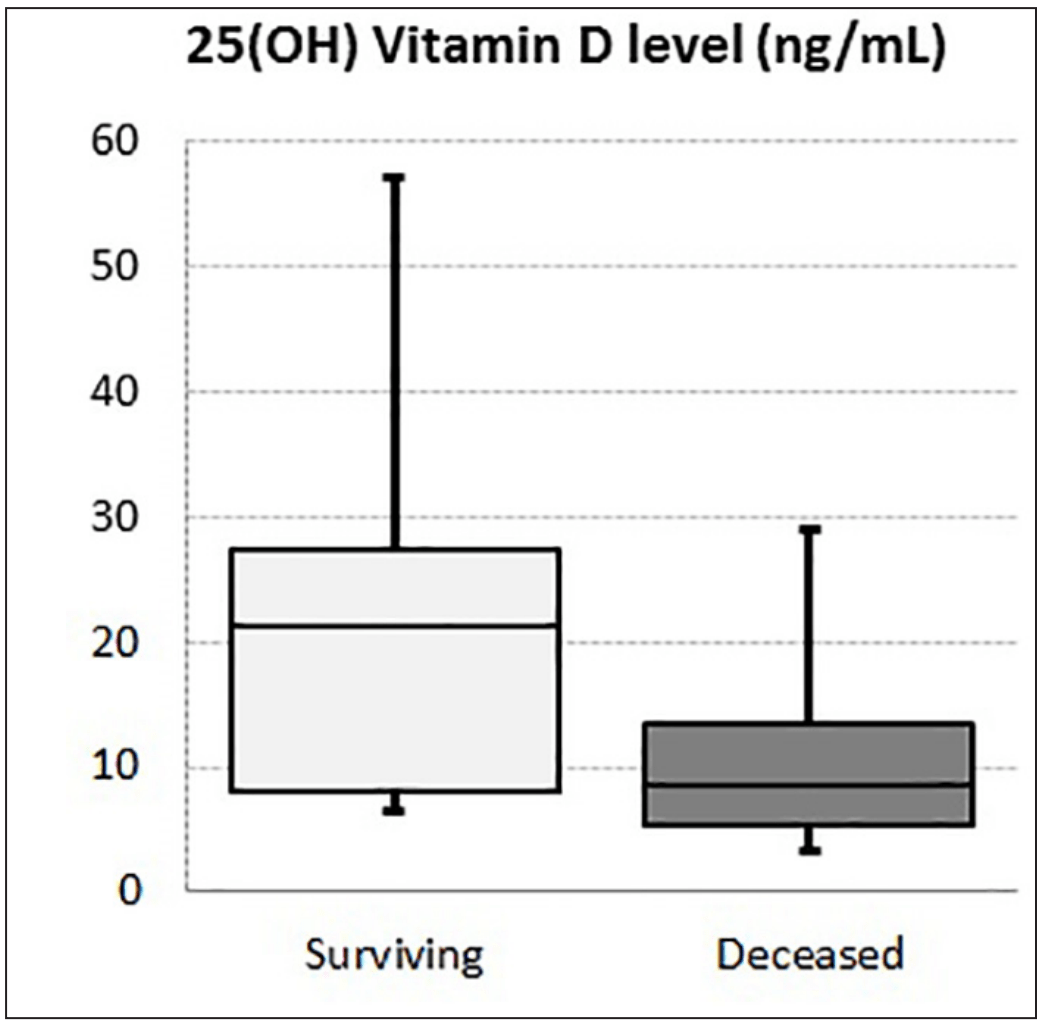
Retrospective 149 COVID-19 patients, 69.1% with vitamin D deficiency, showing lower vitamin D levels associated with higher mortality.
This is the 17th of 228 COVID-19 sufficiency studies for vitamin D, which collectively show higher levels reduce risk with p<0.0000000001.
|
risk of death, 82.5% lower, RR 0.17, p < 0.001, high D levels 5 of 46 (10.9%), low D levels 64 of 103 (62.1%), NNT 2.0, >20nmol/L.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Karahan et al., 5 Oct 2020, retrospective, Turkey, peer-reviewed, 2 authors.
IMPACT OF SERUM 25(OH) VITAMIN D LEVEL ON MORTALITY IN PATIENTS WITH COVID-19 IN TURKEY
Background: Because of the lack of sufficient data, we aimed to investigate the role of serum 25(OH) vitamin D level on COVID severity and related mortality. Methods: This was a retrospective observational study. Data, including sociodemographic features, clinical characteristics, and laboratory data, and 25(OH) vitamin D levels were recorded for each study participant. Patients were stratified into different vitamin D groups; Normal (Serum 25(OH) vitamin D level >30 ng/mL), Vitamin D insufficiency (21-29 ng/mL), and deficiency (<20 ng/ mL). The severity of COVID was classified according to the Chinese Clinical Guideline for classification of COVID-19 severity. Mortality data were determined for participants. Univariate and multivariate Logistic regression analysis was performed to determine independent predictors of in-hospital mortality. Results: Overall, 149 COVID-19 patients (females 45.6%, mean age 63.5 ± 15.3 (range 24-90 years) years) were included. Fortyseven patients (31.5%) had moderate COVID-19, whereas 102 patients (68.5%) had severe-critical COVID-19. The mean 25(OH) vitamin D level was 15.2 ± 10.3 ng/mL. Thirty-four (22.8%) and 103 (69.1%) patients had vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency, respectively. Mean serum 25(OH) vitamin D level was significantly lower in patients with severe-critical COVID-19 compared with moderate COVID-19 (10.1 ± 6.2 vs. 26.3 ± 8.4 ng/mL, respectively, p<0.001). Vitamin D insufficiency was present in 93.1% of the patients with severe-critical COVID-19. Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that only lymphocyte count, white blood cell count, serum albumin and, 25(OH) vitamin D level were independent predictors of mortality. Conclusion: Serum 25(OH) vitamin D was independently associated with mortality in COVID-19 patients.
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards: The study protocol was approved by the Hospital Clinical Studies Ethical Committee (2020.06.1.01.072 and 12 June 2020).
References
Aglipay, Birken, Parkin, Loeb, Thorpe et al., Effect of High-Dose vs Standard-Dose Wintertime Vitamin D Supplementation on Viral Upper Respiratory Tract Infections in Young Healthy Children, JAMA
Alipio, Vitamin D Supplementation Could Possibly Improve Clinical Outcomes of Patients Infected with Coronavirus, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3571484
Aranow, Vitamin D and the immune system, J Investig Med
Arihiro, Nakashima, Matsuoka, Suto, Uchiyama et al., Randomized Trial of Vitamin D Supplementation to Prevent Seasonal Influenza and Upper Respiratory Infection in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Inflamm Bowel Dis
Aygun, Vitamin D can prevent COVID-19 infection-induced multiple organ damage, Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol
Cannell, Vieth, Umhau, Holick, Grant et al., Epidemic influenza and vitamin D, Epidemiol Infect
Cantorna, Snyder, Lin, Yang, Vitamin D and 1,25(OH)2D regulation of T cells, Nutrients
D'avolio, Avataneo, Manca, Cusato, Nicolo et al., 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations Are Lower in Patients with Positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2, Nutrients
Daneshkhah, Agrawal, Eshein, Subramanian, Roy et al., The Possible Role of Vitamin D in Suppressing Cytokine Storm and Associated Mortality in COVID-19 Patients, medRxiv
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients
Guan, Liang, Zhao, Liang, Chen et al., Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with COVID-19 in China: a nationwide analysis, Eur Respir J
Hastie, Mackay, Ho, Celis-Morales, Katikireddi et al., Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Holick, Vitamin D status: measurement, interpretation, and clinical application, Ann Epidemiol
Hueniken, Aglipay, Birken, Parkin, Loeb et al., Effect of High-Dose Vitamin D Supplementation on Upper Respiratory Tract Infection Symptom Severity in Healthy Children, Pediatr Infect Dis J
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality, Aging Clin Exp Res
Jeffery, Burke, Mura, Zheng, Qureshi et al., 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 and IL-2 combine to inhibit T cell production of inflammatory cytokines and promote development of regulatory T cells expressing CTLA-4 and FoxP3, J Immunol
Kara, Ekiz, Ricci, Kara, Chang et al., Scientific Strabismus' or Two Related Pandemics: COVID-19 & Vitamin D Deficiency, Br J Nutr
Kaur, Ferguson, Freitas, Miller, Bemben et al., Association of Vitamin D Status with Chronic Disease Risk Factors and Cognitive Dysfunction in
Liu, Chen, Lin, Han, Clinical features of COVID-19 in elderly patients: A comparison with young and middle-aged patients, J Infect
Marik, Kory, Varon, Does vitamin D status impact mortality from SARS-CoV-2 infection?, Med Drug Discov
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ
Raharusun, Priambada, Sadiah, Budiarti, Agung et al., Patterns of COVID-19 Mortality and Vitamin D: An Indonesian Study, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3585561
Rhodes, Subramanian, Laird, Kenny, Editorial: low population mortality from COVID-19 in countries south of latitude 35 degrees North supports vitamin D as a factor determining severity, Aliment Pharmacol Ther
Rondanelli, Miccono, Lamburghini, Avanzato, Riva et al., Self-Care for Common Colds: The Pivotal Role of Vitamin D, Vitamin C, Zinc, and Echinacea in Three Main Immune Interactive Clusters (Physical Barriers, Innate and Adaptive Immunity) Involved during an Episode of Common Colds-Practical Advice on Dosages and on the Time to Take These Nutrients/Botanicals in order to Prevent or Treat Common Colds, Evid Based Complement Alternat Med
Sharifi, Vahedi, Nedjat, Rafiei, Hosseinzadeh-Attar, Effect of singledose injection of vitamin D on immune cytokines in ulcerative colitis patients: a randomized placebo-controlled trial, APMIS
Teymoori-Rad, Shokri, Salimi, Marashi, The interplay between vitamin D and viral infections, Rev Med Virol
Wang, Li, Lu, Huang, Does comorbidity increase the risk of patients with COVID-19: evidence from meta-analysis, Aging
Ye, Wang, Mao, The pathogenesis and treatment of the `Cytokine Storm' in COVID-19, J Infect
Zheng, Peng, Xu, Zhao, Liu et al., Risk factors of critical & mortal COVID-19 cases: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis, J Infect
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0",
"ISSN": [
"1279-7707"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0",
"alternative-id": [
"S1279770723009983"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Impact of Serum 25(OH) Vitamin D Level on Mortality in Patients with COVID-19 in Turkey"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "The Journal of nutrition, health and aging"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2020 SERDI Publisher."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karahan",
"given": "Serkan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Katkat",
"given": "F.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Journal of nutrition, health and aging",
"container-title-short": "The Journal of nutrition, health and aging",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-05T10:04:55Z",
"timestamp": 1601892295000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-30T22:47:46Z",
"timestamp": 1706654866000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-26T23:11:15Z",
"timestamp": 1711494675883
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 76,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1612137600000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 1033,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1701388800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1279770723009983?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1279770723009983?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "189-196",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib1",
"unstructured": "Johns Hopkins University Coronavirus Resource Center, https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html, accessed 14th June, 2020."
},
{
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J.",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib2",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.103000",
"article-title": "Does comorbidity increase the risk of patients with COVID-19: evidence from meta-analysis",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6049",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Aging (Albany NY)",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib3",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apt.15777",
"article-title": "Editorial: low population mortality from COVID-19 in countries south of latitude 35 degrees North supports vitamin D as a factor determining severity",
"author": "Rhodes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1434",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Aliment Pharmacol Ther.",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib4",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-21211/v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib5",
"unstructured": "Ilie PC, Stefanescu S, Smith L. The role of vitamin D in the prevention of Coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2020."
},
{
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib6",
"unstructured": "Kara M, Ekiz T, Ricci V, Kara O, Chang KV, Ozcakar L. ‘Scientific Strabismus’ or Two Related Pandemics: COVID-19 & Vitamin D Deficiency. Br J Nutr. 2020:1–20."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2310/JIM.0b013e31821b8755",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and the immune system",
"author": "Aranow",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "881",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Investig Med.",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib7",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2032",
"article-title": "The interplay between vitamin D and viral infections",
"author": "Teymoori-Rad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2032",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Rev Med Virol.",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib8",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data",
"author": "Martineau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "i6583",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib9",
"volume": "356",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib10",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.050",
"article-title": "Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank",
"author": "Hastie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "561",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr.",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib11",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.3585561",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib12",
"unstructured": "Raharusun, Prabowo and Priambada, Sadiah and Budiarti, Cahni and Agung, Erdie and Budi, Cipta, Patterns of COVID-19 Mortality and Vitamin D: An Indonesian Study (April 26, 2020). Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3585561 or https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3585561."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.annepidem.2007.12.001",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status: measurement, interpretation, and clinical application",
"author": "Holick",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "73",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Ann Epidemiol.",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib13",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CM9.0000000000000819",
"article-title": "Diagnosis and Treatment Protocol for Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia (Trial Version 7)",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1087",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Chin Med J (Engl).",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib14",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib15",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2018/5813095",
"author": "Rondanelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5813095",
"journal-title": "Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib16",
"volume": "2018",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.037",
"article-title": "The pathogenesis and treatment of the “Cytokine Storm’ in COVID-19",
"author": "Ye",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "607",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Infect.",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib17",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apm.12982",
"article-title": "Effect of single-dose injection of vitamin D on immune cytokines in ulcerative colitis patients: a randomized placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Sharifi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "681",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "APMIS",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib18",
"volume": "127",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00210-020-01911-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib19",
"unstructured": "Aygun H. Vitamin D can prevent COVID-19 infection-induced multiple organ damage. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.0803217",
"article-title": "1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 and IL-2 combine to inhibit T cell production of inflammatory cytokines and promote development of regulatory T cells expressing CTLA-4 and FoxP3",
"author": "Jeffery",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5458",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "J Immunol.",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib20",
"volume": "183",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu7043011",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and 1,25(OH)2D regulation of T cells",
"author": "Cantorna",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3011",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib21",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.005",
"article-title": "Clinical features of COVID-19 in elderly patients: A comparison with young and middle-aged patients",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Infect.",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib22",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.021",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib23",
"unstructured": "Zheng Z, Peng F, Xu B, Zhao J, Liu H, Peng J, et al. Risk factors of critical & mortal COVID-19 cases: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. J Infect. 2020."
},
{
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib24",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ibd/izy346",
"article-title": "Randomized Trial of Vitamin D Supplementation to Prevent Seasonal Influenza and Upper Respiratory Infection in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease",
"author": "Arihiro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1088",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Inflamm Bowel Dis.",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib25",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0950268806007175",
"article-title": "Epidemic influenza and vitamin D",
"author": "Cannell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1129",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Epidemiol Infect.",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib26",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2017.8708",
"article-title": "Effect of High-Dose vs Standard-Dose Wintertime Vitamin D Supplementation on Viral Upper Respiratory Tract Infections in Young Healthy Children",
"author": "Aglipay",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "245",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib27",
"volume": "318",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/INF.0000000000002225",
"article-title": "Effect of High-Dose Vitamin D Supplementation on Upper Respiratory Tract Infection Symptom Severity in Healthy Children",
"author": "Hueniken",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "564",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Pediatr Infect Dis J.",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib28",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100041",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib29",
"unstructured": "Marik PE, Kory P, Varon J. Does vitamin D status impact mortality from SARS-CoV-2 infection? Med Drug Discov. 2020:100041."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.08.20058578",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib30",
"unstructured": "Daneshkhah A, Agrawal V, Eshein A, Subramanian H, Roy HK, Backman V. The Possible Role of Vitamin D in Suppressing Cytokine Storm and Associated Mortality in COVID-19 Patients. medRxiv. 2020:2020.04.08.20058578."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.3571484",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0_bib31",
"unstructured": "Alipio, Mark, Vitamin D Supplementation Could Possibly Improve Clinical Outcomes of Patients Infected with Coronavirus-2019 (COVID-19) (April 9, 2020). Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3571484 or https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3571484."
}
],
"reference-count": 31,
"references-count": 31,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1279770723009983"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Geriatrics and Gerontology",
"Nutrition and Dietetics",
"Medicine (miscellaneous)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Impact of Serum 25(OH) Vitamin D Level on Mortality in Patients with COVID-19 in Turkey",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "25"
}
