A critical update on the role of mild and serious vitamin D deficiency prevalence and the COVID-19 epidemic in Europe
et al., Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441, Jan 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
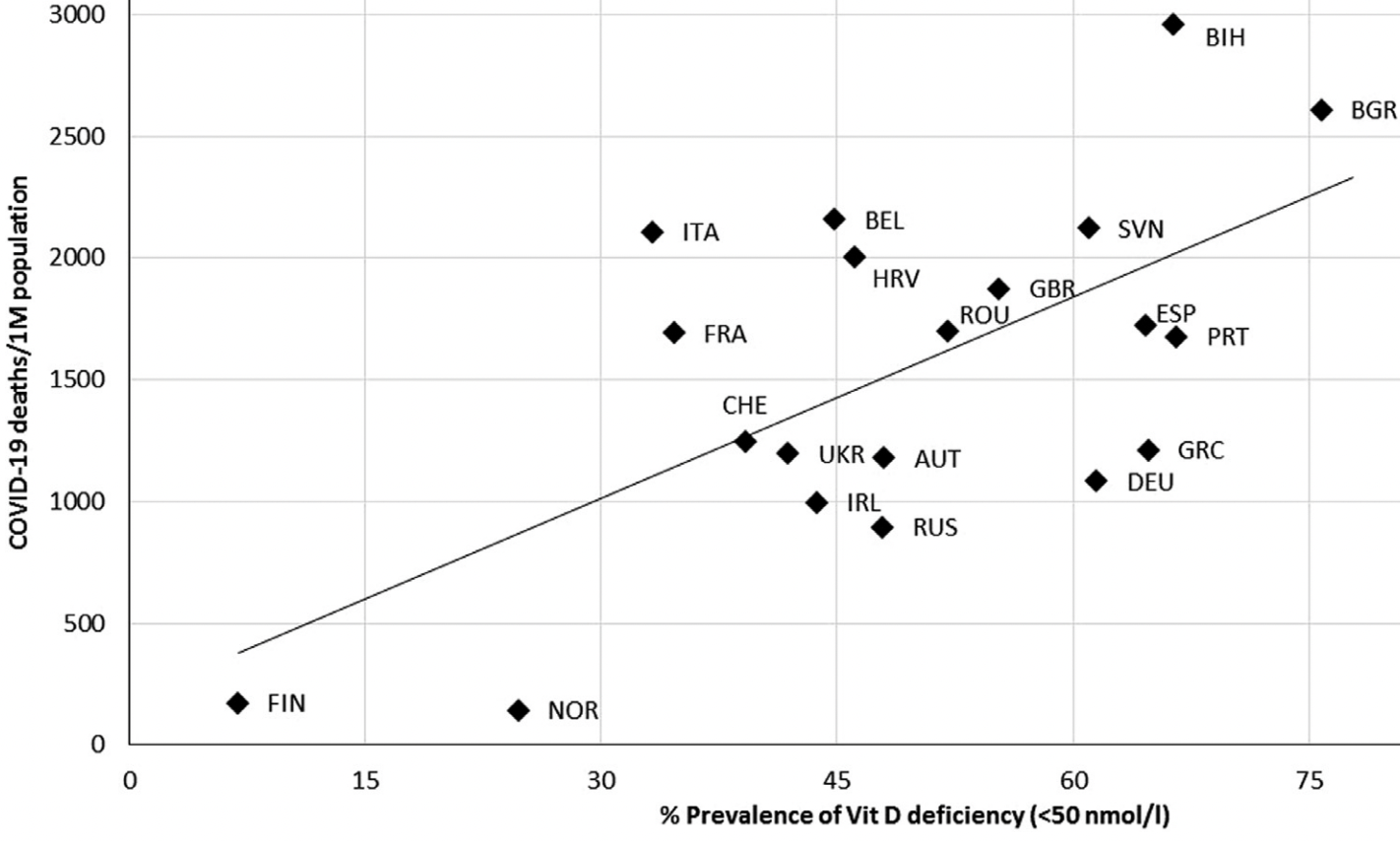
Analysis of vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 cases and mortality in European countries showing significant correlation between mortality and prevalence of both mild vitamin D deficiency (r = 0.634, p = 0.003) and severe vitamin D deficiency (r = 0.538, p = 0.021).
Bakaloudi et al., 29 Jan 2021, retrospective, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, 2 authors.
A critical update on the role of mild and serious vitamin D deficiency prevalence and the COVID-19 epidemic in Europe
Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441
Objectives: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has emerged as a pandemic, affecting nearly 180 million people worldwide as of June 22, 2021. Previous studies have examined the association between the mean vitamin D (Vit D) concentration of each country and COVID-19 infection and mortality rate in European countries. The aim of the present study was to critically evaluate the relationship between prevalence of mild and severe Vit D deficiency in each country and COVID-19 infection, recovery, and mortality using updated data and a different methodological approach. Methods: Information on Vit D concentration or deficiency for each country was retrieved through a literature search. COVID-19 infections and mortalities per million people and total recoveries, as of June 22, 2021, were obtained. The associations between Vit D deficiency and COVID-19 infection, recovery, and mortality were explored using correlation coefficients and scatterplots. Results: Non-significant correlations were observed between both number of COVID-19 infections (r = 0.363, P = 0.116) and number of recoveries (r = 0.388, P = 0.091) and the prevalence of mild Vit D deficiency (<50 nmol/L). Similarly, non-significant correlations were observed between both infections (r = 0.215, P = 0.392) and recoveries (r = 0.242, P = 0.332) and the prevalence of severe Vit D deficiency (<30 nmol/L). Significant correlations were found between COVID-19 mortality and prevalence of both mild Vit D deficiency (r = 0.634, P = 0.003) and severe Vit D deficiency (r = 0.538, P = 0.021). Conclusions: The prevalence of neither mild nor severe Vit D deficiency was associated with the number of COVID-19 infections in European countries. Thus, it is an important parameter to consider when implementing preventive measures to face COVID-19.
Supplementary materials Supplementary material associated with this article can be found in the online version at doi:10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441.
References
Adebayo, Itkonen, Lilja, Lundqvist, Laatikainen, Prevalence and determinants of vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency among three immigrant groups in Finland: evidence from a population-based study using standardised 25-hydroxyvitamin D data, Public Health Nutr
Ali, Role of vitamin D in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity, J Infect Public Health
Annweiler, Beaudenon, Gautier, Simon, Dub Ee et al., COvid-19 and high-dose VITamin D supplementation TRIAL in high-risk older patients (COVIT-TRIAL): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial, Trials
Arteh, Narra, Nair, Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in chronic liver disease, Dig Dis Sci
Aspell, Laird, Healy, Shannon, Lawlor et al., The prevalence and determinants of vitamin D status in community-dwelling older adults: results from the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing (ELSA), Nutrients
Bahrami, Sadeghnia, Tabatabaeizadeh, Bahrami-Taghanaki, Behboodi et al., Genetic and epigenetic factors influencing vitamin D status, J Cell Physiol
Bakaloudi, Halloran, Rippin, Oikonomidou, Dardavesis et al., Intake and adequacy of the vegan diet: a systematic review of the evidence, Clin Nutr
Bergman, The link between vitamin D and COVID-19: distinguishing facts from fiction, J Intern Med
Borissova, Shinkov, Vlahov, Dakovska, Todorov et al., Vitamin D status in Bulgaria-winter data, Arch Osteoporos
Brodin, Why is COVID-19 so mild in children?, Acta Paediatr
Carpagnano, Lecce, Quaranta, Zito, Buonamico et al., Vitamin D deficiency as a predictor of poor prognosis in patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19, J Endocrinol Invest
Cashman, Kiely, Kinsella, Durazo-Arvizu, Tian et al., Evaluation of Vitamin D Standardization Program protocols for standardizing serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D data: a case study of the program's potential for national nutrition and health surveys, Am J Clin Nutr
Cereda, Bogliolo, Lobascio, Barichella, Zecchinelli et al., Vitamin D supplementation and outcomes in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients from the outbreak area of Lombardy. Italy, Nutrition
Chaudhry, Dranitsaris, Mubashir, Bartoszko, Riazi, A country level analysis measuring the impact of government actions, country preparedness and socioeconomic factors on COVID-19 mortality and related health outcomes, EClinicalMedicine
Cherrie, Clemens, Colandrea, Feng, Webb et al., Ultraviolet A radiation and COVID-19 deaths in the USA with replication studies in England and Italy
Clark, Jit, Warren-Gash, Guthrie, Wang et al., Global, regional, and national estimates of the population at increased risk of severe COVID-19 due to underlying health conditions in 2020: a modelling study, Lancet Glob Health
Coli C Bari C, Keser, Bituh, Rumbak, Samarin et al., Vitamin D status and prevalence of inadequacy in Croatian population
Cui, Xu, Li, Qiao, Han et al., Vitamin D receptor activation regulates microglia polarization and oxidative stress in spontaneously hypertensive rats and angiotensin II-exposed microglial cells: role of renin-angiotensin system, Redox Biol
Daneshkhah, Agrawal, Eshein, Subramanian, Roy et al., Evidence for possible association of vitamin D status with cytokine storm and unregulated inflammation in COVID-19 patients, Aging Clin Exp Res
Dimakopoulos, Magriplis, Mitsopoulou, Karageorgou, Bakogianni et al., Association of serum vitamin D status with dietary intake and sun exposure in adults, Clin Nutr ESPEN
Duarte, Carvalheiro, Rodrigues, Dias, Marques et al., Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and its predictors in the Portuguese population: a nationwide population-based study, Arch Osteoporos
Díaz, Opez, Paz-Graniel, Alonso-Sanz, Es Baldero et al., Vitamin D deficiency in primary health care users at risk in Spain, Nutr Hosp
El Din, Fayed, Nokeety, Abdulazim, Salem, Vitamin-D deficiency is encountered in almost all Egyptian stage 3À5 chronic kidney disease patients in spite of the sunny weather, Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl
Elmadfa, Meyer, Wottawa, Wagner, Hasenegger, Vitamin D intake and status in Austria and its effects on some health indicators, Austin J Nutr Metab
Fedele, Francesco, Riso, Collo, Obesity, malnutrition, and trace element deficiency in the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic: an overview, Nutrition
Giuliani, Barbieri, Pierro, Rossi, Widmann et al., LC-MS/MS based 25(OH)D status in a large Southern European outpatient cohort: gender-and age-specific differences, Eur J Nutr
Gorman, Weller, Investigating the potential for ultraviolet light to modulate morbidity and mortality from COVID-19: a narrative review and update, Front Cardiovasc Med
Gupta, Vashi, Trukova, Lis, Lammersfeld, Prevalence of serum vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency in cancer: review of the epidemiological literature, Exp Ther Med
Hoge, Donneau, Streel, Kolh, Chapelle et al., Vitamin D deficiency is common among adults in Wallonia (Belgium, 51°30 0 North): findings from the Nutrition, Environment and Cardio-Vascular Health study, Nutr Res
Holick, Sunlight and vitamin D for bone health and prevention of autoimmune diseases, cancers, and cardiovascular disease, Am J Clin Nutr
Hribar, Hristov, Gregori C M, Blaznik, Zaletel et al., Nutrihealth study: seasonal variation in vitamin D status among the Slovenian adult and elderly population, Nutrients
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality, Aging Clin Exp Res
Isaia, Di Emoz, Maluta, Fountoulakis, Ceccon et al., Does solar ultraviolet radiation play a role in COVID-19 infection and deaths? an environmental ecological study in Italy, Sci Total Environ
Jayawardena, Sooriyaarachchi, Chourdakis, Jeewandara, Ranasinghe, Enhancing immunity in viral infections, with special emphasis on COVID-19: a review, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Karonova, Andreeva, Nikitina, Belyaeva, Mokhova et al., Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in the north-west region of Russia: a crosssectional study, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol
Kasapidou, Oikonomidou, Chourdakis, Vitamin D status among Mediterranean regions, Hippokratia
Kazemi, Mohammadi, Aghababaee, Golzarand, Clark et al., Association of vitamin D status with SARS-CoV-2 infection or COVID-19 severity: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Kuster, Pfister, Burkard, Zhou, Twerenbold et al., SARS-CoV2: should inhibitors of the reninÀangiotensin system be withdrawn in patients with COVID-19?, Eur Heart J
Li, Li, Prevalence and influencing factors of vitamin D deficiency in chronic kidney disease: a cross-sectional study, Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther
Li, Qiao, Uskokovic, Xiang, Zheng et al., Vitamin D: a negative endocrine regulator of the reninÀangiotensin system and blood pressure, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol
Li, Zeng, Cao, Liu, Ping et al., Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced rat acute lung injury via suppressing the ERK1/2 and NF-kB signaling pathways, Sci Rep
Lips, Cashman, Lamberg-Allardt, Bischoff-Ferrari, Obermayer-Pietsch et al., Current vitamin D status in European and Middle East countries and strategies to prevent vitamin D deficiency: a position statement of the European Calcified Tissue Society, Eur J Endocrinol
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ
Mathieu, Badenhoop, Vitamin D and type 1 diabetes mellitus: state of the art, Trends Endocrinol Metab
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of vitamin D levels, race/ethnicity, and clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results, JAMA Netw Open
Mendes, Darling, Hart, Morse, Murphy et al., Impact of high latitude, urban living and ethnicity on 25-hydroxyvitamin D status: a need for multidisciplinary action?, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol
Mishal, Effects of different dress styles on vitamin D levels in healthy young Jordanian women, Osteoporos Int
Murdaca, Pioggia, Negrini, Vitamin D and COVID-19: an update on evidence and potential therapeutic implications, Clin Mol Allergy
Neale, Khan, Lucas, Waterhouse, Whiteman et al., The effect of sunscreen on vitamin D: a review, Br J Dermatol
Niculescu, Capatina, Dusceac, Caragheorgheopol, Ghemigian et al., Seasonal variation of serum vitamin D levels in Romania, Arch Osteoporos
Parohan, Yaghoubi, Seraji, Javanbakht, Sarraf et al., Risk factors for mortality in patients with Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies, Aging Male
Petrenya, Lamberg-Allardt, Melhus, Broderstad, Brustad, Vitamin D status in a multi-ethnic population of northern Norway: the SAMINOR 2 Clinical Survey, Public Health Nutr
Rabenberg, Scheidt-Nave, Busch, Rieckmann, Hintzpeter et al., Vitamin D status among adults in Germany-results from the German Health Interview and Examination Survey for Adults (DEGS1), BMC Public Health
Rhodes, Subramanian, Laird, Griffin, Kenny, Perspective: vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 severity-plausibly linked by latitude, ethnicity, impacts on cytokines, ACE2 and thrombosis, J Intern Med
Sakem, Nock, Stanga, Medina, Nydegger et al., Serum concentrations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D and immunoglobulins in an older Swiss cohort: results of the Senior Labor Study, BMC Med
Schramm, Lahner, J€ Ockel K-H, Erbel, F€ et al., Recall Study Group. Impact of season and different vitamin D thresholds on prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in epidemiological cohortsa note of caution, Endocrine
Shchubelka, Vitamin D status in adults and children in Transcarpathia, Ukraine in 2019, BMC Nutr
Singh, Kaur, Singh, Revisiting the role of vitamin D levels in the prevention of COVID-19 infection and mortality in European countries post infections peak, Aging Clin Exp Res
Snijder, Van Dam, Visser, Deeg, Dekker et al., Adiposity in relation to vitamin D status and parathyroid hormone levels: a population-based study in older men and women, J Clin Endocrinol Metab
Sokolovic, Alimanovic-Alagic, Dzananovic, Cavaljuga, Beslic et al., Vitamin D status in Bosnia and Herzegovina: the crosssectional epidemiological analysis, Osteoporos Int
Souberbielle, Massart, Brailly-Tabard, Cavalier, Chanson, Prevalence and determinants of vitamin D deficiency in healthy French adults: the VARI-ETE study, Endocrine
Stafford, Covid-19: why Germany's case fatality rate seems so low, BMJ
Szeto, Zucker, Lasota, Rubin, Walker et al., Vitamin D status and COVID-19 clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients, Endocr Res
S€ Oderstr€ Om, Rosenblad, Adolfsson, Bergkvist, Malnutrition is associated with increased mortality in older adults regardless of the cause of death, Br J Nutr
The, Diabetes, Endocrinology, Vitamin D and COVID-19: why the controversy?, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol
Theodoratou, Tzoulaki, Zgaga, Ioannidis, Vitamin D and multiple health outcomes: umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational studies and randomised trials, BMJ
Van Schoor, Lips, Worldwide vitamin D status
Wacker, Holick, Vitamin D-effects on skeletal and extraskeletal health and the need for supplementation, Nutrients
Webb, Kift, Durkin, 'brien, Vail et al., The role of sunlight exposure in determining the vitamin D status of the U.K. white adult population, Br J Dermatol
Worldometer, COVID-19 Coronavirus Pandemic
Zheng, Peng, Xu, Zhao, Liu et al., Risk factors of critical & mortal COVID-19 cases: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis, J Infect
Zhu, Wei, Niu, The novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan. China, Glob Health Res Policy
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441",
"ISSN": [
"0899-9007"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441",
"alternative-id": [
"S0899900721003038"
],
"article-number": "111441",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "A critical update on the role of mild and serious vitamin D deficiency prevalence and the COVID-19 epidemic in Europe"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Nutrition"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bakaloudi",
"given": "Dimitra Rafailia",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9490-8356",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Chourdakis",
"given": "Michail",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Nutrition"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.fr",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-30T03:07:54Z",
"timestamp": 1627614474000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-02T14:59:55Z",
"timestamp": 1638457195000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-09T16:30:40Z",
"timestamp": 1644424240345
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 3,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "0899-9007"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1640995200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0899900721003038?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0899900721003038?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "111441",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0001",
"unstructured": "Worldometer, COVID-19 Coronavirus Pandemic 2020. Available at: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/coronavirus-cases/. Accessed June 23rd, 2021."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s41256-020-00135-6",
"article-title": "The novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6",
"journal-title": "China. Glob Health Res Policy",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0002",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100464",
"article-title": "A country level analysis measuring the impact of government actions, country preparedness and socioeconomic factors on COVID-19 mortality and related health outcomes",
"author": "Chaudhry",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0003",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Obesity, malnutrition, and trace element deficiency in the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic: an overview",
"author": "Fedele",
"journal-title": "Nutrition",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0004",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30264-3",
"article-title": "Global, regional, and national estimates of the population at increased risk of severe COVID-19 due to underlying health conditions in 2020: a modelling study",
"author": "Clark",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1003",
"journal-title": "Lancet Glob Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0005",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114517000435",
"article-title": "Malnutrition is associated with increased mortality in older adults regardless of the cause of death",
"author": "Söderström",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "532",
"journal-title": "Br J Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0006",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.015",
"article-title": "Enhancing immunity in viral infections, with special emphasis on COVID-19: a review",
"author": "Jayawardena",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "367",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0007",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu5010111",
"article-title": "Vitamin D—effects on skeletal and extraskeletal health and the need for supplementation",
"author": "Wacker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "111",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0008",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data",
"author": "Martineau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "i6583",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0009",
"volume": "356",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.06.021",
"article-title": "Role of vitamin D in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity",
"author": "Ali",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1373",
"journal-title": "J Infect Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0010",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13158",
"article-title": "The link between vitamin D and COVID-19: distinguishing facts from fiction",
"author": "Bergman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "131",
"journal-title": "J Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0011",
"volume": "289",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12948-020-00139-0",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and COVID-19: an update on evidence and potential therapeutic implications",
"author": "Murdaca",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "23",
"journal-title": "Clin Mol Allergy",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0012",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation and outcomes in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients from the outbreak area of Lombardy",
"author": "Cereda",
"journal-title": "Italy. Nutrition",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0013",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.4117",
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D levels, race/ethnicity, and clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results",
"author": "Meltzer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0014",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2019.101295",
"article-title": "Vitamin D receptor activation regulates microglia polarization and oxidative stress in spontaneously hypertensive rats and angiotensin II-exposed microglial cells: role of renin-angiotensin system",
"author": "Cui",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Redox Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0015",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep27911",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced rat acute lung injury via suppressing the ERK1/2 and NF-κB signaling pathways",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "27911",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0016",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13149",
"article-title": "Perspective: vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 severity—plausibly linked by latitude, ethnicity, impacts on cytokines, ACE2 and thrombosis",
"author": "Rhodes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "97",
"journal-title": "J Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0017",
"volume": "289",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2004.03.004",
"article-title": "Vitamin D: a negative endocrine regulator of the renin–angiotensin system and blood pressure",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "387",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0018",
"volume": "89–90",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa235",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV2: should inhibitors of the renin–angiotensin system be withdrawn in patients with COVID-19?",
"author": "Kuster",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1801",
"journal-title": "Eur Heart J",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0019",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40618-020-01370-x",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency as a predictor of poor prognosis in patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19",
"author": "Carpagnano",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "765",
"journal-title": "J Endocrinol Invest",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0020",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01677-y",
"article-title": "Evidence for possible association of vitamin D status with cytokine storm and unregulated inflammation in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Daneshkhah",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2141",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin Exp Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0021",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01619-8",
"article-title": "Revisiting the role of vitamin D levels in the prevention of COVID-19 infection and mortality in European countries post infections peak",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1609",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin Exp Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0022",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8",
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality",
"author": "Ilie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1195",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin Exp Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0023",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0024",
"unstructured": "ISO 3166 Country Codes. The International Standard for country codes and codes for their subdivisions: International Organization for Standardization. 2021 Available at: https://www.iso.org/iso-3166-country-codes.html. Accessed June 23rd, 2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D intake and status in Austria and its effects on some health indicators",
"author": "Elmadfa",
"first-page": "1050",
"journal-title": "Austin J Nutr Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0025",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nutres.2015.06.005",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency is common among adults in Wallonia (Belgium, 51°30′ North): findings from the Nutrition, Environment and Cardio-Vascular Health study",
"author": "Hoge",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "716",
"journal-title": "Nutr Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0026",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00198-016-3831-0",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status in Bosnia and Herzegovina: the cross-sectional epidemiological analysis",
"author": "Sokolovic",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1021",
"journal-title": "Osteoporos Int",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0027",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11657-013-0133-4",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status in Bulgaria—winter data",
"author": "Borissova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "133",
"journal-title": "Arch Osteoporos",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0028",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D status and prevalence of inadequacy in Croatian population",
"author": "Colić Barić",
"first-page": "97",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0029",
"series-title": "Book of Abstracts of 4th International Congress of Nutritionists Zadar, Hrvatska",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S1368980019004312",
"article-title": "Prevalence and determinants of vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency among three immigrant groups in Finland: evidence from a population-based study using standardised 25-hydroxyvitamin D data",
"author": "Adebayo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1254",
"journal-title": "Public Health Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0030",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12020-016-0960-3",
"article-title": "Prevalence and determinants of vitamin D deficiency in healthy French adults: the VARIETE study",
"author": "Souberbielle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "543",
"journal-title": "Endocrine",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0031",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12889-015-2016-7",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status among adults in Germany—results from the German Health Interview and Examination Survey for Adults (DEGS1)",
"author": "Rabenberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "641",
"journal-title": "BMC Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0032",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2019.09.008",
"article-title": "Association of serum vitamin D status with dietary intake and sun exposure in adults",
"author": "Dimakopoulos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "23",
"journal-title": "Clin Nutr ESPEN",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0033",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.112.057182",
"article-title": "Evaluation of Vitamin D Standardization Program protocols for standardizing serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D data: a case study of the program's potential for national nutrition and health surveys",
"author": "Cashman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1235",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0034",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00394-018-1803-1",
"article-title": "LC-MS/MS based 25(OH)D status in a large Southern European outpatient cohort: gender- and age-specific differences",
"author": "Giuliani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2511",
"journal-title": "Eur J Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0035",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S1368980018003816",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status in a multi-ethnic population of northern Norway: the SAMINOR 2 Clinical Survey",
"author": "Petrenya",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1186",
"journal-title": "Public Health Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0036",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11657-020-0695-x",
"article-title": "Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and its predictors in the Portuguese population: a nationwide population-based study",
"author": "Duarte",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "36",
"journal-title": "Arch Osteoporos",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0037",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11657-017-0407-3",
"article-title": "Seasonal variation of serum vitamin D levels in Romania",
"author": "Niculescu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "113",
"journal-title": "Arch Osteoporos",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0038",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.03.026",
"article-title": "Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in the north-west region of Russia: a cross-sectional study",
"author": "Karonova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "230",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0039",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12061838",
"article-title": "Nutrihealth study: seasonal variation in vitamin D status among the Slovenian adult and elderly population",
"author": "Hribar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1838",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0040",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1741-7015-11-176",
"article-title": "Serum concentrations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D and immunoglobulins in an older Swiss cohort: results of the Senior Labor Study",
"author": "Sakem",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "176",
"journal-title": "BMC Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0041",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11061253",
"article-title": "The prevalence and determinants of vitamin D status in community-dwelling older adults: results from the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing (ELSA)",
"author": "Aspell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1253",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0042",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40795-020-00380-5",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status in adults and children in Transcarpathia, Ukraine in 2019",
"author": "Shchubelka",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "48",
"journal-title": "BMC Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0043",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency in primary health care users at risk in Spain",
"author": "Díaz-López",
"first-page": "03565",
"journal-title": "Nutr Hosp",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0044",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/advances/nmab012",
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D status with SARS-CoV-2 infection or COVID-19 severity: a systematic review and meta-analysis [e-pub ahead of print]",
"author": "Kazemi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Adv Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0045",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12020-017-1292-7",
"article-title": "Moebus S; on behalf of the Heinz Nixdorf Recall Study Group. Impact of season and different vitamin D thresholds on prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in epidemiological cohorts—a note of caution",
"author": "Schramm",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "658",
"journal-title": "Endocrine",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0046",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2133.2010.09975.x",
"article-title": "The role of sunlight exposure in determining the vitamin D status of the U.K. white adult population",
"author": "Webb",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1050",
"journal-title": "Br J Dermatol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0047",
"volume": "163",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.12.012",
"article-title": "Impact of high latitude, urban living and ethnicity on 25-hydroxyvitamin D status: a need for multidisciplinary action?",
"author": "Mendes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "95",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0048",
"volume": "188",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s001980170021",
"article-title": "Effects of different dress styles on vitamin D levels in healthy young Jordanian women",
"author": "Mishal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "931",
"journal-title": "Osteoporos Int",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0049",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bjd.17980",
"article-title": "The effect of sunscreen on vitamin D: a review",
"author": "Neale",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "907",
"journal-title": "Br J Dermatol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0050",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2005-0216",
"article-title": "Adiposity in relation to vitamin D status and parathyroid hormone levels: a population-based study in older men and women",
"author": "Snijder",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4119",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0051",
"volume": "90",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnu.2020.11.035",
"article-title": "Intake and adequacy of the vegan diet: a systematic review of the evidence",
"author": "Bakaloudi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3503",
"journal-title": "Clin Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0052",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5414/CP203737",
"article-title": "Prevalence and influencing factors of vitamin D deficiency in chronic kidney disease: a cross-sectional study",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "595",
"journal-title": "Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0053",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/1319-2442.275483",
"article-title": "Vitamin-D deficiency is encountered in almost all Egyptian stage 3–5 chronic kidney disease patients in spite of the sunny weather",
"author": "El Din",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1389",
"journal-title": "Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0054",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10620-009-1069-9",
"article-title": "Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in chronic liver disease",
"author": "Arteh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2624",
"journal-title": "Dig Dis Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0055",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/etm.2011.205",
"article-title": "Prevalence of serum vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency in cancer: review of the epidemiological literature",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "181",
"journal-title": "Exp Ther Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0056",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcp.26216",
"article-title": "Genetic and epigenetic factors influencing vitamin D status",
"author": "Bahrami",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4033",
"journal-title": "J Cell Physiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0057",
"volume": "233",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/80.6.1678S",
"article-title": "Sunlight and vitamin D for bone health and prevention of autoimmune diseases, cancers, and cardiovascular disease",
"author": "Holick",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8S",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0058",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tem.2005.06.004",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and type 1 diabetes mellitus: state of the art",
"author": "Mathieu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "261",
"journal-title": "Trends Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0059",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.021",
"article-title": "Risk factors of critical & mortal COVID-19 cases: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e16",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0060",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/13685538.2020.1774748",
"article-title": "Risk factors for mortality in patients with Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies",
"author": "Parohan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1416",
"journal-title": "Aging Male",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0061",
"volume": "2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bjd.20093",
"article-title": "Ultraviolet A radiation and COVID-19 deaths in the USA with replication studies in England and Italy [e-pub ahead of print]",
"author": "Cherrie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "363",
"journal-title": "Br J Dermatol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0062",
"volume": "185",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143757",
"article-title": "Does solar ultraviolet radiation play a role in COVID-19 infection and deaths? an environmental ecological study in Italy",
"author": "Isaia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci Total Environ",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0063",
"volume": "757",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcvm.2020.616527",
"article-title": "Investigating the potential for ultraviolet light to modulate morbidity and mortality from COVID-19: a narrative review and update",
"author": "Gorman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Cardiovasc Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0064",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D status among Mediterranean regions",
"author": "Kasapidou",
"first-page": "191",
"journal-title": "Hippokratia",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0065",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Worldwide vitamin D status",
"author": "van Schoor",
"first-page": "15",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0066",
"series-title": "Vitamin D, Vol. 2: health, disease and therapeutics",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00003-6",
"article-title": "The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology. Vitamin D and COVID-19: why the controversy?",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "53",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0067",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07435800.2020.1867162",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status and COVID-19 clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients",
"author": "Szeto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "66",
"journal-title": "Endocr Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0068",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.g2035",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and multiple health outcomes: umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational studies and randomised trials",
"author": "Theodoratou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "g2035",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0069",
"volume": "348",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0070",
"unstructured": "WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Situation by WHO Region, Country, Territory & Area. Available at: https://covid19.who.int Accessed June 23rd, 2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1395",
"article-title": "Covid-19: why Germany's case fatality rate seems so low",
"author": "Stafford",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m1395",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0071",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apa.15271",
"article-title": "Why is COVID-19 so mild in children?",
"author": "Brodin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1082",
"journal-title": "Acta Paediatr",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0072",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/EJE-18-0736",
"article-title": "Current vitamin D status in European and Middle East countries and strategies to prevent vitamin D deficiency: a position statement of the European Calcified Tissue Society",
"author": "Lips",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "23",
"journal-title": "Eur J Endocrinol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0073",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-020-04928-5",
"article-title": "COvid-19 and high-dose VITamin D supplementation TRIAL in high-risk older patients (COVIT-TRIAL): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Annweiler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1031",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111441_bib0074",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 74,
"references-count": 74,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Nutrition"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Nutrition and Dietetics",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"A critical update on the role of mild and serious vitamin D deficiency prevalence and the COVID-19 epidemic in Europe"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "93"
}
