Vitamin D and Lung Outcomes in Elderly COVID-19 Patients
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13030717 , Feb 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
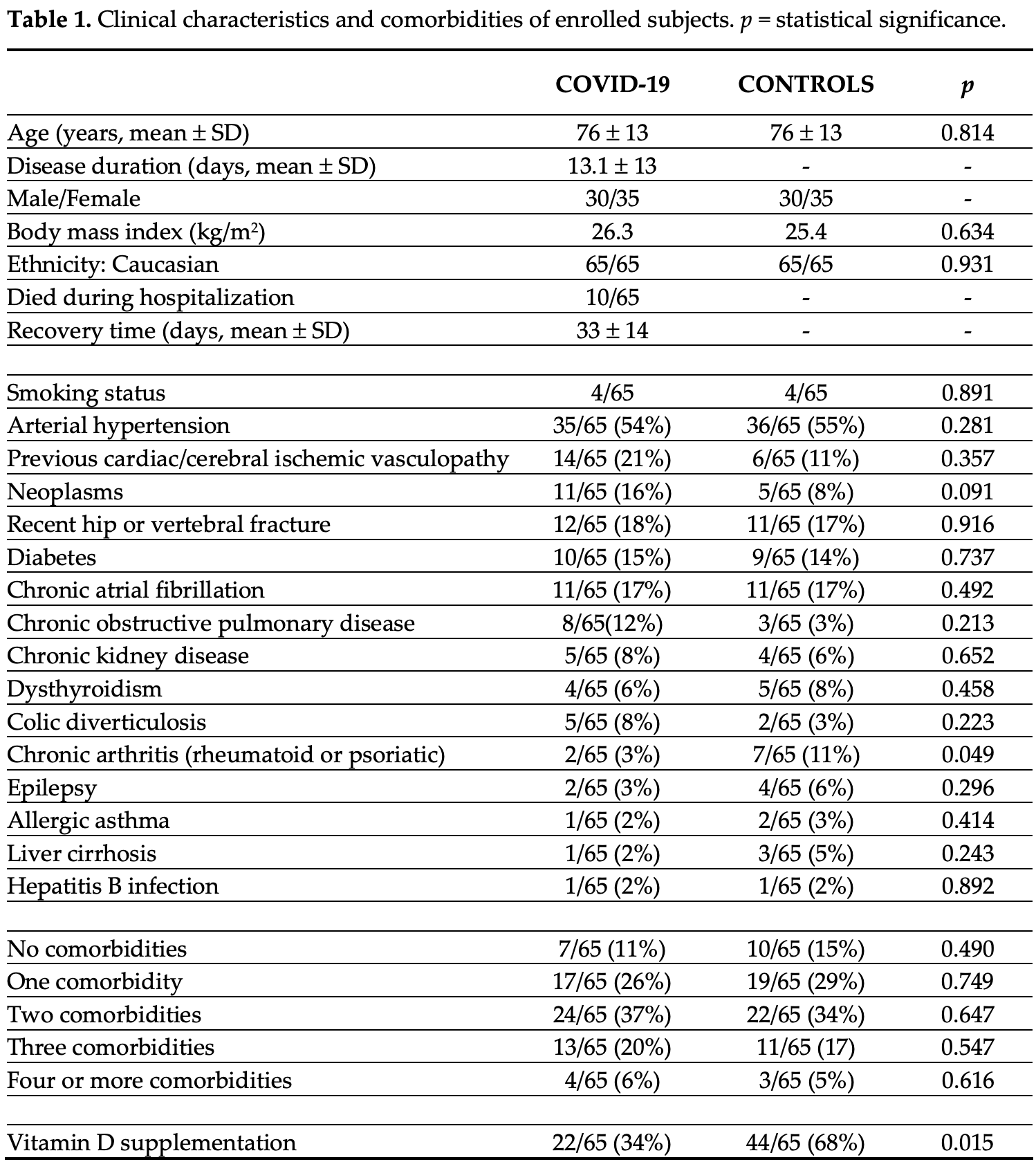
Retrospective 65 elderly COVID-19 patients and 65 matched controls, showing lower vitamin D levels associated with more severe lung involvement, longer disease duration, and higher mortality. Vitamin D supplementation was less common in the COVID-19 group compared to the control group.
This is the 22nd of 135 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p<0.0000000001.
40 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.0000001.
|
risk of case, 75.6% lower, OR 0.24, p < 0.001, treatment 22 of 65 (33.8%) cases,
44 of 65 (67.7%) controls, NNT 3.0, case control OR, vitamin D supplementation.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Sulli et al., 24 Feb 2021, retrospective, Italy, peer-reviewed, 10 authors, dosage not specified.
Vitamin D and Lung Outcomes in Elderly COVID-19 Patients
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13030717
Background and aim: Vitamin D deficiency is frequently reported in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. The aim of this study was to correlate the 25OH-Vitamin D serum concentrations with clinical parameters of lung involvement, in elderly patients hospitalized for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Methods: Sixty-five consecutive COVID-19 patients (mean age 76 ± 13 years) and sixtyfive sex-and age-matched control subjects (CNT) were analyzed. The following clinical parameters, including comorbidities, were collected at admission: type of pulmonary involvement, respiratory parameters (PaO 2 , SO 2 , PaCO 2 , PaO 2 /FiO 2 ), laboratory parameters (including 25OH-vitamin D, D-dimer, C-reactive protein). Results: Significantly lower vitamin D serum levels were found in COVID-19 patients than in CNT (median 7.9 vs. 16.3 ng/mL, p = 0.001). Interestingly, a statistically significant positive correlation was observed between vitamin D serum levels and PaO 2 (p = 0.03), SO 2 (p = 0.05), PaO 2 /FiO 2 (p = 0.02), while a statistically significant negative correlation was found between vitamin D serum levels and D-dimer (p = 0.04), C-reactive protein (p = 0.04) and percentage of O 2 in a venturi mask (p = 0.04). A negative correlation was also observed between vitamin D serum levels and severity of radiologic pulmonary involvement, evaluated by computed tomography: in particular, vitamin D was found significantly lower in COVID-19 patients with either multiple lung consolidations (p = 0.0001) or diffuse/severe interstitial lung involvement than in those with mild involvement (p = 0.05). Finally, significantly lower vitamin D serum levels were found in the elderly COVID-19 patients who died during hospitalization, compared to those who survived (median 3.0 vs. 8.4 ng/mL, p = 0.046). Conclusions: This study confirms that 25OH-vitamin D serum deficiency is associated with more severe lung involvement, longer disease duration and risk of death, in elderly COVID-19 patients. The detection of low vitamin D levels also in younger COVID-19 patients with less comorbidities further suggests vitamin D deficiency as crucial risk factor at any age.
Conflicts of Interest: All Authors declare no conflict of interest concerning this manuscript.
References
Adam, Key, Greenberg, D-dimer antigen: Current concepts and future prospects, Blood, doi:10.1182/blood-2008-06-165845
Adorini, Penna, Control of autoimmune diseases by the vitamin D endocrine system, Nat. Clin. Pract. Rheumatol, doi:10.1038/ncprheum0855
Aibana, Huang, Aboud, Arnedo-Pena, Becerra et al., Vitamin D status and risk of incident tuberculosis disease: A nested case-control study, systematic review, and individual-participant data meta-analysis, PLoS Med, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1002907
Baktash, Hosack, Patel, Shah, Kandiah et al., Vitamin D status and outcomes for hospitalised older patients with COVID-19, Postgrad Med. J, doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-138712
Beard, Bearden, Striker, Vitamin D and the anti-viral state, J. Clin. Virol, doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2010.12.006
Berry, Hesketh, Power, Hypponen, Vitamin D status has a linear association with seasonal infections and lung function in British adults, Br. J. Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114511001991
Bilezikian, Bikle, Hewison, Lazaretti-Castro, Formenti et al., Mechanisms in Endocrinology: Vitamin D and COVID-19, Eur. J. Endocrinol, doi:10.1530/EJE-20-0665
Bourgonje, Abdulle, Timens, Hillebrands, Navis et al., Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), SARS-CoV-2 and the pathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), J. Pathol, doi:10.1002/path.5471
Carpagnano, Di Lecce, Quaranta, Zito, Buonamico et al., Vitamin D deficiency as a predictor of poor prognosis in patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19, J. Endocrinol. Invest, doi:10.1007/s40618-020-01370-x
Charoenngam, Holick, Immunologic Effects of Vitamin D on Human Health and Disease, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12072097
Chen, Guo, Pan, Zhao, Structure analysis of the receptor binding of 2019-nCoV, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.02.071
Chen, Wilson, Bennett, Zosky, Identification of vitamin D sensitive pathways during lung development, Respir. Res, doi:10.1186/s12931-016-0362-3
Cianferotti, Bertoldo, Bischoff-Ferrari, Bruyere, Cooper et al., Vitamin D supplementation in the prevention and management of major chronic diseases not related to mineral homeostasis in adults: Research for evidence and a scientific statement from the European society for clinical and economic aspects of osteoporosis and osteoarthritis (ESCEO), Endocrine
Cutolo, Further emergent evidence for the vitamin D endocrine system involvement in autoimmune rheumatic disease risk and prognosis, Ann. Rheum. Dis, doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202538
Cutolo, Paolino, Smith, Evidences for a protective role of vitamin D in COVID-19, RMD Open, doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001454
Cutolo, Paolino, Sulli, Smith, Pizzorni et al., steroid hormones, and autoimmunity, Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1111/nyas.12432
Cutolo, Pizzorni, Sulli, Vitamin D endocrine system involvement in autoimmune rheumatic diseases, Autoimmun. Rev, doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2011.08.003
Cutolo, Plebani, Shoenfeld, Adorini, Tincani, Vitamin D endocrine system and the immune response in rheumatic diseases, Vitam. Horm
Dall'ara, Cutolo, Andreoli, Tincani, Paolino, Vitamin D and systemic lupus erythematous: A review of immunological and clinical aspects, Clin. Exp. Rheumatol
Giustina, Formenti, Preventing a covid-19 pandemic Can high prevalence of severe hypovitaminosis D play a role in the high impact of Covid infection in Italy?, BMJ
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12040988
Grosse, Grosse, Salzer, Dünser, Motz et al., Analysis of cardiopulmonary findings in COVID-19 fatalities: High incidence of pulmonary artery thrombi and acute suppurative bronchopneumonia, Cardiovasc. Pathol, doi:10.1016/j.carpath.2020.107263
Hardie, Vollmer, Buist Saellingsen, Mørkve, Reference values for arterial blood gases in the elderly, Chest, doi:10.1378/chest.125.6.2053
Hastie, Mackay, Ho, Celis-Morales, Katikireddi et al., Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank Diabetes, Metab. Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.050
Hill, Granic, Davies, Collerton, Martin-Ruiz et al., Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration and its determinants in the very old: The Newcastle 85+ Study, Osteoporos. Int, doi:10.1007/s00198-015-3366-9
Holick, Binkley, Bischoff-Ferrari, Gordon, Hanley et al., Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1210/jc.2011-0385
Im, Je, Baek, Chung, Kwon et al., Nutritional status of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Int. J. Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.08.018
Kaminetzky, Moore, Fansiwala, Babb, Kaminetzky et al., Pulmonary Embolism on CTPA in COVID-19 Patients, Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging, doi:10.1148/ryct.2020200308
Kim, Meza, Clarke, Kim, Hickner, Vitamin D and Endothelial Function, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12020575
Kommoss, Schwab, Tavernar, Schreck, Wagner et al., The Pathology of Severe COVID-19-Related Lung Damage, Dtsch. Arztebl. Int
Kong, Zhu, Shi, Liu, Chen et al., VDR attenuates acute lung injury by blocking Ang-2-Tie-2 pathway and renin-angiotensin system, Mol. Endocrinol, doi:10.1210/me.2013-1146
Kuba, Imai, Rao, Gao, Guo et al., A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/nm1267
Kühn, Trotz, Stangl, Prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency and evidence for disease prevention in the older population, Z. Gerontol. Geriatr, doi:10.1007/s00391-018-1390-z
Li, Molecular mechanism of vitamin D in the cardiovascular system, J. Investig. Med, doi:10.2310/JIM.0b013e31820ee448
Lu, Zhang, Ma, Yue, Zou et al., Link between community-acquired pneumonia and vitamin D levels in older patients, Z. Gerontol. Geriatr, doi:10.1007/s00391-017-1237-z
Lu, Zhao, Li, Niu, Yang et al., Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding, Lancet
Machado, Ferro Aissa, Ribeiro, Antunes, Vitamin D supplementation alters the expression of genes associated with hypertension and did not induce DNA damage in rats, J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A, doi:10.1080/15287394.2019.1592044
Malek Mahdavi, A brief review of interplay between vitamin D and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: Implications for a potential treatment for COVID-19, Rev. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2119
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: Systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.i6583
Mason, Thoughts on the alveolar phase of COVID-19, Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajplung.00126.2020
Mcgonagle, O'donnell, Sharif, Emery, Bridgewood, Immune mechanisms of pulmonary intravascular coagulopathy in COVID-19 pneumonia, Lancet Rheumatol, doi:10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30121-1
Mitchell, Vitamin-D and COVID-19: Do deficient risk a poorer outcome?, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30183-2
Mohammad, Mishra, Ashraf, Emerging role of vitamin D and its associated molecules in pathways related to pathogenesis of thrombosis, Biomolecules, doi:10.3390/biom9110649
Munshi, Hussein, Toraih, Elshazli, Jardak et al., Vitamin D insufficiency as a potential culprit in critical COVID-19 patients, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26360
Ohaegbulam, Swalih, Patel, Smith, Perrin, Vitamin D Supplementation in COVID-19 Patients: A Clinical Case Series, Am. J Ther, doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001222
Orgaz-Molina, Buendia-Eisman, Arrabal-Polo, Ruiz, Arias-Santiago, Deficiency of serum concentration of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in psoriatic patients: A case-control study, J. Am. Acad. Derm, doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.01.040
Panagiotou, Tee, Ihsan, Athar, Marchitelli et al., Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 are associated with greater disease severity, Clin. Endocrinol, doi:10.1111/cen.14276
Pereira, Dantas Damascena, Galvão Azevedo, De Almeida Oliveira, Da Mota Santana, Vitamin D deficiency aggravates COVID-19: Systematic review and meta-analysis, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr, doi:10.1080/10408398.2020.1841090
Phokela, Peleg, Moya, Alcorn, Regulation of human pulmonary surfactant protein gene expression by 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajplung.00129.2004
Ranieri, Rubenfeld, Thompson, Ferguson, Caldwell et al., Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin Definition, JAMA
Rehan, Torday, Peleg, Gennaro, Vouros et al., 1Alpha,25-dihydroxy-3-epi-vitamin D3, a natural metabolite of 1alpha,25dihydroxy vitamin D3: Production and biological activity studies in pulmonary alveolar type II cells, Mol. Genet. Metab, doi:10.1016/S1096-7192(02)00022-7
Rhodes, Subramanian, Laird, Griffin, Kenny, Perspective: Vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 severityplausibly linked by latitude, ethnicity, impacts on cytokines, ACE2 and thrombosis, J. Intern. Med, doi:10.1111/joim.13149
Sakka, Connors, Hékimian, Martin-Toutain, Crichi et al., Association between D-Dimer levels and mortality in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review and pooled analysis, J. Med. Vasc, doi:10.1016/j.jdmv.2020.05.003
Sassi, Tamone, D'amelio, Vitamin, Nutrient, hormone, and immunomodulator, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu10111656
Science, Maguire, Russell, Smieja, Walter et al., Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and risk of upper respiratory tract infection in children and adolescents, Clin. Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/cit289
Trombetta, Smith, Gotelli, Ghio, Paolino et al., Vitamin D deficiency and clinical correlations in systemic sclerosis patients: A retrospective analysis for possible future developments, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0179062
Vojinovic, Tincani, Sulli, Soldano, Andreoli et al., European multicentre pilot survey to assess vitamin D status in rheumatoid arthritis patients and early development of a new Patient Reported Outcome questionnaire (D-PRO), Autoimmun. Rev, doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2017.03.002
Waldron, Ashby, Cornes, Bechervaise, Razavi et al., Vitamin D: A negative acute phase reactant, J. Clin. Pathol, doi:10.1136/jclinpath-2012-201301
Wang, Koh, Pang, Association between micronutrient deficiency and acute respiratory infections in healthy adults: A systematic review of observational studies, Nutr. J, doi:10.1186/s12937-019-0507-6
Weir, Thenappan, Bhargava, Chen, Does vitamin D deficiency increase the severity of COVID-19?, Clin. Med, doi:10.7861/clinmed.2020-0301
Xu, Chen, Wang, Feng, Zhou et al., Evolution of the novel coronavirus from the ongoing Wuhan outbreak and modeling of its spike protein for risk of human transmission, Sci. China Life Sci, doi:10.1007/s11427-020-1637-5
Zhou, Yang, Zhang, Li, Liu et al., Clinical Course of 195 Critically ILL COVID-19 Patients, A Retrospective Multi-Center Study, Shock, doi:10.1097/SHK.0000000000001629
Zittermann, Pilz, Hoffmann, März, Vitamin D and airway infections: A European perspective, Eur. J. Med. Res, doi:10.1186/s40001-016-0208-y
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13030717",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu13030717",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background and aim: Vitamin D deficiency is frequently reported in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. The aim of this study was to correlate the 25OH-Vitamin D serum concentrations with clinical parameters of lung involvement, in elderly patients hospitalized for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Methods: Sixty-five consecutive COVID-19 patients (mean age 76 ± 13 years) and sixty-five sex- and age-matched control subjects (CNT) were analyzed. The following clinical parameters, including comorbidities, were collected at admission: type of pulmonary involvement, respiratory parameters (PaO2, SO2, PaCO2, PaO2/FiO2), laboratory parameters (including 25OH-vitamin D, D-dimer, C-reactive protein). Results: Significantly lower vitamin D serum levels were found in COVID-19 patients than in CNT (median 7.9 vs. 16.3 ng/mL, p = 0.001). Interestingly, a statistically significant positive correlation was observed between vitamin D serum levels and PaO2 (p = 0.03), SO2 (p = 0.05), PaO2/FiO2 (p = 0.02), while a statistically significant negative correlation was found between vitamin D serum levels and D-dimer (p = 0.04), C-reactive protein (p = 0.04) and percentage of O2 in a venturi mask (p = 0.04). A negative correlation was also observed between vitamin D serum levels and severity of radiologic pulmonary involvement, evaluated by computed tomography: in particular, vitamin D was found significantly lower in COVID-19 patients with either multiple lung consolidations (p = 0.0001) or diffuse/severe interstitial lung involvement than in those with mild involvement (p = 0.05). Finally, significantly lower vitamin D serum levels were found in the elderly COVID-19 patients who died during hospitalization, compared to those who survived (median 3.0 vs. 8.4 ng/mL, p = 0.046). Conclusions: This study confirms that 25OH-vitamin D serum deficiency is associated with more severe lung involvement, longer disease duration and risk of death, in elderly COVID-19 patients. The detection of low vitamin D levels also in younger COVID-19 patients with less comorbidities further suggests vitamin D deficiency as crucial risk factor at any age.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu13030717"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sulli",
"given": "Alberto",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4732-0306",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Gotelli",
"given": "Emanuele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Casabella",
"given": "Andrea",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paolino",
"given": "Sabrina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pizzorni",
"given": "Carmen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alessandri",
"given": "Elisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grosso",
"given": "Marco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ferone",
"given": "Diego",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Vanessa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5396-0932",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Cutolo",
"given": "Maurizio",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-25T07:36:13Z",
"timestamp": 1614238573000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2021-03-05T06:00:40Z",
"timestamp": 1614924040000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-02T15:11:01Z",
"timestamp": 1712070661390
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 58,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
24
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-24T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1614124800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/3/717/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "717",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
24
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
24
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2011.08.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/B978-0-12-386960-9.00014-9",
"article-title": "Vitamin D endocrine system and the immune response in rheumatic diseases",
"author": "Cutolo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "327",
"journal-title": "Vitam. Horm.",
"key": "ref2",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ncprheum0855",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D and systemic lupus erythematous: A review of immunological and clinical aspects",
"author": "Dall’Ara",
"first-page": "153",
"journal-title": "Clin. Exp. Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref4",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/nyas.12432",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40001-016-0208-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7861/clinmed.2020-0301",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26360",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2011-0385",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/EJE-20-0665",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2017.03.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202538",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaad.2012.01.040",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0179062",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12072097",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/cit289",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114511001991",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00391-017-1237-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1002907",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12937-019-0507-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.08.018",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22"
},
{
"article-title": "Preventing a covid-19 pandemic Can high prevalence of severe hypovitaminosis D play a role in the high impact of Covid infection in Italy?",
"author": "Giustina",
"first-page": "m810",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref23",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30183-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.050",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cen.14276",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13149",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00391-018-1390-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00198-015-3366-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref29"
},
{
"article-title": "Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin Definition",
"author": "Ranieri",
"first-page": "2526",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref30",
"volume": "307",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1378/chest.125.6.2053",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/SHK.0000000000001629",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40618-020-01370-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2010.12.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2119",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11427-020-1637-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.02.071",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm1267",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref39"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2310/JIM.0b013e31820ee448",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref40"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/15287394.2019.1592044",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref41"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/path.5471",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref42"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/me.2013-1146",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref43"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajplung.00126.2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref44"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1096-7192(02)00022-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref45"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajplung.00129.2004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref46"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12931-016-0362-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref47"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12020575",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref48"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biom9110649",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref49"
},
{
"article-title": "The Pathology of Severe COVID-19-Related Lung Damage",
"author": "Kommoss",
"first-page": "500",
"journal-title": "Dtsch. Arztebl. Int.",
"key": "ref50",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30121-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref51"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood-2008-06-165845",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref52"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jdmv.2020.05.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref53"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-138712",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref54"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001454",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref55"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10111656",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref56"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/jclinpath-2012-201301",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref57"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MJT.0000000000001222",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref58"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1148/ryct.2020200308",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref59"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.carpath.2020.107263",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref60"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref61"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12020-017-1290-9",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation in the prevention and management of major chronic diseases not related to mineral homeostasis in adults: Research for evidence and a scientific statement from the European society for clinical and economic aspects of osteoporosis and osteoarthritis (ESCEO)",
"author": "Cianferotti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "245",
"journal-title": "Endocrine",
"key": "ref62",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2020.1841090",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref63"
}
],
"reference-count": 63,
"references-count": 63,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/3/717"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Food Science",
"Nutrition and Dietetics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Vitamin D and Lung Outcomes in Elderly COVID-19 Patients",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "13"
}
