Vitamin D Status is Associated With In-hospital Mortality and Mechanical Ventilation: A Cohort of COVID-19 Hospitalized Patients
et al., Mayo Clinic Proceedings, doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001, Jan 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 144 patients in the USA showing significantly lower mortality for vitamin D levels ≥30ng/mL.
This is the 38th of 228 COVID-19 sufficiency studies for vitamin D, which collectively show higher levels reduce risk with p<0.0000000001.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
This may explain in part the very high mortality seen in this study.
Results may differ in countries with improved SOC.
|
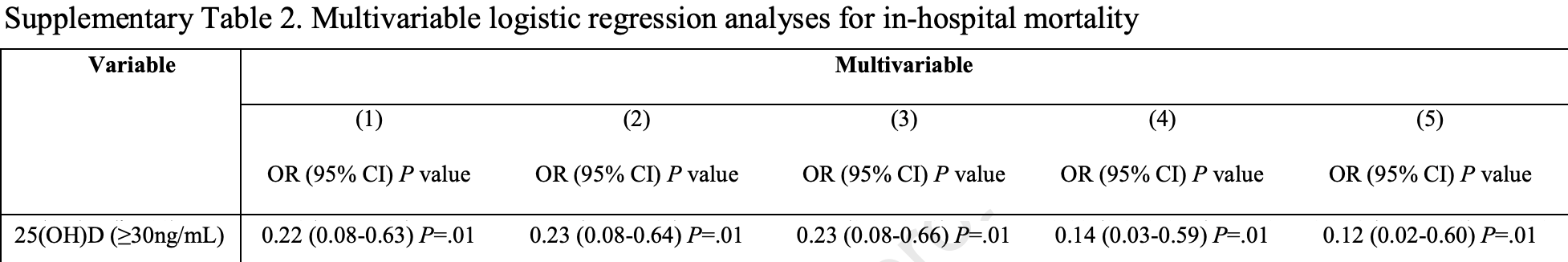
risk of death, 88.0% lower, RR 0.12, p = 0.01, high D levels 6 of 65 (9.2%), low D levels 20 of 79 (25.3%), NNT 6.2, adjusted per study, >30ng/mL, supplementary table 2, multivariable logistic regression model 5.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Angelidi et al., 9 Jan 2021, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
Vitamin D Status Is Associated With In-Hospital Mortality and Mechanical Ventilation: A Cohort of COVID-19 Hospitalized Patients
Mayo Clinic Proceedings, doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001
Since January 2020 Elsevier has created a COVID-19 resource centre with free information in English and Mandarin on the novel coronavirus COVID-19. The COVID-19 resource centre is hosted on Elsevier Connect, the company's public news and information website. Elsevier hereby grants permission to make all its COVID-19-related research that is available on the COVID-19 resource centre -including this research content -immediately available in PubMed Central and other publicly funded repositories, such as the WHO COVID database with rights for unrestricted research re-use and analyses in any form or by any means with acknowledgement of the original source. These permissions are granted for free by Elsevier for as long as the COVID-19 resource centre remains active.
References
Adams, Ren, Liu, Vitamin Dedirected rheostatic regulation of monocyte antibacterial responses, J Immunol
Cantorna, Snyder, Lin, Yang, Vitamin D and 1, 25(OH)2D regulation of T cells, Nutrients
Chakhtoura, Napoli, Hajj Fuleihan, Commentary: myths and facts on vitamin D amidst the COVID-19 pandemic, Metabolism
D'avolio, Avataneo, Manca, 25-Hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are lower in patients with positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2, Nutrients
Dancer, Parekh, Lax, Vitamin D deficiency contributes directly to the acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), Thorax
Demer, Hsu, Tintut, Steroid hormone vitamin D: Implications for cardiovascular disease, Circ Res
Docherty, Harrison, Green, Features of 20 133 UK patients in hospital with covid-19 using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol: prospective observational cohort study, BMJ
Freeman, Wilson, Spears, Shalhoub, Sibley, Performance evaluation of four 25-hydroxyvitamin D assays to measure 25-hydroxyvitamin D2, Clin Biochem
Giménez, Inserra, Tajer, Lungs as target of COVID-19 infection: protective common molecular mechanisms of vitamin D and melatonin as a new potential synergistic treatment, Life Sci
Ginde, Brower, Caterino, Early high-dose vitamin D 3 for critically ill, vitamin Dedeficient patients, N Engl J Med
Ginde, Camargo, Jr, Shapiro, Vitamin D insufficiency and sepsis severity in emergency department patients with suspected infection, Acad Emerg Med
Giustina, Adler, Binkley, Controversies in vitamin D: summary statement from an international conference, J Clin Endocrinol Metab
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Evidence that vitamin D supplementation Could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients
Greiller, Martineau, Modulation of the immune response to respiratory viruses by vitamin D, Nutrients
Hastie, Mackay, Ho, Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Herr, Shaykhiev, Bals, The role of cathelicidin and defensins in pulmonary inflammatory diseases, Expert Opin Biol Ther
Holick, Binkley, Bischoff-Ferrari, Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline, J Clin Endocrinol Metab
Holick, Chen, Vitamin D deficiency: a worldwide problem with health consequences, Am J Clin Nutr
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality, Aging Clin Exp Res
Jeffery, Burke, Mura, 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D 3 and IL-2 combine to inhibit T cell production of inflammatory cytokines and promote development of regulatory T cells expressing CTLA-4 and FoxP3, J Immunol
Laaksi, Vitamin D and respiratory infection in adults, Proc Nutr Soc
Langlois, Szwec, 'aragon, Heyland, Manzanares, Vitamin D supplementation in the critically ill: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Clin Nutr
Lemire, Adams, Kermani-Arab, Bakke, Sakai et al., 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D 3 suppresses human T helper/inducer lymphocyte activity in vitro, J Immunol
Liu, Stenger, Li, Toll-like receptor triggering of a vitamin Demediated human antimicrobial response, Science
Mahdavi, A brief review of interplay between vitamin D and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: implications for a potential treatment for COVID-19, Rev Med Virol
Manson, Bassuk, Commentary. Eliminating vitamin D deficiency during the COVID-19 pandemic: a call to action, Metabolism
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of vitamin D status and other clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results, JAMA Netw Open
Nair, Venkatesh, Center, Vitamin D deficiency and supplementation in critical illnessdthe known knowns and known unknowns, Crit Care
Palacios, Gonzalez, Is vitamin D deficiency a major global public health problem?, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol
Palaiodimos, Kokkinidis, Li, Severe obesity, increasing age and male sex are independently associated with worse in-hospital outcomes, and higher in-hospital mortality, in a cohort of patients with COVID-19 in the Bronx, Metabolism
Pham, Rahman, Majidi, Waterhouse, Neale, Acute respiratory tract infection and 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Int J Environ Res Public Health
Putzu, Belletti, Cassina, Vitamin D and outcomes in adult critically ill patients. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials, J Crit Care
Raisi-Estabragh, Mccracken, Bethell, Greater risk of severe COVID-19 in Black, Asian and minority ethnic populations is not explained by cardiometabolic, socioeconomic or behavioural factors, or by 25(OH)-vitamin D status: study of 1326 cases from the UK Biobank, J Public Health (Oxf)
Rhodes, Subramanian, Laird, Griffin, Kenny, Perspective: Vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 severitydplausibly linked by latitude, ethnicity, impacts on cytokines, ACE2, and thrombosis, J Intern Med
Rhodes, Subramanian, Laird, Kenny, Editorial: low population mortality from COVID-19 in countries south of latitude 35 degrees North supports vitamin D as a factor determining severity, Aliment Pharmacol Ther
Tay, Poh, Rénia, Macary, Ng, The trinity of COVID-19: immunity, inflammation and intervention, Nat Rev Immunol
Vitamin, Outcomes, None
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, JAMA
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001",
"ISSN": [
"0025-6196"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001",
"alternative-id": [
"S002561962100001X"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Vitamin D Status Is Associated With In-Hospital Mortality and Mechanical Ventilation: A Cohort of COVID-19 Hospitalized Patients"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Mayo Clinic Proceedings"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2021 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9886-7785",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Angelidi",
"given": "Angeliki M.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Belanger",
"given": "Matthew J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lorinsky",
"given": "Michael K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karamanis",
"given": "Dimitrios",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chamorro-Pareja",
"given": "Natalia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ognibene",
"given": "Jennifer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Palaiodimos",
"given": "Leonidas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mantzoros",
"given": "Christos S.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Mayo Clinic Proceedings",
"container-title-short": "Mayo Clinic Proceedings",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.jp",
"mayoclinicproceedings.org",
"clinicalkey.com",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.fr",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-11T00:13:00Z",
"timestamp": 1610323980000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-17T09:35:31Z",
"timestamp": 1697535331000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-22T11:48:25Z",
"timestamp": 1711108105184
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 56,
"issue": "4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "4",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1617235200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S002561962100001X?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S002561962100001X?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "875-886",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154276",
"article-title": "Commentary: myths and facts on vitamin D amidst the COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Chakhtoura",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "154276",
"journal-title": "Metabolism",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib2",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph16173020",
"article-title": "Acute respiratory tract infection and 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Pham",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3020",
"issue": "17",
"journal-title": "Int J Environ Res Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib3",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1553-2712.2011.01047.x",
"article-title": "Vitamin D insufficiency and sepsis severity in emergency department patients with suspected infection",
"author": "Ginde",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "551",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Acad Emerg Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib4",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-018-2185-8",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency and supplementation in critical illness—the known knowns and known unknowns",
"author": "Nair",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "276",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib5",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154322",
"article-title": "Commentary. Eliminating vitamin D deficiency during the COVID-19 pandemic: a call to action",
"author": "Manson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "154322",
"journal-title": "Metabolism",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib6",
"volume": "112",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apt.15777",
"article-title": "Editorial: low population mortality from COVID-19 in countries south of latitude 35 degrees North supports vitamin D as a factor determining severity",
"author": "Rhodes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1434",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Aliment Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib7",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8",
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality",
"author": "Ilie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1195",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin Exp Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib8",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12051359",
"article-title": "25-Hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are lower in patients with positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "D'Avolio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1359",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib9",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.050",
"article-title": "Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank",
"author": "Hastie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "561",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib10",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Greater risk of severe COVID-19 in Black, Asian and minority ethnic populations is not explained by cardiometabolic, socioeconomic or behavioural factors, or by 25(OH)-vitamin D status: study of 1326 cases from the UK Biobank",
"author": "Raisi-Estabragh",
"first-page": "451",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Public Health (Oxf)",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib11",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722",
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D status and other clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results",
"author": "Meltzer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2019722",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib12",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2015.05.021",
"article-title": "Performance evaluation of four 25-hydroxyvitamin D assays to measure 25-hydroxyvitamin D2",
"author": "Freeman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1097",
"issue": "16-17",
"journal-title": "Clin Biochem",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib13",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/87.4.1080S",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency: a worldwide problem with health consequences",
"author": "Holick",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1080S",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib15",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2013.11.003",
"article-title": "Is vitamin D deficiency a major global public health problem?",
"author": "Palacios",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "138",
"issue": "pt A",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib16",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2018-01414",
"article-title": "Controversies in vitamin D: summary statement from an international conference",
"author": "Giustina",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "234",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib17",
"volume": "104",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-206680",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency contributes directly to the acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)",
"author": "Dancer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "617",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Thorax",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib18",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0311-8",
"article-title": "The trinity of COVID-19: immunity, inflammation and intervention",
"author": "Tay",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "363",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib19",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2011-0385",
"article-title": "Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline",
"author": "Holick",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1911",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib20",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.311585",
"article-title": "Steroid hormone vitamin D: Implications for cardiovascular disease",
"author": "Demer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1576",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Circ Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib21",
"volume": "122",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.134.5.3032",
"article-title": "1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 suppresses human T helper/inducer lymphocyte activity in vitro",
"author": "Lemire",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3032",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib22",
"volume": "134",
"year": "1985"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu7043011",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and 1,25(OH)2D regulation of T cells",
"author": "Cantorna",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3011",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib23",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.0803217",
"article-title": "1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 and IL-2 combine to inhibit T cell production of inflammatory cytokines and promote development of regulatory T cells expressing CTLA-4 and FoxP3",
"author": "Jeffery",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5458",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "J Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib24",
"volume": "183",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"article-title": "Evidence that vitamin D supplementation Could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths",
"author": "Grant",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "988",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib25",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu7064240",
"article-title": "Modulation of the immune response to respiratory viruses by vitamin D",
"author": "Greiller",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4240",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib26",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1123933",
"article-title": "Toll-like receptor triggering of a vitamin D–mediated human antimicrobial response",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1770",
"issue": "5768",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib27",
"volume": "311",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.0803736",
"article-title": "Vitamin D–directed rheostatic regulation of monocyte antibacterial responses",
"author": "Adams",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4289",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib28",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0029665111003351",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and respiratory infection in adults",
"author": "Laaksi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "90",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Proc Nutr Soc",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib29",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1517/14712598.7.9.1449",
"article-title": "The role of cathelicidin and defensins in pulmonary inflammatory diseases",
"author": "Herr",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1449",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Expert Opin Biol Ther",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib30",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117808",
"article-title": "Lungs as target of COVID-19 infection: protective common molecular mechanisms of vitamin D and melatonin as a new potential synergistic treatment",
"author": "Martín Giménez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "117808",
"journal-title": "Life Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib31",
"volume": "254",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2119",
"article-title": "A brief review of interplay between vitamin D and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: implications for a potential treatment for COVID-19",
"author": "Malek Mahdavi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2119",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Rev Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib32",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13149",
"article-title": "Perspective: Vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 severity—plausibly linked by latitude, ethnicity, impacts on cytokines, ACE2, and thrombosis",
"author": "Rhodes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "97",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib33",
"volume": "289",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"article-title": "Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1239",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib34",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1985",
"article-title": "Features of 20 133 UK patients in hospital with covid-19 using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol: prospective observational cohort study",
"author": "Docherty",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m1985",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib35",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154262",
"article-title": "Severe obesity, increasing age and male sex are independently associated with worse in-hospital outcomes, and higher in-hospital mortality, in a cohort of patients with COVID-19 in the Bronx, New York",
"author": "Palaiodimos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "154262",
"journal-title": "Metabolism",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib36",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnu.2017.05.006",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation in the critically ill: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Langlois",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1238",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Clin Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib37",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcrc.2016.10.029",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and outcomes in adult critically ill patients. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials",
"author": "Putzu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "109",
"journal-title": "J Crit Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib38",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa1911124",
"article-title": "Early high-dose vitamin D3 for critically ill, vitamin D–deficient patients",
"author": "Ginde",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2529",
"issue": "26",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib39",
"volume": "381",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data",
"author": "Martineau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "i6583",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001_bib40",
"volume": "356",
"year": "2017"
}
],
"reference-count": 38,
"references-count": 38,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S002561962100001X"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Vitamin D Status Is Associated With In-Hospital Mortality and Mechanical Ventilation: A Cohort of COVID-19 Hospitalized Patients",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "96"
}
