Zn2+ Inhibits Coronavirus and Arterivirus RNA Polymerase Activity In Vitro and Zinc Ionophores Block the Replication of These Viruses in Cell Culture
et al., PLOS Pathogens 2010, 6:11, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176, Nov 2010
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000019 from 42 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
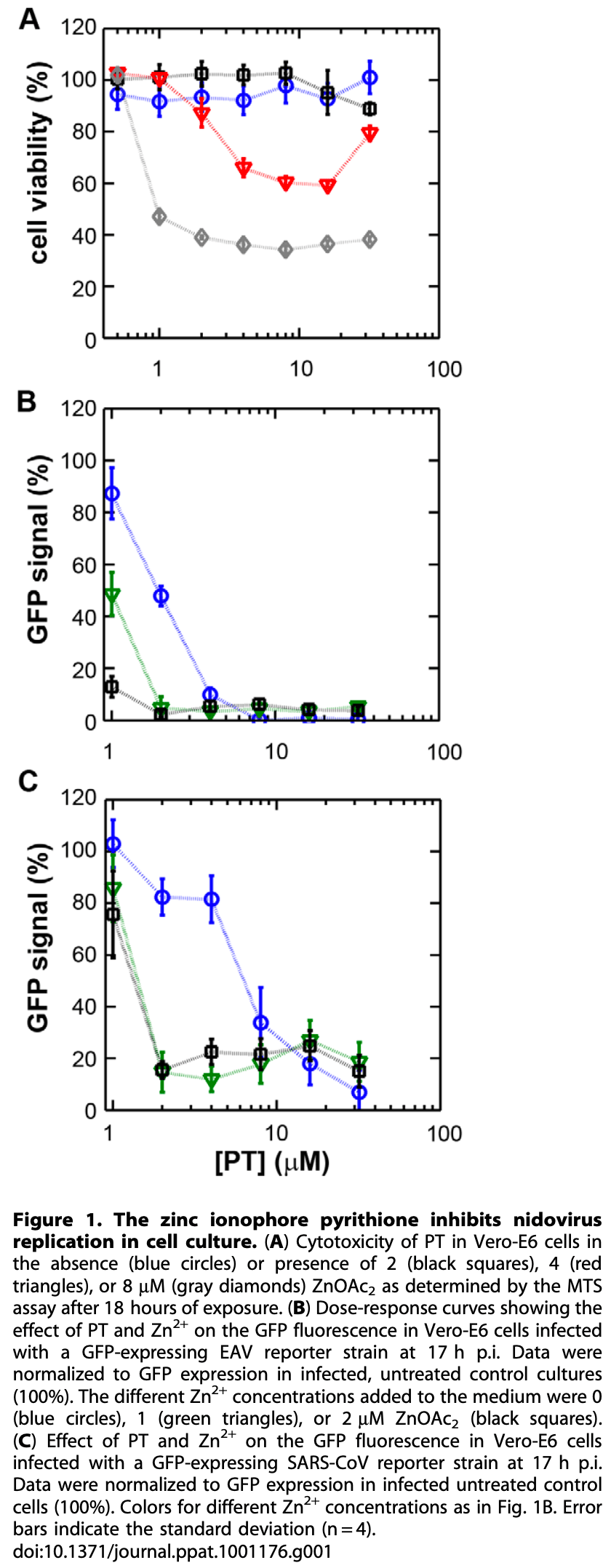
Shows that the combination of Zn2+ and a zinc ionophore (pyrithione) at low concentrations inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV and equine arteritis virus (EAV) in cell culture. Recommends further study of the use of zinc ionophores as antiviral compounds.
12 preclinical studies support the efficacy of zinc for COVID-19:
1.
Agamah et al., Network-based multi-omics-disease-drug associations reveal drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19 disease phases, ScienceOpen, doi:10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1.
2.
Lockwood, T., Coordination chemistry suggests that independently observed benefits of metformin and Zn2+ against COVID-19 are not independent, BioMetals, doi:10.1007/s10534-024-00590-5.
3.
El-Megharbel et al., Chemical and spectroscopic characterization of (Artemisinin/Quercetin/ Zinc) novel mixed ligand complex with assessment of its potent high antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 and antioxidant capacity against toxicity induced by acrylamide in male rats, PeerJ, doi:10.7717/peerj.15638.
4.
Bess et al., Identification of oral therapeutics using an AI platform against the virus responsible for COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1297924.
5.
Pormohammad et al., Zinc and SARS-CoV-2: A molecular modeling study of Zn interactions with RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase and 3C-like proteinase enzymes, International Journal of Molecular Medicine, doi:10.3892/ijmm.2020.4790.
6.
Pelucelli et al., Zn2+ and Cu2+ Interaction with the Recognition Interface of ACE2 for SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms24119202.
7.
Hajdrik et al., In Vitro Determination of Inhibitory Effects of Humic Substances Complexing Zn and Se on SARS-CoV-2 Virus Replication, Foods, doi:10.3390/foods11050694.
8.
Panchariya et al., Zinc2+ ion inhibits SARS-CoV-2 main protease and viral replication in vitro, Chemical Communications, doi:10.1039/D1CC03563K.
te Velthuis et al., 4 Nov 2010, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Zn2+ Inhibits Coronavirus and Arterivirus RNA Polymerase Activity In Vitro and Zinc Ionophores Block the Replication of These Viruses in Cell Culture
PLoS Pathogens, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176
Increasing the intracellular Zn 2+ concentration with zinc-ionophores like pyrithione (PT) can efficiently impair the replication of a variety of RNA viruses, including poliovirus and influenza virus. For some viruses this effect has been attributed to interference with viral polyprotein processing. In this study we demonstrate that the combination of Zn 2+ and PT at low concentrations (2 mM Zn 2+ and 2 mM PT) inhibits the replication of SARS-coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and equine arteritis virus (EAV) in cell culture. The RNA synthesis of these two distantly related nidoviruses is catalyzed by an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), which is the core enzyme of their multiprotein replication and transcription complex (RTC). Using an activity assay for RTCs isolated from cells infected with SARS-CoV or EAV-thus eliminating the need for PT to transport Zn 2+ across the plasma membrane-we show that Zn 2+ efficiently inhibits the RNA-synthesizing activity of the RTCs of both viruses. Enzymatic studies using recombinant RdRps (SARS-CoV nsp12 and EAV nsp9) purified from E. coli subsequently revealed that Zn 2+ directly inhibited the in vitro activity of both nidovirus polymerases. More specifically, Zn 2+ was found to block the initiation step of EAV RNA synthesis, whereas in the case of the SARS-CoV RdRp elongation was inhibited and template binding reduced. By chelating Zn 2+ with MgEDTA, the inhibitory effect of the divalent cation could be reversed, which provides a novel experimental tool for in vitro studies of the molecular details of nidovirus replication and transcription.
Author Contributions Copyright of PLoS Pathogens is the property of Public Library of Science and its content may not be copied or emailed to multiple sites or posted to a listserv without the copyright holder's express written permission. However, users may print, download, or email articles for individual use.
References
Alirezaei, Nairn, Glowinski, Premont, Marin, Zinc inhibits protein synthesis in neurons: potential rol of phosphorylation of translation initiation factor-2a, J Biol Chem
Arnold, Ghosh, Cameron, Divalent cation modulation of primer, template and nucleotide selection, J Biol Chem
Baum, Bebernitz, Palant, Mueller, Plotch, Purification, properties, and mutagenesis of poliovirus 3C protease, Virology
Beerens, Selisko, Ricagno, Imbert, Van Der Zanden, De Novo Initiation of RNA Synthesis by the Arterivirus RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase, J Virol
Butterworth, Korant, Characterization of the large picornaviral polypeptides produced in the presence of zinc ion, J Virol
Castro, Smidansky, Maksimchuk, Arnold, Korneeva, Two proton transfers in the transition state for nucleotidyl transfer catalyzed by RNA-and DNA-dependent RNA and DNA polymerases, Proc Natl Acad Sci
Clercq, Antivirals and antiviral strategies, Nat Rev Microbiol
Cordingley, Register, Callahan, Garsky, Colonno, Cleavage of small peptides in vitro by human rhinovirus 14 3C protease expressed in Escherichia coli, J Virol
Denison, Perlman, Translation and processing of mouse hepatitis virus virion RNA in a cell-free system, J Virol
Denison, Zoltick, Hughes, Giangreco, Olson, Intracellular processing of the N-terminal ORF 1a proteins of the coronavirus MHV-A59 requires multiple proteolytic events, Virology
Ferrari, Wright-Minogue, Fang, Baroudy, Lau, Characterization of soluble hepatitis C virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase expressed in Escherichia coli, J Virol
Frederickson, Koh, Bush, Neurobiology of zinc in health and disease, Nat Rev Neurosci
Gaudernak, Seipelt, Triendl, Grassauer, Kuechler, Antiviral Effects of Pyrrolidine Dithiocarbamate on Human Rhinoviruses, J Virol
Gorbalenya, Enjuanes, Ziebuhr, Snijder, Nidovirales: evolving the largest RNA virus genome, Virus Res
Hung, Gibbs, Tsiang, Biochemical characterization of rhinovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, Antiviral Res
Iuchi, Three classes of C2H2 zinc finger proteins, Cell Mol Life Sci
Korant, Kauer, Butterworth, Zinc ions inhibit replication of rhinoviruses, Nature
Krenn, Gaudernak, Holzer, Lanke, Van Kuppeveld, Antiviral Activity of the Zinc Ionophores Pyrithione and Hinokitiol against Picornavirus Infections, J Virol
Lanke, Krenn, Melchers, Seipelt, Van Kuppeveld, PDTC inhibits picornavirus polyprotein processing and RNA replication by transporting zinc ions into cells, J Gen Virol
Lazarczyk, Favre, Role of Zn 2+ ions in host-virus interactions, J Virol
Magda, Lecane, Wang, Hu, Thiemann, Synthesis and anticancer properties of water-soluble zinc ionophores, Cancer Res
Pasternak, Spaan, Snijder, Nidovirus transcription: how to make sense…?, J Gen Virol
Perlman, Netland, Coronaviruses post-SARS: update on replication and pathogenesis, Nat Rev Micro
Polatnick, Bachrach, Effect of zinc and other chemical agents on footand-mouth-disease virus replication, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Sawicki, Sawicki, Siddell, A Contemporary View of Coronavirus Transcription, J Virol
Si, Mcmanus, Zhang, Yuan, Cheung, Pyrrolidine Dithiocarbamate Reduces Coxsackievirus B3 Replication through Inhibition of the Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway, J Virol
Sims, Burkett, Yount, Pickles, SARS-CoV replication and pathogenesis in an in vitro model of the human conducting airway epithelium, Virus Res
Snijder, Bredenbeek, Dobbe, Thiel, Ziebuhr, Unique and conserved features of genome and proteome of SARS-coronavirus, an early split-off from the coronavirus group 2 lineage, J Mol Biol
Snijder, Van Der Meer, Zevenhoven-Dobbe, Onderwater, Van Der Meulen, Ultrastructure and Origin of Membrane Vesicles Associated with the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Replication Complex, J Virol
Snyder, De Jesus, Towfighi, Jacoby, Wedig, Neurological, microscopic and enzyme-histochemical assessment of zinc pyrithione toxicity, Food Cosmet Toxicol
Stockman, Bellamy, Garner, SARS: Systematic Review of Treatment Effects, PLoS Med
Studier, Protein production by auto-induction in high density shaking cultures, Protein Expr Purif
Suara, Crowe, Effect of zinc salts on respiratory syncytial virus replication, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Thompson, Mchutchison, Antiviral resistance and specifically targeted therapy for HCV (STAT-C), J Viral Hepat
Thompson, Patel, Tillman, Mchutchison, Directly acting antivirals for the treatment of patients with hepatitis C infection: A clinical development update addressing key future challenges, J Hepatol
Uchide, Ohyama, Bessho, Yuan, Yamakawa, Effect of antioxidants on apoptosis induced by influenza virus infection: inhibition of viral gene replication and transcription with pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate, Antiviral Res
Van Den Born, Posthuma, Knoops, Snijder, An infectious recombinant equine arteritis virus expressing green fluorescent protein from its replicase gene, J Gen Virol
Van Hemert, De Wilde, Gorbalenya, Snijder, The in Vitro RNA Synthesizing Activity of the Isolated Arterivirus Replication/Transcription Complex Is Dependent on a Host Factor, J Biol Chem
Van Hemert, Van Den Worm, She, Knoops, Mommaas et al., SARS-Coronavirus Replication/Transcription Complexes Are Membrane-Protected and Need a Host Factor for Activity In Vitro, PLoS Pathog
Velthuis, Arnold, Cameron, Van Den Worm, Snijder, The RNA polymerase activity of SARS-coronavirus nsp12 is primer dependent, Nucleic Acids Res
Winek, Buehler, Intravenous toxicity of zinc pyridinethione and several zinc salts, Toxicol Appl Pharmacol
Xf, Catalytic domain architecture of metzincin metalloproteases, J Biol Chem
Xu, Liu, Weiss, Arnold, Sarafianos, Molecular model of SARS coronavirus polymerase: implications for biochemical functions and drug design, Nucleic Acids Res
Yang, Lee, Nowotny, Making and Breaking Nucleic Acids: Two-Mg2+-Ion Catalysis and Substrate Specificity, Mol Cell
Yap, Xu, Chen, Malet, Egloff, Crystal Structure of the Dengue Virus RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Catalytic Domain at 1.85-Angstrom Resolution, J Virol
Zalewski, Forbes, Betts, Correlation of apoptosis with change in intracellular labile Zn(II) using Zinquin [(2-methyl-8-p-toluenesulphonamide-6-quinolyloxy)acetic acid], a new specific fluorescent probe for Zn(II), Biochem J
Zhai, Sun, Li, Pang, Xu, Insights into SARS-CoV transcription and replication from the structure of the nsp7-nsp8 hexadecamer, Nat Struct Mol Biol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176",
"ISSN": [
"1553-7374"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "te Velthuis",
"given": "Aartjan J. W.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "van den Worm",
"given": "Sjoerd H. E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sims",
"given": "Amy C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baric",
"given": "Ralph S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Snijder",
"given": "Eric J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "van Hemert",
"given": "Martijn J.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "PLoS Pathogens",
"container-title-short": "PLoS Pathog",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"www.plospathogens.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2010,
11,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2010-11-04T19:49:17Z",
"timestamp": 1288900157000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2020-06-13T14:19:00Z",
"timestamp": 1592057940000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Andino",
"given": "Raul",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-13T16:40:51Z",
"timestamp": 1715618451259
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 636,
"issue": "11",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2010,
11,
4
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "11",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2010,
11,
4
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2010,
11,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2010-11-04T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1288828800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "340",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e1001176",
"prefix": "10.1371",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2010,
11,
4
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2010,
11,
4
]
]
},
"publisher": "Public Library of Science (PLoS)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01314-08",
"article-title": "Role of Zn<sup>2+</sup> ions in host-virus interactions.",
"author": "M Lazarczyk",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11486",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "ref1",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrn1671",
"article-title": "Neurobiology of zinc in health and disease.",
"author": "CJ Frederickson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "449",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Neurosci",
"key": "ref2",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.274.45.32433",
"article-title": "Zinc inhibits protein synthesis in neurons: potential rol of phosphorylation of translation initiation factor-2a.",
"author": "M Alirezaei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "32433",
"journal-title": "J Biol Chem",
"key": "ref3",
"volume": "274",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0166-3542(02)00109-2",
"article-title": "Effect of antioxidants on apoptosis induced by influenza virus infection: inhibition of viral gene replication and transcription with pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate.",
"author": "N Uchide",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "207",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "ref4",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.48.3.783-790.2004",
"article-title": "Effect of zinc salts on respiratory syncytial virus replication.",
"author": "RO Suara",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "783",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "ref5",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.76.12.6004-6015.2002",
"article-title": "Antiviral Effects of Pyrrolidine Dithiocarbamate on Human Rhinoviruses.",
"author": "E Gaudernak",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6004",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "ref6",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.79.13.8014-8023.2005",
"article-title": "Pyrrolidine Dithiocarbamate Reduces Coxsackievirus B3 Replication through Inhibition of the Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway.",
"author": "X Si",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8014",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "ref7",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/248588a0",
"article-title": "Zinc ions inhibit replication of rhinoviruses.",
"author": "BD Korant",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "588",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref8",
"volume": "248",
"year": "1974"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.13.5.731",
"article-title": "Effect of zinc and other chemical agents on foot-and-mouth-disease virus replication.",
"author": "J Polatnick",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "731",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "ref9",
"volume": "13",
"year": "1978"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/vir.0.82634-0",
"article-title": "PDTC inhibits picornavirus polyprotein processing and RNA replication by transporting zinc ions into cells.",
"author": "K Lanke",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1206",
"journal-title": "J Gen Virol",
"key": "ref10",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01543-08",
"article-title": "Antiviral Activity of the Zinc Ionophores Pyrithione and Hinokitiol against Picornavirus Infections.",
"author": "BM Krenn",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "58",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "ref11",
"volume": "83",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/bj2960403",
"article-title": "Correlation of apoptosis with change in intracellular labile Zn(II) using Zinquin [(2-methyl-8-p-toluenesulphonamide-6-quinolyloxy)acetic acid], a new specific fluorescent probe for Zn(II).",
"author": "PD Zalewski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "403",
"journal-title": "Biochem J",
"key": "ref12",
"volume": "296",
"year": "1993"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0042-6822(91)90762-Z",
"article-title": "Purification, properties, and mutagenesis of poliovirus 3C protease.",
"author": "EZ Baum",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "140",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "ref13",
"volume": "165",
"year": "1991"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.63.12.5037-5045.1989",
"article-title": "Cleavage of small peptides in vitro by human rhinovirus 14 3C protease expressed in Escherichia coli.",
"author": "MG Cordingley",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5037",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "ref14",
"volume": "63",
"year": "1989"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.73.2.1649-1654.1999",
"article-title": "Characterization of soluble hepatitis C virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase expressed in Escherichia coli.",
"author": "E Ferrari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1649",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "ref15",
"volume": "73",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0166-3542(02)00101-8",
"article-title": "Biochemical characterization of rhinovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.",
"author": "M Hung",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "99",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "ref16",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrmicro2147",
"article-title": "Coronaviruses post-SARS: update on replication and pathogenesis.",
"author": "S Perlman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "439",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Micro",
"key": "ref17",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2006.01.017",
"article-title": "Nidovirales: evolving the largest RNA virus genome.",
"author": "AE Gorbalenya",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "17",
"journal-title": "Virus Res",
"key": "ref18",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0022-2836(03)00865-9",
"article-title": "Unique and conserved features of genome and proteome of SARS-coronavirus, an early split-off from the coronavirus group 2 lineage.",
"author": "EJ Snijder",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "991",
"journal-title": "J Mol Biol",
"key": "ref19",
"volume": "331",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/vir.0.81611-0",
"article-title": "Nidovirus transcription: how to make sense…?",
"author": "AO Pasternak",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1403",
"journal-title": "J Gen Virol",
"key": "ref20",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01358-06",
"article-title": "A Contemporary View of Coronavirus Transcription.",
"author": "SG Sawicki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "ref21",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.14.2.282-291.1974",
"article-title": "Characterization of the large picornaviral polypeptides produced in the presence of zinc ion.",
"author": "BE Butterworth",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "282",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "ref22",
"volume": "14",
"year": "1974"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.60.1.12-18.1986",
"article-title": "Translation and processing of mouse hepatitis virus virion RNA in a cell-free system.",
"author": "MR Denison",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "ref23",
"volume": "60",
"year": "1986"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0042-6822(92)90703-R",
"article-title": "Intracellular processing of the N-terminal ORF 1a proteins of the coronavirus MHV-A59 requires multiple proteolytic events.",
"author": "MR Denison",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "274",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "ref24",
"volume": "189",
"year": "1992"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M708136200",
"article-title": "The in Vitro RNA Synthesizing Activity of the Isolated Arterivirus Replication/Transcription Complex Is Dependent on a Host Factor.",
"author": "MJ van Hemert",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "16525",
"journal-title": "J Biol Chem",
"key": "ref25",
"volume": "283",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1000054",
"article-title": "SARS-Coronavirus Replication/Transcription Complexes Are Membrane-Protected and Need a Host Factor for Activity In Vitro.",
"author": "MJ van Hemert",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1000054",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog",
"key": "ref26",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkp904",
"article-title": "The RNA polymerase activity of SARS-coronavirus nsp12 is primer dependent.",
"author": "AJ te Velthuis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "203",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res",
"key": "ref27",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00564-07",
"article-title": "De Novo Initiation of RNA Synthesis by the Arterivirus RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase.",
"author": "N Beerens",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8384",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "ref28",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/vir.0.82590-0",
"article-title": "An infectious recombinant equine arteritis virus expressing green fluorescent protein from its replicase gene.",
"author": "E van den Born",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1196",
"journal-title": "J Gen Virol",
"key": "ref29",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2007.03.013",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV replication and pathogenesis in an in vitro model of the human conducting airway epithelium.",
"author": "AC Sims",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "33",
"journal-title": "Virus Res",
"key": "ref30",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkg916",
"article-title": "Molecular model of SARS coronavirus polymerase: implications for biochemical functions and drug design.",
"author": "X Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7117",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res",
"key": "ref31",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nsmb999",
"article-title": "Insights into SARS-CoV transcription and replication from the structure of the nsp7-nsp8 hexadecamer.",
"author": "Y Zhai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "980",
"journal-title": "Nat Struct Mol Biol",
"key": "ref32",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.0030343",
"article-title": "SARS: Systematic Review of Treatment Effects.",
"author": "LJ Stockman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e343",
"journal-title": "PLoS Med",
"key": "ref33",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2008.10.011",
"article-title": "Directly acting antivirals for the treatment of patients with hepatitis C infection: A clinical development update addressing key future challenges.",
"author": "A Thompson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "184",
"journal-title": "J Hepatol",
"key": "ref34",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrmicro975",
"article-title": "Antivirals and antiviral strategies.",
"author": "E De Clercq",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "704",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Microbiol",
"key": "ref35",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2893.2009.01124.x",
"article-title": "Antiviral resistance and specifically targeted therapy for HCV (STAT-C).",
"author": "AJV Thompson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "377",
"journal-title": "J Viral Hepat",
"key": "ref36",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molcel.2006.03.013",
"article-title": "Making and Breaking Nucleic Acids: Two-Mg2+-Ion Catalysis and Substrate Specificity.",
"author": "W Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5",
"journal-title": "Mol Cell",
"key": "ref37",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.0608952104",
"article-title": "Two proton transfers in the transition state for nucleotidyl transfer catalyzed by RNA- and DNA-dependent RNA and DNA polymerases.",
"author": "C Castro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4267",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci USA",
"key": "ref38",
"volume": "104",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.274.52.37060",
"article-title": "Poliovirus RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase (3Dpol). Divalent cation modulation of primer, template and nucleotide selection.",
"author": "JJ Arnold",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "37060",
"journal-title": "J Biol Chem",
"key": "ref39",
"volume": "274",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/PL00000885",
"article-title": "Three classes of C2H2 zinc finger proteins.",
"author": "S Iuchi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "625",
"journal-title": "Cell Mol Life Sci",
"key": "ref40",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.R800069200",
"article-title": "Catalytic domain architecture of metzincin metalloproteases.",
"author": "XF Gomis-Ruth",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "15353",
"journal-title": "J Biol Chem",
"key": "ref41",
"volume": "284",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02283-06",
"article-title": "Crystal Structure of the Dengue Virus RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Catalytic Domain at 1.85-Angstrom Resolution.",
"author": "TL Yap",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4753",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "ref42",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0041-008X(66)90121-9",
"article-title": "Intravenous toxicity of zinc pyridinethione and several zinc salts.",
"author": "CL Winek",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "296",
"journal-title": "Toxicol Appl Pharmacol",
"key": "ref43",
"volume": "9",
"year": "1966"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0015-6264(79)90126-3",
"article-title": "Neurological, microscopic and enzyme-histochemical assessment of zinc pyrithione toxicity.",
"author": "DR Snyder",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "651",
"journal-title": "Food Cosmet Toxicol",
"key": "ref44",
"volume": "17",
"year": "1979"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0601",
"article-title": "Synthesis and anticancer properties of water-soluble zinc ionophores.",
"author": "D Magda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5318",
"journal-title": "Cancer Res",
"key": "ref45",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02501-05",
"article-title": "Ultrastructure and Origin of Membrane Vesicles Associated with the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Replication Complex.",
"author": "EJ Snijder",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5927",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "ref46",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pep.2005.01.016",
"article-title": "Protein production by auto-induction in high density shaking cultures.",
"author": "F Studier",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "207",
"journal-title": "Protein Expr Purif",
"key": "ref47",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2005"
}
],
"reference-count": 47,
"references-count": 47,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Zn2+ Inhibits Coronavirus and Arterivirus RNA Polymerase Activity In Vitro and Zinc Ionophores Block the Replication of These Viruses in Cell Culture",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.corrections_policy",
"volume": "6"
}
