Zinc and SARS-CoV-2: A molecular modeling study of Zn interactions with RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase and 3C-like proteinase enzymes
et al., International Journal of Molecular Medicine, doi:10.3892/ijmm.2020.4790, Nov 2020
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000028 from 47 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
In silico analysis supporting the hypothesis that Zn would bind and regulate the enzymatic activities of 3CLpro and RdRp of SARS-CoV-2 and therefore inhibit viral replication. Since Zn has established immune health benefits, is readily available, inexpensive and safe, the authors propose that Zn could help ameliorate COVID-19.
12 preclinical studies support the efficacy of zinc for COVID-19:
1.
Agamah et al., Network-based multi-omics-disease-drug associations reveal drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19 disease phases, ScienceOpen, doi:10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1.
2.
Lockwood, T., Coordination chemistry suggests that independently observed benefits of metformin and Zn2+ against COVID-19 are not independent, BioMetals, doi:10.1007/s10534-024-00590-5.
3.
El-Megharbel et al., Chemical and spectroscopic characterization of (Artemisinin/Quercetin/ Zinc) novel mixed ligand complex with assessment of its potent high antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 and antioxidant capacity against toxicity induced by acrylamide in male rats, PeerJ, doi:10.7717/peerj.15638.
4.
Bess et al., Identification of oral therapeutics using an AI platform against the virus responsible for COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1297924.
5.
Pormohammad et al., Zinc and SARS-CoV-2: A molecular modeling study of Zn interactions with RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase and 3C-like proteinase enzymes, International Journal of Molecular Medicine, doi:10.3892/ijmm.2020.4790.
6.
Pelucelli et al., Zn2+ and Cu2+ Interaction with the Recognition Interface of ACE2 for SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms24119202.
7.
Hajdrik et al., In Vitro Determination of Inhibitory Effects of Humic Substances Complexing Zn and Se on SARS-CoV-2 Virus Replication, Foods, doi:10.3390/foods11050694.
8.
Panchariya et al., Zinc2+ ion inhibits SARS-CoV-2 main protease and viral replication in vitro, Chemical Communications, doi:10.1039/D1CC03563K.
Pormohammad et al., 18 Nov 2020, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
In silico studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Zinc and SARS‑CoV‑2: A molecular modeling study of Zn interactions with RNA‑dependent RNA‑polymerase and 3C‑like proteinase enzymes
International Journal of Molecular Medicine, doi:10.3892/ijmm.2020.4790
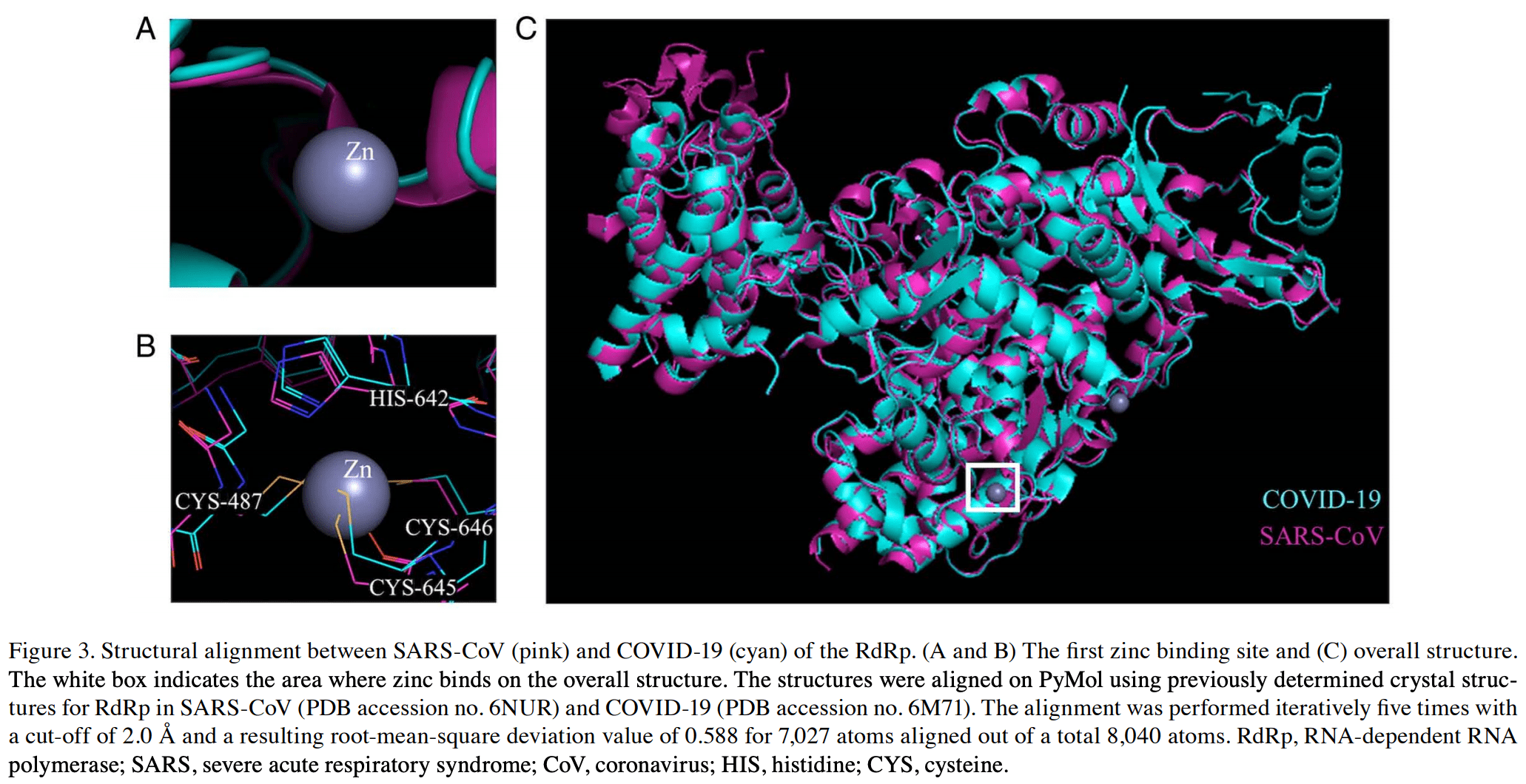
RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase (RdRp) and 3c-like proteinase (3cL pro ) are two main enzymes that play a key role in the replication of SARS-coV-2. Zinc (Zn) has strong immunogenic properties and is known to bind to a number of proteins, modulating their activities. Zn also has a history of use in viral infection control. Thus, the present study models potential Zn binding to RdRp and the 3cL pro . Through molecular modeling, the Zn binding sites in the aforementioned two important enzymes of viral replication were found to be conserved between severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-coronavirus (coV) and SARS-coV-2. The location of these sites may influence the enzymatic activity of 3cL pro and RdRp in coronavirus disease 2019 . Since Zn has established immune health benefits, is readily available, non-expensive and a safe food supplement, with the comparisons presented here between SARS-coV and cOVId-19, the present study proposes that Zn could help ameliorate the disease process of cOVId-19 infection.
Authors' contributions AP and RJT conceived and designed the study; NKM and AP performed comprehensive research; AP and NKM analyzed the data; AP, NKM and RJT wrote and revised the paper; AP, NKM and RJT participated in data analysis and manuscript editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication Not applicable.
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
Bd, Butterworth, Inhibition by zinc of rhinovirus protein cleavage: Interaction of zinc with capsid polypeptides, J Virol
Bd, Jc, Butterworth, Zinc ions inhibit replication of rhinoviruses, Nature
Bd, Welch, Food system strategies for preventing micronutrient malnutrition
Bjerrum, Antimicrobial resistance: Risk associated with antibiotic overuse and initiatives to reduce the problem, Ther Adv drug Saf
Caruso, Cg, Gwaltney, Treatment of naturally acquired common colds with zinc: A structured review, clin Infect dis
Conti, Ronconi, Gallenga C, Ross, Frydas et al., Induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1 and IL-6) and lung inflammation by coronavirus-19 (COVI-19 or SARS-CoV-2): Anti-inflammatory strategies, J Biol Regul Homeost Agents
Denny, De Wale, Laupland, Harris, Lipman, When not to start antibiotics: Avoiding antibiotic overuse in the intensive care unit, clin Microbiol Infect
Essack, Bell, Burgoyne, Shephard, Topical (local) antibiotics for respiratory infections with sore throat: An antibiotic stewardship perspective, J clin Pharm Ther
Fan, Wei, Feng, Chen, Huang C et al., Biosynthesis, purification, and substrate specificity of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 3c-like proteinase, J Biol chem
Favalli, Ingegnoli, De Lucia, cOVId-19 infection and rheumatoid arthritis: Faraway, so close!, Autoimmun Rev
Fc, Bateman, Hayden, In vitro activity of zinc salts against human rhinoviruses, Antimicrob Agents chemother
Fischer, Yajjala, Bansal, Bauer C, Sun, Monocytes represent one source of bacterial shielding from antibiotics following influenza virus infection, J Immunol
Gammoh, Rink, Zinc in infection and inflammation, Nutrients
Gao, Yan, Huang, Liu, Zhao et al., Structure of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from cOVId-19 virus, Science
Ghaffari, Tavakoli, Moradi, Tabarraei, Bokharaei-Salim et al., Inhibition of H1N1 influenza virus infection by zinc oxide nanoparticles: Another emerging application of nanomedicine, J Biomed Sci
Gugala, Lemire, Turner, The efficacy of different anti-microbial metals at preventing the formation of, and eradicating bacterial biofilms of pathogenic indicator strains, J Antibiot
Gugala, Vu, Parkins, Turner, Specificity in the susceptibilities of escherichia coli, pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates to six metal antimicrobials, Antibiotics
Gupta, Sakhuja, Kumar, Mcgrath, Nanchal et al., culture-negative severe sepsis: Nationwide trends and outcomes, chest
Haase, Functions of zinc in signaling, proliferation and differentiation of mammalian cells, Biometals
Hemilä, Fitzgerald, Petrus, Zinc acetate lozenges may improve the recovery rate of common cold patients: An individual patient data meta-analysis, Open Forum Infect dis
Hsu, Kuo Cj, Hsieh, Yc, Huang et al., Evaluation of metal-conjugated compounds as inhibitors of 3cL protease of SARS-coV, FEBS Lett
Hulisz, Efficacy of zinc against common cold viruses: An overview, J Am Pharm Assoc
Hung, Tsiang, Biochemical characterization of rhinovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, Antiviral Res
Jarosz, Olbert, Wyszogrodzka, Młyniec, Librowski, Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of zinc. Zinc-dependent NF-κB signaling, Inflammopharmacology
Jesline, John, Narayanan, Murugan, Antimicrobial activity of zinc and titanium dioxide nanoparticles against biofilm-producing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Appl Nanosci
Kaushik, Subramani C, Anang, Muthumohan, Shalimar, Nayak et al., Zinc salts block hepatitis E virus replication by inhibiting the activity of viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, J Virol
Kenealy, Is intranasal zinc effective and safe for the common cold? A systematic review and meta-analysis, J Prim Health care
Kirchdoerfer, Ward, Structure of the SARS-coV nsp12 polymerase bound to nsp7 and nsp8 co-factors, Nat commun
Knoell Dl, Da, Sapkota, Heires, Ck et al., Insufficient zinc intake enhances lung inflammation in response to agricultural organic dust exposure, J Nutr Biochem
Kochańczyk, Drozd, Krężel, Relationship between the architecture of zinc coordination and zinc binding affinity in proteins-Insights into zinc regulation, Metallomics
Kostoff, Briggs, Porter, Hernández, Abdollahi et al., The under-reported role of toxic substance exposures in the cOVId-19 pandemic, Food chem Toxicol
Krenn, Gaudernak, Holzer, Lanke, Kuppeveld et al., Antiviral activity of the zinc ionophores pyrithione and hinokitiol against picornavirus infections, J Virol
Krenn, Holzer, Gaudernak, Triendl, Van Kuppeveld et al., Inhibition of polyprotein processing and RNA replication of human rhinovirus by pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate involves metal ions, J Virol
Lan Ke, Renn, Melchers, Seipelt, Van Kuppeveld, PdTc inhibits picornavirus polyprotein processing and RNA replication by transporting zinc ions into cells, J Gen Virol
Lee Cc, Kuo Cj, Hsu, Liang, Fang et al., Structural basis of mercury-and zinc-conjugated complexes as SARS-coV 3c-like protease inhibitors, FEBS Lett
Lee Cc, Kuo Cj, Ko, Hsu, Yc et al., Structural basis of inhibition specificities of 3C and 3C-like proteases by zinc-coordinating and peptidomimetic compounds, J Biol chem
Lemire, Harrison, Turner, Antimicrobial activity of metals: Mechanisms, molecular targets and applications, Nat Rev Microbiol
Lemire, Turner, Mechanisms underlying the antimicrobial capacity of metals
Lung, Lin, Yang, Chou, Shu et al., The potential chemical structure of anti-SARS-coV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, J Med Virol
Marreiro D Do, Cruz, Morais, Beserra, Severo et al., Zinc and oxidative stress: current mechanisms, Antioxidants
Matson, Stock, Shupert, Bushmaker, Feldmann et al., compatibility of maximum-containment virus-inactivation protocols with identification of bacterial coinfections by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry, J Infect dis
Maywald, Wessels, Rink, Zinc signals and immunity, Int J Mol Sci
Mehta, Df, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., HLH Across Speciality collaboration, UK: cOVId-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet
Monych, Gugala, Turner, chapter 9. Metal-based Antimicrobials
Nitulescu, Paunescu, Moschos, Petrakis D, Nitulescu et al., comprehensive analysis of drugs to treat SARS-coV-2 infection: Mechanistic insights into current cOVId-19 therapies (Review), Int J Mol Med
Plum, Rink, Hajo, The essential toxin: Impact of zinc on human health, Int J Environ Res Public Health
Pormohammad, Ghorbani, Khatami, Farzi, Baradaran et al., comparison of confirmed cOVId-19 with SARS and MERS cases-clinical characteristics, laboratory findings, radiographic signs and outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Rev Med Virol
Pormohammad, Ghorbani, Khatami, Razizadeh, Alborzi et al., comparison of influenza type A and B with COVID-19: A global systematic review and meta-analysis on clinical, laboratory and radiographic findings, Rev Med Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2179
Prasad, Impact of the discovery of human zinc deficiency on health, J Am coll Nutr
Prentice, Mcauliffe, Lu, Subbarao, Denison Mr, Identification and characterization of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus replicase proteins, J Virol
Read, Obeid, Ahlenstiel, The role of zinc in antiviral immunity, Adv Nutr
Science, Johnstone, De, Guyatt, Loeb, Zinc for the treatment of the common cold: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, cMAJ
Serin, Pullukçu, Çiçek, Sipahi, Taşbakan et al., Pneumonia Study Group: Bacterial and viral etiology in hospitalized community acquired pneumonia with molecular methods and clinical evaluation, J Infect dev ctries
Shankar, Prasad, Zinc and immune function: The biological basis of altered resistance to infection, Am J clin Nutr
Shi, Wang, Shao C, Huang, Gan et al., cOVId-19 infection: The perspectives on immune responses, cell death differ
Skalny, Rink, Ajsuvakova, Aschner, Gritsenko et al., Zinc and respiratory tract infections: Perspectives for covid'19 (Review), Int J Mol Med
Sohrabi, Alsafi, Neill, Khan, Kerwan et al., World Health Organization declares global emergency: A review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (cOVId-19), Int J Surg
Song, Hu, Zheng, Zhao, Hospital pharmacists' pharmaceutical care for hospitalized patients with cOVId-19: Recommendations and guidance from clinical experience, Res Social Adm Pharm
Srivastava, Rawall, Vijayan, Khanna, Influenza a virus induced apoptosis: Inhibition of dNA laddering & caspase-3 activity by zinc supplementation in cultured HeLa cells, Indian J Med Res
Stebbing, Phelan, Griffin, Tucker, Oechsle et al., COVID-19: Combining antiviral and anti-inflammatory treatments, Lancet Infect dis
Stevens, Patel, Nori, Involving antimicrobial stewardship programs in cOVId-19 response efforts: All hands on deck, Infect control Hosp Epidemiol
Suara, Effect of zinc salts on respiratory syncytial virus replication, Antimicrob Agents chemother
Subissi, Imbert, Ferron, SARS-coV ORF1b-encoded nonstructural proteins 12-16: Replicative enzymes as antiviral targets, Antiviral Res
Turner, Gugala, Lemire, can metals replace traditional antibiotics, Adjac Gov
Turner, Metal-based antimicrobial strategies, Microb Biotechnol
Velthuis, Van Den Worml, Ac, Baric, Snijder et al., Zn 2+ inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture, PLoS Pathog
Wang, Liu, Preparation, characterization and antimicrobial activity of chitosan-Zn complex, carbohydr Polym
Wessels, Rolles, Rink, The potential impact of zinc supplementation on cOVId-19 pathogenesis, Front Immunol
Wu, Lin, Hsu, Hsieh, Antiviral drug discovery against SARS-coV, curr Med chem
Zhang, Forst Cv, Gordon, Gussin, Geber et al., characterization of antibiotic resistance and host-microbiome interactions in the human upper respiratory tract during influenza infection, Microbiome
Zhang, Zhao, Zhang, Wang, Li et al., The use of anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of people with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (cOVId-19): The experience of clinical immunologists from china, clin Immunol
Zhou, Fu, Zheng, Zhao C, Qi et al., Pathogenic T cells and inflammatory monocytes incite inflammatory storm in severe COVID-19 patients, Natl Sci Rev, doi:10.1093/nsr/nwaa041
Zhou, Hou, Shen, Huang, Network-based drug repurposing for novel coronavirus 2019-ncoV/SARS-coV-2, cell discov
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3892/ijmm.2020.4790",
"ISSN": [
"1107-3756",
"1791-244X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2020.4790",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biological Sciences, University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta T2N4V8, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Pormohammad",
"given": "Ali",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biological Sciences, University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta T2N4V8, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Monych",
"given": "Nadia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biological Sciences, University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta T2N4V8, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Turner",
"given": "Raymond",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Molecular Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Int J Mol Med",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2020-11-18T10:35:28Z",
"timestamp": 1605695728000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2020-11-30T14:02:18Z",
"timestamp": 1606744938000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-27T15:12:48Z",
"timestamp": 1714230768259
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 37,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
18
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
18
]
]
}
},
"member": "2249",
"original-title": [],
"page": "326-334",
"prefix": "10.3892",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
18
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
18
]
]
},
"publisher": "Spandidos Publications",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://www.spandidos-publications.com/10.3892/ijmm.2020.4790"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Zinc and SARS‑CoV‑2: A molecular modeling study of Zn interactions with RNA‑dependent RNA‑polymerase and 3C‑like proteinase enzymes",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "47"
}
