In Vitro Determination of Inhibitory Effects of Humic Substances Complexing Zn and Se on SARS-CoV-2 Virus Replication
et al., Foods, doi:10.3390/foods11050694, Feb 2022
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000019 from 42 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
In vitro study of a humic substance containing vitamin C, selemium ions, and zinc ions, showing 50% SARS-CoV-2 inhibition at picomolar concentrations.
12 preclinical studies support the efficacy of zinc for COVID-19:
1.
Agamah et al., Network-based multi-omics-disease-drug associations reveal drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19 disease phases, ScienceOpen, doi:10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1.
2.
Lockwood, T., Coordination chemistry suggests that independently observed benefits of metformin and Zn2+ against COVID-19 are not independent, BioMetals, doi:10.1007/s10534-024-00590-5.
3.
El-Megharbel et al., Chemical and spectroscopic characterization of (Artemisinin/Quercetin/ Zinc) novel mixed ligand complex with assessment of its potent high antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 and antioxidant capacity against toxicity induced by acrylamide in male rats, PeerJ, doi:10.7717/peerj.15638.
4.
Bess et al., Identification of oral therapeutics using an AI platform against the virus responsible for COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1297924.
5.
Pormohammad et al., Zinc and SARS-CoV-2: A molecular modeling study of Zn interactions with RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase and 3C-like proteinase enzymes, International Journal of Molecular Medicine, doi:10.3892/ijmm.2020.4790.
6.
Pelucelli et al., Zn2+ and Cu2+ Interaction with the Recognition Interface of ACE2 for SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms24119202.
7.
Hajdrik et al., In Vitro Determination of Inhibitory Effects of Humic Substances Complexing Zn and Se on SARS-CoV-2 Virus Replication, Foods, doi:10.3390/foods11050694.
8.
Panchariya et al., Zinc2+ ion inhibits SARS-CoV-2 main protease and viral replication in vitro, Chemical Communications, doi:10.1039/D1CC03563K.
Hajdrik et al., 26 Feb 2022, peer-reviewed, 11 authors.
Contact: domokos.mathe@hcemm.eu (corresponding author), h.polett0809@gmail.com, kovacsnoi@hotmail.com, veres.daniel@med.semmelweis-univ.hu, krisztian.szigeti@gmail.com, hegedus.imre1@med.semmelweis-univ.hu, rkbergmann@web.de, palyi.bernadett@nnk.gov.hu, kis.zoltan@nnk.gov.hu, budfer2@gmail.com, kovacstiborjanos@gmail.com.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
In Vitro Determination of Inhibitory Effects of Humic Substances Complexing Zn and Se on SARS-CoV-2 Virus Replication
Foods, doi:10.3390/foods11050694
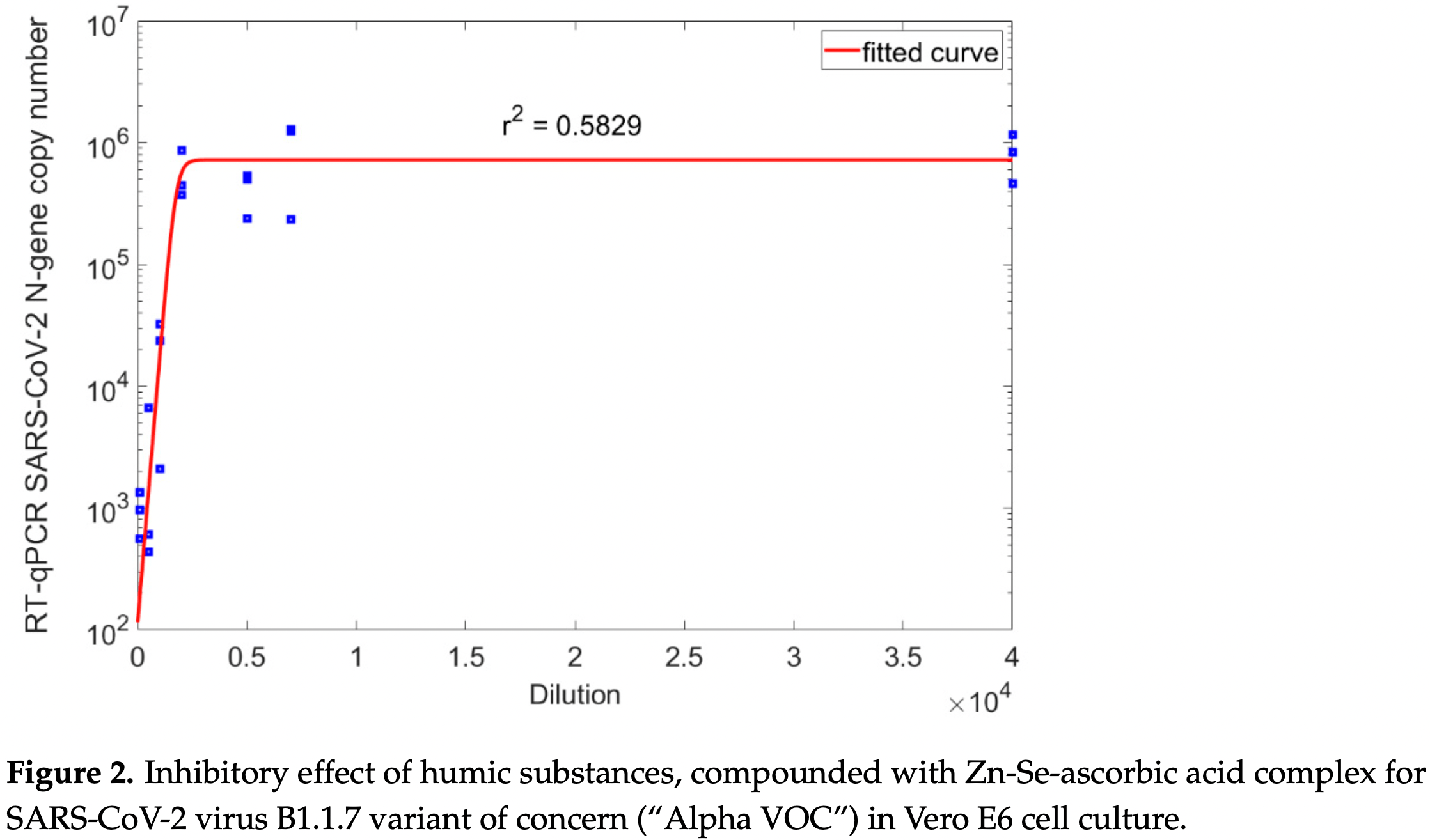
1) Background: Humic substances are well-known human nutritional supplement materials and they play an important performance-enhancing role as animal feed additives. For decades, ingredients of humic substances have been proven to carry potent antiviral effects against different viruses. (2) Methods: Here, the antiviral activity of a humic substance containing ascorbic acid, Se − and Zn 2+ ions intended as a nutritional supplement material was investigated against SARS-CoV-2 virus B1.1.7 Variant of Concern ("Alpha Variant") in a VeroE6 cell line. (3) Results: This combination has a significant in vitro antiviral effect at a very low concentration range of its intended active ingredients. (4) Conclusions: Even picomolar concentration ranges of humic substances, Vitamin C and Zn/Se ions in the given composition, were enough to achieve 50% viral replication inhibition in the applied SARS-CoV-2 virus inhibition test.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
Abobaker, Alzwi, Alraied, Overview of the possible role of vitamin C in management of COVID-19, Pharmacol. Rep, doi:10.1007/s43440-020-00176-1
Aguilar, Charrondiere, Dusemund, Galtier, Gilbert et al., Chromium(III)-, iron(II)-and selenium-humic acid/fulvic acid chelate and supplemented humifulvate added for nutritional purposes to food supplements, EFSA J
Alvarez-Puebla, Garrido, Aroca, Surface-Enhanced Vibrational Microspectroscopy of Fulvic Acid Micelles, Anal. Chem, doi:10.1021/ac049076u
Alvarez-Puebla, Valenzuela-Calahorro, Garrido, Theoretical study on fulvic acid structure, conformation and aggregation. A molecular modelling approach, Sci. Total Environ, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.11.026
Asakawa, Kiyota, Yanagi, Fujitake, Optimization of Conditions for High-Performance Size-Exclusion Chromatography of Different Soil Humic Acids, Anal. Sci, doi:10.2116/analsci.24.607
Ash, Nutritional Support for Immunity Against Viruses Including the Coronavirus
Bae, Kim, The role of vitamin C, vitamin D, and selenium in immune system against COVID-19, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules25225346
Bertoli, Garcia, Trevisan, Ramalho, Freitas, Interactions fulvate-metal (Zn(2)(+), Cu(2)(+) and Fe(2)(+)): Theoretical investigation of thermodynamic, structural and spectroscopic properties, Biometals, doi:10.1007/s10534-016-9914-8
Boguta, Sokołowska, Interactions of Zn(II) Ions with Humic Acids Isolated from Various Type of Soils. Effect of pH, Zn Concentrations and Humic Acids Chemical Properties, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0153626
Béres, Kabdebó, Ferenc, Nemeséri, Szélsy et al., Studies on therapeutic application of fulvic acids, with special regard to their liver protecting function, Magy Állatorv. Lapja
Béres, Király, Bóna, Lővei, Róbert, Tőzeg-fulvósavval szerzett therapiás tapasztalataink, Orvosi Hetilap
Chen, Liang, An overview of functional nanoparticles as novel emerging antiviral therapeutic agents, Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl, doi:10.1016/j.msec.2020.110924
Chesworth, None
Chin, Aiken, O'loughlin, Molecular weight, polydispersity, and spectroscopic properties of aquatic humic substances, Environ. Sci. Technol, doi:10.1021/es00060a015
Chon, Cho, Shon, Advanced characterization of algogenic organic matter, bacterial organic matter, humic acids and fulvic acids, Water Sci. Technol, doi:10.2166/wst.2013.118
Constantinescu-Aruxandei, Frîncu, Capră, Oancea, Selenium Analysis and Speciation in Dietary Supplements Based on Next-Generation Selenium Ingredients, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu10101466
Cornejo, Jiménez, Caballero, Melo, Maccioni, Fulvic acid inhibits aggregation and promotes disassembly of tau fibrils associated with Alzheimer's disease, J. Alzheimer's Dis, doi:10.3233/JAD-2011-110623
De Melo, Motta, Santana, Humic acids: Structural properties and multiple functionalities for novel technological developments, Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl, doi:10.1016/j.msec.2015.12.001
Elsayed, Ame, Ha, Deeb, The Effect of Humic Acid and Ascorbic Acid on Immunization of Chickens Against Infectious Bursal Disease, Assuit Venetrary Med. J
Erdtman, Studies on the formation of complex oxidation and condensation products of phenols. A contribution to the investigation of the origin and nature of humic acid. Part I.-Studies of the reactivity of simple monocyclic quinones, Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. A Contain. Pap. A Math. Phys. Character
Ghosal, Baumik, Chattopadhyay, Shilajit induced morphometric and functional changes in mouse peritoneal macrophages, Phytother. Res, doi:10.1002/ptr.2650090308
Ghosal, Lal, Singh, Goel, Jaiswal et al., The need for formulation of Shilajit by its isolated active constituents, Phytother. Res, doi:10.1002/ptr.2650050505
Gnananath, Nataraj, Rao, Kumar, Mahnashi et al., Exploration of fulvic acid as a functional excipient in line with the regulatory requirement, Environ. Res, doi:10.1016/j.envres.2020.109642
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12040988
Hafez, Popov, Zelenkov, Teplyakova, Rashad, Humic substances as an environmental-friendly organic wastes potentially help as natural anti-virus to inhibit COVID-19, Sci. Arch, doi:10.47587/SA.2020.1202
He, Zhao, Wang, Liu, Fan et al., Using nano-selenium to combat Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), Nano Today, doi:10.1016/j.nantod.2020.101037
Helbig, Klöckinq, Wutzler, Anti-herpes simplex virus type 1 activity of humic acid-like polymers and their o-diphenolic starting compounds, Antivir. Chem. Chemother, doi:10.1177/095632029700800310
Hullar, Vucskits, Berta, Andrasofszky, Bersenyi et al., Effect of fulvic and humic acids on copper and zinc homeostasis in rats, Acta Vet. Hung, doi:10.1556/004.2018.005
Jacob, Prashob, Chandramohanakumar, Humic Substances as a Potent Biomaterials for Therapeutic and Drug Delivery System-A Review, Int. J. Appl. Pharm, doi:10.22159/ijap.2019v11i3.31421
Jones, Bryan, Colloidal properties of humic substances, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci, doi:10.1016/S0001-8686(98)00058-X
Jooné, Dekker, Jansen Van Rensburg, Investigation of the Immunostimulatory Properties of Oxihumate, Z. Für Nat. C, doi:10.1515/znc-2003-3-421
Kim, Rehman, Amin, Kim, Enhanced neuroprotection of anthocyanin-loaded PEG-gold nanoparticles against Abeta1-42-induced neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration via the NF-KB /JNK/GSK3beta signaling pathway, Nanomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.nano.2017.06.022
Klöcking, Björn, Medical aspects and applications of humic substances
Klöcking, Helbig, Schötz, Schacke, Wutzler, Anti-HSV-1 Activity of Synthetic Humic Acid-Like Polymers Derived from p -Diphenolic Starting Compounds, Antivir. Chem. Chemother, doi:10.1177/095632020201300405
Klöcking, Sprössig, Antiviral properties of humic acids, Experientia, doi:10.1007/BF01931906
Kornilaeva, Becovich, New Humic Acid Derivative as Potent Inhibitor of HIV-1 Replication, Med. Gen. Med
Kotwal, Genetic diversity-independent neutralization of pandemic viruses (e.g., HIV), potentially pandemic (e.g., H5N1 strain of influenza) and carcinogenic (e.g., HBV and HCV) viruses and possible agents of bioterrorism (variola) by enveloped virus neutralizing com, Vaccine
Kotwal, Kaczmarek, Leivers, Ghebremariam, Kulkarni et al., Anti-HIV, anti-poxvirus, and anti-SARS activity of a nontoxic, acidic plant extract from the Trifollium species Secomet-V/anti-vac suggests that it contains a novel broad-spectrum antiviral, Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1196/annals.1352.014
Kretzschmar, Christl, Proton and metal cation binding to humic substances in relation to chemical composition and molecular size, Spec. Publ. R. Soc. Chem
Krezel, Maret, The biological inorganic chemistry of zinc ions, Arch. Biochem. Biophys, doi:10.1016/j.abb.2016.04.010
Kumar Gautam, Navaratna, Muthukumaran, Singh, Islamuddin; More, Humic Substances: Its Toxicology, Chemistry and Biology Associated with Soil, Plants and Environment
Kumar, Kubota, Chernov, Kasuya, Potential role of zinc supplementation in prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19, Med. Hypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109848
Kunavue, Lien, Effects of Fulvic Acid and Probiotic on Growth Prerformance, Nutrient Digestibility, Blood Parameters and immunity of Pigs, J. Anim. Sci. Adv
Köntös, Efficacy of "Essential Iodine Drops" against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0254341
Lag, Hadas, Fairbridge, Muñoz, Pombal et al., Humic Substances, Encyclopedia of Soil Science
Larenas-Linnemann, Rodriguez-Perez, Arias-Cruz, Blandon-Vijil, Del Rio-Navarro et al., Enhancing innate immunity against virus in times of COVID-19: Trying to untangle facts from fictions, World Allergy Organ. J, doi:10.1016/j.waojou.2020.100476
Li, Li, Li, Liu, Cui et al., Effects of Na-FA on gastrointestinal movement and gastric ulcer in mice, J. Chin. Med. Mater
Lieke, Steinberg, Pan, Perminova, Meinelt et al., Phenol-rich fulvic acid as a water additive enhances growth, reduces stress, and stimulates the immune system of fish in aquaculture, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-80449-0
Lu, Tseng, Li, Shih, In vitro anti-influenza virus activity of synthetic humate analogues derived from protocatechuic acid, Arch. Virol, doi:10.1007/s705-002-8319-5
Marreiro, Cruz, Oliveira, Morais, Freitas et al., Antiviral and immunological activity of zinc and possible role in COVID-19, Br. J. Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114521002099
Mishra, Dhaliwal, Singh, Singh, Shilajit, Mumie): Current Status of Biochemical, Therapeutic and Clinical Advances, Curr. Nutr. Food Sci, doi:10.2174/1573401313666170823160217
Molnar, The beneficial effects of humic acid on gastric ulcers in pigs, Int. Pig Top
Mosa, Taha, Elsaeid, Agro-environmental applications of humic substances: A critical review. Egypt, J. Soil Sci, doi:10.21608/ejss.2020.27425.1351
Murbach, Glavits, Endres, Clewell, Hirka et al., A toxicological evaluation of a fulvic and humic acids preparation, Toxicol. Rep, doi:10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.08.030
Nebbioso, Piccolo, Molecular characterization of dissolved organic matter (DOM): A critical review, Anal. Bioanal. Chem, doi:10.1007/s00216-012-6363-2
Nieder, Benbi, Reichl, Soil Components and Human Health
Orlov, Zherebker, Eletskaya, Chernikov, Kozlovskaya et al., Examination of molecular space and feasible structures of bioactive components of humic substances by FTICR MS data mining in ChEMBL database, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-019-48000-y
Pant, Singh, Thakur, Shilajit: A Humic Matter Panacea for Cancer, Int. J. Toxicol. Pharmacol. Res
Quiles, Rivas-Garcia, Varela-Lopez, Llopis, Battino et al., Do nutrients and other bioactive molecules from foods have anything to say in the treatment against COVID-19?, Environ. Res, doi:10.1016/j.envres.2020.110053
Rakib, Nain, Sami, Mahmud, Islam et al., A molecular modelling approach for identifying antiviral selenium-containing heterocyclic compounds that inhibit the main protease of SARS-CoV-2: An in silico investigation, Brief. Bioinform, doi:10.1093/bib/bbab045
Saar, Weber, Fulvic acid: Modifier of metal-ion chemistry, Environ. Sci. Technol, doi:10.1021/es00103a723
Schellekens, Buurman, Kalbitz, Zomeren, Vidal-Torrado et al., Molecular Features of Humic Acids and Fulvic Acids from Contrasting Environments, Environ. Sci. Technol, doi:10.1021/acs.est.6b03925
Schepetkin, Khlebnikov, Kwon, Medical drugs from humus matter: Focus on mumie, Drug Dev. Res
Schnitzer, Humic Substances: Chemistry and Reactions
Smirnova, Efimova, Khil'ko, Antioxidant and pro-oxidant activity of ascorbic and humic acids in radical-chain oxidation processes, Russ. J. Appl. Chem, doi:10.1134/S1070427212020164
Steinberg, Meinelt, Timofeyev, Bittner, Menzel, Humic substances, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res, doi:10.1065/espr2007.07.434
Stevenson, Humus Chemistry: Genesis, Composition, Reactions
Sutton, Sposito, Molecular structure in soil humic substances: The new view, Environ. Sci. Technol
Szabo, Vucskits, Berta, Andrasofszky, Bersenyi et al., Effect of fulvic and humic acids on iron and manganese homeostasis in rats, Acta Vet. Hung, doi:10.1556/004.2017.007
Tiwari, Dicks, Popov, Karaseva, Ermakov et al., Probiotics at War Against Viruses: What Is Missing from the Picture? Front, Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.01877
Tomo, Saikiran, Banerjee, Paul, Selenium to selenoproteins-Role in COVID-19, EXCLI J
Uspenskaya, Syroeshkin, Pleteneva, Kazimova, Grebennikova et al., Nanodispersions of Polyelectrolytes Based on Humic Substances: Isolation, Physico-Chemical Characterization and Evaluation of Biological Activity, Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics13111954
Van Rensburg, Dekker, Weis, Smith, Van Rensburg et al., Investigation of the Anti-HIV Properties of Oxihumate, Chemotherapy, doi:10.1159/000064919
Van Rensburg, The Antiinflammatory Properties of Humic Substances: A Mini Review, Phytother. Res, doi:10.1002/ptr.5319
Velthuis, Van Den Worm, Sims, Baric, Snijder et al., Zn(2+) inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176
Vetvicka, Vashishta, Fuentes, Baigorri, Garcia-Mina et al., The Relative Abundance of Oxygen Alkyl-Related Groups in Aliphatic Domains Is Involved in the Main Pharmacological-Pleiotropic Effects of Humic Acids, J. Med. Food, doi:10.1089/jmf.2012.0212
Vucskits, Hullár, Bersenyi, Andrásofszky, Tuboly et al., Effect of fulvic acid and humic acid. Part 1. Economic indexes, immunostimulant effect. Magyar Állatorvosok, Lapja
Vucskits, Hullár, Bersényi, Andrásofszky, Kulcsár et al., Effect of fulvic and humic acids on performance, immune response and thyroid function in rats, J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr, doi:10.1111/j.1439-0396.2010.01023.x
Waksman, Húmus Origin, Chemical Composition, and Importance in Nature
Winkler, Ghosh, Therapeutic Potential of Fulvic Acid in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases and Diabetes, J. Diabetes Res, doi:10.1155/2018/5391014
Zhang, Saad, Taylor, Rayman, Selenium and selenoproteins in viral infection with potential relevance to COVID-19, Redox Biol, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2020.101715
Zhernov, Konstantinov, Zherebker, Nikolaev, Orlov et al., Antiviral activity of natural humic substances and shilajit materials against HIV-1: Relation to structure, Environ. Res, doi:10.1016/j.envres.2020.110312
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/foods11050694",
"ISSN": [
"2304-8158"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/foods11050694",
"abstract": "<jats:p>(1) Background: Humic substances are well-known human nutritional supplement materials and they play an important performance-enhancing role as animal feed additives. For decades, ingredients of humic substances have been proven to carry potent antiviral effects against different viruses. (2) Methods: Here, the antiviral activity of a humic substance containing ascorbic acid, Se− and Zn2+ ions intended as a nutritional supplement material was investigated against SARS-CoV-2 virus B1.1.7 Variant of Concern (“Alpha Variant”) in a VeroE6 cell line. (3) Results: This combination has a significant in vitro antiviral effect at a very low concentration range of its intended active ingredients. (4) Conclusions: Even picomolar concentration ranges of humic substances, Vitamin C and Zn/Se ions in the given composition, were enough to achieve 50% viral replication inhibition in the applied SARS-CoV-2 virus inhibition test.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"foods11050694"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hajdrik",
"given": "Polett",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pályi",
"given": "Bernadett",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kis",
"given": "Zoltán",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kovács",
"given": "Noémi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Veres",
"given": "Dániel Sándor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Szigeti",
"given": "Krisztián",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1562-9496",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Budán",
"given": "Ferenc",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1438-3511",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hegedüs",
"given": "Imre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2606-0397",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kovács",
"given": "Tibor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bergmann",
"given": "Ralf",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Máthé",
"given": "Domokos",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Foods",
"container-title-short": "Foods",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-28T01:46:17Z",
"timestamp": 1646012777000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-02T14:24:18Z",
"timestamp": 1646231058000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100000780",
"award": [
"739593"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "European Commission"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100003549",
"award": [
"2020.1.16-Jövő-2021-00013"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Hungarian Scientific Research Fund"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-12T07:06:51Z",
"timestamp": 1649747211949
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
26
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-26T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1645833600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2304-8158/11/5/694/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "694",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
26
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
26
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Studies on the formation of complex oxidation and condensation products of phenols. A contribution to the investigation of the origin and nature of humic acid. Part I.—Studies of the reactivity of simple monocyclic quinones",
"author": "Erdtman",
"first-page": "177",
"journal-title": "Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. A Contain. Pap. A Math. Phys. Character",
"key": "ref1",
"volume": "143",
"year": "1933"
},
{
"author": "Waksman",
"key": "ref2",
"series-title": "Húmus Origin, Chemical Composition, and Importance in Nature",
"year": "1936"
},
{
"author": "Stevenson",
"key": "ref3",
"series-title": "Humus Chemistry: Genesis, Composition, Reactions",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1065/espr2007.07.434",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"article-title": "Humic Substances: Chemistry and Reactions",
"author": "Schnitzer",
"first-page": "1",
"key": "ref5",
"series-title": "Soil Organic Matter",
"year": "1978"
},
{
"author": "Nieder",
"key": "ref6",
"series-title": "Soil Components and Human Health",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Humic Substances",
"author": "Lag",
"first-page": "315",
"key": "ref7",
"series-title": "Encyclopedia of Soil Science",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.11.026",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/ac049076u",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-80449-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2166/wst.2013.118",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/es00060a015",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2116/analsci.24.607",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.est.6b03925",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/es050778q",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00216-012-6363-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.2650050505",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.2650090308",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"article-title": "Shilajit: A Humic Matter Panacea for Cancer",
"author": "Pant",
"first-page": "17",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Toxicol. Pharmacol. Res.",
"key": "ref19",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1573401313666170823160217",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20"
},
{
"author": "Kumar Gautam",
"key": "ref21",
"series-title": "Humic Substances: Its Toxicology, Chemistry and Biology Associated with Soil, Plants and Environment",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Studies on therapeutic application of fulvic acids, with special regard to their liver protecting function",
"author": "Béres",
"first-page": "351",
"journal-title": "Magy Állatorv. Lapja",
"key": "ref22",
"volume": "12",
"year": "1957"
},
{
"article-title": "Tőzeg-fulvósavval szerzett therapiás tapasztalataink",
"author": "Béres",
"first-page": "567",
"journal-title": "Orvosi Hetilap",
"key": "ref23",
"volume": "17",
"year": "1958"
},
{
"article-title": "Medical aspects and applications of humic substances",
"author": "Klöcking",
"first-page": "3",
"key": "ref24",
"series-title": "Biopolymers for Medical and Pharmaceutical Applications",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.msec.2015.12.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.08.030",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21608/ejss.2020.27425.1351",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1556/004.2017.007",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref28"
},
{
"article-title": "The beneficial effects of humic acid on gastric ulcers in pigs",
"author": "Molnar",
"first-page": "9",
"journal-title": "Int. Pig Top.",
"key": "ref29",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Effects of Na-FA on gastrointestinal movement and gastric ulcer in mice",
"author": "Li",
"first-page": "1565",
"journal-title": "J. Chin. Med. Mater.",
"key": "ref30",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"article-title": "Effects of Fulvic Acid and Probiotic on Growth Prerformance, Nutrient Digestibility, Blood Parameters and immunity of Pigs",
"author": "Kunavue",
"first-page": "711",
"journal-title": "J. Anim. Sci. Adv.",
"key": "ref31",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1556/004.2018.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nano.2017.06.022",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3233/JAD-2011-110623",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.envres.2020.109642",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.22159/ijap.2019v11i3.31421",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ddr.10058",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/jmf.2012.0212",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2018/5391014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref39"
},
{
"article-title": "Effect of fulvic acid and humic acid. Part 1. Economic indexes, immunostimulant effect",
"author": "Vucskits",
"first-page": "278",
"journal-title": "Magyar Állatorvosok. Lapja",
"key": "ref40",
"volume": "132",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1439-0396.2010.01023.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref41"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.5319",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref42"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1196/annals.1352.014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref43"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF01931906",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref44"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/095632029700800310",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref45"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/095632020201300405",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref46"
},
{
"key": "ref47",
"series-title": "Humic Acid Inhibition of HSV Infection",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s705-002-8319-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref48"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/znc-2003-3-421",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref49"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000064919",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref50"
},
{
"article-title": "New Humic Acid Derivative as Potent Inhibitor of HIV-1 Replication",
"author": "Kornilaeva",
"first-page": "A10360",
"journal-title": "Med. Gen. Med.",
"key": "ref51",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-019-48000-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref52"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.envres.2020.110312",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref53"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.12.008",
"article-title": "Genetic diversity-independent neutralization of pandemic viruses (e.g., HIV), potentially pandemic (e.g., H5N1 strain of influenza) and carcinogenic (e.g., HBV and HCV) viruses and possible agents of bioterrorism (variola) by enveloped virus neutralizing com",
"author": "Kotwal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3055",
"journal-title": "Vaccine",
"key": "ref54",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2020.01877",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref55"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0254341",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref56"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pharmaceutics13111954",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref57"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.waojou.2020.100476",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref58"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref59"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules25225346",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref60"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nantod.2020.101037",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref61"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.envres.2020.110053",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref62"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref63"
},
{
"article-title": "Nutritional Support for Immunity Against Viruses Including the Coronavirus",
"author": "Ash",
"key": "ref64",
"series-title": "Clinical Educatuion",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/es00103a723",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref65"
},
{
"article-title": "Proton and metal cation binding to humic substances in relation to chemical composition and molecular size",
"author": "Kretzschmar",
"first-page": "153",
"journal-title": "Spec. Publ. R. Soc. Chem.",
"key": "ref66",
"volume": "273",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10534-016-9914-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref67"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0001-8686(98)00058-X",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref68"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.msec.2020.110924",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref69"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1134/S1070427212020164",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref70"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.abb.2016.04.010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref71"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114521002099",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref72"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2020.101715",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref73"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bib/bbab045",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref74"
},
{
"DOI": "10.47587/SA.2020.1202",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref75"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0153626",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref76"
},
{
"article-title": "Chromium(III)-, iron(II)- and selenium-humic acid/fulvic acid chelate and supplemented humifulvate added for nutritional purposes to food supplements",
"author": "Aguilar",
"first-page": "1147",
"journal-title": "EFSA J.",
"key": "ref77",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10101466",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref78"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s43440-020-00176-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref79"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21608/avmj.2007.178001",
"article-title": "The Effect of Humic Acid and Ascorbic Acid on Immunization of Chickens Against Infectious Bursal Disease",
"author": "ELSayed",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Assuit Venetrary Med. J.",
"key": "ref80",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"article-title": "Selenium to selenoproteins—Role in COVID-19",
"author": "Tomo",
"first-page": "781",
"journal-title": "EXCLI J.",
"key": "ref81",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109848",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref82"
}
],
"reference-count": 82,
"references-count": 82,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2304-8158/11/5/694"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Plant Science",
"Health Professions (miscellaneous)",
"Health (social science)",
"Microbiology",
"Food Science"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "In Vitro Determination of Inhibitory Effects of Humic Substances Complexing Zn and Se on SARS-CoV-2 Virus Replication",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "11"
}
