Zn2+ and Cu2+ Interaction with the Recognition Interface of ACE2 for SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein
et al., International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms24119202, May 2023
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000031 from 44 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
In vitro biochemical study showing that zinc and copper ions bind to peptide fragments from the ACE2 recognition interface for SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. The results suggest that zinc and copper could potentially reduce spike binding affinity and therefore SARS-CoV-2 infection by altering ACE2 receptor conformation.
12 preclinical studies support the efficacy of zinc for COVID-19:
1.
Agamah et al., Network-based multi-omics-disease-drug associations reveal drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19 disease phases, ScienceOpen, doi:10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1.
2.
Lockwood, T., Coordination chemistry suggests that independently observed benefits of metformin and Zn2+ against COVID-19 are not independent, BioMetals, doi:10.1007/s10534-024-00590-5.
3.
El-Megharbel et al., Chemical and spectroscopic characterization of (Artemisinin/Quercetin/ Zinc) novel mixed ligand complex with assessment of its potent high antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 and antioxidant capacity against toxicity induced by acrylamide in male rats, PeerJ, doi:10.7717/peerj.15638.
4.
Bess et al., Identification of oral therapeutics using an AI platform against the virus responsible for COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1297924.
5.
Pormohammad et al., Zinc and SARS-CoV-2: A molecular modeling study of Zn interactions with RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase and 3C-like proteinase enzymes, International Journal of Molecular Medicine, doi:10.3892/ijmm.2020.4790.
6.
Pelucelli et al., Zn2+ and Cu2+ Interaction with the Recognition Interface of ACE2 for SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms24119202.
7.
Hajdrik et al., In Vitro Determination of Inhibitory Effects of Humic Substances Complexing Zn and Se on SARS-CoV-2 Virus Replication, Foods, doi:10.3390/foods11050694.
8.
Panchariya et al., Zinc2+ ion inhibits SARS-CoV-2 main protease and viral replication in vitro, Chemical Communications, doi:10.1039/D1CC03563K.
Pelucelli et al., 24 May 2023, peer-reviewed, 7 authors.
Contact: peana@uniss.it (corresponding author), alessiopelucelli@gmail.com, sere@uniss.it, zoroddu@uniss.it, bartosz.orzel@chem.uni.wroc.pl, elzbieta.gumienna-kontecka@chem.uni.wroc.pl.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Zn2+ and Cu2+ Interaction with the Recognition Interface of ACE2 for SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein
International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms24119202
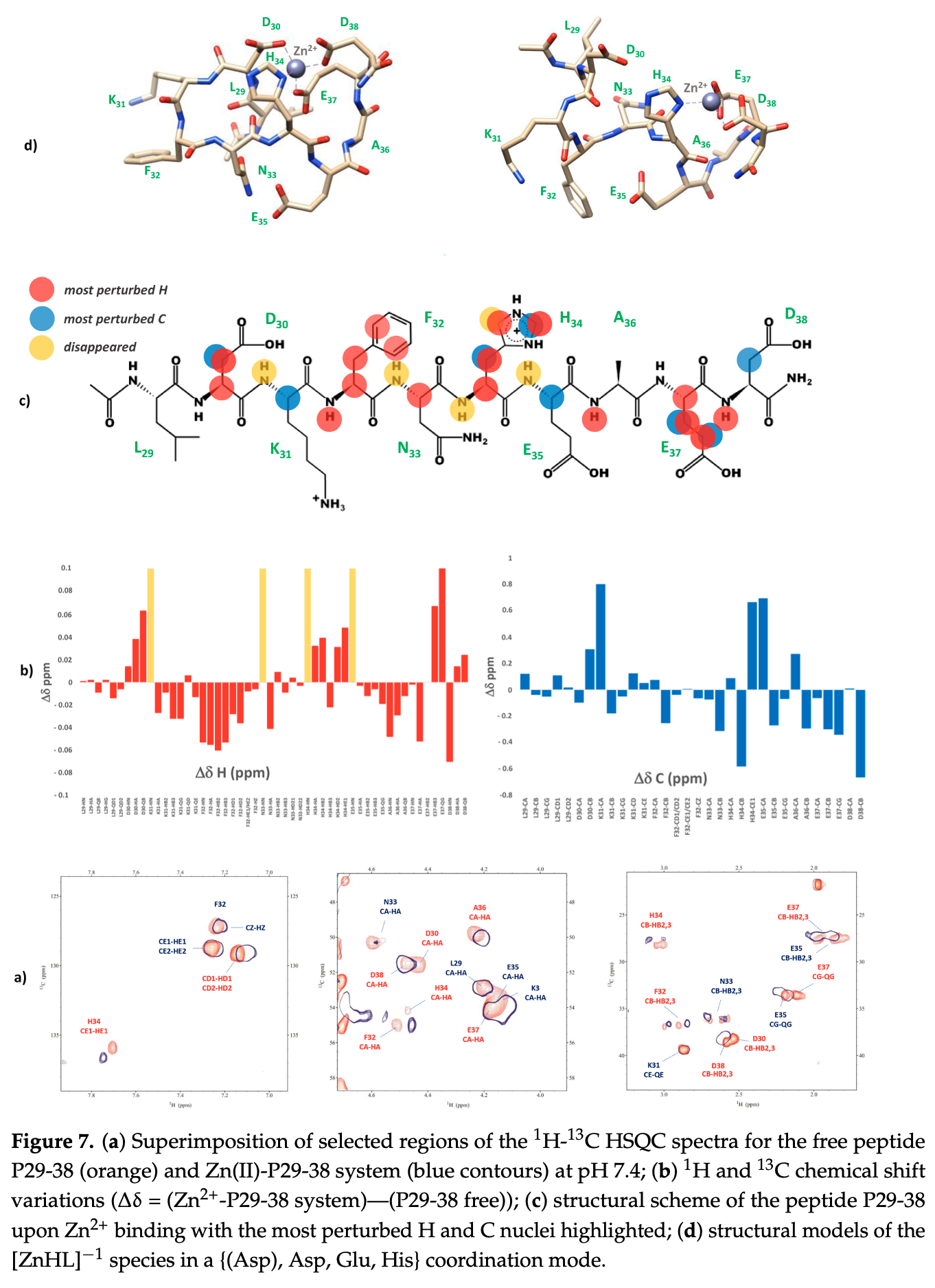
The spike protein (S) of SARS-CoV-2 is able to bind to the human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor with a much higher affinity compared to other coronaviruses. The binding interface between the ACE2 receptor and the spike protein plays a critical role in the entry mechanism of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. There are specific amino acids involved in the interaction between the S protein and the ACE2 receptor. This specificity is critical for the virus to establish a systemic infection and cause COVID-19 disease. In the ACE2 receptor, the largest number of amino acids playing a crucial role in the mechanism of interaction and recognition with the S protein is located in the C-terminal part, which represents the main binding region between ACE2 and S. This fragment is abundant in coordination residues such as aspartates, glutamates, and histidine that could be targeted by metal ions. Zn 2+ ions bind to the ACE2 receptor in its catalytic site and modulate its activity, but it could also contribute to the structural stability of the entire protein. The ability of the human ACE2 receptor to coordinate metal ions, such as Zn 2+ , in the same region where it binds to the S protein could have a crucial impact on the mechanism of recognition and interaction of ACE2-S, with consequences on their binding affinity that deserve to be investigated. To test this possibility, this study aims to characterize the coordination ability of Zn 2+ , and also Cu 2+ for comparison, with selected peptide models of the ACE2 binding interface using spectroscopic and potentiometric techniques.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Alderighi, Gans, Ienco, Peters, Sabatini et al., Hyperquad simulation and speciation (HySS): A utility program for the investigation of equilibria involving soluble and partially soluble species, Coord. Chem. Rev, doi:10.1016/S0010-8545(98)00260-4
Ali, Vijayan, Dynamics of the ACE2-SARS-CoV-2/SARS-CoV spike protein interface reveal unique mechanisms, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-71188-3
Astuti, Ysrafil, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): An overview of viral structure and host response, Diabetes Metab. Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.020
Baes, Mesmer, The Hydrolysis of Cations, doi:10.1002/bbpc.19770810252
Bal, Sokolowska, Kurowska, Faller, Binding of transition metal ions to albumin: Sites, affinities and rates, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.06.018
Bellotti, Miller, Rowinska-Zyrek, Remelli, Zn(2+) and Cu(2+) Binding to the Extramembrane Loop of Zrt2, a Zinc Transporter of Candida albicans, Biomolecules, doi:10.3390/biom12010121
Bellotti, Sinigaglia, Guerrini, Marzola, Rowinska-Zyrek et al., The N-terminal domain of Helicobacter pylori's Hpn protein: The role of multiple histidine residues, J. Inorg. Biochem, doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2020.111304
Benton, Wrobel, Xu, Roustan, Martin et al., Receptor binding and priming of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 for membrane fusion, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2772-0
Beyerstedt, Casaro, Rangel, COVID-19: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) expression and tissue susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection, Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1007/s10096-020-04138-6
Brown, Ekberg, Hydrolysis of Metal Ions
Fatouros, Roy, Sur, Implications of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein interactions with Zn-bound form of ACE2: A computational structural study, Biometals, doi:10.1007/s10534-023-00491-z
Gampp, Maeder, Meyer, Zuberbuhler, Calculation of equilibrium constants from multiwavelength spectroscopic data-II: SPECFIT: Two user-friendly programs in basic and standard FORTRAN 77, Talanta, doi:10.1016/0039-9140(85)80077-1
Gans, Sabatini, Vacca, Investigation of equilibria in solution. Determination of equilibrium constants with the HYPERQUAD suite of programs, Talanta, doi:10.1016/0039-9140(96)01958-3
Gans, Sabatini, Vacca, Superquad-A new computer program for determination of stability constants of complexes by potentiometric titration, Inorg. Chim. Acta, doi:10.1016/S0020-1693(00)95255-1
Gong, Parkkila, Wu, Aspatwar, SARS-CoV-2 variants and COVID-19 vaccines: Current challenges and future strategies, Int. Rev. Immunol, doi:10.1080/08830185.2022.2079642
Gran, Dahlenborg, Laurell, Rottenberg, Determination of the equivalent point in potentiometric titrations, Acta Chem. Scand, doi:10.3891/acta.chem.scand.04-0559
Hamming, Cooper, Haagmans, Hooper, Korstanje et al., The emerging role of ACE2 in physiology and disease, J. Pathol, doi:10.1002/path.2162
Han, Su, Zhang, Bai, Zheng et al., Molecular insights into receptor binding of recent emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-26401-w
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Pohlmann, A Multibasic Cleavage Site in the Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Is Essential for Infection of Human Lung Cells, Mol. Cell, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.04.022
Irving, Williams, The stability of transition-metal complexes, J. Chem. Soc. Resumed, doi:10.1039/jr9530003192
Jackson, Farzan, Chen, Choe, Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol, doi:10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x
Jones, Klewpatinond, Abdelraheim, Brown, Viles, Probing copper 2+ binding to the prion protein using diamagnetic nickel 2+ and 1H NMR: The unstructured N terminus facilitates the coordination of six copper 2+ ions at physiological concentrations, J. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2004.12.043
Jothimani, Kailasam, Danielraj, Nallathambi, Ramachandran et al., COVID-19: Poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014
Kowalik-Jankowska, Kadej, Kuczer, Czarniewska, Copper(II) complexes of the Neb-colloostatin analogues containing histidine residue structure stability biological activity, Polyhedron, doi:10.1016/j.poly.2017.06.023
Kozlowski, Luczkowski, Remelli, Prion proteins and copper ions. Biological and chemical controversies, Dalton Trans, doi:10.1039/c001267j
Krezel, Bal, Coordination chemistry of glutathione, Acta Biochim. Pol, doi:10.18388/abp.1999_4129
Lan, Ge, Yu, Shan, Zhou et al., Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2180-5
Lesiow, Pietrzyk, Bienko, Kowalik-Jankowska, Stability of Cu(ii) complexes with FomA protein fragments containing two His residues in the peptide chain, Metallomics, doi:10.1039/c9mt00131j
Li, Zhang, Sui, Kuhn, Moore et al., Receptor and viral determinants of SARS-coronavirus adaptation to human ACE2, EMBO J, doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600640
Lim, Baek, Kim, Kim, Liu et al., Hot spot profiles of SARS-CoV-2 and human ACE2 receptor protein protein interaction obtained by density functional tight binding fragment molecular orbital method, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-73820-8
Liu, Zheng, Xu, Wang, Hu et al., Reduced graphene oxide membrane as supporting film for high-resolution cryo-EM, Biophys. Rep, doi:10.52601/bpr.2021.210007
Lu, Chen, Yu, Liu, Liu et al., MIB2: Metal ion-binding site prediction and modeling server, Bioinformatics, doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btac534
Magri, Tabbi, Di Natale, La Mendola, Pietropaolo et al., Zinc Interactions with a Soluble Mutated Rat Amylin to Mimic Whole Human Amylin: An Experimental and Simulation Approach to Understand Stoichiometry, Speciation and Coordination of the Metal Complexes, Chemistry, doi:10.1002/chem.202002114
Maret, Analyzing free zinc(II) ion concentrations in cell biology with fluorescent chelating molecules, Metallomics, doi:10.1039/C4MT00230J
Medici, Peana, Nurchi, Zoroddu, The involvement of amino acid side chains in shielding the nickel coordination site: An NMR study, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules181012396
Ni, Yang, Yang, Bao, Li et al., Role of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in COVID-19, Crit. Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03120-0
Oudit, Wang, Viveiros, Kellner, Penninger, Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2-at the heart of the COVID-19 pandemic, Cell
Ozono, Zhang, Ode, Sano, Tan et al., SARS-CoV-2 D614G spike mutation increases entry efficiency with enhanced ACE2-binding affinity, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-21118-2
Peana, Gumienna-Kontecka, Piras, Ostrowska, Piasta et al., Exploring the Specificity of Rationally Designed Peptides Reconstituted from the Cell-Free Extract of Deinococcus radiodurans toward Mn(II) and Cu(II), Inorg. Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b03737
Peana, Medici, Ledda, Nurchi, Zoroddu, Interaction of Cu(II) and Ni(II) with Ypk9 protein fragment via NMR studies, Sci. World J, doi:10.1155/2014/656201
Peana, Zdyb, Medici, Pelucelli, Simula et al., Ni(II) interaction with a peptide model of the human TLR4 ectodomain, J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2017.07.006
Perrotta, Matera, Cazzola, Bianco, Severe respiratory SARS-CoV2 infection: Does ACE2 receptor matter?, Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2020.105996
Pettersen, Goddard, Huang, Couch, Greenblatt et al., UCSF Chimera-A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis, J. Comput. Chem, doi:10.1002/jcc.20084
Prenesti, Daniele, Prencipe, Ostacoli, Spectrum-structure correlation for visible absorption spectra of copper(II) complexes in aqueous solution, Polyhedron, doi:10.1016/S0277-5387(99)00279-X
Rae, Schmidt, Pufahl, Culotta, O'halloran, Undetectable intracellular free copper: The requirement of a copper chaperone for superoxide dismutase, Science, doi:10.1126/science.284.5415.805
Rossotti, Rossotti, Whewell, The use of electronic computing techniques in the calculation of stability constants, J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem, doi:10.1016/0022-1902(71)80567-5
Rowinska-Zyrek, Wiech, Wa Tly, Wieczorek, Witkowska et al., Copper(II)-Binding Induces a Unique Polyproline Type II Helical Structure within the Ion-Binding Segment in the Intrinsically Disordered F-Domain of Ecdysteroid Receptor from Aedes aegypti, Inorg. Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b01826
Shang, Ye, Shi, Wan, Luo et al., Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2179-y
Towler, Staker, Prasad, Menon, Tang et al., ACE2 X-ray structures reveal a large hinge-bending motion important for inhibitor binding and catalysis, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M311191200
Verdecchia, Cavallini, Spanevello, Angeli, The pivotal link between ACE2 deficiency and SARS-CoV-2 infection, Eur. J. Intern. Med, doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2020.04.037
Wessels, Rolles, Rink, The Potential Impact of Zinc Supplementation on COVID-19 Pathogenesis, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01712
Wessels, Rolles, Slusarenko, Rink, Zinc deficiency as a possible risk factor for increased susceptibility and severe progression of Corona Virus Disease 19, Br. J. Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114521000738
Wu, Peng, Wilken, Geraghty, Li, Mechanisms of host receptor adaptation by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.325803
Yan, Zhang, Li, Xia, Guo et al., Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abb2762
Zheng, Wu, Ma, Han, Huang et al., A binding-enhanced but enzymatic activity-eliminated human ACE2 efficiently neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 variants, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00821-y
Zoroddu, Kowalik-Jankowska, Medici, Peana, Kozlowski, Copper(II) binding to Cap43 protein fragments, Dalton Trans, doi:10.1039/b808600a
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms24119202",
"ISSN": [
"1422-0067"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119202",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The spike protein (S) of SARS-CoV-2 is able to bind to the human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor with a much higher affinity compared to other coronaviruses. The binding interface between the ACE2 receptor and the spike protein plays a critical role in the entry mechanism of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. There are specific amino acids involved in the interaction between the S protein and the ACE2 receptor. This specificity is critical for the virus to establish a systemic infection and cause COVID-19 disease. In the ACE2 receptor, the largest number of amino acids playing a crucial role in the mechanism of interaction and recognition with the S protein is located in the C-terminal part, which represents the main binding region between ACE2 and S. This fragment is abundant in coordination residues such as aspartates, glutamates, and histidine that could be targeted by metal ions. Zn2+ ions bind to the ACE2 receptor in its catalytic site and modulate its activity, but it could also contribute to the structural stability of the entire protein. The ability of the human ACE2 receptor to coordinate metal ions, such as Zn2+, in the same region where it binds to the S protein could have a crucial impact on the mechanism of recognition and interaction of ACE2–S, with consequences on their binding affinity that deserve to be investigated. To test this possibility, this study aims to characterize the coordination ability of Zn2+, and also Cu2+ for comparison, with selected peptide models of the ACE2 binding interface using spectroscopic and potentiometric techniques.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"ijms24119202"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9502-7585",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Chemical, Physical, Mathematical and Natural Sciences, University of Sassari, 07100 Sassari, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Pelucelli",
"given": "Alessio",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3306-0419",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Chemical, Physical, Mathematical and Natural Sciences, University of Sassari, 07100 Sassari, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Peana",
"given": "Massimiliano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Chemistry, University of Wroclaw, 50-383 Wroclaw, Poland"
}
],
"family": "Orzeł",
"given": "Bartosz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Chemistry, University of Wroclaw, 50-383 Wroclaw, Poland"
}
],
"family": "Piasta",
"given": "Karolina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9556-6378",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Chemistry, University of Wroclaw, 50-383 Wroclaw, Poland"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Gumienna-Kontecka",
"given": "Elzbieta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4304-0251",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Chemical, Physical, Mathematical and Natural Sciences, University of Sassari, 07100 Sassari, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Medici",
"given": "Serenella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9583-4750",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Chemical, Physical, Mathematical and Natural Sciences, University of Sassari, 07100 Sassari, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zoroddu",
"given": "Maria Antonietta",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Molecular Sciences",
"container-title-short": "IJMS",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-25T06:58:48Z",
"timestamp": 1684997928000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2025-01-15T13:35:03Z",
"timestamp": 1736948103000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"UA2002DOTTRIC2021 articolo 9, comma 3, D.M. 8 febbraio 2013, n. 45"
],
"name": "Progetto"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2025-06-27T07:32:08Z",
"timestamp": 1751009528417,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 4,
"issue": "11",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
24
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "11",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-24T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1684886400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/24/11/9202/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "9202",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
24
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
24
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03120-0",
"article-title": "Role of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in COVID-19",
"author": "Ni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "422",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10096-020-04138-6",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) expression and tissue susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Beyerstedt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "905",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/path.2162",
"article-title": "The emerging role of ACE2 in physiology and disease",
"author": "Hamming",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Pathol.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "212",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells",
"author": "Jackson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.rmed.2020.105996",
"article-title": "Severe respiratory SARS-CoV2 infection: Does ACE2 receptor matter?",
"author": "Perrotta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105996",
"journal-title": "Respir. Med.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "168",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejim.2020.04.037",
"article-title": "The pivotal link between ACE2 deficiency and SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Verdecchia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "14",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.020",
"article-title": "Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): An overview of viral structure and host response",
"author": "Astuti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "407",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. Syndr.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molcel.2020.04.022",
"article-title": "A Multibasic Cleavage Site in the Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Is Essential for Infection of Human Lung Cells",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "779",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-21118-2",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 D614G spike mutation increases entry efficiency with enhanced ACE2-binding affinity",
"author": "Ozono",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "848",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb2762",
"article-title": "Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1444",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "367",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/08830185.2022.2079642",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_11",
"unstructured": "Gong, W., Parkkila, S., Wu, X., and Aspatwar, A. (2022). SARS-CoV-2 variants and COVID-19 vaccines: Current challenges and future strategies. Int. Rev. Immunol., 1–22."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2180-5",
"article-title": "Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor",
"author": "Lan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "215",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "581",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2179-y",
"article-title": "Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Shang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "221",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "581",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-73820-8",
"article-title": "Hot spot profiles of SARS-CoV-2 and human ACE2 receptor protein protein interaction obtained by density functional tight binding fragment molecular orbital method",
"author": "Lim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "16862",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.emboj.7600640",
"article-title": "Receptor and viral determinants of SARS-coronavirus adaptation to human ACE2",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1634",
"journal-title": "EMBO J.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-71188-3",
"article-title": "Dynamics of the ACE2-SARS-CoV-2/SARS-CoV spike protein interface reveal unique mechanisms",
"author": "Ali",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "14214",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01712",
"article-title": "The Potential Impact of Zinc Supplementation on COVID-19 Pathogenesis",
"author": "Wessels",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1712",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M311191200",
"article-title": "ACE2 X-ray structures reveal a large hinge-bending motion important for inhibitor binding and catalysis",
"author": "Towler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "17996",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "279",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10534-023-00491-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_19",
"unstructured": "Fatouros, P.R., Roy, U., and Sur, S. (2023). Implications of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein interactions with Zn-bound form of ACE2: A computational structural study. Biometals, 1–10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bioinformatics/btac534",
"article-title": "MIB2: Metal ion-binding site prediction and modeling server",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4428",
"journal-title": "Bioinformatics",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2772-0",
"article-title": "Receptor binding and priming of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 for membrane fusion",
"author": "Benton",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "327",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "588",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M111.325803",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of host receptor adaptation by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8904",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "287",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.52601/bpr.2021.210007",
"article-title": "Reduced graphene oxide membrane as supporting film for high-resolution cryo-EM",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "227",
"journal-title": "Biophys. Rep.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-26401-w",
"article-title": "Molecular insights into receptor binding of recent emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6103",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00821-y",
"article-title": "A binding-enhanced but enzymatic activity-eliminated human ACE2 efficiently neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 variants",
"author": "Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b03737",
"article-title": "Exploring the Specificity of Rationally Designed Peptides Reconstituted from the Cell-Free Extract of Deinococcus radiodurans toward Mn(II) and Cu(II)",
"author": "Peana",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4661",
"journal-title": "Inorg. Chem.",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/chem.202002114",
"article-title": "Zinc Interactions with a Soluble Mutated Rat Amylin to Mimic Whole Human Amylin: An Experimental and Simulation Approach to Understand Stoichiometry, Speciation and Coordination of the Metal Complexes",
"author": "Magri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "13072",
"journal-title": "Chemistry",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0039-9140(85)80077-1",
"article-title": "Calculation of equilibrium constants from multiwavelength spectroscopic data—II: SPECFIT: Two user-friendly programs in basic and standard FORTRAN 77",
"author": "Gampp",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "257",
"journal-title": "Talanta",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "32",
"year": "1985"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0277-5387(99)00279-X",
"article-title": "Spectrum–structure correlation for visible absorption spectra of copper(II) complexes in aqueous solution",
"author": "Prenesti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3233",
"journal-title": "Polyhedron",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "18",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/c9mt00131j",
"article-title": "Stability of Cu(ii) complexes with FomA protein fragments containing two His residues in the peptide chain",
"author": "Lesiow",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1518",
"journal-title": "Metallomics",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/b808600a",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_31",
"unstructured": "Zoroddu, M.A., Kowalik-Jankowska, T., Medici, S., Peana, M., and Kozlowski, H. (2008). Copper(II) binding to Cap43 protein fragments. Dalton Trans., 6127–6134."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.poly.2017.06.023",
"article-title": "Copper(II) complexes of the Neb-colloostatin analogues containing histidine residue structure stability biological activity",
"author": "Kadej",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "365",
"journal-title": "Polyhedron",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b01826",
"article-title": "Copper(II)-Binding Induces a Unique Polyproline Type II Helical Structure within the Ion-Binding Segment in the Intrinsically Disordered F-Domain of Ecdysteroid Receptor from Aedes aegypti",
"author": "Wiech",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11782",
"journal-title": "Inorg. Chem.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules181012396",
"article-title": "The involvement of amino acid side chains in shielding the nickel coordination site: An NMR study",
"author": "Medici",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12396",
"journal-title": "Molecules",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jtemb.2017.07.006",
"article-title": "Ni(II) interaction with a peptide model of the human TLR4 ectodomain",
"author": "Peana",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "151",
"journal-title": "J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmb.2004.12.043",
"article-title": "Probing copper2+ binding to the prion protein using diamagnetic nickel2+ and 1H NMR: The unstructured N terminus facilitates the coordination of six copper2+ ions at physiological concentrations",
"author": "Jones",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1393",
"journal-title": "J. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "346",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2014/656201",
"article-title": "Interaction of Cu(II) and Ni(II) with Ypk9 protein fragment via NMR studies",
"author": "Peana",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "656201",
"journal-title": "Sci. World J.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "2014",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/jr9530003192",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_38",
"unstructured": "Irving, H., and Williams, R.J.P. (1953). 637. The stability of transition-metal complexes. J. Chem. Soc. Resumed, 3192–3210."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.284.5415.805",
"article-title": "Undetectable intracellular free copper: The requirement of a copper chaperone for superoxide dismutase",
"author": "Rae",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "805",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "284",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/C4MT00230J",
"article-title": "Analyzing free zinc(II) ion concentrations in cell biology with fluorescent chelating molecules",
"author": "Maret",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "202",
"journal-title": "Metallomics",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/c001267j",
"article-title": "Prion proteins and copper ions. Biological and chemical controversies",
"author": "Kozlowski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6371",
"journal-title": "Dalton Trans.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2020.111304",
"article-title": "The N-terminal domain of Helicobacter pylori’s Hpn protein: The role of multiple histidine residues",
"author": "Bellotti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "111304",
"journal-title": "J. Inorg. Biochem.",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "214",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biom12010121",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_43",
"unstructured": "Bellotti, D., Miller, A., Rowinska-Zyrek, M., and Remelli, M. (2022). Zn(2+) and Cu(2+) Binding to the Extramembrane Loop of Zrt2, a Zinc Transporter of Candida albicans. Biomolecules, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.06.018",
"article-title": "Binding of transition metal ions to albumin: Sites, affinities and rates",
"author": "Bal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5444",
"journal-title": "Biochim. Biophys. Acta",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "1830",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18388/abp.1999_4129",
"article-title": "Coordination chemistry of glutathione",
"author": "Krezel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "567",
"journal-title": "Acta Biochim. Pol.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "46",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3891/acta.chem.scand.04-0559",
"article-title": "Determination of the equivalent point in potentiometric titrations",
"author": "Gran",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "559",
"journal-title": "Acta Chem. Scand.",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "4",
"year": "1950"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0039-9140(96)01958-3",
"article-title": "Investigation of equilibria in solution. Determination of equilibrium constants with the HYPERQUAD suite of programs",
"author": "Gans",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1739",
"journal-title": "Talanta",
"key": "ref_47",
"volume": "43",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0020-1693(00)95255-1",
"article-title": "Superquad—A new computer program for determination of stability constants of complexes by potentiometric titration",
"author": "Gans",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "219",
"journal-title": "Inorg. Chim. Acta",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "79",
"year": "1983"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/9783527656189",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_49",
"unstructured": "Brown, P.L., and Ekberg, C. (2016). Hydrolysis of Metal Ions, John Wiley & Sons."
},
{
"key": "ref_50",
"unstructured": "Baes, C.F., and Mesmer, R.S. (1976). The Hydrolysis of Cations, John Wiley & Sons."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0010-8545(98)00260-4",
"article-title": "Hyperquad simulation and speciation (HySS): A utility program for the investigation of equilibria involving soluble and partially soluble species",
"author": "Alderighi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "311",
"journal-title": "Coord. Chem. Rev.",
"key": "ref_51",
"volume": "184",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0022-1902(71)80567-5",
"article-title": "The use of electronic computing techniques in the calculation of stability constants",
"author": "Rossotti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2051",
"journal-title": "J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem.",
"key": "ref_52",
"volume": "33",
"year": "1971"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcc.20084",
"article-title": "UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis",
"author": "Pettersen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1605",
"journal-title": "J. Comput. Chem.",
"key": "ref_53",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency",
"author": "Jothimani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "343",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_54",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114521000738",
"article-title": "Zinc deficiency as a possible risk factor for increased susceptibility and severe progression of Corona Virus Disease 19",
"author": "Wessels",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "214",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_55",
"volume": "127",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2023.01.039",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2-at the heart of the COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Oudit",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "906",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_56",
"volume": "186",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 56,
"references-count": 56,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/24/11/9202"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Zn2+ and Cu2+ Interaction with the Recognition Interface of ACE2 for SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "24"
}
