Lower levels of vitamin D are associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection and mortality in the Indian population: An observational study
et al., International Immunopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001, Sep 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
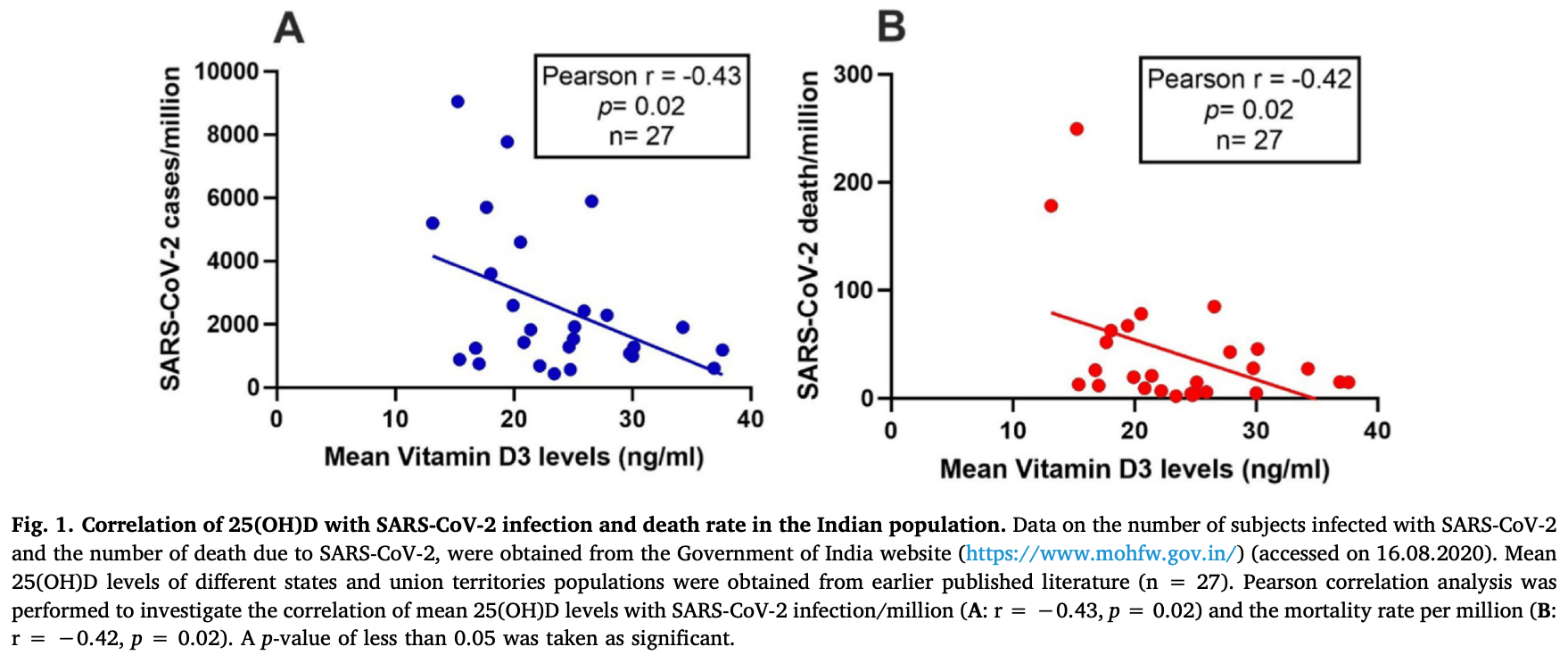
Analysis of vitamin D levels and COVID-19 in Indian states and union territories, showing an inverse correlation of vitamin D levels with SARS-CoV-2 cases and mortality.
Padhi et al., 14 Sep 2021, peer-reviewed, 5 authors.
Lower levels of vitamin D are associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection and mortality in the Indian population: An observational study
International Immunopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001
Background: The role of vitamin D in the susceptibility and severity of various viral diseases has been well documented. Recently, some reports highlighted the possible importance of vitamin D in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Although India receives adequate sunlight throughout the year, the majority of Indians are deficient in vitamin D levels. In the present study, we hypothesized that vitamin D deficiency would be associated with the SARS-CoV-2 infection rate and mortality in the Indian population. Materials and methods: SARS-CoV-2 infection and mortality data were obtained from the Government of India's official website (accessed on 16th August 2020). Various literature databases like PubMed and Google Scholar were searched to find the mean of 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] levels in different states and union territories of India, Pearson correlation was carried out to investigate the possible link between mean 25(OH)D levels and SARS-CoV-2 infection and mortality per million of the population. Results: An inverse correlation was observed between the mean level of 25(OH)D and SARS-CoV-2 infection rate (r = −0.43, p = 0.02) and mortality rate (r = −0.42, p = 0.02). Conclusions: The present observational study revealed an association of vitamin D with SARS-CoV-2 infection and related mortality. Further studies are required to validate our observations.
Writing -review & editing.
Appendix A. Supplementary material Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001.
References
Abraham, Krishnan, Narayanan Subhakumari, Chakkalakkudy, None, Vitamin D Levels In Depressive Disorder
Agarwal, Mithal, Dhingra, Kaur, Godbole et al., Effect of two different doses of oral cholecalciferol supplementation on serum 25-hydroxy-vitamin D levels in healthy Indian postmenopausal women: A randomized controlled trial, Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab
Agarwal, Mithal, Kaur, Dhingra, Godbole et al., Vitamin D and insulin resistance in postmenopausal Indian women, Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab
Aggarwal, Yadav, Ramachandran, Kumar, Kumar et al., Bioavailable vitamin D levels are reduced and correlate with bone mineral density and markers of mineral metabolism in adults with nephrotic syndrome, Nephrology
Agrawal, Mehta, Verma, Level of Vitamin D in hypothyroid subjects: a study on the suburban population of North-West Delhi, Int. J. Clin. Biochem. Res
Agrawal, Sharma, Prevalence of osteoporosis in otherwise healthy Indian males aged 50 years and above, Arch. Osteoporosis
Aparna, Muthathal, Nongkynrih, Gupta, Vitamin D deficiency in India, J. Family Med. Prim. Care
Aranow, Vitamin D and the immune system, J. Invest. Med
Arya, Bhambri, Godbole, Mithal, Vitamin D status and its relationship with bone mineral density in healthy Asian Indians, Osteoporosis Int.: J. Established Result Cooperation Europ. Found. Osteoporosis National Osteoporosis Found
Bachali, Dasu, Ramalingam, Naidu, Vitamin d deficiency and insulin resistance in normal and type 2 diabetes subjects, Indian J. Clin. Biochem.: IJCB
Baidya, Chowdhury, Mukhopadhyay, Ghosh, Profile of vitamin D in a cohort of physicians and diabetologists in Kolkata, Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab
Barman, Mattack, A Study Of Serum Vitamin D In Psoriatic Patients In A Tertiary Care Hospital Of Assam, Paripex Indian J. Res
Basu, Gupta, Mitra, Ghosh, Prevalence of vitamin d deficiency in a pediatric hospital of eastern India, Indian J. Clin. Biochem.: IJCB
Bawaskar, Bawaskar, Bawaskar, Pakhare, Profile of Vitamin D in patients attending at general hospital Mahad India, Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab
Beard, Bearden, Striker, Vitamin D and the anti-viral state, J. Clin. Virol
Bhatt, Misra, Sharma, Guleria, Pandey et al., Vitamin D insufficiency is associated with abdominal obesity in urban Asian Indians without diabetes in North India, Diabetes Technol. Ther
Bikle, Vitamin D metabolism, mechanism of action, and clinical applications, Chem. Biol
Carpagnano, Di Lecce, Quaranta, Zito, Buonamico et al., Vitamin D deficiency as a predictor of poor prognosis in patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19, J. Endocrinol. Invest
Castillo, Costa, Vaquero Barrios, Alcalá Díaz, Miranda et al., Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol
Chakraborty, Choudhury, Saha, Development of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) in Young Obese Tribal Subjects of Tripura: Link between Low 25 (OH) Vitamin-D Levels and Immune Modulators, J. Assoc. Phys. India
Chakravarti, Bharara, Kapoor, Ashraf, Levels of 25-hydroxy Vitamin D3 and Vitamin D Receptor Polymorphism in Severe Dengue Cases from New Delhi, Trop. Med. Infect. Dis
Chandrashekar, Kumari, Rajappa, Revathy, Munisamy, Thappa, 25-hydroxy vitamin D and ischaemia-modified albumin levels in psoriasis and their association with disease severity, Br. J. Biomed. Sci
Chopra, Singh, Singh, Is there A Need to Reasses Reference Levels of Vitamin D for India ?-A Preliminary Survey of Vitamin D Levels in the Normal Population of Punjab
Cole, Too many digits: the presentation of numerical data, Arch. Dis. Child
D'avolio, Avataneo, Manca, Cusato, De Nicolò et al., 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations Are Lower in Patients with Positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2, Nutrients
Daroach, Narang, Saikia, Sachdeva, Sendhil Kumaran, Correlation of vitamin D and vitamin D receptor expression in patients with alopecia areata: a clinical paradigm
Dasgupta, Saikia, Sarma, Status of 25(OH)D levels in pregnancy: A study from the North Eastern part of India, Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab
Debbarma, Dasgupta, Biswas, Study of Vitamin D levels in patients of acute myocardial infarction, J. Evidence Based Med. Healthcare
Dhanwal, Sahoo, Gautam, Saha, Hip fracture patients in India have vitamin D deficiency and secondary hyperparathyroidism, Osteoporosis Int.: J. Established Result Cooperation Between Europ. Found. Osteoporosis National Osteoporosis Found
Dharmshaktu, Saha, Kar, Sreenivas, Ramakrishnan et al., Absence of vitamin D deficiency among common outdoor workers in Delhi, Clin. Endocrinol
Din, Majid, Rashid, Hussain, Koul et al., Combinatorial effect of leptin, tumor necrosis factor-Αlpha, and vitamin d in progression of type 2 diabetes in kashmiri population, Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res
Dutta, Kakati, Barman, Bora, Vitamin D status and its relationship with systemic lupus erythematosus as a determinant and outcome of disease activity, Hormone Mol. Biol. Clin. Invest
Dutta, Maisnam, Shrivastava, Sinha, Ghosh et al., Serum vitamin-D predicts insulin resistance in individuals with prediabetes, Indian J. Med. Res
Fang, Li, Yu, Wang, Zhang et al., Epidemiological, comorbidity factors with severity and prognosis of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Aging
Gade, Mony, Munisamy, Chandrashekar, Rajappa, An investigation of vitamin D status in alopecia areata, Clin. Exp. Med
Gandhe, Velu, Shyamini, Saha, Ramesh et al., Circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D status in apparently healthy adolescents and its association with body mass index in Puducherry population, Indian J. Child Health
García De Tena, Hachem Debek, Hernández Gutiérrez, Alonso, The role of vitamin D in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma and other respiratory diseases, Arch. Bronconeumol
Garg, Dasgupta, Maharana, Paul, Bandyopadhyay et al., Sun exposure and Vitamin D in rural India: A cross-sectional study
Garg, Marwaha, Tandon, Bhadra, Mahalle, Relationship of lipid parameters with bone mineral density in Indian population, Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab
Garg, Patidar, Dhamija, Vitamin D Status and Risk of Stroke: The Rotterdam Study, Stroke
Goswami, Gupta, Goswami, Marwaha, Tandon et al., Prevalence and significance of low 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations in healthy subjects in Delhi, Am. J. Clin. Nutrit
Goswami, Kochupillai, Gupta, Goswami, Singh et al., Presence of 25(OH) D deficiency in a rural North Indian village despite abundant sunshine, J. Assoc. Phys. India
Goswami, Marwaha, Gupta, Tandon, Sreenivas et al., Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and its relationship with thyroid autoimmunity in Asian Indians: a community-based survey, Brit. J. Nutrit
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients
Gupta, Comparison of Calcium, Phosphorous and 25 (OH)D2 Levels in Sedentary and Labourer Females, Ann. Clin. Lab. Res
Gupta, Prabhakar, Modi, Bhadada, Lal et al., Vitamin D status and risk of ischemic stroke in North Indian patients, Indian J. Endocrinol Metab
Gupta, Soin, Garg, Prevalence of vitamin d levels in patients of diabetes mallitus in rural and urban population of Malwa region of Punjab, J. Adv. Med. Dent. Sci. Res
Harinarayan, Gupta, Kochupillai, Vitamin D status in primary hyperparathyroidism in India, Clin. Endocrinol
Harinarayan, Ramalakshmi, Prasad, Sudhakar, Srinivasarao et al., High prevalence of low dietary calcium, high phytate consumption, and vitamin D deficiency in healthy south Indians, Am. J. Clin. Nutrit
Harinarayan, Ramalakshmi, Venkataprasad, High prevalence of low dietary calcium and low vitamin D status in healthy south Indians, Asia Pacific, J. Clin. Nutrit
Harinarayan, Sachan, Reddy, Satish, Prasad et al., Vitamin D status and bone mineral density in women of reproductive and postmenopausal age groups: a cross-sectional study from south India, J. Assoc. Phys. India
Hastie, Mackay, Ho, Celis-Morales, Katikireddi et al., Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank, Diabetes Metabolic Syndrome
Himani, Kumar, Ansari, Mahdi, Sharma et al., Blood Lead Levels in Occupationally Exposed Workers Involved in Battery Factories of Delhi-NCR Region: Effect on Vitamin D and Calcium Metabolism, Indian J. Clin. Biochem
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality, Aging Clin. Exp. Res
Jabbar, Aggarwal, Chandel, Kohli, Gupta et al., High prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in north Indian adults is exacerbated in those with chronic kidney, disease
Jain, Shaikh, Comparative study of serum vitamin d levels and other biomarkers in patients attending tertiary cardiac care center, Int. J. Bioassays
Joseph, George, Pulimood, Seshadri, Chacko, OH) vitamin D level in Crohn's disease: association with sun exposure & disease activity, Indian J. Med. Res
Joseph, Nagrale, Joseraj, Pradeep Kumar, Kaziyarakath et al., Low levels of serum Vitamin D in chronic periodontitis patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A hospital-based cross-sectional clinical study, J. Indian Soc. Periodontol
Kadam, Chiplonkar, Khadilkar, Divate, Khadilkar, Low bone mass in urban Indian women above 40 years of age: prevalence and risk factors, Gynecological endocrinology: the official journal of the International Society of, Gynecol. Endocrinol
Kalra, Kalra, Vitamin D deficiency in Healthy Postmenopausal Women in Haryana
Karthikayan, Sureshkumar, Kadambari, Vijayakumar, Low serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels are associated with aggressive breast cancer variants and poor prognostic factors in patients with breast carcinoma, Arch. Endocrinol. Metabolism
Kienreich, Grubler, Tomaschitz, Schmid, Verheyen et al., Vitamin D, arterial hypertension & cerebrovascular disease, Indian J. Med. Res
Kiran, Thilagavathi, Serum 25-Hydroxy Vitamin D, Calcium, Phosphorus and Alkaline Phosphatase Levels In Healthy Adults Above the age of 20 Living in Potheri Village of Kancheepuram District, Tamilnadu, J. App. Pharm. Sci
Klingberg, Oleröd, Konar, Petzold, Hammarsten, Seasonal variations in serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels in a Swedish cohort, Endocrine
Kumar, Nanda, Bharathy, Ravichandran, Dinakaran, Evaluation of vitamin D status and its correlation with glycated haemoglobin in type 2 diabetes mellitus, Biomed. Res
Laway, Kotwal, Shah, Pattern of 25 hydroxy vitamin D status in North Indian people with newly detected type 2 diabetes: A prospective case control study, Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab
Lodh, Goswami, Mahajan, Sen, Jajodia et al., Assessment of Vitamin D status In Patients of Chronic Low Back Pain of Unknown Etiology, Indian J. Clin. Biochem.: IJCB
Maisnam, Dutta, Mukhopadhyay, Chowdhury, Lean mass is the strongest predictor of bone mineral content in type-2 diabetes and normal individuals: an eastern India perspective, J. Diabetes Metabolic Disorders
Majumdar, Prabhakar, Kulkarni, Christopher, Vitamin D status, hypertension and ischemic stroke: a clinical perspective, J. Hum. Hypertens
Malhotra, Mithal, Gupta, Shukla, Godbole, Effect of vitamin D supplementation on bone health parameters of healthy young Indian women, Arch. Osteoporosis
Malik, Giri, Madhu, Rathi, Banerjee et al., Relationship of levels of Vitamin D with flow-mediated dilatation of brachial artery in patients of myocardial infarction and healthy control: A case-control study, Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab
Mangaraj, Choudhury, Swain, Sarangi, Mohanty et al., Evaluation of Vitamin D Status and its Impact on Thyroid Related Parameters in New Onset Graves' Disease-A Cross-sectional Observational Study, Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab
Marwaha, Tandon, Shivaprasad, Kanwar, Mani et al., Peak bone mineral density of physically active healthy Indian men with adequate nutrition and no known current constraints to bone mineralization, J. Clin. Densitometry: Off. J. Int. Soc. Clin. Densitometry
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of Vitamin D Status and Other Clinical Characteristics With COVID-19 Test Results, JAMA Network Open
Merzon, Tworowski, Gorohovski, Vinker, Golan Cohen et al., Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: an Israeli population-based study, FEBS J
Mukherjee, Patra, Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in type-2 diabetes mellitus patients and its correlation with glycemic control, Int. J. Bioassays
Mukherjee, Patra, Sibasish, Evaluation of Vitamin D Status in Urban Population Employed In Office Jobs, IOSR J. Dental Med. Sci
Multani, Sarathi, Shivane, Bandgar, Menon et al., Study of bone mineral density in resident doctors working at a teaching hospital, J. Postgrad. Med
Muthukrishnan, Dhruv, Vitamin D status and gestational diabetes mellitus, Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab
Nagarjunakonda, Amalakanti, Uppala, Rajanala, Athina, Vitamin D in epilepsy: vitamin D levels in epilepsy patients, patients on antiepileptic drug polytherapy and drug-resistant epilepsy sufferers, Eur. J. Clin. Nutr
Nagpal, Pande, Bhartia, A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of the short-term effect of vitamin D3 supplementation on insulin sensitivity in apparently healthy, middle-aged, centrally obese men, Diabetic Med, J. Brit. Diabetic Assoc
Nayak, Garg, Mithra, Manjrekar, Serum Vitamin D(3) Levels and Diffuse Hair Fall among the Student Population in South India: A Case-Control Study, Int. J. Trichol
Oberoi, Mehrotra, Rawat, Vitamin D" as a profile marker for cardiovascular diseases, Ann. Cardiac Anaesthesia
Ohaegbulam, Swalih, Patel, Smith, Perrin, Vitamin D Supplementation in COVID-19 Patients: A Clinical Case Series, Am. J. Therap
Padhi, Panda, Jagati, Patra, Vitamin D status in adult critically ill patients in Eastern India: An observational retrospective study
Pan, Banerjee, Dasgupta, Paul, Vitamin D status among women aged 40 years and above in a rural area of West Bengal: A community-based study, J. Family Med. Prim. Care
Panagiotou, Tee, Ihsan, Athar, Marchitelli et al., Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 are associated with greater disease severity, Clin. Endocrinol
Panda, Tiwari, Luthra, Sharma, Singh, Status of vitamin D and the associated host factors in pulmonary tuberculosis patients and their household contacts: A cross sectional study, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol
Patwardhan, Mughal, Chiplonkar, Webb, Kift et al., Duration of casual sunlight exposure necessary for adequate Vitamin D status in, Indian Men
Paul, Thomas, Seshadri, Oommen, Jose et al., Prevalence of osteoporosis in ambulatory postmenopausal women from a semiurban region in Southern India: relationship to calcium nutrition and vitamin D status, Endocrine Practice: Off, J. Am. College Endocrinol. Am. Assoc. Clin. Endocrinol
Pk, Vitamin D Status In Hypertension, Am. Int. J. Res. Formal, Appl. Nat. Sci
Prakash, Rathore, Makwana, Dave, Joshi et al., Vitamin D Deficiency in Patients With Chronic Tension-Type Headache: A Case-Control Study, Headache
Priyambada, Bhatia, Singh, Bhatia, Serum 25 hydroxyvitamin D profile after single large oral doses of cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) in medical staff in North India: a pilot study, J. Postgrad. Med
Pruthvi, Correlation of Vitamin-D Levels With Blood Sugar Levels in Diabetes Mellitus, Galore Int. J. Health Sci. Res
Ramakrishnan, Bhansali, Bhadada, Sharma, Walia et al., Vitamin D status and its seasonal variability in healthy young adults in an Asian Indian urban population, Endocrine Practice: Off, J. Am. College Endocrinol. Am. Assoc. Clin. Endocrinol
Rath, Nanda, Mishra, Patra, Evaluation of Serum 25 Hydroxy Vitamin D level in acute myocardial infarction patients in a tertiary care hospital, Asian J. Med. Sci
Rathored, Sharma, Singh, Banavaliker, Sreenivas et al., Risk and outcome of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and serum 25(OH)D, Int. J. Tuberculosis Lung Disease: Off, J. Int. Union against Tuberculosis Lung Disease
Reddy, Kulkarni, Shatrugna, Thilak Ravindra Reddy, Nagalla et al., Bone mass of overweight affluent Indian youth and its sex-specific association with body composition, Arch. Osteoporosis
Rehman, Dogra, Wani, Serum Vitamin D Levels and Alopecia Areata-A Hospital Based Case-Control Study from North-India, Int J Trichology
Rosa, Malaguarnera, Nicoletti, Malaguarnera, Vitamin D3: a helpful immuno-modulator, Immunology
Roy, Lakshmy, Tarik, Tandon, Reddy et al., Independent association of severe vitamin D deficiency as a risk of acute myocardial infarction in Indians, Indian Heart J
Sahasrabuddhe, Pitale, Gupta, Chari, Sagdeo, Study of vitamin D levels and its correlation with insulin resistance, Nat. J. Physiol., Pharm. Pharmacol
Samuel, Association of Vitamin D deficiency and Hypothyroidism in a tertiary teaching hospital in Kerala, J. Med. Sci. Clin. Res
Sasidharan, Rajeev, Vijayakumari, Tuberculosis and vitamin D deficiency, J. Assoc. Physicians India
Sehrawat, Arora, Chauhan, Kar, Poonia et al., Correlation of Vitamin D Levels with Pigmentation in Vitiligo Patients Treated with NBUVB Therapy, ISRN Dermatol
Shaikh, Malapati, Gokani, Patel, Chatriwala, Serum Magnesium and Vitamin D Levels as Indicators of Asthma Severity, Pulmonary Med
Sharma, Saxena, Saxena, Sharma, Lal, Systemic inflammation and alteration in vitamin D levels in pregnancy induced hypertension, Asian J. Med. Sci
Sharma, Sharma, Singh, Gupta, Sharma et al., Vitamin D Status in Cold Trans-Himalayan Deserts at Altitude of 4000 meter and above in India, Indian J. Community Health
Shetty, Kapoor, Naik, Asha, Prabu et al., Osteoporosis in healthy South Indian males and the influence of life style factors and vitamin d status on bone mineral density, J. Osteoporosis
Shivane, Sarathi, Lila, Bandgar, Joshi et al., Peak bone mineral density and its determinants in an Asian Indian population, J. Clin. Densitometry: Off. J. Int. Soc. Clin. Densitometry
Shukla, Sharma, Gupta, Raizada, Vinayak, Current Scenario of Prevalence of Vitamin D Deficiency in Ostensibly Healthy Indian Population: A Hospital Based Retrospective Study, Indian J. Clin. Biochem.: IJCB
Shylla, Devi, Wann, Khongwir, Longmei, Vitamin D Deficiency : Highly Prevalent Among Apparently Healthy Female Adolescents In Both Urban And Rural Population Of Manipur
Singh, Barik, Imam, Level in Women with Uterine Fibroid: An Observational Study in Eastern Indian Population, J. Obstetrics Gynaecol. India
Singh, Kaur, Singh, Revisiting the role of vitamin D levels in the prevention of COVID-19 infection and mortality in European countries post infections peak, Aging Clin. Exp. Res
Singh, Lavania, Pathak, Ahuja, Turankar et al., VDR polymorphism, gene expression and vitamin D levels in leprosy patients from North Indian population, PLoS Negl.Trop. Dis
Singla, Gurung, Aggarwal, Dutta, Kochhar, Relationship between preeclampsia and vitamin D deficiency: a case control study, Arch. Gynecol. Obstet
Smith, Seasonal, ethnic and gender variations in serum vitamin D3 levels in the local population of Peterborough, Biosci. Horizons: Int. J. Student Res
Soam, Singh, Chaturvedi, Sarkar, A Study on Association of Degree of Physical Exercise and Plasma 25-(OH) Vitamin D Levels, Indian J. Med. Biochem
Speeckaert, Delanghe, Association between low vitamin D and COVID-19: don't forget the vitamin D binding protein, Aging Clin. Exp. Res
Sun, Zhang, Zou, Liu, Li et al., Serum calcium as a biomarker of clinical severity and prognosis in patients with coronavirus disease, Aging
Tandon, Marwaha, Kalra, Gupta, Dudha et al., Bone mineral parameters in healthy young Indian adults with optimal vitamin D availability, Nat. Med. J. India
Tandon, Sharma, Mahajan, Raina, Mahajan et al., Prevalence of vitamin d deficiency among Indian menopausal women and its correlation with diabetes: A first Indian cross sectional data, J. Mid-Life Health
Teymoori-Rad, Marashi, Vitamin D and Covid-19: From potential therapeutic effects to unanswered questions, Rev. Med. Virol
Tyagi, Mohanty, Kaur, Kabi, Kumari et al., A study of vitamin D levels in patients of coronary artery disease, World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci
Usmani, Poonam, Sinha, Haque, Evaluation of Calcium, Phosphorus and Vitamin D Level in Different Stages of Pregnancy in East Indian Population, Int. J. Dental Med. Specialty
Vedak, Ganwir, Shah, Pinto, Lele et al., Vitamin D as a marker of cognitive decline in elderly Indian population, Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol
Vupputuri, Goswami, Gupta, Ray, Tandon et al., Prevalence and functional significance of 25-hydroxyvitamin D deficiency and vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms in Asian Indians, Am. J. Clin. Nutrit
Wan, Wang, Liu, Tong, Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range, BMC Med. Res. Method
Wang, Pencina, Booth, Jacques, Ingelsson et al., Vitamin D Deficiency and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease, Circulation
Whittemore, COVID-19 fatalities, latitude, sunlight, and vitamin D, Am. J. Infect. Control
Williams, Malatesta, Norris, Vitamin D and chronic kidney disease, Ethn. Dis
Wu, Zhao, Yu, Chen, Wang et al., A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China, Nature
Xu, Baylink, Chen, Reeves, Xiao et al., The importance of vitamin d metabolism as a potential prophylactic, immunoregulatory and neuroprotective treatment for COVID-19, J. Trans. Med
Yasovanthi, Venkata Karunakar, Sri, Manjari, Reddy et al., Association of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms with BMD and their effect on 1, 25-dihydroxy vitamin D3 levels in pre-and postmenopausal South Indian women from Andhra Pradesh, Clin. Chim. Acta; Int. J. Clin. Chem
Zargar, Ahmad, Masoodi, Wani, Bashir et al., Vitamin D status in apparently healthy adults in Kashmir Valley of Indian subcontinent, Postgrad. Med. J
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001",
"ISSN": [
"1567-5769"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001",
"alternative-id": [
"S1567576920330186"
],
"article-number": "107001",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Lower levels of vitamin D are associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection and mortality in the Indian population: An observational study"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "International Immunopharmacology"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Padhi",
"given": "Sunali",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suvankar",
"given": "Subham",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Panda",
"given": "Venketesh K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pati",
"given": "Abhijit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Panda",
"given": "Aditya K.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Immunopharmacology",
"container-title-short": "International Immunopharmacology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-14T20:39:52Z",
"timestamp": 1600115992000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-18T07:06:12Z",
"timestamp": 1668755172000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-01T08:06:08Z",
"timestamp": 1714550768691
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 22,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2020-11-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1604188800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1567576920330186?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1567576920330186?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "107001",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3",
"article-title": "A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "265",
"issue": "7798",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0005",
"volume": "579",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2310/JIM.0b013e31821b8755",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and the immune system",
"author": "Aranow",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "881",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J. Invest. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0010",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2013.12.016",
"article-title": "Vitamin D metabolism, mechanism of action, and clinical applications",
"author": "Bikle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "319",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Chem. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0015",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03482.x",
"article-title": "Vitamin D3: a helpful immuno-modulator",
"author": "Di Rosa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "123",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Immunology",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0020",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2010.12.006",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and the anti-viral state",
"author": "Beard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "194",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0025",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"article-title": "25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations Are Lower in Patients with Positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "D'Avolio",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0030",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.15495",
"article-title": "Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: an Israeli population-based study",
"author": "Merzon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "FEBS J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0035",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MJT.0000000000001222",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Supplementation in COVID-19 Patients: A Clinical Case Series",
"author": "Ohaegbulam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Therap.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0040",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 are associated with greater disease severity",
"author": "Panagiotou",
"journal-title": "Clin. Endocrinol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0045",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.103526",
"article-title": "Serum calcium as a biomarker of clinical severity and prognosis in patients with coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11287",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Aging",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0050",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2159",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and Covid-19: From potential therapeutic effects to unanswered questions",
"author": "Teymoori-Rad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Rev. Med. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0055",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency as a predictor of poor prognosis in patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19",
"author": "Carpagnano",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Endocrinol. Invest.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0060",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722",
"article-title": "Association of Vitamin D Status and Other Clinical Characteristics With COVID-19 Test Results",
"author": "Meltzer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "JAMA Network Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0065",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12967-020-02488-5",
"article-title": "The importance of vitamin d metabolism as a potential prophylactic, immunoregulatory and neuroprotective treatment for COVID-19",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "322",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Trans. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0070",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_78_18",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency in India",
"author": "Aparna",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "324",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J. Family Med. Prim. Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0075",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/archdischild-2014-307149",
"article-title": "Too many digits: the presentation of numerical data",
"author": "Cole",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "608",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Arch. Dis. Child.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0080",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2288-14-135",
"article-title": "Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range",
"author": "Wan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "135",
"journal-title": "BMC Med. Res. Method.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0085",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.050",
"article-title": "Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank",
"author": "Hastie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "561",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metabolic Syndrome",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0090",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8",
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality",
"author": "Ilie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1195",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin. Exp. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0095",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"article-title": "Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths",
"author": "Grant",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "988",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0100",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Revisiting the role of vitamin D levels in the prevention of COVID-19 infection and mortality in European countries post infections peak",
"author": "Singh",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin. Exp. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0105",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajic.2020.06.193",
"article-title": "COVID-19 fatalities, latitude, sunlight, and vitamin D",
"author": "Whittemore",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Infect. Control",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0110",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.103579",
"article-title": "Epidemiological, comorbidity factors with severity and prognosis of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Fang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12493",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "Aging",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0115",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D and chronic kidney disease",
"author": "Williams",
"first-page": "S5",
"issue": "4 Suppl 5",
"journal-title": "Ethn. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0120",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arbres.2013.11.023",
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma and other respiratory diseases",
"author": "García de Tena",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "179",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Arch. Bronconeumol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0125",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D, arterial hypertension & cerebrovascular disease",
"author": "Kienreich",
"first-page": "669",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Med. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0130",
"volume": "137",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.706127",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Deficiency and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "503",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0135",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0140",
"unstructured": "M.E. Castillo, L.M. Entrenas Costa, J.M. Vaquero Barrios, J.F. Alcalá Díaz, J.L. Miranda, R. Bouillon, J.M. Quesada Gomez, Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. (2020) 105751."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12020-015-0548-3",
"article-title": "Seasonal variations in serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels in a Swedish cohort",
"author": "Klingberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "800",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Endocrine",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0145",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/biohorizons/hzq016",
"article-title": "Seasonal, ethnic and gender variations in serum vitamin D3 levels in the local population of Peterborough",
"author": "Smith",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "124",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Biosci. Horizons: Int. J. Student Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0150",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01607-y",
"article-title": "Association between low vitamin D and COVID-19: don't forget the vitamin D binding protein",
"author": "Speeckaert",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1207",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin. Exp. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0155",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/85.4.1062",
"article-title": "High prevalence of low dietary calcium, high phytate consumption, and vitamin D deficiency in healthy south Indians",
"author": "Harinarayan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1062",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutrit.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0160",
"volume": "85",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2265.1995.tb02043.x",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status in primary hyperparathyroidism in India",
"author": "Harinarayan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "351",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Clin. Endocrinol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0165",
"volume": "43",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D status and bone mineral density in women of reproductive and postmenopausal age groups: a cross-sectional study from south India",
"author": "Harinarayan",
"first-page": "698",
"journal-title": "J. Assoc. Phys. India",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0170",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"article-title": "High prevalence of low dietary calcium and low vitamin D status in healthy south Indians",
"author": "Harinarayan",
"first-page": "359",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Asia Pacific J. Clin. Nutrit.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0175",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ejcn.2015.127",
"article-title": "Vitamin D in epilepsy: vitamin D levels in epilepsy patients, patients on antiepileptic drug polytherapy and drug-resistant epilepsy sufferers",
"author": "Nagarjunakonda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "140",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0180",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "A Study Of Serum Vitamin D In Psoriatic Patients In A Tertiary Care Hospital Of Assam",
"author": "Barman",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Paripex Indian J. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0185",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/2230-8210.104109",
"article-title": "Status of 25(OH)D levels in pregnancy: A study from the North Eastern part of India",
"author": "Dasgupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S405",
"issue": "Suppl 2",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0190",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0195",
"unstructured": "D. J, P. D, M. N, J.E. T, A Study on the Biological Reference Interval of Vitamin D in North-East India, Nat. J. Lab. Med. 8(2) (2019) BO01-BO04."
},
{
"DOI": "10.5958/2394-4196.2016.00016.9",
"article-title": "Evaluation of Calcium, Phosphorus and Vitamin D Level in Different Stages of Pregnancy in East Indian Population",
"author": "Usmani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "16",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Dental Med. Specialty",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0200",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/nep.12638",
"article-title": "Bioavailable vitamin D levels are reduced and correlate with bone mineral density and markers of mineral metabolism in adults with nephrotic syndrome",
"author": "Aggarwal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "483",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Nephrology",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0205",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1440-1797.2008.01082.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0210",
"unstructured": "Z. Jabbar, P.K. Aggarwal, N. Chandel, H.S. Kohli, K.L. Gupta, V. Sakhuja, V. Jha, High prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in north Indian adults is exacerbated in those with chronic kidney disease 14(3) (2009) 345-349."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0215",
"unstructured": "M. Daroach, T. Narang, U.N. Saikia, N. Sachdeva, M. Sendhil Kumaran, Correlation of vitamin D and vitamin D receptor expression in patients with alopecia areata: a clinical paradigm 57(2) (2018) 217-222."
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/2230-8210.139241",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status and risk of ischemic stroke in North Indian patients",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "721",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0220",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4158/EP10155.OR",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status and its seasonal variability in healthy young adults in an Asian Indian urban population",
"author": "Ramakrishnan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "185",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Endocrine Practice: Off. J. Am. College Endocrinol. Am. Assoc. Clin. Endocrinol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0225",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00404-014-3550-8",
"article-title": "Relationship between preeclampsia and vitamin D deficiency: a case control study",
"author": "Singla",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1247",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Arch. Gynecol. Obstet.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0230",
"volume": "291",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12291-018-0797-z",
"article-title": "Datta, Blood Lead Levels in Occupationally Exposed Workers Involved in Battery Factories of Delhi-NCR Region: Effect on Vitamin D and Calcium Metabolism",
"author": "Himani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "80",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Clin. Biochem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0235",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.105419",
"article-title": "Status of vitamin D and the associated host factors in pulmonary tuberculosis patients and their household contacts: A cross sectional study",
"author": "Panda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0240",
"volume": "193",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jocd.2009.05.004",
"article-title": "Peak bone mineral density of physically active healthy Indian men with adequate nutrition and no known current constraints to bone mineralization",
"author": "Marwaha",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "314",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Densitometry: Off. J. Int. Soc. Clin. Densitometry",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0245",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.027523",
"article-title": "Letter by Garg et al Regarding Article, “Vitamin D Status and Risk of Stroke: The Rotterdam Study”",
"author": "Garg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Stroke",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0250",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/dia.2013.0303",
"article-title": "Vitamin D insufficiency is associated with abdominal obesity in urban Asian Indians without diabetes in North India",
"author": "Bhatt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "392",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Technol. Ther.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0255",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/83.6.1411",
"article-title": "Prevalence and functional significance of 25-hydroxyvitamin D deficiency and vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms in Asian Indians",
"author": "Vupputuri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1411",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutrit.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0260",
"volume": "83",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/72.2.472",
"article-title": "Prevalence and significance of low 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations in healthy subjects in Delhi",
"author": "Goswami",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "472",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutrit.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0265",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"article-title": "Presence of 25(OH) D deficiency in a rural North Indian village despite abundant sunshine",
"author": "Goswami",
"first-page": "755",
"journal-title": "J. Assoc. Phys. India",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0270",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"article-title": "Bone mineral parameters in healthy young Indian adults with optimal vitamin D availability",
"author": "Tandon",
"first-page": "298",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med. J. India",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0275",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/2230-8210.117237",
"article-title": "Effect of two different doses of oral cholecalciferol supplementation on serum 25-hydroxy-vitamin D levels in healthy Indian postmenopausal women: A randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Agarwal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "883",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0280",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/2230-8210.126583",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and insulin resistance in postmenopausal Indian women",
"author": "Agarwal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "89",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0285",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1464-5491.2008.02636.x",
"article-title": "A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of the short-term effect of vitamin D3 supplementation on insulin sensitivity in apparently healthy, middle-aged, centrally obese men",
"author": "Nagpal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "19",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Diabetic Med.: J. Brit. Diabetic Assoc.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0290",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114509220824",
"article-title": "Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and its relationship with thyroid autoimmunity in Asian Indians: a community-based survey",
"author": "Goswami",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "382",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Brit. J. Nutrit.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0295",
"volume": "102",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/tropicalmed5020072",
"article-title": "Levels of 25-hydroxy Vitamin D3 and Vitamin D Receptor Polymorphism in Severe Dengue Cases from New Delhi",
"author": "Chakravarti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "72",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Trop. Med. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0300",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5588/ijtld.12.0122",
"article-title": "Risk and outcome of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and serum 25(OH)D",
"author": "Rathored",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1522",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Tuberculosis Lung Disease: Off. J. Int. Union against Tuberculosis Lung Disease",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0305",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/2230-8210.190558",
"article-title": "Relationship of levels of Vitamin D with flow-mediated dilatation of brachial artery in patients of myocardial infarction and healthy control: A case-control study",
"author": "Malik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "684",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0310",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18231/j.ijcbr.2020.023",
"article-title": "Level of Vitamin D in hypothyroid subjects: a study on the suburban population of North-West Delhi",
"author": "Agrawal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "116",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Clin. Biochem. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0315",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00198-012-1993-y",
"article-title": "Hip fracture patients in India have vitamin D deficiency and secondary hyperparathyroidism",
"author": "Dhanwal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "553",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Osteoporosis Int.: J. Established Result Cooperation Between Europ. Found. Osteoporosis National Osteoporosis Found. USA",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0320",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cen.14012",
"article-title": "Absence of vitamin D deficiency among common outdoor workers in Delhi",
"author": "Dharmshaktu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "356",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Clin. Endocrinol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0325",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ihj.2015.02.002",
"article-title": "Independent association of severe vitamin D deficiency as a risk of acute myocardial infarction in Indians",
"author": "Roy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "27",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Indian Heart J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0330",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pntd.0006823",
"article-title": "VDR polymorphism, gene expression and vitamin D levels in leprosy patients from North Indian population",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "PLoS Negl.Trop. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0335",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0340",
"unstructured": "N. Tyagi, A. Mohanty, C. Kaur, A. Kabi, S. Kumari, Mamta, S. Sharma, S. Rani, D. Sahu, J. Prasad, C. Bhaskar, Kabi, A study of vitamin D levels in patients of coronary artery disease, World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 8 (2019) 1179-1186."
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/2230-8210.196004",
"article-title": "Profile of Vitamin D in patients attending at general hospital Mahad India",
"author": "Bawaskar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "125",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0345",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2016/1643717",
"article-title": "Serum Magnesium and Vitamin D Levels as Indicators of Asthma Severity",
"author": "Shaikh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1643717",
"journal-title": "Pulmonary Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0350",
"volume": "2016",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/head.13096",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Deficiency in Patients With Chronic Tension-Type Headache: A Case-Control Study",
"author": "Prakash",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1096",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Headache",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0355",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0360",
"unstructured": "S. Kalra, B. Kalra, S. Khandelwal, Vitamin D deficiency in Healthy Postmenopausal Women in Haryana, 2011."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2014/493213",
"article-title": "Correlation of Vitamin D Levels with Pigmentation in Vitiligo Patients Treated with NBUVB Therapy",
"author": "Sehrawat",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "ISRN Dermatol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0365",
"volume": "2014",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12291-016-0552-2",
"article-title": "Current Scenario of Prevalence of Vitamin D Deficiency in Ostensibly Healthy Indian Population: A Hospital Based Retrospective Study",
"author": "Shukla",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "452",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Clin. Biochem.: IJCB",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0370",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.47203/IJCH.2018.v30i04.017",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Status in Cold Trans-Himalayan Deserts at Altitude of 4000 meter and above in India",
"author": "Sharma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "400",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Community Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0375",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/2230-8210.139242",
"article-title": "Pattern of 25 hydroxy vitamin D status in North Indian people with newly detected type 2 diabetes: A prospective case control study",
"author": "Laway",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "726",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0380",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/ijt.ijt_3_19",
"article-title": "Serum Vitamin D Levels and Alopecia Areata- A Hospital Based Case-Control Study from North-India",
"author": "Rehman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "49",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Int J Trichology",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0385",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/pgmj.2007.059113",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status in apparently healthy adults in Kashmir Valley of Indian subcontinent",
"author": "Zargar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "713",
"issue": "985",
"journal-title": "Postgrad. Med. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0390",
"volume": "83",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/0976-7800.141188",
"article-title": "Prevalence of vitamin d deficiency among Indian menopausal women and its correlation with diabetes: A first Indian cross sectional data",
"author": "Tandon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "121",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J. Mid-Life Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0395",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.22159/ajpcr.2018.v11i10.28097",
"article-title": "Combinatorial effect of leptin, tumor necrosis factor-Αlpha, and vitamin d in progression of type 2 diabetes in kashmiri population",
"author": "Din",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "477",
"journal-title": "Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0400",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13224-018-1195-4",
"article-title": "Vitamin D(3) Level in Women with Uterine Fibroid: An Observational Study in Eastern Indian Population",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "161",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J. Obstetrics Gynaecol. India",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0405",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/jhh.2015.10",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status, hypertension and ischemic stroke: a clinical perspective",
"author": "Majumdar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "669",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "J. Hum. Hypertens.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0410",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/ijt.ijt_57_16",
"article-title": "Serum Vitamin D(3) Levels and Diffuse Hair Fall among the Student Population in South India: A Case-Control Study",
"author": "Nayak",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "160",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Trichol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0415",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/0972-124X.167162",
"article-title": "Low levels of serum Vitamin D in chronic periodontitis patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A hospital-based cross-sectional clinical study",
"author": "Joseph",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "501",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J. Indian Soc. Periodontol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0420",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"article-title": "Tuberculosis and vitamin D deficiency",
"author": "Sasidharan",
"first-page": "554",
"journal-title": "J. Assoc. Physicians India",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0425",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0430",
"unstructured": "V. G, S. PK, Vitamin D Status In Hypertension, Am. Int. J. Res. Formal, Appl. Nat. Sci. 8(1) (2014) 28-30."
},
{
"DOI": "10.18410/jebmh/2019/181",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0435",
"unstructured": "Angel Abraham, Sajitha Krishnan, Kuzhikandathil Narayanan Subhakumari, G.G. Chakkalakkudy, Vitamin D Levels In Depressive Disorder, 3(6) (2019) 862-865."
},
{
"DOI": "10.18535/jmscr/v7i4.01",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0440",
"unstructured": "S. Samuel, Association of Vitamin D deficiency and Hypothyroidism in a tertiary teaching hospital in Kerala, J. Med. Sci. Clin. Res. 7 (2019)."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0445",
"unstructured": "Jain V, Shaikh MKS, J. S, M. M, Comparative study of serum vitamin d levels and other biomarkers in patients attending tertiary cardiac care center, Int. J. Bioassays 4(4) (2015) 3812-3814."
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/ijem.IJEM_473_17",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0450",
"unstructured": "V. Patwardhan, Z. Mughal, S. Chiplonkar, A. Webb, R. Kift, V. Khadilkar, R. Padidela, A. Khadilkar, Duration of casual sunlight exposure necessary for adequate Vitamin D status in Indian Men 22(2) (2018) 249-255."
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/2230-8210.163175",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status and gestational diabetes mellitus",
"author": "Muthukrishnan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "616",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0455",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/2230-8210.131165",
"article-title": "Relationship of lipid parameters with bone mineral density in Indian population",
"author": "Garg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "325",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0460",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/09513590.2010.487604",
"article-title": "Low bone mass in urban Indian women above 40 years of age: prevalence and risk factors, Gynecological endocrinology: the official journal of the International Society of",
"author": "Kadam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "909",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Gynecol. Endocrinol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0465",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/0022-3859.65272",
"article-title": "Study of bone mineral density in resident doctors working at a teaching hospital",
"author": "Multani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "65",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J. Postgrad. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0470",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jocd.2011.12.007",
"article-title": "Peak bone mineral density and its determinants in an Asian Indian population",
"author": "Shivane",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "152",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Densitometry: Off. J. Int. Soc. Clin. Densitometry",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0475",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5455/njppp.2017.7.0309424042017",
"article-title": "Study of vitamin D levels and its correlation with insulin resistance",
"author": "Sahasrabuddhe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat. J. Physiol., Pharm. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0480",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/0972-2327.160052",
"article-title": "Vitamin D as a marker of cognitive decline in elderly Indian population",
"author": "Vedak",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "314",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0485",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0490",
"unstructured": "S.K. Shylla, G. Devi, C. Wann, B. Khongwir, G. Longmei, Vitamin D Deficiency : Highly Prevalent Among Apparently Healthy Female Adolescents In Both Urban And Rural Population Of Manipur, India, 2018."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/hmbci-2018-0064",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status and its relationship with systemic lupus erythematosus as a determinant and outcome of disease activity",
"author": "Dutta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Hormone Mol. Biol. Clin. Invest.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0495",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/ijem.IJEM_183_18",
"article-title": "Evaluation of Vitamin D Status and its Impact on Thyroid Related Parameters in New Onset Graves' Disease- A Cross-sectional Observational Study",
"author": "Mangaraj",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "35",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0500",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0505",
"unstructured": "R. Padhi, B. Panda, S. Jagati, S. Patra, Vitamin D status in adult critically ill patients in Eastern India: An observational retrospective study, 31(3) (2014) 212-216."
},
{
"article-title": "Evaluation of Vitamin D Status in Urban Population Employed In Office Jobs",
"author": "Mukherjee",
"first-page": "18",
"journal-title": "IOSR J. Dental Med. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0510",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3126/ajms.v7i6.15699",
"article-title": "Evaluation of Serum 25 Hydroxy Vitamin D level in acute myocardial infarction patients in a tertiary care hospital",
"author": "Rath",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "Asian J. Med. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0515",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in type-2 diabetes mellitus patients and its correlation with glycemic control",
"author": "Mukherjee",
"first-page": "3313",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Bioassays",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0520",
"volume": "03",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0525",
"unstructured": "Akshay Kumar, Nanda SK, Bharathy N, Ravichandran K, Dinakaran A, R. L, Evaluation of vitamin D status and its correlation with glycated haemoglobin in type 2 diabetes mellitus, Biomed. Res. 28(1) (2017)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/09674845.2015.11666797",
"article-title": "25-hydroxy vitamin D and ischaemia-modified albumin levels in psoriasis and their association with disease severity",
"author": "Chandrashekar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "56",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Biomed. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0530",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20945/2359-3997000000062",
"article-title": "Low serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels are associated with aggressive breast cancer variants and poor prognostic factors in patients with breast carcinoma",
"author": "Karthikayan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "452",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Arch. Endocrinol. Metabolism",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0535",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D status in apparently healthy adolescents and its association with body mass index in Puducherry population",
"author": "Gandhe",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Child Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0540",
"volume": "110",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10238-018-0511-8",
"article-title": "An investigation of vitamin D status in alopecia areata",
"author": "Gade",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "577",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Clin. Exp. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0545",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0550",
"unstructured": "B. Chopra, S. Singh, K. Singh, Is there A Need to Reasses Reference Levels of Vitamin D for India ?-A Preliminary Survey of Vitamin D Levels in the Normal Population of Punjab, 2015."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0555",
"unstructured": "Gupta A, Soin D, Garg R, G. G., Prevalence of vitamin d levels in patients of diabetes mallitus in rural and urban population of Malwa region of Punjab., J. Adv. Med. Dent. Sci. Res. 5(2) (2017) 111-115."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0560",
"unstructured": "J. S, S.J. C, S. M, Association of Deficiency of Maternal Vitamin D Levels with Severity of Preeclampsia, Epidem. Int. 4(3) (2019) 2455-7048."
},
{
"DOI": "10.36106/ijsr/9402249",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0565",
"unstructured": "D.M. N, P. U, Role of vitamin d and risk of prostate cancer, Int. J. Sci. Res. 8(8) (2019) 76-77."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0570",
"unstructured": "P.A. Kiran B., Thilagavathi R., J.R. R., Serum 25- Hydroxy Vitamin D, Calcium,Phosphorus and Alkaline Phosphatase Levels In Healthy Adults Above the age of 20 Living in Potheri Village of Kancheepuram District, Tamilnadu, J. App. Pharm. Sci. 4 (12) (2014) 030-034."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2014/723238",
"article-title": "Osteoporosis in healthy South Indian males and the influence of life style factors and vitamin d status on bone mineral density",
"author": "Shetty",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J. Osteoporosis",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0575",
"volume": "2014",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4158/EP.14.6.665",
"article-title": "Prevalence of osteoporosis in ambulatory postmenopausal women from a semiurban region in Southern India: relationship to calcium nutrition and vitamin D status",
"author": "Paul",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "665",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Endocrine Practice: Off. J. Am. College Endocrinol. Am. Assoc. Clin. Endocrinol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0580",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12291-012-0239-2",
"article-title": "Vitamin d deficiency and insulin resistance in normal and type 2 diabetes subjects",
"author": "Bachali",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "74",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Clin. Biochem.: IJCB",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0585",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0590",
"unstructured": "A.J. Joseph, Biju George, A.B. Pulimood, M.S. Seshadri, A. Chacko, 25 (OH) vitamin D level in Crohn's disease: association with sun exposure & disease activity, Indian J. Med. Res. (2009) 133-137."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0595",
"unstructured": "N.K. S, N.K. M, Pruthvi, V. B, Correlation of Vitamin-D Levels With Blood Sugar Levels in Diabetes Mellitus, Galore Int. J. Health Sci. Res. 3(3) (2018) 8-13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11657-009-0024-x",
"article-title": "Bone mass of overweight affluent Indian youth and its sex-specific association with body composition",
"author": "Amarendra Reddy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "31",
"issue": "1–2",
"journal-title": "Arch. Osteoporosis",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0600",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cca.2010.11.035",
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms with BMD and their effect on 1, 25-dihydroxy vitamin D3 levels in pre- and postmenopausal South Indian women from Andhra Pradesh",
"author": "Yasovanthi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "541",
"issue": "7–8",
"journal-title": "Clin. Chim. Acta; Int. J. Clin. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0605",
"volume": "412",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18410/jebmh/2018/374",
"article-title": "Study of Vitamin D levels in patients of acute myocardial infarction",
"author": "Debbarma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1788",
"journal-title": "J. Evidence Based Med. Healthcare",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0610",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Development of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) in Young Obese Tribal Subjects of Tripura: Link between Low 25 (OH) Vitamin-D Levels and Immune Modulators",
"author": "Chakraborty",
"first-page": "52",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "J. Assoc. Phys. India",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0615",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3126/ajms.v5i4.9809",
"article-title": "Systemic inflammation and alteration in vitamin D levels in pregnancy induced hypertension",
"author": "Sharma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Asian J. Med. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0620",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11657-012-0116-x",
"article-title": "Prevalence of osteoporosis in otherwise healthy Indian males aged 50 years and above",
"author": "Agrawal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "116",
"journal-title": "Arch. Osteoporosis",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0625",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11657-009-0026-8",
"article-title": "Effect of vitamin D supplementation on bone health parameters of healthy young Indian women",
"author": "Malhotra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "47",
"issue": "1–2",
"journal-title": "Arch. Osteoporosis",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0630",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00198-003-1491-3",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status and its relationship with bone mineral density in healthy Asian Indians",
"author": "Arya",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "56",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Osteoporosis Int.: J. Established Result Cooperation Europ. Found. Osteoporosis National Osteoporosis Found. USA",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0635",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5005/jp-journals-10054-0062",
"article-title": "A Study on Association of Degree of Physical Exercise and Plasma 25-(OH) Vitamin D Levels",
"author": "Soam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "90",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Med. Biochem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0640",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/0022-3859.128812",
"article-title": "Serum 25 hydroxyvitamin D profile after single large oral doses of cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) in medical staff in North India: a pilot study",
"author": "Priyambada",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "52",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Postgrad. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0645",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0650",
"unstructured": "B. M, Gupta BK, N. O, C. N, G. A, Comparison of Calcium, Phosphorous and 25 (OH)D2 Levels in Sedentary and Labourer Females, Ann. Clin. Lab. Res. 7(1) (2019) 289."
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/aca.ACA_66_18",
"article-title": "“Vitamin D” as a profile marker for cardiovascular diseases",
"author": "Oberoi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "47",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Ann. Cardiac Anaesthesia",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0655",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_130_18",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status among women aged 40 years and above in a rural area of West Bengal: A community-based study",
"author": "Pan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1263",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J. Family Med. Prim. Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0660",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0665",
"unstructured": "S. Garg, A. Dasgupta, S. Maharana, B. Paul, L. Bandyopadhyay, A. Bhattacharya, Sun exposure and Vitamin D in rural India: A cross-sectional study, 62(3) (2018) 175-181."
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/2230-8210.104113",
"article-title": "Profile of vitamin D in a cohort of physicians and diabetologists in Kolkata",
"author": "Baidya",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S416",
"issue": "Suppl 2",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0670",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"article-title": "Serum vitamin-D predicts insulin resistance in individuals with prediabetes",
"author": "Dutta",
"first-page": "853",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Med. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0675",
"volume": "138",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40200-014-0090-5",
"article-title": "Lean mass is the strongest predictor of bone mineral content in type-2 diabetes and normal individuals: an eastern India perspective",
"author": "Maisnam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "90",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Diabetes Metabolic Disorders",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0680",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12291-014-0435-3",
"article-title": "Assessment of Vitamin D status In Patients of Chronic Low Back Pain of Unknown Etiology",
"author": "Lodh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "174",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Clin. Biochem.: IJCB",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0685",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12291-014-0428-2",
"article-title": "Prevalence of vitamin d deficiency in a pediatric hospital of eastern India",
"author": "Basu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "167",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Clin. Biochem.: IJCB",
"key": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001_b0690",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2015"
}
],
"reference-count": 138,
"references-count": 138,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1567576920330186"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Lower levels of vitamin D are associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection and mortality in the Indian population: An observational study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "88"
}
