Crosstalk between neutrophil extracellular traps and immune regulation: insights into pathobiology and therapeutic implications of transfusion-related acute lung injury
et al., Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1324021, Dec 2023
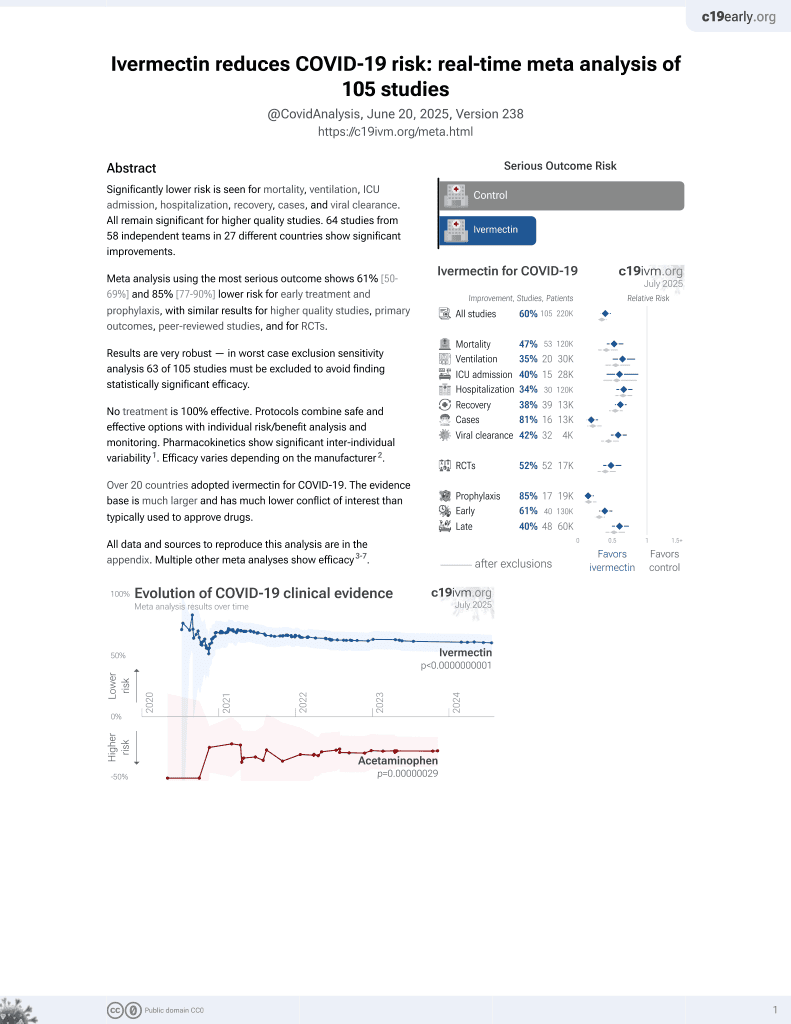
Ivermectin for COVID-19
4th treatment shown to reduce risk in
August 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 106 studies, recognized in 24 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
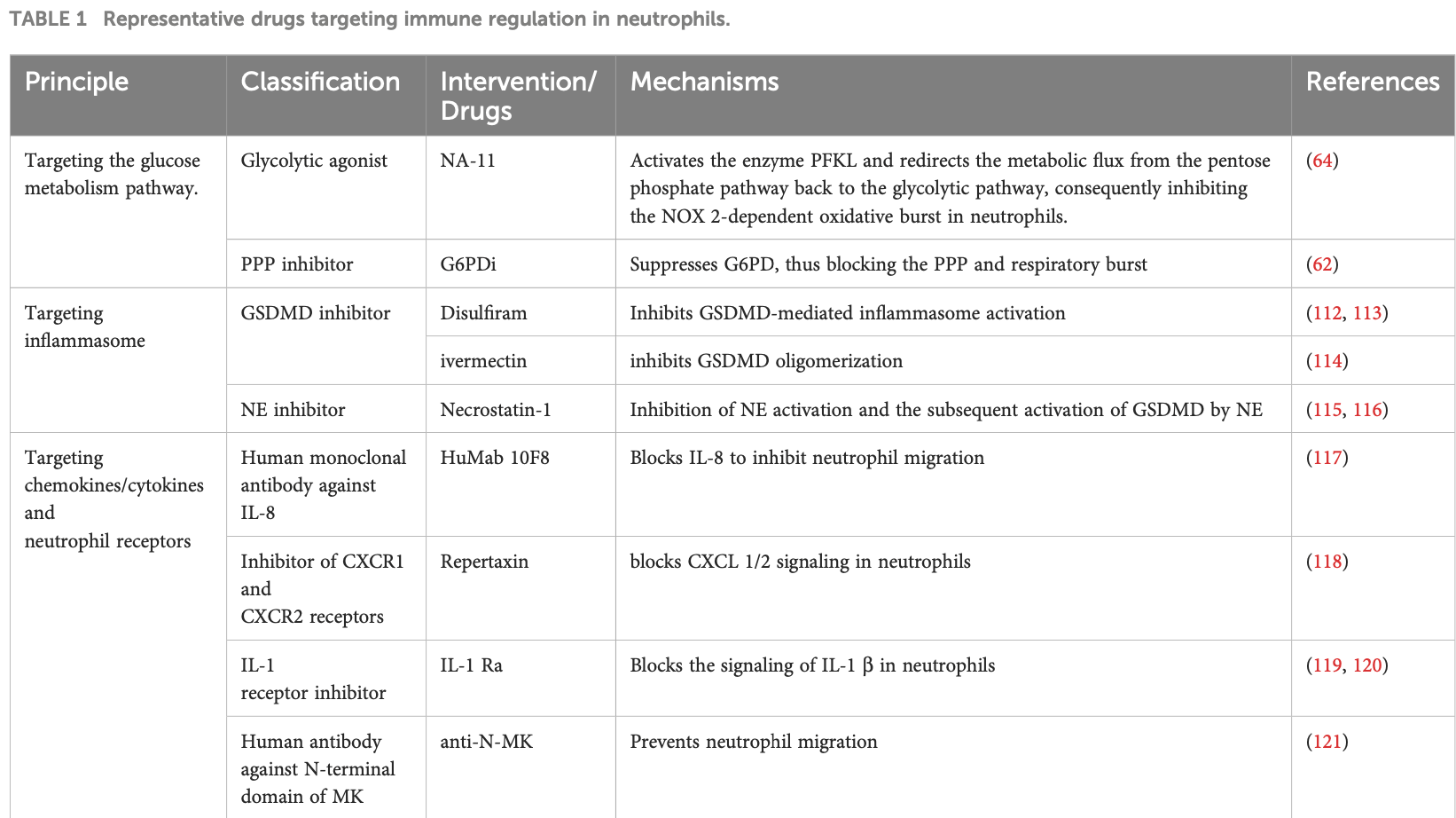
Ivermectin may be beneficial for COVID-19 ARDS by blocking GSDMD and NET formation.
Authors review the role of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) in transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI). Authors discusses the mechanisms of NET formation, including vital NETosis and NETosis involving cell death. They examine the evidence showing that NETs contribute to endothelial and lung epithelial damage in TRALI. Authors explore the interactions of NETs with other immune cells like macrophages, dendritic cells, and T cells, which create inflammatory feedback loops that exacerbate tissue injury. Authors suggest potential therapeutic approaches targeting NET formation, NET clearance, cytokine signaling, and glucose metabolism pathways to dampen detrimental inflammation in TRALI.
Authors note that ivermectin was shown to inhibit GSDMD oligomerization, alleviating the release of NETs, and that increased NET formation was observed in ARDS induced by COVID-19.
This suggests that ivermectin may be beneficial for COVID-19 ARDS by inhibiting NET formation. Specifically: ivermectin can inhibit GSDMD oligomerization, which the authors note plays an important role in NET release. By blocking GSDMD, ivermectin may suppress detrimental NETosis. Authors state that in COVID-19 ARDS, there is downregulation of respiratory bursts but increased NET formation. So while ROS production from neutrophils may be impaired, excessive NETs are still an issue driving lung damage. By alleviating NET release through GSDMD inhibition, ivermectin could therefore target one of the key pathological pathways - NETosis - that is overactivated in COVID-19 ARDS.
74 preclinical studies support the efficacy of ivermectin for COVID-19:
Ivermectin, better known for antiparasitic activity, is a broad spectrum antiviral with activity against many viruses including H7N771, Dengue37,72,73 , HIV-173, Simian virus 4074, Zika37,75,76 , West Nile76, Yellow Fever77,78, Japanese encephalitis77, Chikungunya78, Semliki Forest virus78, Human papillomavirus57, Epstein-Barr57, BK Polyomavirus79, and Sindbis virus78.
Ivermectin inhibits importin-α/β-dependent nuclear import of viral proteins71,73,74,80 , shows spike-ACE2 disruption at 1nM with microfluidic diffusional sizing38, binds to glycan sites on the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein preventing interaction with blood and epithelial cells and inhibiting hemagglutination41,81, shows dose-dependent inhibition of wildtype and omicron variants36, exhibits dose-dependent inhibition of lung injury61,66, may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 via IMPase inhibition37, may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 induced formation of fibrin clots resistant to degradation9, inhibits SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro54, may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 RdRp activity28, may minimize viral myocarditis by inhibiting NF-κB/p65-mediated inflammation in macrophages60, may be beneficial for COVID-19 ARDS by blocking GSDMD and NET formation82, may interfere with SARS-CoV-2's immune evasion via ORF8 binding4, may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 by disrupting CD147 interaction83-86, may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 attachment to lipid rafts via spike NTD binding2, shows protection against inflammation, cytokine storm, and mortality in an LPS mouse model sharing key pathological features of severe COVID-1959,87, may be beneficial in severe COVID-19 by binding IGF1 to inhibit the promotion of inflammation, fibrosis, and cell proliferation that leads to lung damage8, may minimize SARS-CoV-2 induced cardiac damage40,48, may counter immune evasion by inhibiting NSP15-TBK1/KPNA1 interaction and restoring IRF3 activation88, may disrupt SARS-CoV-2 N and ORF6 protein nuclear transport and their suppression of host interferon responses1, reduces TAZ/YAP nuclear import, relieving SARS-CoV-2-driven suppression of IRF3 and NF-κB antiviral pathways35, increases Bifidobacteria which play a key role in the immune system89, has immunomodulatory51 and anti-inflammatory70,90 properties, and has an extensive and very positive safety profile91.
1.
Gayozo et al., Binding affinities analysis of ivermectin, nucleocapsid and ORF6 proteins of SARS-CoV-2 to human importins α isoforms: A computational approach, Biotecnia, doi:10.18633/biotecnia.v27.2485.
2.
Lefebvre et al., Characterization and Fluctuations of an Ivermectin Binding Site at the Lipid Raft Interface of the N-Terminal Domain (NTD) of the Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Variants, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v16121836.
3.
Haque et al., Exploring potential therapeutic candidates against COVID-19: a molecular docking study, Discover Molecules, doi:10.1007/s44345-024-00005-5.
4.
Bagheri-Far et al., Non-spike protein inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 by natural products through the key mediator protein ORF8, Molecular Biology Research Communications, doi:10.22099/mbrc.2024.50245.2001.
5.
de Oliveira Só et al., In Silico Comparative Analysis of Ivermectin and Nirmatrelvir Inhibitors Interacting with the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease, Preprints, doi:10.20944/preprints202404.1825.v1.
6.
Agamah et al., Network-based multi-omics-disease-drug associations reveal drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19 disease phases, ScienceOpen, doi:10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1.
7.
Oranu et al., Validation of the binding affinities and stabilities of ivermectin and moxidectin against SARS-CoV-2 receptors using molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation, GSC Biological and Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.30574/gscbps.2024.26.1.0030.
8.
Zhao et al., Identification of the shared gene signatures between pulmonary fibrosis and pulmonary hypertension using bioinformatics analysis, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1197752.
9.
Vottero et al., Computational Prediction of the Interaction of Ivermectin with Fibrinogen, Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms241411449.
10.
Chellasamy et al., Docking and molecular dynamics studies of human ezrin protein with a modelled SARS-CoV-2 endodomain and their interaction with potential invasion inhibitors, Journal of King Saud University - Science, doi:10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277.
11.
Umar et al., Inhibitory potentials of ivermectin, nafamostat, and camostat on spike protein and some nonstructural proteins of SARS-CoV-2: Virtual screening approach, Jurnal Teknologi Laboratorium, doi:10.29238/teknolabjournal.v11i1.344.
12.
Alvarado et al., Interaction of the New Inhibitor Paxlovid (PF-07321332) and Ivermectin With the Monomer of the Main Protease SARS-CoV-2: A Volumetric Study Based on Molecular Dynamics, Elastic Networks, Classical Thermodynamics and SPT, Computational Biology and Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2022.107692.
13.
Aminpour et al., In Silico Analysis of the Multi-Targeted Mode of Action of Ivermectin and Related Compounds, Computation, doi:10.3390/computation10040051.
14.
Parvez et al., Insights from a computational analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Host–pathogen interaction, pathogenicity, and possible drug therapeutics, Immunity, Inflammation and Disease, doi:10.1002/iid3.639.
15.
Francés-Monerris et al., Microscopic interactions between ivermectin and key human and viral proteins involved in SARS-CoV-2 infection, Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, doi:10.1039/D1CP02967C.
16.
González-Paz et al., Comparative study of the interaction of ivermectin with proteins of interest associated with SARS-CoV-2: A computational and biophysical approach, Biophysical Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677.
17.
González-Paz (B) et al., Structural Deformability Induced in Proteins of Potential Interest Associated with COVID-19 by binding of Homologues present in Ivermectin: Comparative Study Based in Elastic Networks Models, Journal of Molecular Liquids, doi:10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284.
18.
Rana et al., A Computational Study of Ivermectin and Doxycycline Combination Drug Against SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-755838/v1.
19.
Muthusamy et al., Virtual Screening Reveals Potential Anti-Parasitic Drugs Inhibiting the Receptor Binding Domain of SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein, Journal of Virology & Antiviral Research, www.scitechnol.com/abstract/virtual-screening-reveals-potential-antiparasitic-drugs-inhibiting-the-receptor-binding-domain-of-sarscov2-spike-protein-16398.html.
20.
Qureshi et al., Mechanistic insights into the inhibitory activity of FDA approved ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2: old drug with new implications, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2021.1906750.
21.
Schöning et al., Highly-transmissible Variants of SARS-CoV-2 May Be More Susceptible to Drug Therapy Than Wild Type Strains, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-379291/v1.
22.
Bello et al., Elucidation of the inhibitory activity of ivermectin with host nuclear importin α and several SARS-CoV-2 targets, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2021.1911857.
23.
Udofia et al., In silico studies of selected multi-drug targeting against 3CLpro and nsp12 RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase proteins of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV, Network Modeling Analysis in Health Informatics and Bioinformatics, doi:10.1007/s13721-021-00299-2.
24.
Choudhury et al., Exploring the binding efficacy of ivermectin against the key proteins of SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis: an in silico approach, Future Medicine, doi:10.2217/fvl-2020-0342.
25.
Kern et al., Modeling of SARS-CoV-2 Treatment Effects for Informed Drug Repurposing, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.625678.
26.
Saha et al., The Binding mechanism of ivermectin and levosalbutamol with spike protein of SARS-CoV-2, Structural Chemistry, doi:10.1007/s11224-021-01776-0.
27.
Eweas et al., Molecular Docking Reveals Ivermectin and Remdesivir as Potential Repurposed Drugs Against SARS-CoV-2, Frontiers in Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.592908.
28.
Parvez (B) et al., Prediction of potential inhibitors for RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2 using comprehensive drug repurposing and molecular docking approach, International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.09.098.
29.
Francés-Monerris (B) et al., Has Ivermectin Virus-Directed Effects against SARS-CoV-2? Rationalizing the Action of a Potential Multitarget Antiviral Agent, ChemRxiv, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12782258.v1.
30.
Kalhor et al., Repurposing of the approved small molecule drugs in order to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 S protein and human ACE2 interaction through virtual screening approaches, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1824816.
31.
Swargiary, A., Ivermectin as a promising RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitor and a therapeutic drug against SARS-CoV2: Evidence from in silico studies, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-73308/v1.
32.
Maurya, D., A Combination of Ivermectin and Doxycycline Possibly Blocks the Viral Entry and Modulate the Innate Immune Response in COVID-19 Patients, American Chemical Society (ACS), doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12630539.v1.
33.
Lehrer et al., Ivermectin Docks to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-binding Domain Attached to ACE2, In Vivo, 34:5, 3023-3026, doi:10.21873/invivo.12134.
34.
Suravajhala et al., Comparative Docking Studies on Curcumin with COVID-19 Proteins, Preprints, doi:10.20944/preprints202005.0439.v3.
35.
Kofler et al., M-Motif, a potential non-conventional NLS in YAP/TAZ and other cellular and viral proteins that inhibits classic protein import, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2025.112105.
36.
Shahin et al., The selective effect of Ivermectin on different human coronaviruses; in-vitro study, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-4180797/v1.
37.
Jitobaom et al., Identification of inositol monophosphatase as a broad‐spectrum antiviral target of ivermectin, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29552.
38.
Fauquet et al., Microfluidic Diffusion Sizing Applied to the Study of Natural Products and Extracts That Modulate the SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD/ACE2 Interaction, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules28248072.
39.
García-Aguilar et al., In Vitro Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and Ivermectin Interaction, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms242216392.
40.
Liu et al., SARS-CoV-2 viral genes Nsp6, Nsp8, and M compromise cellular ATP levels to impair survival and function of human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes, Stem Cell Research & Therapy, doi:10.1186/s13287-023-03485-3.
41.
Boschi et al., SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Induces Hemagglutination: Implications for COVID-19 Morbidities and Therapeutics and for Vaccine Adverse Effects, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.11.24.517882.
42.
De Forni et al., Synergistic drug combinations designed to fully suppress SARS-CoV-2 in the lung of COVID-19 patients, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0276751.
43.
Saha (B) et al., Manipulation of Spray-Drying Conditions to Develop an Inhalable Ivermectin Dry Powder, Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics14071432.
44.
Jitobaom (B) et al., Synergistic anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity of repurposed anti-parasitic drug combinations, BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology, doi:10.1186/s40360-022-00580-8.
45.
Croci et al., Liposomal Systems as Nanocarriers for the Antiviral Agent Ivermectin, International Journal of Biomaterials, doi:10.1155/2016/8043983.
46.
Zheng et al., Red blood cell-hitchhiking mediated pulmonary delivery of ivermectin: Effects of nanoparticle properties, International Journal of Pharmaceutics, doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121719.
47.
Delandre et al., Antiviral Activity of Repurposing Ivermectin against a Panel of 30 Clinical SARS-CoV-2 Strains Belonging to 14 Variants, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph15040445.
48.
Liu (B) et al., Genome-wide analyses reveal the detrimental impacts of SARS-CoV-2 viral gene Orf9c on human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes, Stem Cell Reports, doi:10.1016/j.stemcr.2022.01.014.
49.
Segatori et al., Effect of Ivermectin and Atorvastatin on Nuclear Localization of Importin Alpha and Drug Target Expression Profiling in Host Cells from Nasopharyngeal Swabs of SARS-CoV-2- Positive Patients, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13102084.
50.
Jitobaom (C) et al., Favipiravir and Ivermectin Showed in Vitro Synergistic Antiviral Activity against SARS-CoV-2, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-941811/v1.
51.
Munson et al., Niclosamide and ivermectin modulate caspase-1 activity and proinflammatory cytokine secretion in a monocytic cell line, British Society For Nanomedicine Early Career Researcher Summer Meeting, 2021, web.archive.org/web/20230401070026/https://michealmunson.github.io/COVID.pdf.
52.
Mountain Valley MD, Mountain Valley MD Receives Successful Results From BSL-4 COVID-19 Clearance Trial on Three Variants Tested With Ivectosol™, 5/18, www.globenewswire.com/en/news-release/2021/05/18/2231755/0/en/Mountain-Valley-MD-Receives-Successful-Results-From-BSL-4-COVID-19-Clearance-Trial-on-Three-Variants-Tested-With-Ivectosol.html.
53.
Yesilbag et al., Ivermectin also inhibits the replication of bovine respiratory viruses (BRSV, BPIV-3, BoHV-1, BCoV and BVDV) in vitro, Virus Research, doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2021.198384.
54.
Mody et al., Identification of 3-chymotrypsin like protease (3CLPro) inhibitors as potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents, Communications Biology, doi:10.1038/s42003-020-01577-x.
55.
Jeffreys et al., Remdesivir-ivermectin combination displays synergistic interaction with improved in vitro activity against SARS-CoV-2, International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2022.106542.
56.
Surnar et al., Clinically Approved Antiviral Drug in an Orally Administrable Nanoparticle for COVID-19, ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci., doi:10.1021/acsptsci.0c00179.
57.
Li et al., Quantitative proteomics reveals a broad-spectrum antiviral property of ivermectin, benefiting for COVID-19 treatment, J. Cellular Physiology, doi:10.1002/jcp.30055.
58.
Caly et al., The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antiviral Research, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787.
59.
Zhang et al., Ivermectin inhibits LPS-induced production of inflammatory cytokines and improves LPS-induced survival in mice, Inflammation Research, doi:10.1007/s00011-008-8007-8.
60.
Gao et al., Ivermectin ameliorates acute myocarditis via the inhibition of importin-mediated nuclear translocation of NF-κB/p65, International Immunopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112073.
61.
Abd-Elmawla et al., Suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome by ivermectin ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis, Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE B, doi:10.1631/jzus.B2200385.
62.
Uematsu et al., Prophylactic administration of ivermectin attenuates SARS-CoV-2 induced disease in a Syrian Hamster Model, The Journal of Antibiotics, doi:10.1038/s41429-023-00623-0.
63.
Albariqi et al., Pharmacokinetics and Safety of Inhaled Ivermectin in Mice as a Potential COVID-19 Treatment, International Journal of Pharmaceutics, doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121688.
64.
Errecalde et al., Safety and Pharmacokinetic Assessments of a Novel Ivermectin Nasal Spray Formulation in a Pig Model, Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.xphs.2021.01.017.
65.
Madrid et al., Safety of oral administration of high doses of ivermectin by means of biocompatible polyelectrolytes formulation, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05820.
66.
Ma et al., Ivermectin contributes to attenuating the severity of acute lung injury in mice, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113706.
67.
de Melo et al., Attenuation of clinical and immunological outcomes during SARS-CoV-2 infection by ivermectin, EMBO Mol. Med., doi:10.15252/emmm.202114122.
68.
Arévalo et al., Ivermectin reduces in vivo coronavirus infection in a mouse experimental model, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-86679-0.
69.
Chaccour et al., Nebulized ivermectin for COVID-19 and other respiratory diseases, a proof of concept, dose-ranging study in rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-74084-y.
70.
Yan et al., Anti-inflammatory effects of ivermectin in mouse model of allergic asthma, Inflammation Research, doi:10.1007/s00011-011-0307-8.
71.
Götz et al., Influenza A viruses escape from MxA restriction at the expense of efficient nuclear vRNP import, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/srep23138.
72.
Tay et al., Nuclear localization of dengue virus (DENV) 1–4 non-structural protein 5; protection against all 4 DENV serotypes by the inhibitor Ivermectin, Antiviral Research, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.06.002.
73.
Wagstaff et al., Ivermectin is a specific inhibitor of importin α/β-mediated nuclear import able to inhibit replication of HIV-1 and dengue virus, Biochemical Journal, doi:10.1042/BJ20120150.
74.
Wagstaff (B) et al., An AlphaScreen®-Based Assay for High-Throughput Screening for Specific Inhibitors of Nuclear Import, SLAS Discovery, doi:10.1177/1087057110390360.
75.
Barrows et al., A Screen of FDA-Approved Drugs for Inhibitors of Zika Virus Infection, Cell Host & Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.chom.2016.07.004.
76.
Yang et al., The broad spectrum antiviral ivermectin targets the host nuclear transport importin α/β1 heterodimer, Antiviral Research, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104760.
77.
Mastrangelo et al., Ivermectin is a potent inhibitor of flavivirus replication specifically targeting NS3 helicase activity: new prospects for an old drug, Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, doi:10.1093/jac/dks147.
78.
Varghese et al., Discovery of berberine, abamectin and ivermectin as antivirals against chikungunya and other alphaviruses, Antiviral Research, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.12.012.
79.
Bennett et al., Role of a nuclear localization signal on the minor capsid Proteins VP2 and VP3 in BKPyV nuclear entry, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2014.10.013.
80.
Kosyna et al., The importin α/β-specific inhibitor Ivermectin affects HIF-dependent hypoxia response pathways, Biological Chemistry, doi:10.1515/hsz-2015-0171.
81.
Scheim et al., Sialylated Glycan Bindings from SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein to Blood and Endothelial Cells Govern the Severe Morbidities of COVID-19, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms242317039.
82.
Liu (C) et al., Crosstalk between neutrophil extracellular traps and immune regulation: insights into pathobiology and therapeutic implications of transfusion-related acute lung injury, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1324021.
83.
Shouman et al., SARS-CoV-2-associated lymphopenia: possible mechanisms and the role of CD147, Cell Communication and Signaling, doi:10.1186/s12964-024-01718-3.
84.
Scheim (B), D., Ivermectin for COVID-19 Treatment: Clinical Response at Quasi-Threshold Doses Via Hypothesized Alleviation of CD147-Mediated Vascular Occlusion, SSRN, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3636557.
85.
Scheim (C), D., From Cold to Killer: How SARS-CoV-2 Evolved without Hemagglutinin Esterase to Agglutinate and Then Clot Blood Cells, Center for Open Science, doi:10.31219/osf.io/sgdj2.
86.
Behl et al., CD147-spike protein interaction in COVID-19: Get the ball rolling with a novel receptor and therapeutic target, Science of The Total Environment, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072.
87.
DiNicolantonio et al., Ivermectin may be a clinically useful anti-inflammatory agent for late-stage COVID-19, Open Heart, doi:10.1136/openhrt-2020-001350.
88.
Mothae et al., SARS-CoV-2 host-pathogen interactome: insights into more players during pathogenesis, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2025.110607.
89.
Hazan et al., Treatment with Ivermectin Increases the Population of Bifidobacterium in the Gut, ACG 2023, acg2023posters.eventscribe.net/posterspeakers.asp.
90.
DiNicolantonio (B) et al., Anti-inflammatory activity of ivermectin in late-stage COVID-19 may reflect activation of systemic glycine receptors, Open Heart, doi:10.1136/openhrt-2021-001655.
91.
Descotes, J., Medical Safety of Ivermectin, ImmunoSafe Consultance, web.archive.org/web/20240313025927/https://www.medincell.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/Clinical_Safety_of_Ivermectin-March_2021.pdf.
92.
Reich, S., Methodological Analysis of Bias Risks in Adaptive Multi-Arm Platform Trials: A Case-Series from Three COVID-19 Studies, Center for Open Science, doi:10.31222/osf.io/h5kc8_v1.
93.
Zhang (B) et al., Rho-GTPases subfamily: cellular defectors orchestrating viral infection, Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, doi:10.1186/s11658-025-00722-w.
94.
Saha (C) et al., Inhaled Dry Powder of Antiviral Agents: A Promising Approach to Treating Respiratory Viral Pathogens, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v17020252.
95.
Ulloa-Aguilar et al., The Nucleolus and Its Interactions with Viral Proteins Required for Successful Infection, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells13181591.
96.
Enyeji et al., Effective Treatment of COVID-19 Infection with Repurposed Drugs: Case Reports, Viral Immunology, doi:10.1089/vim.2024.0034.
97.
Wimalawansa, S., Unlocking Insights: Navigating COVID-19 Challenges and Emulating Future Pandemic Resilience Strategies with Strengthening Natural Immunity, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34691.
98.
Mehraeen et al., Treatments for Olfactory Dysfunction in COVID-19: A Systematic Review, International Archives of Otorhinolaryngology, doi:10.1055/s-0044-1786046.
99.
Scheim (D) et al., Back to the Basics of SARS-CoV-2 Biochemistry: Microvascular Occlusive Glycan Bindings Govern Its Morbidities and Inform Therapeutic Responses, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v16040647.
100.
Yagisawa et al., Global trends in clinical trials of ivermectin for COVID-19—Part 2, The Japanese Journal of Antibiotics, doi:10.11553/antibiotics.77.1_45.
101.
Yemeke et al., Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the quality of medical products in Zimbabwe: a qualitative study based on key informant interviews with health system stakeholders, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2022-068923.
102.
Kory, P., The Global War on Ivermectin, International Covid Summit III, European Parliament, Brussels, covid19criticalcare.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/GLOBAL-WAR-ON-IVERMECTIN-PARLIAMENT.pdf.
103.
Babalola et al., The Place of Ivermectin in the Management of Covid-19: State of the Evidence, Medical Research Archives, doi:10.18103/mra.v11i4.3778.
104.
Loo et al., Recent Advances in Inhaled Nanoformulations of Vaccines and Therapeutics Targeting Respiratory Viral Infections, Pharmaceutical Research, doi:10.1007/s11095-023-03520-1.
105.
Kory (B), P., The Criminal Censorship of Ivermectin's Efficacy By The High-Impact Medical Journals - Part 1, Pierre Kory’s Medical Musings, pierrekory.substack.com/p/the-criminal-censorship-of-ivermectins.
106.
Al-kuraishy et al., Central effects of Ivermectin in alleviation of Covid-19-induced dysautonomia, Current Drug Targets, doi:10.2174/1389450123666220810102406.
107.
Schwartz, E., Does ivermectin have a place in the treatment of mild Covid-19?, New Microbes and New Infections, doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2022.100989.
108.
Marques et al., Ivermectin as a possible treatment for COVID-19: a review of the 2022 protocols, Brazilian Journal of Biology, doi:10.1590/1519-6984.258325.
109.
Semiz, S., SIT1 transporter as a potential novel target in treatment of COVID-19, Biomolecular Concepts, doi:10.1515/bmc-2021-0017.
110.
Zaidi et al., The mechanisms of action of ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2—an extensive review, The Journal of Antibiotics, doi:10.1038/s41429-021-00491-6.
111.
Low et al., Repositioning Ivermectin for Covid-19 treatment: Molecular mechanisms of action against SARS-CoV-2 replication, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease, doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166294.
112.
Fordham et al., The uses and abuses of systematic reviews, OSF Preprints, doi:10.31219/osf.io/mp4f2.
113.
Kow et al., Pitfalls in Reporting Sample Size Calculation Across Randomized Controlled Trials Involving Ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19, American Journal of Therapeutics, doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001441.
114.
Santin et al., Ivermectin: a multifaceted drug of Nobel prize-honored distinction with indicated efficacy against a new global scourge, COVID-19, New Microbes and New Infections, doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100924.
115.
Adegboro et al., A review of the anti-viral effects of ivermectin, African Journal of Clinical and Experimental Microbiology, doi:10.4314/ajcem.v22i3.2.
116.
Turkia, M., A Continuation of a Timeline of Ivermectin-Related Events in the COVID-19 Pandemic [June 30, 2021], ResearchGate, doi:10.13140/RG.2.2.16973.36326.
117.
Jagiasi et al., Variation in therapeutic strategies for the management of severe COVID-19 in India- A nationwide cross-sectional survey, The International Journal of Clinical Practice, doi:10.1111/ijcp.14574.
118.
Lind et al., Increase in Outpatient Ivermectin Dispensing in the US During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Analysis, Journal of General Internal Medicine, doi:10.1007/s11606-021-06948-6.
119.
Wang et al., Minimum manufacturing costs, national prices and estimated global availability of new repurposed therapies for COVID-19, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.06.01.21258147.
120.
Kory (C) et al., Review of the Emerging Evidence Demonstrating the Efficacy of Ivermectin in the Prophylaxis and Treatment of COVID-19, American Journal of Therapeutics, doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001377.
121.
Turkia (B), M., A timeline of ivermectin-related events in the COVID-19 pandemic, Research Gate, www.researchgate.net/publication/350610718_A_Timeline_of_Ivermectin-Related_Events_in_the_COVID-19_Pandemic_April_3_2021.
122.
Wehbe et al., Repurposing Ivermectin for COVID-19: Molecular Aspects and Therapeutic Possibilities, Front. Immunol., doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.663586.
123.
Yagisawa (B) et al., Global trends in clinical studies of ivermectin in COVID-19, The Japanese Journal of Antibiotics, 74-1, Mar 2021, jja-contents.wdc-jp.com/pdf/JJA74/74-1-open/74-1_44-95.pdf.
124.
Jans et al., The broad spectrum host-directed agent ivermectin as an antiviral for SARS-CoV-2 ?, Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.10.042.
125.
Kory (D) et al., Review of the Emerging Evidence Demonstrating the Efficacy of Ivermectin in the Prophylaxis and Treatment of COVID-19, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.643369.
126.
Formiga et al., Ivermectin: an award-winning drug with expected antiviral activity against COVID-19, J. Control Release, doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009.
127.
Turkia (C), M., FLCCC Alliance MATH+ ascorbic acid and I-MASK+ ivermectin protocols for COVID-19 — a brief review, ResearchGate, www.researchgate.net/profile/Mika_Turkia/publication/345694745_FLCCC_Alliance_MATH_ascorbic_acid_and_I-MASK_ivermectin_protocols_for_COVID-19_-_A_Brief_Review/links/5fab010f4585150781078260/FLCCC-Alliance-MATH-ascorbic-acid-and-I-MASK-ivermectin-protocols-for-COVID-19-A-Brief-Review.pdf.
128.
Jans (B) et al., Ivermectin as a Broad-Spectrum Host-Directed Antiviral: The Real Deal?, Cells 2020, 9:9, 2100, doi:10.3390/cells9092100.
129.
Elkholy et al., Ivermectin: A Closer Look at a Potential Remedy, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.10378.
130.
Vora et al., White paper on Ivermectin as a potential therapy for COVID-19, Indian Journal of Tuberculosis, doi:10.1016/j.ijtb.2020.07.031.
Liu et al., 7 Dec 2023, peer-reviewed, 9 authors.
Crosstalk between neutrophil extracellular traps and immune regulation: insights into pathobiology and therapeutic implications of transfusion-related acute lung injury
Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1324021
Transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI) is the leading cause of transfusionassociated death, occurring during or within 6 hours after transfusion. Reports indicate that TRALI can be categorized as having or lacking acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) risk factors. There are two types of TRALI in terms of its pathogenesis: antibody-mediated and non-antibody-mediated. The key initiation steps involve the priming and activation of neutrophils, with neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) being established as effector molecules formed by activated neutrophils in response to various stimuli. These NETs contribute to the production and release of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and participate in the destruction of pulmonary vascular endothelial cells. The significant role of NETs in TRALI is well recognized, offering a potential pathway for TRALI treatment. Moreover, platelets, macrophages, endothelial cells, and complements have been identified as promoters of NET formation. Concurrently, studies have demonstrated that the storage of platelets and concentrated red blood cells (RBC) can induce TRALI through bioactive lipids. In this article, recent clinical and pre-clinical studies on the pathophysiology and pathogenesis of TRALI are reviewed to further illuminate the mechanism through which NETs induce TRALI. This review aims to propose new therapeutic strategies for TRALI, with the hope of effectively improving its poor prognosis.
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Appendix The proteins/genes described in this review.
References
Adrover, Carrau, Daßler-Plenker, Bram, Chandar et al., Disulfiram inhibits neutrophil extracellular trap formation and protects rodents from acute lung injury and SARS-CoV-2 infection, JCI Insight, doi:10.1172/jci.insight.157342
Alfaro, Teijeira, Onate, Perez, Sanmamed et al., Tumor-produced interleukin-8 attracts human myeloid-derived suppressor cells and elicits extrusion of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), Clin Cancer Res, doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2463
Amara, Cooper, Voronkova, Webb, Lynch et al., Selective activation of PFKL suppresses the phagocytic oxidative burst, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.07.004
Apel, Andreeva, Knackstedt, Streeck, Frese et al., The cytosolic DNA sensor cGAS recognizes neutrophil extracellular traps, Sci Signal, doi:10.1126/scisignal.aax7942
Awasthi, Nagarkoti, Sadaf, Chandra, Kumar et al., Glycolysis dependent lactate formation in neutrophils: A metabolic link between NOX-dependent and independent NETosis, Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.165542
Aymonnier, Ng, Fredenburgh, Zambrano-Vera, Munzer et al., Inflammasome activation in neutrophils of patients with severe COVID-19, Blood Adv, doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2021005949
Azevedo, Rochael, Guimaraes-Costa, De Souza-Vieira, Ganilho et al., A metabolic shift toward pentose phosphate pathway is necessary for amyloid fibriland phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-induced neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M115.640094
Baudel, Vigneron, Pras-Landre, Joffre, Marjot et al., Transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI) after intravenous immunoglobulins: French multicentre study and literature review, Clin Rheumatol, doi:10.1007/s10067-019-04832-7
Bertini, Allegretti, Bizzarri, Moriconi, Locati et al., Noncompetitive allosteric inhibitors of the inflammatory chemokine receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2: prevention of reperfusion injury, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1084/jem.20181102
Borella, Biasi, Paolini, Boraldi, Tartaro et al., Metabolic reprograming shapes neutrophil functions in severe COVID-19, Eur J Immunol, doi:10.1002/eji.202149481
Brinkmann, Reichard, Goosmann, Fauler, Uhlemann et al., Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria, Science, doi:10.1126/science.1092385
Britt, Lika, Giese, Schoen, Seim et al., Switching to the cyclic pentose phosphate pathway powers the oxidative burst in activated neutrophils, Nat Metab, doi:10.1038/s42255-022-00550-8
Cao, Zhang, Wang, Yang, Ma et al., Inhibition of the glycolytic activator PFKFB3 in endothelium induces tumor vessel normalization, impairs metastasis, and improves chemotherapy, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2016.10.006
Caudrillier, Kessenbrock, Gilliss, Nguyen, Marques et al., Platelets induce neutrophil extracellular traps in transfusion-related acute lung injury, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI61303
Chapman, Lyon, Simpson, Mason, Beynon et al., Caught in a trap? Proteomic analysis of neutrophil extracellular traps in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.00423
Chauhan, Demon, Walle, Paerewijck, Zecchin et al., GSDMD drives canonical inflammasome-induced neutrophil pyroptosis and is dispensable for NETosis, EMBO Rep, doi:10.15252/embr.202154277
Chen, Gross, Sotomayor, Stacey, Tschopp et al., The neutrophil NLRC4 inflammasome selectively promotes IL-1beta maturation without pyroptosis during acute Salmonella challenge, Cell Rep, doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2014.06.028
Chen, Monteleone, Boucher, Sollberger, Ramnath et al., Noncanonical inflammasome signaling elicits gasdermin D-dependent neutrophil extracellular traps, Sci Immunol, doi:10.1126/sciimmunol.aar6676
Chen, Zhao, Lai, Zhang, Yang et al., Neutrophil extracellular traps promote macrophage pyroptosis in sepsis, Cell Death Dis, doi:10.1038/s41419-017-0090-8
Cieloch, Kuzmicka, Mroczek, Stelmaszczyk-Emmel, Demkow, Secretomes of M1 and M2 macrophages decrease the release of neutrophil extracellular traps, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-42167-1
Cleary, Kwaan, Tian, Calabrese, Mallavia et al., C5aR1 signaling triggers lung immunopathology in COVID-19 through neutrophil extracellular traps, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI163105
Cui, Yang, Tao, Peng, Luo et al., Neutrophil extracellular traps induce alveolar macrophage pyroptosis by regulating NLRP3 deubiquitination, aggravating the development of septic lung injury, J Inflamm Res, doi:10.2147/JIR.S366436
Domer, Walther, Moller, Behnen, Laskay, Neutrophil extracellular traps activate proinflammatory functions of human neutrophils, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.636954
Doring, Libby, Soehnlein, Neutrophil extracellular traps participate in cardiovascular diseases: recent experimental and clinical insights, Circ Res, doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.315931
Douda, Khan, Grasemann, Palaniyar, SK3 channel and mitochondrial ROS mediate NADPH oxidase-independent NETosis induced by calcium influx, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.1414055112
Eelen, De Zeeuw, Simons, Carmeliet, Endothelial cell metabolism in normal and diseased vasculature, Circ Res, doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.302855
Farrera, Fadeel, Macrophage clearance of neutrophil extracellular traps is a silent process, J Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1300436
Folco, Mawson, Vromman, Bernardes-Souza, Franck et al., Neutrophil extracellular traps induce endothelial cell activation and tissue factor production through interleukin-1alpha and cathepsin G, Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311150
Ghergurovich, Garcia-Canaveras, Wang, Schmidt, Zhang et al., A small molecule G6PD inhibitor reveals immune dependence on pentose phosphate pathway, Nat Chem Biol, doi:10.1038/s41589-020-0533-x
Goldspink, Schmitz, Babyak, Brauns, Milleck et al., Kidney medullary sodium chloride concentrations induce neutrophil and monocyte extracellular DNA traps that defend against pyelonephritis, vivo Kidney Int, doi:10.1016/j.kint.2023.03.034
Gomes, Varady, Lourenco, Mizurini, Rondon et al., IL-1beta blockade attenuates thrombosis in a neutrophil extracellular trap-dependent breast cancer model, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.02088
Gregoire, Uhel, Lesouhaitier, Gacouin, Guirriec et al., Impaired efferocytosis and neutrophil extracellular trap clearance by macrophages in ARDS, Eur Respir J, doi:10.1183/13993003.02590-2017
Haider, Kral-Pointner, Mayer, Richter, Kaun et al., Neutrophil extracellular trap degradation by differently polarized macrophage subsets, Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314883
Herre, Cedervall, Mackman, Olsson, Neutrophil extracellular traps in the pathology of cancer and other inflammatory diseases, Physiol Rev, doi:10.1152/physrev.00062.2021
Hu, Liu, Xia, Zhang, Zhang et al., FDA-approved disulfiram inhibits pyroptosis by blocking gasdermin D pore formation, Nat Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41590-020-0669-6
Humphries, Shmuel-Galia, Ketelut-Carneiro, Li, Wang et al., Necrostatin-1 alleviates diffuse pulmonary haemorrhage by preventing the release of NETs via inhibiting NE/ GSDMD activation in murine lupus, Front Immunol, doi:10.1155/2023/4743975
Jaillon, Peri, Delneste, Fremaux, Doni et al., The humoral pattern recognition receptor PTX3 is stored in neutrophil granules and localizes in extracellular traps, J Exp Med, doi:10.1084/jem.20061301
Jayne, Merkel, Schall, Bekker, Group, Avacopan for the treatment of ANCA-associated vasculitis, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2023386
Jiao, Zhang, Liu, Zhou, Qi et al., Exosomal PGE2 from M2 macrophages inhibits neutrophil recruitment and NET formation through lipid mediator class switching in sepsis, J BioMed Sci, doi:10.1186/s12929-023-00957-9
Kambara, Liu, Zhang, Liu, Bajrami et al., Gasdermin D exerts anti-inflammatory effects by promoting neutrophil death, Cell Rep, doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2018.02.067
Kapur, Kasetty, Rebetz, Egesten, Semple et al., Osteopontin mediates murine transfusion-related acute lung injury via stimulation of pulmonary neutrophil accumulation, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04802-1
Karmakar, Minns, Greenberg, Diaz-Aponte, Pestonjamasp et al., N-GSDMD trafficking to neutrophil organelles facilitates IL-1beta release independently of plasma membrane pores and pyroptosis, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-16043-9
Kim, Jang, Dharaneeswaran, Li, Bhide et al., Endothelial pyruvate kinase M2 maintains vascular integrity, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI120912
Kono, Saigo, Takagi, Kawauchi, Wada et al., Morphological and flow-cytometric analysis of haemin-induced human neutrophil activation: implications for transfusion-related acute lung injury, Blood Transfus, doi:10.2450/2012.0141-11
Kono, Saigo, Takagi, Takahashi, Kawauchi et al., Hemerelated molecules induce rapid production of neutrophil extracellular traps, Transfusion, doi:10.1111/trf.12700
Kovacs, Oh, Maltez, Mcglaughon, Verma et al., Neutrophil caspase-11 is essential to defend against a cytosol-invasive bacterium, Cell Rep, doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107967
Lambeth, Neish, Nox enzymes and new thinking on reactive oxygen: a double-edged sword revisited, Annu Rev Pathol, doi:10.1146/annurev-pathol-012513-104651
Lande, Ganguly, Facchinetti, Frasca, Conrad et al., Neutrophils activate plasmacytoid dendritic cells by releasing self-DNA-peptide complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus, Sci Transl Med, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3001180
Lande, Gregorio, Facchinetti, Chatterjee, Wang et al., Plasmacytoid dendritic cells sense self-DNA coupled with antimicrobial peptide, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature06116
Lauth, Kockritz-Blickwede, Mcnamara, Myskowski, Zinkernagel et al., M1 protein allows Group A streptococcal survival in phagocyte extracellular traps through cathelicidin inhibition, J Innate Immun, doi:10.1159/000203645
Lazzaretto, Fadeel, Intra-and extracellular degradation of neutrophil extracellular traps by macrophages and dendritic cells, J Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1800159
Le, Wu, Liu, Wu, Hu et al., MiR-144-induced KLF2 inhibition and NF-kappaB/CXCR1 activation promote neutrophil extracellular trap-induced transfusion-related acute lung injury, J Cell Mol Med, doi:10.1111/jcmm.16650
Leffler, Martin, Gullstrand, Tyden, Lood et al., Neutrophil extracellular traps that are not degraded in systemic lupus erythematosus activate complement exacerbating the disease, J Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1102404
Leppkes, Knopf, Naschberger, Lindemann, Singh et al., Vascular occlusion by neutrophil extracellular traps in COVID-19, EBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102925
Li, Hook, Ding, Chung, Mettlen, Neutrophil metabolomics in severe COVID-19 reveal GAPDH as a suppressor of neutrophil extracellular trap formation, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-023-37567-w
Li, Wang, Liu, Li, Zhang et al., Neutrophil extracellular traps induce intestinal damage and thrombotic tendency in inflammatory bowel disease, J Crohns Colitis, doi:10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjz132
Lin, Hu, Hu, Li, Wang et al., NET-triggered NLRP3 activation and IL18 release drive oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy, Cancer Immunol Res, doi:10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-22-0197
Liu, Xiao, Zhou, Wang, Peng et al., PFKFB3 promotes sepsisinduced acute lung injury by enhancing NET formation by CXCR4(hi) neutrophils, Int Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110737
Liu, Yang, Gao, Yu, Shi et al., NLRP3 activation induced by neutrophil extracellular traps sustains inflammatory response in the diabetic wound, Clin Sci (Lond), doi:10.1042/CS20180600
Lood, Blanco, Purmalek, Carmona-Rivera, Ravin et al., Neutrophil extracellular traps enriched in oxidized mitochondrial DNA are interferogenic and contribute to lupus-like disease, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/nm.4027
Luo, Dai, Feng, Ding, Shao et al., Suppression of lncRNA NLRP3 inhibits NLRP3-triggered inflammatory responses in early acute lung injury, Cell Death Dis, doi:10.1038/s41419-021-04180-y
Mcdonald, Davis, Kim, Tse, Esmon et al., Platelets and neutrophil extracellular traps collaborate to promote intravascular coagulation during sepsis in mice, Blood, doi:10.1182/blood-2016-09-741298
Metzler, Goosmann, Lubojemska, Zychlinsky, Papayannopoulos, A myeloperoxidase-containing complex regulates neutrophil elastase release and actin dynamics during NETosis, Cell Rep, doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2014.06.044
Mistry, Nakabo, Neil, Goel, Jiang et al., Transcriptomic, epigenetic, and functional analyses implicate neutrophil diversity in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.1908576116
Munzer, Negro, Fukui, Di Meglio, Aymonnier et al., NLRP3 inflammasome assembly in neutrophils is supported by PAD4 and promotes NETosis under sterile conditions, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.683803
Papayannopoulos, Neutrophil extracellular traps in immunity and disease, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/nri.2017.105
Peters, Van Hezel, Cortjens, Boer, Van Bruggen et al., Transfusion of 35-day stored RBCs in the presence of endotoxemia does not result in lung injury in humans, Crit Care Med, doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000001614
Peters, Van Stein, Vlaar, Antibody-mediated transfusion-related acute lung injury; from discovery to prevention, Br J Haematol, doi:10.1111/bjh.13459
Peters, Vervaart, Van Bruggen, De Korte, Nieuwland et al., Non-polar lipids accumulate during storage of transfusion products and do not 12, Immunity, doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2021.06.006
Pilsczek, Salina, Poon, Fahey, Yipp et al., A novel mechanism of rapid nuclear neutrophil extracellular trap formation in response to Staphylococcus aureus, J Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1000675
Rathkey, Zhao, Liu, Chen, Yang et al., Chemical disruption of the pyroptotic pore-forming protein gasdermin D inhibits inflammatory cell death and sepsis, Sci Immunol, doi:10.1126/sciimmunol.aat2738
Rodriguez-Espinosa, Rojas-Espinosa, Moreno-Altamirano, Lopez-Villegas, Sanchez-Garcia, Metabolic requirements for neutrophil extracellular traps formation, Immunology, doi:10.1111/imm.12437
Sadiku, Willson, Dickinson, Murphy, Harris et al., Prolyl hydroxylase 2 inactivation enhances glycogen storage and promotes excessive neutrophilic responses, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI90848
Sano, Maejima, Nakagama, Shiheido-Watanabe, Tamura et al., Neutrophil extracellular traps-mediated Beclin-1 suppression aggravates atherosclerosis by inhibiting macrophage autophagy, Front Cell Dev Biol, doi:10.3389/fcell.2022.876147
Santoni, Pericat, Gorse, Buyck, Pinilla et al., Caspase-1driven neutrophil pyroptosis and its role in host susceptibility to Pseudomonas aeruginosa, PloS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1010305
Schauer, Janko, Munoz, Zhao, Kienhofer et al., Aggregated neutrophil extracellular traps limit inflammation by degrading cytokines and chemokines, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/nm.3547
Schmickl, Mastrobuoni, Filippidis, Shah, Radic et al., Male-predominant plasma transfusion strategy for preventing transfusion-related acute lung injury: a systematic review, Crit Care Med, doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000000675
Schneider, Machado, Veras, Maganin, De Souza et al., Neutrophil extracellular traps mediate joint hyperalgesia induced by immune inflammation, Rheumatol, doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keaa794
Schnitzler, Hoogeveen, Ali, Prange, Waissi et al., Atherogenic lipoprotein(a) increases vascular glycolysis, thereby facilitating inflammation and leukocyte extravasation, Circ Res, doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.316206
Semple, Rebetz, Kapur, Transfusion-associated circulatory overload and transfusion-related acute lung injury, Blood, doi:10.1182/blood-2018-10-860809
Shi, Liu, Cao, Ma, Zhu et al., Inhibition of neutrophil extracellular trap formation ameliorates neuroinflammation and neuronal apoptosis via STING-dependent IRE1alpha/ASK1/JNK signaling pathway in mice with traumatic brain injury, J Neuroinflamm, doi:10.1186/s12974-023-02903-w
Shi, Zhao, Wang, Shi, Wang et al., Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature15514
Silliman, Kelher, Khan, Lasarre, West et al., Experimental prestorage filtration removes antibodies and decreases lipids in RBC supernatants mitigating TRALI in vivo, Blood, doi:10.1182/blood-2013-10-532424
Silliman, The two-event model of transfusion-related acute lung injury, Crit Care Med, doi:10.1097/01.CCM.0000214292.62276.8E
Silva, Wanderley, Veras, Sonego, Nascimento et al., Gasdermin D inhibition prevents multiple organ dysfunction during sepsis by blocking NET formation, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-022-04062-5
Skov, Beurskens, Zachariae, Reitamo, Teeling et al., IL-8 as antibody therapeutic target in inflammatory diseases: reduction of clinical activity in palmoplantar pustulosis, J Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.181.1.669
Sollberger, Choidas, Burn, Habenberger, Lucrezia et al., Gasdermin D plays a vital role in the generation of neutrophil extracellular traps, Sci Immunol, doi:10.1126/sciimmunol.aar6689
Stojkov, Claus, Kozlowski, Oberson, Scharen et al., NET formation is independent of gasdermin D and pyroptotic cell death, Sci Signal, doi:10.1126/scisignal.abm0517
Suksawad, Udompornpitak, Thawinpipat, Korwattanamongkol, Visitchanakun et al., Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) deletion reduces severity in bilateral nephrectomy mice through changes in neutrophil extracellular traps and mitochondrial respiration, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines11041208
Swiecki, Colonna, The multifaceted biology of plasmacytoid dendritic cells, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/nri3865
Teijeira, Garasa, Gato, Alfaro, Migueliz et al., CXCR1 and CXCR2 chemokine receptor agonists produced by tumors induce neutrophil extracellular traps that interfere with immune cytotoxicity, Immunity, doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2020.03.001
Thomas, Carbo, Curtis, Martinod, Mazo et al., Extracellular DNA traps are associated with the pathogenesis of TRALI in humans and mice, Blood, doi:10.1182/blood-2012-01-405183
Torres Caban, Yang, Lai, Yang, Subach et al., Tuning the sensitivity of genetically encoded fluorescent potassium indicators through structure-guided and genome mining strategies, ACS Sens, doi:10.1021/acssensors.1c02201
Toy, Gajic, Bacchetti, Looney, Gropper et al., Transfusion-related acute lung injury: incidence and risk factors, Blood, doi:10.1182/blood-2011-08-370932
Urban, Ermert, Schmid, Abu-Abed, Goosmann et al., Neutrophil extracellular traps contain calprotectin, a cytosolic protein complex involved in host defense against Candida albicans, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000639
Van Der Velden, Van Osch, Seghier, Bentlage, Mok et al., Complement C5a induces the generation of neutrophil extracellular traps by inhibiting mitochondrial STAT3 to promote the development of arterial thrombosis, Thromb J, doi:10.1186/s12959-022-00384-0
Van Hezel, Boshuizen, Peters, Straat, Vlaar et al., Red blood cell transfusion results in adhesion of neutrophils in human endotoxemia and in critically ill patients with sepsis, Transfusion, doi:10.1111/trf.15613
Van Raam, Sluiter, De Wit, Roos, Verhoeven et al., Mitochondrial membrane potential in human neutrophils is maintained by complex III activity in the absence of supercomplex organisation, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002013
Vlaar, Toy, Fung, Looney, Juffermans et al., A consensus redefinition of transfusion-related acute lung injury, Transfusion, doi:10.1111/trf.15311
Wang, Cao, Gorshkov, Zhou, Yang et al., Ablation of endothelial Pfkfb3 protects mice from acute lung injury in LPS-induced endotoxemia, Pharmacol Res, doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104292
Wang, Li, Chen, Yuan, Su et al., GSDMD-dependent neutrophil extracellular traps promote macrophage-to-myofibroblast transition and renal fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy, Cell Death Dis, doi:10.1038/s41419-022-05138-4
Wang, Li, Stadler, Correll, Li et al., Histone hypercitrullination mediates chromatin decondensation and neutrophil extracellular trap formation, J Cell Biol, doi:10.1083/jcb.200806072
Wang, Wang, Zhao, Chen, Pluthero et al., NETosing neutrophils activate complement both on their own NETs and bacteria via alternative and non-alternative pathways, Clin Exp Immunol, doi:10.1159/000356980
Wang, Wu, Yan, Wang, Wu, M1-polarized alveolar macrophages are crucial in a mouse model of transfusion-related acute lung injury, Transfusion, doi:10.1111/trf.15609
Warnatsch, Ioannou, Wang, Papayannopoulos, Inflammation. Neutrophil extracellular traps license macrophages for cytokine production in atherosclerosis, Science, doi:10.1126/science.aaa8064
Wei, Zou, Xie, Wang, Huang et al., EDIL3 deficiency ameliorates adverse cardiac remodelling by neutrophil extracellular traps (NET)mediated macrophage polarization, Cardiovasc Res, doi:10.1093/cvr/cvab269
Wigerblad, Kaplan, Neutrophil extracellular traps in systemic autoimmune and autoinflammatory diseases, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-022-00787-0
Wu, Huang, Hamanaka, Krause, Oh et al., HIF-1alpha is required for disturbed flow-induced metabolic reprogramming in human and porcine vascular endothelium, Elife, doi:10.7554/eLife.25217
Xie, Yang, Zhu, Gao, Jiang et al., Microparticles in red cell concentrates prime polymorphonuclear neutrophils and cause acute lung injury in a two-event mouse model, Int Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2017.11.029
Xie, Zhu, Wan, Zhao, Meng et al., GSDMD-mediated NETosis promotes the development of acute respiratory distress syndrome, Eur J Immunol, doi:10.1002/eji.202250011
Xu, Zhang, Pelayo, Monestier, Ammollo et al., Extracellular histones are major mediators of death in sepsis, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/nm.2053
Yalcinkaya, Fotakis, Liu, Endo-Umeda, Dou et al., Cholesterol accumulation in macrophages drives NETosis in atherosclerotic plaques via IL-1beta secretion, Cardiovasc Res, doi:10.1093/cvr/cvac189
Yang, Duan, Liu, Xiong, Guan et al., A COX-2/ sEH dual inhibitor PTUPB alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation, Theranostics, doi:10.7150/thno.43108
Yang, Feng, Chen, Wang, Chen et al., Disulfiram accelerates diabetic foot ulcer healing by blocking NET formation via suppressing the NLRP3/ Caspase-1/GSDMD pathway, Transl Res, doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2022.10.008
Yipp, Petri, Salina, Jenne, Scott et al., Infectioninduced NETosis is a dynamic process involving neutrophil multitasking in vivo, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/nm.2847
Yousefi, Mihalache, Kozlowski, Schmid, Hu, Viable neutrophils release mitochondrial DNA to form neutrophil extracellular traps, Cell Death Differ, doi:10.1038/cdd.2009.96
Zhang, Xu, Xu, Ye, Drug repurposing of ivermectin abrogates neutrophil extracellular traps and prevents melanoma metastasis, Front Oncol, doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.989167
Zhao, Liang, Ye, Wu, Qin et al., GSDMD promotes neutrophil extracellular traps via mtDNA-cGAS-STING pathway during lung ischemia/reperfusion, Cell Death Discov, doi:10.1038/s41420-023-01663-z
Zhao, Pan, Zhang, Ma, Zhang et al., Neutrophil extracellular traps in inflammatory bowel diseases: Implications in pathogenesis and therapeutic targets, Semin Cancer Biol, doi:10.1038/ncomms7673
Ziogas, Sajib, Lim, Alves, Das et al., PKM2 regulates endothelial cell junction dynamics and angiogenesis via ATP production, FASEB J, doi:10.1038/s41598-019-50866-x
Zuber, Fakhouri, Roumenina, Loirat, Vfrench et al., for a HCG. Use of eculizumab for atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome and C3 glomerulopathies, Nat Rev Nephrol, doi:10.1038/nrneph.2012.214
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2023.1324021",
"ISSN": [
"1664-3224"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1324021",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI) is the leading cause of transfusion-associated death, occurring during or within 6 hours after transfusion. Reports indicate that TRALI can be categorized as having or lacking acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) risk factors. There are two types of TRALI in terms of its pathogenesis: antibody-mediated and non-antibody-mediated. The key initiation steps involve the priming and activation of neutrophils, with neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) being established as effector molecules formed by activated neutrophils in response to various stimuli. These NETs contribute to the production and release of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and participate in the destruction of pulmonary vascular endothelial cells. The significant role of NETs in TRALI is well recognized, offering a potential pathway for TRALI treatment. Moreover, platelets, macrophages, endothelial cells, and complements have been identified as promoters of NET formation. Concurrently, studies have demonstrated that the storage of platelets and concentrated red blood cells (RBC) can induce TRALI through bioactive lipids. In this article, recent clinical and pre-clinical studies on the pathophysiology and pathogenesis of TRALI are reviewed to further illuminate the mechanism through which NETs induce TRALI. This review aims to propose new therapeutic strategies for TRALI, with the hope of effectively improving its poor prognosis.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fimmu.2023.1324021"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Yi",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Rong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Song",
"given": "Congkuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ding",
"given": "Song",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zuo",
"given": "Yifan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yi",
"given": "Ke",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Ning",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Bo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Geng",
"given": "Qing",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Immunology",
"container-title-short": "Front. Immunol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-07T10:20:22Z",
"timestamp": 1701944422000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-07T10:20:27Z",
"timestamp": 1701944427000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"8210082163, 81800343"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Natural Science Foundation of China"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100012226",
"award": [
"2042021kf0081"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-08T00:48:14Z",
"timestamp": 1701996494882
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
7
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-07T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1701907200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1324021/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
7
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1111/trf.15311",
"article-title": "A consensus redefinition of transfusion-related acute lung injury",
"author": "Vlaar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Transfusion",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood-2018-10-860809",
"article-title": "Transfusion-associated circulatory overload and transfusion-related acute lung injury",
"author": "Semple",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bjh.13459",
"article-title": "Antibody-mediated transfusion-related acute lung injury; from discovery to prevention",
"author": "Peters",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "597",
"journal-title": "Br J Haematol",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "170",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood-2011-08-370932",
"article-title": "Transfusion-related acute lung injury: incidence and risk factors",
"author": "Toy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0000000000000675",
"article-title": "Male-predominant plasma transfusion strategy for preventing transfusion-related acute lung injury: a systematic review",
"author": "Schmickl",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Med",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/01.CCM.0000214292.62276.8E",
"article-title": "The two-event model of transfusion-related acute lung injury",
"author": "Silliman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Med",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood-2013-10-532424",
"article-title": "Experimental prestorage filtration removes antibodies and decreases lipids in RBC supernatants mitigating TRALI in vivo",
"author": "Silliman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "123",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2017.11.029",
"article-title": "Microparticles in red cell concentrates prime polymorphonuclear neutrophils and cause acute lung injury in a two-event mouse model",
"author": "Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "98",
"journal-title": "Int Immunopharmacol",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0000000000001614",
"article-title": "Transfusion of 35-day stored RBCs in the presence of endotoxemia does not result in lung injury in humans",
"author": "Peters",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Med",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/vox.12453",
"article-title": "Non-polar lipids accumulate during storage of transfusion products and do not contribute to the onset of transfusion-related acute lung injury",
"author": "Peters",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "25",
"journal-title": "Vox Sang",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "112",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.blre.2021.100926",
"article-title": "Transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI): Potential pathways of development, strategies for prevention and treatment, and future research directions",
"author": "Tung",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100926",
"journal-title": "Blood Rev",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2021.06.006",
"article-title": "The neutrophil",
"author": "Burn",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nri.2017.105",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps in immunity and disease",
"author": "Papayannopoulos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2014.06.044",
"article-title": "A myeloperoxidase-containing complex regulates neutrophil elastase release and actin dynamics during NETosis",
"author": "Metzler",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.kint.2023.03.034",
"article-title": "Kidney medullary sodium chloride concentrations induce neutrophil and monocyte extracellular DNA traps that defend against pyelonephritis",
"author": "Goldspink",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "vivo Kidney Int",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "104",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acssensors.1c02201",
"article-title": "Tuning the sensitivity of genetically encoded fluorescent potassium indicators through structure-guided and genome mining strategies",
"author": "Torres Caban",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "ACS Sens",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1083/jcb.200806072",
"article-title": "Histone hypercitrullination mediates chromatin decondensation and neutrophil extracellular trap formation",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Cell Biol",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1000675",
"article-title": "A novel mechanism of rapid nuclear neutrophil extracellular trap formation in response to Staphylococcus aureus",
"author": "Pilsczek",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Immunol",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "185",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm.2847",
"article-title": "Infection-induced NETosis is a dynamic process involving neutrophil multitasking in vivo",
"author": "Yipp",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/cdd.2009.96",
"article-title": "Viable neutrophils release mitochondrial DNA to form neutrophil extracellular traps",
"author": "Yousefi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Differ",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm.4027",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps enriched in oxidized mitochondrial DNA are interferogenic and contribute to lupus-like disease",
"author": "Lood",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1092385",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria",
"author": "Brinkmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "303",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.20061301",
"article-title": "The humoral pattern recognition receptor PTX3 is stored in neutrophil granules and localizes in extracellular traps",
"author": "Jaillon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "793",
"journal-title": "J Exp Med",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "204",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000203645",
"article-title": "M1 protein allows Group A streptococcal survival in phagocyte extracellular traps through cathelicidin inhibition",
"author": "Lauth",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Innate Immun",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1000639",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps contain calprotectin, a cytosolic protein complex involved in host defense against Candida albicans",
"author": "Urban",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-022-00787-0",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps in systemic autoimmune and autoinflammatory diseases",
"author": "Wigerblad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/physrev.00062.2021",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps in the pathology of cancer and other inflammatory diseases",
"author": "Herre",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "277",
"journal-title": "Physiol Rev",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.315931",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps participate in cardiovascular diseases: recent experimental and clinical insights",
"author": "Doring",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Circ Res",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "126",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1908576116",
"article-title": "Transcriptomic, epigenetic, and functional analyses implicate neutrophil diversity in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus",
"author": "Mistry",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci USA",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2019.00423",
"article-title": "Caught in a trap? Proteomic analysis of neutrophil extracellular traps in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus",
"author": "Chapman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjz132",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps induce intestinal damage and thrombotic tendency in inflammatory bowel disease",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Crohns Colitis",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm.3547",
"article-title": "Aggregated neutrophil extracellular traps limit inflammation by degrading cytokines and chemokines",
"author": "Schauer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI61303",
"article-title": "Platelets induce neutrophil extracellular traps in transfusion-related acute lung injury",
"author": "Caudrillier",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "122",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm.2053",
"article-title": "Extracellular histones are major mediators of death in sepsis",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "B34",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood-2016-09-741298",
"article-title": "Platelets and neutrophil extracellular traps collaborate to promote intravascular coagulation during sepsis in mice",
"author": "McDonald",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "129",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jcmm.16650",
"article-title": "MiR-144-induced KLF2 inhibition and NF-kappaB/CXCR1 activation promote neutrophil extracellular trap-induced transfusion-related acute lung injury",
"author": "Le",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Cell Mol Med",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood-2012-01-405183",
"article-title": "Extracellular DNA traps are associated with the pathogenesis of TRALI in humans and mice",
"author": "Thomas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/trf.15613",
"article-title": "Red blood cell transfusion results in adhesion of neutrophils in human endotoxemia and in critically ill patients with sepsis",
"author": "van Hezel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "294",
"journal-title": "Transfusion",
"key": "B38",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/trf.12700",
"article-title": "Heme-related molecules induce rapid production of neutrophil extracellular traps",
"author": "Kono",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Transfusion",
"key": "B39",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2450/2012.0141-11",
"article-title": "Morphological and flow-cytometric analysis of haemin-induced human neutrophil activation: implications for transfusion-related acute lung injury",
"author": "Kono",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "53",
"journal-title": "Blood Transfus",
"key": "B40",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1010305",
"article-title": "Caspase-1-driven neutrophil pyroptosis and its role in host susceptibility to Pseudomonas aeruginosa",
"author": "Santoni",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PloS Pathog",
"key": "B41",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2014.06.028",
"article-title": "The neutrophil NLRC4 inflammasome selectively promotes IL-1beta maturation without pyroptosis during acute Salmonella challenge",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep",
"key": "B42",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-16043-9",
"article-title": "N-GSDMD trafficking to neutrophil organelles facilitates IL-1beta release independently of plasma membrane pores and pyroptosis",
"author": "Karmakar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2212",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "B43",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107967",
"article-title": "Neutrophil caspase-11 is essential to defend against a cytosol-invasive bacterium",
"author": "Kovacs",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "107967",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep",
"key": "B44",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.trsl.2022.10.008",
"article-title": "Disulfiram accelerates diabetic foot ulcer healing by blocking NET formation via suppressing the NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD pathway",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Transl Res",
"key": "B45",
"volume": "254",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.683803",
"article-title": "NLRP3 inflammasome assembly in neutrophils is supported by PAD4 and promotes NETosis under sterile conditions",
"author": "Munzer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "B46",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/bloodadvances.2021005949",
"article-title": "Inflammasome activation in neutrophils of patients with severe COVID-19",
"author": "Aymonnier",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Blood Adv",
"key": "B47",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciimmunol.aar6676",
"article-title": "Noncanonical inflammasome signaling elicits gasdermin D-dependent neutrophil extracellular traps",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Sci Immunol",
"key": "B48",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2018.02.067",
"article-title": "Gasdermin D exerts anti-inflammatory effects by promoting neutrophil death",
"author": "Kambara",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep",
"key": "B49",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature15514",
"article-title": "Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death",
"author": "Shi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "B50",
"volume": "526",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciimmunol.aar6689",
"article-title": "Gasdermin D plays a vital role in the generation of neutrophil extracellular traps",
"author": "Sollberger",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Sci Immunol",
"key": "B51",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41420-023-01663-z",
"article-title": "GSDMD promotes neutrophil extracellular traps via mtDNA-cGAS-STING pathway during lung ischemia/reperfusion",
"author": "Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "368",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Discov",
"key": "B52",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines11041208",
"article-title": "Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) deletion reduces severity in bilateral nephrectomy mice through changes in neutrophil extracellular traps and mitochondrial respiration",
"author": "Suksawad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biomedicines",
"key": "B53",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embr.202154277",
"article-title": "GSDMD drives canonical inflammasome-induced neutrophil pyroptosis and is dispensable for NETosis",
"author": "Chauhan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "EMBO Rep",
"key": "B54",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scisignal.abm0517",
"article-title": "NET formation is independent of gasdermin D and pyroptotic cell death",
"author": "Stojkov",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Sci Signal",
"key": "B55",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0002013",
"article-title": "Mitochondrial membrane potential in human neutrophils is maintained by complex III activity in the absence of supercomplex organisation",
"author": "van Raam",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "B56",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-pathol-012513-104651",
"article-title": "Nox enzymes and new thinking on reactive oxygen: a double-edged sword revisited",
"author": "Lambeth",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Annu Rev Pathol",
"key": "B57",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/imm.12437",
"article-title": "Metabolic requirements for neutrophil extracellular traps formation",
"author": "Rodriguez-Espinosa",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Immunology",
"key": "B58",
"volume": "145",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.165542",
"article-title": "Glycolysis dependent lactate formation in neutrophils: A metabolic link between NOX-dependent and independent NETosis",
"author": "Awasthi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "165542",
"journal-title": "Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis",
"key": "B59",
"volume": "1865",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110737",
"article-title": "PFKFB3 promotes sepsis-induced acute lung injury by enhancing NET formation by CXCR4(hi) neutrophils",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "110737",
"journal-title": "Int Immunopharmacol",
"key": "B60",
"volume": "123",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M115.640094",
"article-title": "A metabolic shift toward pentose phosphate pathway is necessary for amyloid fibril- and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-induced neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation",
"author": "Azevedo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Biol Chem",
"key": "B61",
"volume": "290",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41589-020-0533-x",
"article-title": "A small molecule G6PD inhibitor reveals immune dependence on pentose phosphate pathway",
"author": "Ghergurovich",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Chem Biol",
"key": "B62",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42255-022-00550-8",
"article-title": "Switching to the cyclic pentose phosphate pathway powers the oxidative burst in activated neutrophils",
"author": "Britt",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "389",
"journal-title": "Nat Metab",
"key": "B63",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.07.004",
"article-title": "Selective activation of PFKL suppresses the phagocytic oxidative burst",
"author": "Amara",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4480",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "B64",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102925",
"article-title": "Vascular occlusion by neutrophil extracellular traps in COVID-19",
"author": "Leppkes",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102925",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine",
"key": "B65",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/eji.202149481",
"article-title": "Metabolic reprograming shapes neutrophil functions in severe COVID-19",
"author": "Borella",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "484",
"journal-title": "Eur J Immunol",
"key": "B66",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI90848",
"article-title": "Prolyl hydroxylase 2 inactivation enhances glycogen storage and promotes excessive neutrophilic responses",
"author": "Sadiku",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "B67",
"volume": "127",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.636954",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps activate proinflammatory functions of human neutrophils",
"author": "Domer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "B68",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1414055112",
"article-title": "SK3 channel and mitochondrial ROS mediate NADPH oxidase-independent NETosis induced by calcium influx",
"author": "Douda",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci USA",
"key": "B69",
"volume": "112",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-023-37567-w",
"article-title": "Neutrophil metabolomics in severe COVID-19 reveal GAPDH as a suppressor of neutrophil extracellular trap formation",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2610",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "B70",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.aaa8064",
"article-title": "Inflammation. Neutrophil extracellular traps license macrophages for cytokine production in atherosclerosis",
"author": "Warnatsch",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "B71",
"volume": "349",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/CS20180600",
"article-title": "NLRP3 activation induced by neutrophil extracellular traps sustains inflammatory response in the diabetic wound",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Sci (Lond)",
"key": "B72",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/rheumatology/keaa794",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps mediate joint hyperalgesia induced by immune inflammation",
"author": "Schneider",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Rheumatol (Oxford)",
"key": "B73",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41419-022-05138-4",
"article-title": "GSDMD-dependent neutrophil extracellular traps promote macrophage-to-myofibroblast transition and renal fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Dis",
"key": "B74",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-22-0197",
"article-title": "NET-triggered NLRP3 activation and IL18 release drive oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy",
"author": "Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cancer Immunol Res",
"key": "B75",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41419-017-0090-8",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps promote macrophage pyroptosis in sepsis",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "597",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Dis",
"key": "B76",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcell.2022.876147",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps-mediated Beclin-1 suppression aggravates atherosclerosis by inhibiting macrophage autophagy",
"author": "Sano",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Cell Dev Biol",
"key": "B77",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cvr/cvac189",
"article-title": "Cholesterol accumulation in macrophages drives NETosis in atherosclerotic plaques via IL-1beta secretion",
"author": "Yalcinkaya",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cardiovasc Res",
"key": "B78",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/JIR.S366436",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps induce alveolar macrophage pyroptosis by regulating NLRP3 deubiquitination, aggravating the development of septic lung injury",
"author": "Cui",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Inflamm Res",
"key": "B79",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cvr/cvab269",
"article-title": "EDIL3 deficiency ameliorates adverse cardiac remodelling by neutrophil extracellular traps (NET)-mediated macrophage polarization",
"author": "Wei",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cardiovasc Res",
"key": "B80",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12974-023-02903-w",
"article-title": "Inhibition of neutrophil extracellular trap formation ameliorates neuroinflammation and neuronal apoptosis via STING-dependent IRE1alpha/ASK1/JNK signaling pathway in mice with traumatic brain injury",
"author": "Shi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "222",
"journal-title": "J Neuroinflamm",
"key": "B81",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scisignal.aax7942",
"article-title": "The cytosolic DNA sensor cGAS recognizes neutrophil extracellular traps",
"author": "Apel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Sci Signal",
"key": "B82",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1300436",
"article-title": "Macrophage clearance of neutrophil extracellular traps is a silent process",
"author": "Farrera",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Immunol",
"key": "B83",
"volume": "191",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1800159",
"article-title": "Intra- and extracellular degradation of neutrophil extracellular traps by macrophages and dendritic cells",
"author": "Lazzaretto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Immunol",
"key": "B84",
"volume": "203",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314883",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular trap degradation by differently polarized macrophage subsets",
"author": "Haider",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol",
"key": "B85",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.02590-2017",
"article-title": "Impaired efferocytosis and neutrophil extracellular trap clearance by macrophages in ARDS",
"author": "Gregoire",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "B86",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-023-42167-1",
"article-title": "Secretomes of M1 and M2 macrophages decrease the release of neutrophil extracellular traps",
"author": "Manda-Handzlik",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "15633",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "B87",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12929-023-00957-9",
"article-title": "Exosomal PGE2 from M2 macrophages inhibits neutrophil recruitment and NET formation through lipid mediator class switching in sepsis",
"author": "Jiao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "62",
"journal-title": "J BioMed Sci",
"key": "B88",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nri3865",
"article-title": "The multifaceted biology of plasmacytoid dendritic cells",
"author": "Swiecki",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "B89",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature06116",
"article-title": "Plasmacytoid dendritic cells sense self-DNA coupled with antimicrobial peptide",
"author": "Lande",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "B90",
"volume": "449",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.3001180",
"article-title": "Neutrophils activate plasmacytoid dendritic cells by releasing self-DNA-peptide complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus",
"author": "Lande",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "73ra19",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "B91",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.303312",
"article-title": "Peptidylarginine deiminase inhibition reduces vascular damage and modulates innate immune responses in murine models of atherosclerosis",
"author": "Knight",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Circ Res",
"key": "B92",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.3001201",
"article-title": "Netting neutrophils are major inducers of type I IFN production in pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus",
"author": "Garcia-Romo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "73ra20",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "B93",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.046755",
"article-title": "Auto-antigenic protein-DNA complexes stimulate plasmacytoid dendritic cells to promote atherosclerosis",
"author": "Doring",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "B94",
"volume": "125",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thoraxjnl-2016-209887",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps induced by cigarette smoke activate plasmacytoid dendritic cells",
"author": "Qiu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Thorax",
"key": "B95",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41419-019-1909-2",
"article-title": "Erythromycin suppresses neutrophil extracellular traps in smoking-related chronic pulmonary inflammation",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "678",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Dis",
"key": "B96",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41423-018-0024-0",
"article-title": "NETosis, complement, and coagulation: a triangular relationship",
"author": "de Bont",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "19",
"journal-title": "Cell Mol Immunol",
"key": "B97",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jre.12284",
"article-title": "Influence of complement on neutrophil extracellular trap release induced by bacteria",
"author": "Palmer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Periodontal Res",
"key": "B98",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2122716119",
"article-title": "Neutrophils activated by membrane attack complexes increase the permeability of melanoma blood vessels",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci USA",
"key": "B99",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI138136",
"article-title": "Complement activation on endothelium initiates antibody-mediated acute lung injury",
"author": "Cleary",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "B100",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI163105",
"article-title": "C5aR1 signaling triggers lung immunopathology in COVID-19 through neutrophil extracellular traps",
"author": "Silva",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "B101",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.2023020484",
"article-title": "Complement activation drives Transfusion-related acute lung injury via macrophage trafficking and formation of NETs",
"author": "van der Velden",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "B102",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12959-022-00384-0",
"article-title": "Complement C5a induces the generation of neutrophil extracellular traps by inhibiting mitochondrial STAT3 to promote the development of arterial thrombosis",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "24",
"journal-title": "Thromb J",
"key": "B103",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1102404",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps that are not degraded in systemic lupus erythematosus activate complement exacerbating the disease",
"author": "Leffler",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Immunol",
"key": "B104",
"volume": "188",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cei.12654",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps can activate alternative complement pathways",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Exp Immunol",
"key": "B105",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2016.00137",
"article-title": "NETosing neutrophils activate complement both on their own NETs and bacteria via alternative and non-alternative pathways",
"author": "Yuen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "B106",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000356980",
"article-title": "Myeloperoxidase directs properdin-mediated complement activation",
"author": "O'Flynn",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Innate Immun",
"key": "B107",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pharmthera.2022.108328",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps: A novel target for the treatment of stroke",
"author": "Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "108328",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "B108",
"volume": "241",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.07.011",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps in cancer",
"author": "Cristinziano",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "91",
"journal-title": "Semin Cancer Biol",
"key": "B109",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105779",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps in inflammatory bowel diseases: Implications in pathogenesis and therapeutic targets",
"author": "Dos Santos Ramos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "105779",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Res",
"key": "B110",
"volume": "171",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ncomms7673",
"article-title": "Molecular mechanisms of NET formation and degradation revealed by intravital imaging in the liver vasculature",
"author": "Kolaczkowska",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6673",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "B111",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.2021011525",
"article-title": "Gasdermin D inhibition prevents multiple organ dysfunction during sepsis by blocking NET formation",
"author": "Silva",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "B112",
"volume": "138",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-022-04062-5",
"article-title": "Gasdermin-D activation by SARS-CoV-2 triggers NET and mediate COVID-19 immunopathology",
"author": "Silva",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "206",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "B113",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.157342",
"article-title": "Disulfiram inhibits neutrophil extracellular trap formation and protects rodents from acute lung injury and SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Adrover",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "JCI Insight",
"key": "B114",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb9818",
"article-title": "Succination inactivates gasdermin D and blocks pyroptosis",
"author": "Humphries",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "B115",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.00666",
"article-title": "Necrostatin-1 ameliorates neutrophilic inflammation in asthma by suppressing MLKL phosphorylation to inhibiting NETs release",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "B116",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2023/4743975",
"article-title": "Necrostatin-1 alleviates diffuse pulmonary haemorrhage by preventing the release of NETs via inhibiting NE/GSDMD activation in murine lupus",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4743975",
"journal-title": "J Immunol Res",
"key": "B117",
"volume": "2023",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.0402090101",
"article-title": "Noncompetitive allosteric inhibitors of the inflammatory chemokine receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2: prevention of reperfusion injury",
"author": "Bertini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci USA",
"key": "B118",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.20181102",
"article-title": "Midkine drives cardiac inflammation by promoting neutrophil trafficking and NETosis in myocarditis",
"author": "Weckbach",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Exp Med",
"key": "B119",
"volume": "216",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311150",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps induce endothelial cell activation and tissue factor production through interleukin-1alpha and cathepsin G",
"author": "Folco",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol",
"key": "B120",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2020.03.001",
"article-title": "CXCR1 and CXCR2 chemokine receptor agonists produced by tumors induce neutrophil extracellular traps that interfere with immune cytotoxicity",
"author": "Teijeira",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "856",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "B121",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.302855",
"article-title": "Endothelial cell metabolism in normal and diseased vasculature",
"author": "Eelen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Circ Res",
"key": "B122",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.25217",
"article-title": "HIF-1alpha is required for disturbed flow-induced metabolic reprogramming in human and porcine vascular endothelium",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Elife",
"key": "B123",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.316206",
"article-title": "Atherogenic lipoprotein(a) increases vascular glycolysis, thereby facilitating inflammation and leukocyte extravasation",
"author": "Schnitzler",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Circ Res",
"key": "B124",
"volume": "126",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104292",
"article-title": "Ablation of endothelial Pfkfb3 protects mice from acute lung injury in LPS-induced endotoxemia",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "104292",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Res",
"key": "B125",
"volume": "146",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1821401116",
"article-title": "PFKFB3-mediated endothelial glycolysis promotes pulmonary hypertension",
"author": "Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci USA",
"key": "B126",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ccell.2016.10.006",
"article-title": "Inhibition of the glycolytic activator PFKFB3 in endothelium induces tumor vessel normalization, impairs metastasis, and improves chemotherapy",
"author": "Cantelmo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cancer Cell",
"key": "B127",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.202001634R",
"article-title": "Glycolysis is integral to histamine-induced endothelial hyperpermeability",
"author": "Ziogas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "FASEB J",
"key": "B128",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-019-50866-x",
"article-title": "PKM2 regulates endothelial cell junction dynamics and angiogenesis via ATP production",
"author": "Gomez-Escudero",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "15022",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "B129",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI120912",
"article-title": "Endothelial pyruvate kinase M2 maintains vascular integrity",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "B130",
"volume": "128",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/trf.15609",
"article-title": "M1-polarized alveolar macrophages are crucial in a mouse model of transfusion-related acute lung injury",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Transfusion",
"key": "B131",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.2019000972",
"article-title": "Osteopontin mediates murine transfusion-related acute lung injury via stimulation of pulmonary neutrophil accumulation",
"author": "Kapur",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "74",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "B132",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04802-1",
"article-title": "Inflammasome activation in infected macrophages drives COVID-19 pathology",
"author": "Sefik",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "B133",
"volume": "606",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/thno.43108",
"article-title": "A COX-2/sEH dual inhibitor PTUPB alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Theranostics",
"key": "B134",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41419-021-04180-y",
"article-title": "Suppression of lncRNA NLRP3 inhibits NLRP3-triggered inflammatory responses in early acute lung injury",
"author": "Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "898",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Dis",
"key": "B135",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41590-020-0669-6",
"article-title": "FDA-approved disulfiram inhibits pyroptosis by blocking gasdermin D pore formation",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Immunol",
"key": "B136",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/eji.202250011",
"article-title": "GSDMD-mediated NETosis promotes the development of acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Eur J Immunol",
"key": "B137",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fonc.2022.989167",
"article-title": "Drug repurposing of ivermectin abrogates neutrophil extracellular traps and prevents melanoma metastasis",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Oncol",
"key": "B138",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciimmunol.aat2738",
"article-title": "Chemical disruption of the pyroptotic pore-forming protein gasdermin D inhibits inflammatory cell death and sepsis",
"author": "Rathkey",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Sci Immunol",
"key": "B139",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.181.1.669",
"article-title": "IL-8 as antibody therapeutic target in inflammatory diseases: reduction of clinical activity in palmoplantar pustulosis",
"author": "Skov",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Immunol",
"key": "B140",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2463",
"article-title": "Tumor-produced interleukin-8 attracts human myeloid-derived suppressor cells and elicits extrusion of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs)",
"author": "Alfaro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Cancer Res",
"key": "B141",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2019.02088",
"article-title": "IL-1beta blockade attenuates thrombosis in a neutrophil extracellular trap-dependent breast cancer model",
"author": "Gomes",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "B142",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrneph.2012.214",
"article-title": "Use of eculizumab for atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome and C3 glomerulopathies",
"author": "Zuber",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Nephrol",
"key": "B143",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2023386",
"article-title": "Avacopan for the treatment of ANCA-associated vasculitis",
"author": "Jayne",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "599",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "B144",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10067-019-04832-7",
"article-title": "Transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI) after intravenous immunoglobulins: French multicentre study and literature review",
"author": "Baudel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Rheumatol",
"key": "B145",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 145,
"references-count": 145,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1324021/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Immunology",
"Immunology and Allergy"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Crosstalk between neutrophil extracellular traps and immune regulation: insights into pathobiology and therapeutic implications of transfusion-related acute lung injury",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "14"
}